
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 India
India

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 China
China
 India
India
 Iran
Iran
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Haruhiko Kuroda
Haruhiko Kuroda
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Kimimasa Tarumizu
Kimimasa Tarumizu
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masao Fujioka
Masao Fujioka
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masatsugu Asakawa
Masatsugu Asakawa
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Mitsuo Sato
Mitsuo Sato
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Shiro Inoue
Shiro Inoue
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Tadao Chino
Tadao Chino
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takeshi Watanabe
Takeshi Watanabe
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Taroichi Yoshida
Taroichi Yoshida
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sweden
Sweden
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tonga
Tonga
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


亚洲开发银行(英语:Asian Development Bank,缩写:ADB,简称亚银、亚行、亚开行),香港旧译亚洲发展银行,属于亚太地区的政府之间金融机构,其目的是为了促进亚洲经济与社会的发展。1966年12月19日成立,有31个创始会员国,目前有68个成员体,其中亚太有49个。总部设置于菲律宾马尼拉并在世界各地拥有31个办事处。亚洲开发银行仿照世界银行的股权制度,依照成员体的资本比例,得到相应比例的投票权。2014年以来,亚洲开发银行发布亚太创意生产指数年度报告。[3][4]亚洲开发银行为联合国观察员。
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966,[4] which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world[5] to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries.[6] From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public.[7] The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. Upon completion of their study programs, scholars are expected to contribute to the economic and social development of their home countries.[8] ADB is an official United Nations Observer.[9]
El Banco Asiático de Desarrollo (BAsD) es una organización financiera para el desarrollo económico de Asia y el Pacífico. Su objetivo principal es la erradicación de la pobreza y facilitar ayudas para mejorar el nivel de vida de la población de la región a través de préstamos y colaboración técnica.
Creado en 1966 por 31 países. Hoy cuenta con 67 miembros (48 regionales y 19 no regionales). Estados Unidos y Japón son sus principales accionistas, con el 15,6% del capital cada uno.
El Banco tiene como su principal objetivo la lucha contra la pobreza. Para ello busca promover el crecimiento económico y la cooperación en la región de Asia-Pacífico, y acelerar el proceso de desarrollo económico de sus países miembros. Las dos terceras partes de personas pobres del mundo (aquellos que viven con menos de dos dólares diarios por persona), cerca de 1.800 millones de pobres, viven en esta región. El BAsD aprobó una nueva Estrategia a Largo Plazo (2008-2020) centrada en un crecimiento económico, medioambientalmente sostenible e integración regional.
Азиа́тский банк разви́тия (англ. Asian Development Bank) — банк, основанный в 1966 году, его главной задачей является стимулировать рост экономики в Азии и на Дальнем Востоке, направляя в эти регионы прямые займы и оказывая техническое содействие.
Штаб-квартира в Маниле (Филиппины). Президентом АБР с 28 апреля 2013 года является японец Такэхико Накао. 17 января 2020 года президентом станет Масацугу Асакава, избранный 2 декабря 2019 года[1].
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 China
China
 Chūgoku
Chūgoku
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 India
India
 India
India
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Japan
Japan
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō
 Katar
Katar
 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Philippines
Philippines
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand

亚洲运动会(简称亚运会、亚运;英语:Asian Games,简写:Asiad)是亚洲的综合性运动会,为国际奥委会承认的地区性大型综合运动会,由亚洲奥林匹克理事会(亚奥理事会)主办,每4年一届。
Die Asienspiele (englisch Asian Games), auch Panasiatische Spiele genannt, sind sportliche Wettkämpfe asiatischer Staaten mit olympischem Charakter.

