
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
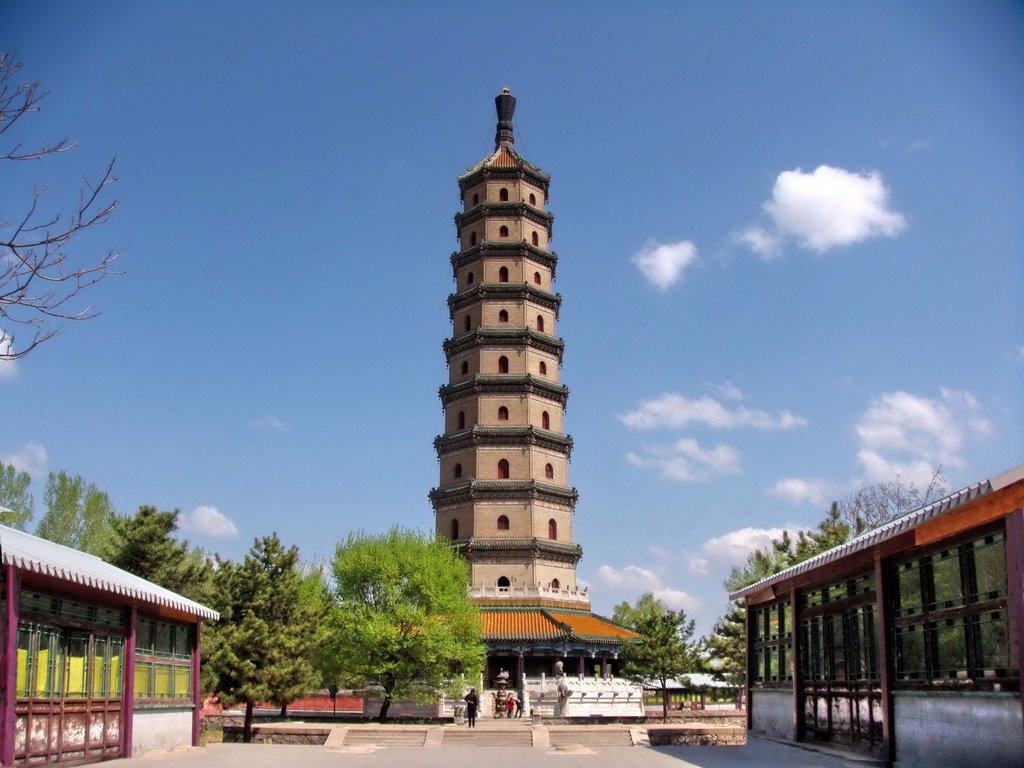
须弥福寿之庙,俗称班禅行宫,位于河北省承德市,是一座藏传佛教格鲁派寺院,为“外八廟”之一。1961年被列为第一批全国重点文物保护单位。
须弥福寿之庙位于避暑山庄北面狮子沟的南坡上,普陀宗乘之庙的东面。须弥福寿之庙建于清朝乾隆四十五年(1780年),是为迎接西藏六世班禅入觐朝贺乾隆帝七旬庆典而仿照班禅居所扎什伦布寺形制兴建。[1]考虑到热河(今承德)、北京比西藏炎热,为六世班禅避暑计,乾隆帝下旨在热河建须弥福寿之庙;在北京香山静宜园(今香山公园)建宗镜大昭之庙,作为班禅夏季驻锡地,将北京西黄寺作为班禅冬季驻锡地。须弥福寿之庙与宗镜大昭之庙有所不同,须弥福寿之庙的白台在后、红台在前,布局和西藏日喀则扎什伦布寺类似。宗镜大昭之庙的布局则是白台在前、红台在后。[3]
六世班禅到达热河后,乾隆帝在避暑山庄为他举办了欢迎仪式,并亲到须弥福寿之庙探望六世班禅。六世班禅向乾隆帝进献礼品40件以及途中日记一册,日记中记载六世班禅在途中每到一站必祈皇帝万寿。乾隆帝将自己身披袈裟的画像赠给六世班禅,并且在须弥福寿之庙中的妙高庄严殿举办法会,请六世班禅讲经,章嘉国师翻译。[1]
1961年,须弥福寿之庙被列为第一批全国重点文物保护单位。1994年,包括须弥福寿之庙在内的“承德避暑山庄及其周围寺庙”被联合国教科文组织评定为世界遗产。
Der Xumi-Fushou-Tempel oder Tempel der Glückseligkeit und des Langen Lebens des Sumeru-Berges (須彌福壽之廟 / 须弥福寿之庙, Xūmí Fúshòu zhī miào, englisch Xumi Fushou Temple / Temple of Sumeru Happiness and Longevity) ist einer der Acht Äußeren Tempel in Chengde (Jehol) in der chinesischen Provinz Hebei. Der buddhistische Tempel befindet sich im Norden des Parkkomplexes des Sommerpalastes östlich des Putuo-Zongcheng-Tempels an der Nordseite des „Löwentales“[1] an einem leicht ansteigenden Berghang. Die Anlage umfasst eine Fläche von 37.900 Quadratmetern.[2]
Der Tempel wurde 1780 zur Feier des 70. Geburtstags des Kaisers Qianlong (reg. 1735–1796, gest. 1799) gebaut, zu der der VI. Penchen Lama der Gelug-Tradition des tibetischen Buddhismus, einer der beiden damaligen religiösen und politischen Führer Tibets, nach Chengde (Jehol), seine Glückwünsche überbringen kam. Für ihn ließ der Kaiser den Tempel bauen. Er ist eine Nachbildung des Tempels Trashilhünpo (tibetisch kurz: Glücksberg), des traditionellen Sitzes des Penchen Lama im tibetischen Samzhubzê, und sollte ihm zur Unterkunft und Meditation dienen. Sein Bau war für die Festigung der Beziehungen zwischen dem Kaiserhof und den Oberhäuptern des tibetischen Buddhismus, und damit für die Festigung des Vielvölkerstaates, von großer Bedeutung.[3]
Sein Hauptgebäude, die Große Rote Terrasse (Dahongtai)[4], hat drei Geschosse und oben dreigeschossige Türme. Die Miaogaozhuangyan-Halle[5], in der der Penchen Lama predigte, bildet das Zentrum der Anlage. Die Jixiangfaxi-Halle[6] mit einem Dach aus goldüberzogenen Kupferziegeln war die Wohnstätte des Penchen Lama. Weitere Bauwerke sind die achteckige siebengeschossige Liuli-Wanshou-Pagode[7] (eine Majolika-Pagode - d. h. eine Pagode aus glasierten Ziegeln) und der ebenfalls daraus angefertigte Gedächtnisbogen (Liuli paifang)[8]. Im Stelenpavillon (Beiting) des Tempels befindet sich eine viersprachige Gedenktafel mit Steingravierungen in mandschurischer, chinesischer, mongolischer und tibetischer Schrift[9] mit einer Inschrift, die an die Ereignisse erinnert.
The Xumi Fushou Temple (Chinese: 须弥福寿之庙) is one of the Eight Outer Temples in Chengde, Hebei, China. This Buddhist temple is in the north of the park complex of the Chengde Mountain Resort, to the east of Putuo Zongcheng Temple on the north side of a slightly upward slope hill. The temple covers an area of 37,900 m2 (408,000 sq ft). The temple was first designed in 1780 to celebrate the 70th birthday of the Qianlong Emperor. It was built for Penchen Lama the VI who came to Chengde from Tibet to convey his congratulations and is a fusion of Chinese and Tibetan architectural style.
Its main building, the Great Red Terrace (Dahongtai, simplified Chinese: 大红台; traditional Chinese: 大紅臺), has three stories, and was furthermore built on a three-story foundation. The Miaogaozhuangyan Hall (妙高莊嚴殿) where the Panchen Lama preached is the center of the temple. The Jixiangfaxi Hall (吉样法喜殿) with a roof made of gold plated copper tiles was the home of Penchen Lama. Other buildings are the seven-story octagonal Liuli-Wanshou pagoda (琉璃万寿塔 "Glazed Tile Pagoda of Longevity") and a glazed tile paifang (琉璃牌坊). In the stele pavilion of the temple is a memorial plaque with stone engraving in Manchu, Chinese, Mongolian and Tibetan script, with an inscription in memory of events.