Heimspielbetrieb Kingfisher East Bengal (seit 1984) Mohun Bagan (seit 1984) Mohammedan Sporting Club (seit 1984) Prayag United (I-League) Atlético de Kolkata (seit 2014) Veranstaltungen Südasienspiele 1987 Spiele der U-17-Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft 2017 Spiele der indischen Fußballnationalmannschaft Fußball Leichtathletik Konzerte Kulturveranstaltungen
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Australia
Australia
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Germany
Germany

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 England
England

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL
 Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft 2017
Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft 2017
 Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft 2018

 Formula 1 World Championship 2025
Formula 1 World Championship 2025
 France
France
 India
India
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Katar
Katar
 Kinki
Kinki

 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Monaco
Monaco

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV
 Austria
Austria

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 São Paulo
São Paulo
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport

 Styria
Styria

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Victoria-VIC
Victoria-VIC

Die Formel 1 ist eine vom Automobil-Dachverband Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA) festgelegte Formelserie. Hersteller konstruieren Autos, die den Formel-1-Regeln entsprechen. Diese Autos treten im Rahmen der Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft zu Rennen in ungefähr 20 Orten pro Jahr an. Am Ende der Saison wird der Fahrer mit den meisten Punkten F1 Fahrerweltmeister und der Hersteller mit den meisten Punkten Konstrukteursweltmeister.
Die Formel 1 ist die höchstrangige von der FIA veranstaltete Rennserie des Formelsports. Sie wird als Königsklasse des Automobilsports bezeichnet, da sie den Anspruch erhebt, die höchsten technischen, fahrerischen, aber auch finanziellen Anforderungen aller Rennserien an Fahrer und Konstrukteure zu stellen. Sie wird auch kurz F1 genannt. Die F1 Weltmeisterschaft heißt offiziell FIA Formula One World Championship, bis 1980 hat sie Automobil-Weltmeisterschaft geheissen.
一级方程式赛车(英语:Formula One,也叫Formula 1或者F1)是由国际汽车联盟举办的最高等级的年度系列场地方程式赛车比赛,正式名称为“国际汽车联合会世界一级方程式锦标赛”。名称中“方程式”是指一组所有参赛车辆都必须遵守的规则[1]。F1赛季包括一系列的比赛,而这些所谓的“大奖赛”(Grand Prix,出自法语,本意Great Prizes)的场地是全封闭的专门赛道或者是临时封闭的普通公路。每场比赛的结果算入积分系统并以此确定两个年度世界冠军:一个给车手和另一个给制造商。F1的车手、制造商、组织者以及赛道都必须持有FIA超级驾驶执照,这是国际汽联颁发的最高级别执照。
一级方程式赛车通过产生大量的空气动力学下压力达到非常高的过弯速度,是风靡全球的赛车运动。发动机性能限制在每分钟最多15000转时,其比赛最高速度就可以超过360公里/小时。赛车过弯的横向加速度超过5个标准重力。F1赛车的性能非常依赖电子系统(牵引力控制系统和其他辅助驾驶装置自2008年已被禁止)、空气动力学、悬挂和轮胎。
Formula One (also Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of single-seater auto racing sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) and owned by the Formula One Group. The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The "formula" in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants' cars must conform.[2] A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as Grands Prix (French for "grand prizes" or "great prizes"), which are held worldwide on purpose-built circuits and public roads.
The results of each race are evaluated using a points system to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Drivers must hold valid Super Licences, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA.[3] The races are required to be held on tracks graded "1" (formerly "A"), the highest grade rating issued by the FIA.[3] Most events are held in rural locations on purpose-built tracks, but there are several events in city centres throughout the world, with the Monaco Grand Prix being the most well-known.
Formula One cars are the fastest regulated road course racing cars in the world, owing to very high cornering speeds achieved through the generation of large amounts of aerodynamic downforce. The cars underwent major changes in 2017,[4] allowing wider front and rear wings, and wider tyres, resulting in cornering forces closing in on 8g and top speeds of up to approximately 375 km/h (230 mph).[5] The hybrid engines are currently limited in performance to a maximum of 15,000 rpm and the cars are very dependent on electronics—although traction control and other driving aids have been banned since 2008—and also on aerodynamics, suspension, and tyres.
While Europe is the sport's traditional base, the championship is truly global, with 11 of the 21 races in the 2018 season taking place outside Europe. With the annual cost of running a mid-tier team—designing, building, and maintaining cars, pay, transport—being US$120 million,[6] Formula One has a significant economic and job-creation effect, and its financial and political battles are widely reported. Its high profile and popularity have created a major merchandising environment, which has resulted in large investments from sponsors and budgets (in the hundreds of millions for the constructors). On 8 September 2016, it was announced that Liberty Media had agreed to buy Delta Topco, the company that controls Formula One, from private equity firm CVC Capital Partners for $4.4 billion in cash, stock, and convertible debt.[7] On 23 January 2017, it was confirmed that the acquisition had been completed, for $8 billion.[8]
La Formule 1, communément abrégée en F1, est une discipline de sport automobile considérée comme la catégorie reine de ce sport. Elle a pris au fil des ans une dimension mondiale et elle est, avec les Jeux olympiques et la Coupe du monde de football, l'un des événements sportifs les plus médiatisés.
Chaque année depuis 1950, un championnat mondial des pilotes est organisé, complété depuis 1958 par un championnat mondial des constructeurs automobiles. La compétition est basée sur des Grands Prix, courses à bord de voitures monoplaces disputées sur circuits routiers fermés permanents mais parfois tracés en ville et temporaires, comme à Monaco, Valence, Singapour, et Bakou.
Cette discipline sportive, régie par la Fédération internationale de l'automobile (FIA), est gérée par la Formula One Administration (FOA) et un ensemble de sociétés satellites contrôlées par Liberty Media. Après l'ère des artisans des années 1960 et 1970, elle a peu à peu attiré les grands constructeurs automobiles mondiaux qui y investissent des sommes élevées, en espérant tirer profit des retombées médiatiques d'éventuels succès. La Formule 1 est considérée comme la vitrine technologique de l'industrie automobile qui y expérimente des nouveautés techniques, parfois issues de la technologie spatiale et susceptibles d'être adaptées ensuite sur les voitures de série.