 *Ancient Times Figures, Myths and Legends
*Ancient Times Figures, Myths and Legends
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX



Der Yongding He (chinesisch 永定河, Pinyin Yǒngdìng Hé, W.-G. Yung-ting Ho) ist der größte Fluss in Peking und der größte Nebenfluss des Hai He in China.
Seine Gesamtlänge beträgt 650 km. Er entspringt im Gebirge Guancen Shan 管涔山 im Kreis Ningwu 宁武县 im Norden der Provinz Shanxi, fließt durch die Innere Mongolei, Hebei sowie die Gebiete der regierungsunmittelbaren Städte Peking und Tianjin.
Zu seinem Flussnetz gehören die Flüsse Sanggan He 桑干河, Yang He 洋河, Qingshui He 清水河 (Zhangjiakou) und Shuiding Xinhe 永定新河.
永定河(满语:ᡝᠨ᠋ᡨᡝ᠋ᡥᡝᠮᡝ
ᡨ᠋ᠣᡴ᠋ᡨ᠋ᠣᡥᠣ
ᠪᡳᡵᠠ,穆麟德转写:Enteheme Toktoho bira),古称㶟水,隋代称桑干河,金代称卢沟,元代称浑河,旧名无定河,海河流域七大水系之一,是河北系的最大河流。流域面积47,016平方千米,其中山区面积45,063平方千米,平原面积1,953平方千米。永定河全长747公里,流经内蒙古、山西、河北三省区、北京、天津两个直辖市、共43个县市。全流域面积4.7万平方公里。
永定河上游的桑干河和洋河两大支流,在河北省怀来县朱官屯汇合,以下的河段称永定河,在延庆区汇入妫水河,经官厅水库流入官厅山峡(官厅水库至三家店区间)。从官厅至朱官屯河长30公里,官厅山峡河长108.7千米,至门头沟三家店流入平原。从三家店以下至天津的入海口,河道全长大约200公里。根据水利系统人们将永定河分为三家店至卢沟桥、卢沟桥至梁各庄、永定河泛区和永定新河四段。
永定河因为经常泛滥更改河道,得名“无定河”。康熙帝改名“永定河”。


 Architecture
Architecture

 Religion
Religion
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Geography
Geography

 History
History
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Sport
Sport