Outre la compétition, le terme Formule 1 désigne l'ensemble des règles techniques des voitures monoplaces qui sont mises à jour tous les ans par la FIA. Ces règles sont très strictes sur les dimensions des voitures, la cylindrée des moteurs, les technologies mises en œuvre ; elles définissent également les mesures de sécurité des voitures pour assurer la protection du pilote. Les monoplaces de course répondant aux caractéristiques de la réglementation de la Formule 1 sont généralement désignées sous le terme générique de Formules 1.
La Formula 1 o Formula Uno,[1] in sigla F1, è la massima categoria (in termini prestazionali) di vetture monoposto a ruote scoperte da corsa su circuito definita dalla Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile (FIA).
La categoria è nata nel 1948 (in sostituzione della Formula A, a sua volta sorta solo qualche anno prima, nel 1946), diventando poi a carattere mondiale nella stagione 1950. Inizialmente definita dalla Commissione Sportiva Internazionale (CSI) dell'Associazione Internazionale degli Automobil Club Riconosciuti (AIACR), associazione antesignana della Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile, oggi la Formula Uno è regolata dal Consiglio Mondiale degli Sport Motoristici (in inglese: World Motor Sport Council, WMSC) della Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile.
Il termine "formula", presente nel nome, fa riferimento a un insieme di regole alle quali tutti i partecipanti, le macchine e i piloti, devono adeguarsi; esse introducono un numero di restrizioni e specifiche nelle auto, al fine di evitare le eccessive disparità tecniche tra le auto, di porre dei limiti al loro sviluppo e di ridurre i rischi di incidenti. La formula ha avuto molti cambiamenti durante la sua storia. Ad esempio, ci sono stati differenti tipi di motori, con schemi da quattro fino a sedici cilindri e con cilindrate da 1,5 a 4,5 l.
La Fórmula 1, abreviada como F1 y también denominada la «categoría reina del automovilismo»1 o «la máxima categoría del automovilismo»,23 es la competición de automovilismo internacional más popular y prestigiosa, superando a categorías de automovilismo como la NASCAR, el Campeonato Mundial de Rally, el Campeonato Mundial de Turismos o la Fórmula E, entre otras.4 A cada carrera se le denomina Gran Premio y el torneo que las agrupa se denomina Campeonato Mundial de Fórmula 1. La entidad que la dirige es la Federación Internacional del Automóvil (FIA). El Formula One Group es controlado por la empresa estadounidense Liberty Media desde septiembre de 2016.5
Los automóviles utilizados son monoplazas con la última tecnología disponible, siempre limitadas por un reglamento técnico; algunas mejoras que fueron desarrolladas en la Fórmula 1 terminaron siendo utilizadas en automóviles comerciales, como el freno de disco.6 La mayoría de los circuitos de carreras donde se celebran los Grandes Premios son autódromos, aunque también se utilizan circuitos callejeros y anteriormente se utilizaron circuitos ruteros.
El inicio de la Fórmula 1 moderna se remonta al año 1950, en el que participaron escuderías como Ferrari, Alfa Romeo y Maserati. Algunas fueron reemplazadas por otras nuevas como McLaren, Williams, Red Bull y Renault, que se han alzado varias veces con el Campeonato Mundial de Constructores. Las escuderías tienen que planear sus fichajes y renovación de contratos 2 o 3 carreras antes del fin de la temporada. Por su parte, los pilotos deben contar con la superlicencia de la FIA para competir, que se obtiene sobre la base de resultados en otros campeonatos.
 -Andaman & Nicobar
-Andaman & Nicobar
 -Chandigarh
-Chandigarh
 Bihar
Bihar
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institute of Culture and Language
Institute of Culture and Language
 Haryana
Haryana
 Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
 Jharkhand
Jharkhand
 Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Rajasthan
Rajasthan
 Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
 Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand
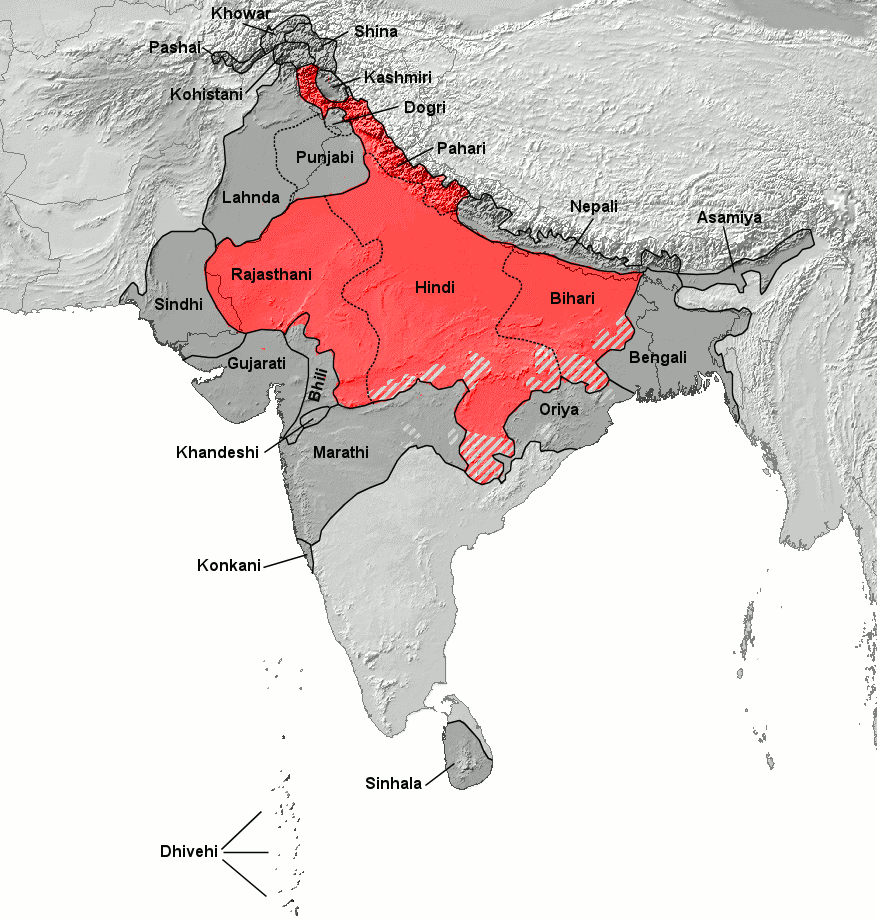
Hindi (हिन्दी hindī /ɦind̪iː/) ist eine indoarische, damit zugleich indoiranische und indogermanische Sprache, die in den meisten nord- und zentralindischen Staaten gesprochen wird und sich von den Prakritsprachen ableitet. Seit 1950 ist es (neben Englisch) die Amtssprache Indiens. Hindi ist eng mit Urdu verwandt.
Unter den meistgesprochenen Sprachen der Welt steht Hindi an dritter Stelle nach Chinesisch und Englisch, noch vor Spanisch. Über 600 Millionen Menschen in Indien und Umgebung gebrauchen es als Mutter- oder Alltagssprache. In Fidschi spricht mehr als ein Drittel der Bevölkerung Fidschi-Hindi, in Guyana und Suriname eine Minderheit, wobei es vor allem in Guyana rasch an Sprechern verliert (das surinamische Hindi wird gelegentlich als Einzelsprache betrachtet).
Hindi wird in Devanagari geschrieben und enthält viele Buchwörter aus dem Sanskrit. Dagegen wird Urdu, als offizielle Sprache Pakistans, mit arabischen Schriftzeichen geschrieben und hat viele Wörter der persischen, türkischen und arabischen Sprache aufgenommen. Beides sind Varietäten des Hindustani.
Die Verwendung von Wörtern unterschiedlicher Herkunft war lange Gegenstand nationaler politischer Bestrebungen. Hindu-Nationalisten ersetzen systematisch Wörter arabischer Herkunft durch Entlehnungen aus dem Sanskrit, um damit ihre kulturelle Eigenständigkeit zu betonen. Ähnliche Bestrebungen zur Förderung von Sanskrit gab es in Form des Popular Sanskrit. Außerdem gibt es eine Vielzahl lokaler Dialekte des Hindi.
印地语(天城文:हिन्दी或हिंदी,拉丁字母转写:Hindī),又译为北印度语、印度语[來源請求][註 2],是印欧语系印度-伊朗语族中印度-雅利安语支下的一种语言。以使用国家来算,印地语是世界排名第八的语言,在1965年1月26日成为印度中央政府的官方语言之一(连同英语)。印地语和乌尔都语(并称印度斯坦语)大同小异,主要区别在于前者用天城文,后者用基于阿拉伯字母的乌尔都字母,前者引进的梵语借词多一点,后者的阿拉伯语和波斯语借词多一些。
标准印地语基于在语言学界称为俱卢口语(天城体梵文:कौरवी Kauravī,意思是“俱卢+呾提多后缀a+所有格”[10])的德里及其近郊口语[11]发展而来。俱卢口语在印度通称“卡里口语”或“标准口语”。
英国统治印度之前,印度敎徒多使用弥梯罗语、摩揭陀语、西弗栗恃语等东部语言,高度波斯化的俱卢口语位格不高。[12]然而,多次虔敬派运动逐降低了印度教徒及其语言的地位[13],最终尽管俱卢口语在印度被英国殖民之前毫无任何文学性可言(当时德里的官方语言是波斯语)[13],其仍然异军突起成为英国殖民时期摩陀耶提舍平原的通用语,今天印地语的分布范围和使用人口远超过其前身俱卢族口语,已成为全体摩陀耶提舍人各个族群进行族际交流的第二语言,在摩陀耶提舍的通用程度超过英语。
印地语和乌尔都语加起来是世界上第二大语言,使用人口超过5亿人,仅次于汉语。2020年的调查发现,40%的印度人会说印地语。根据2001年调查数据,仅在印度就有4亿2,200万左右的人把印地语当作母语,此外有超过5,000万人的母语为“乌尔都语”[14],另外3亿人将印地语当第二语言使用。




 Party and government
Party and government
 Architecture
Architecture
 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Media and press
Media and press
 Companies
Companies



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment