
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
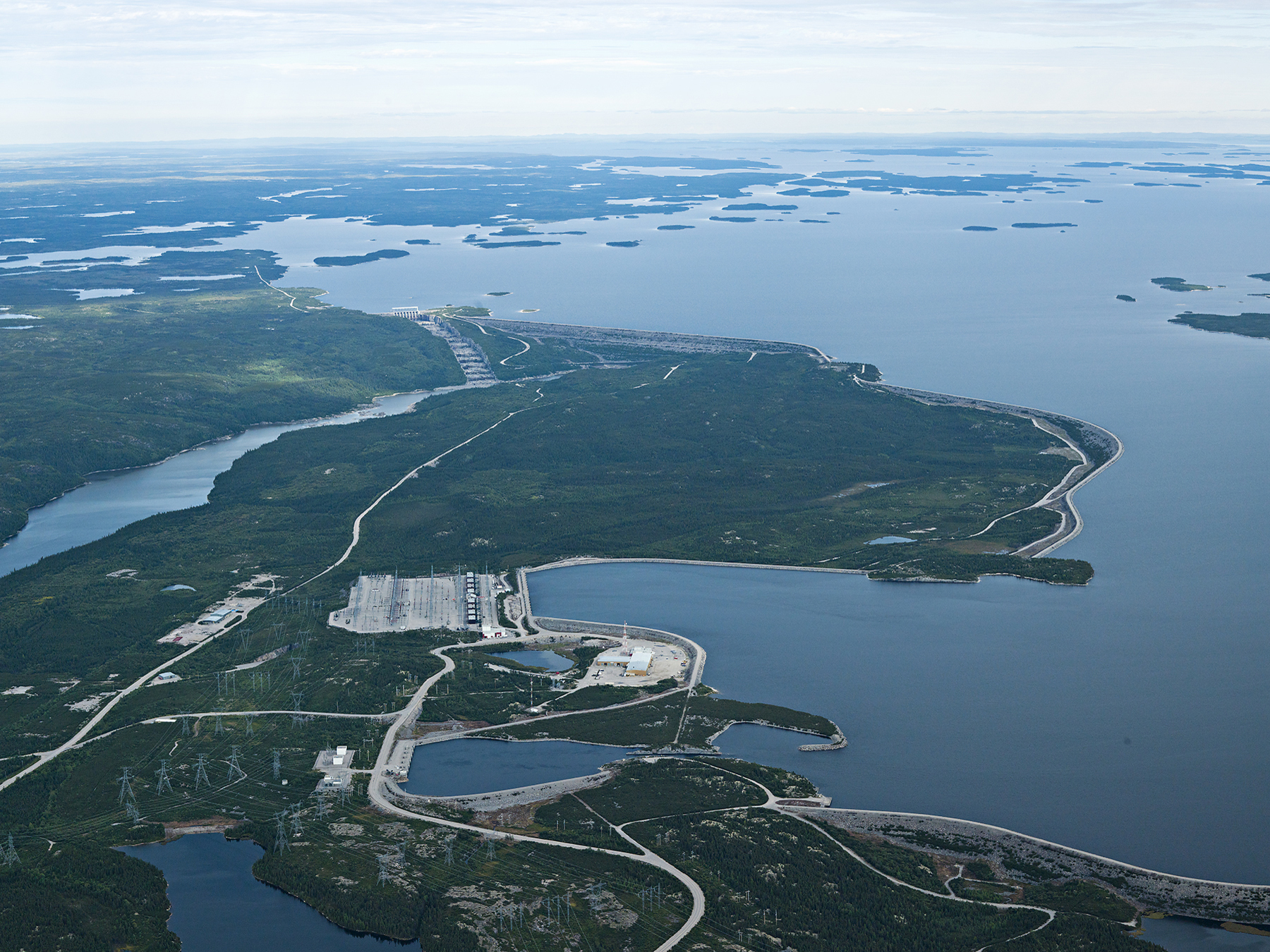





圣劳伦斯河(英語:Saint Lawrence River,法語:Fleuve Saint-Laurent)是北美洲的河流。位于加拿大和美国境内。起源于安大略湖,流经蒙特利尔(加拿大境内)、魁北克市,在加斯佩地区注入大西洋的圣劳伦斯湾。
圣劳伦斯河从安大略湖口的京士顿开始,直到安大略省的康沃尔(Cornwall)是美国和加拿大的界河。康沃尔以下都在加拿大境内。在蒙特利尔西与渥太华河汇流,途径三河市,到魁北克市骤然开阔,最终在加搏海峡入海。全长3056公里。
圣劳伦斯河水量充沛,水质含泥沙量较少,支流有渥太华河、沙陀格威河、黎塞留河(Rivière Richelieu)和萨贵内河(Rivière Saguenay),佛蒙特州的尚普兰湖也是其分支水系。圣劳伦斯水系同五大湖一起构成了世界上最大的淡水水系。
圣劳伦斯河是五大湖水系到大西洋的通路,具有重要的地位。河流两岸集中了魁北克80%的人口和几乎所有的工业。
Der Sankt-Lorenz-Strom (französisch Fleuve Saint-Laurent; englisch Saint Lawrence River; tuscarora Kahnawáˀkye[2]; mohawk Kaniatarowanenneh ‚großer Wasserweg‘) ist mit einem mittleren Abfluss von 10.080 m³/s der drittgrößte Fluss in Nordamerika[3] und entwässert die Großen Seen zum Atlantik. Der Flusslauf ist unterhalb der großen Seen 580 Kilometer lang und verläuft gestreckt nordostwärts. Der Name bezieht sich aber auch auf das anschließende, etwa 660 Kilometer lange Ästuar, das sich trichterförmig zum Atlantik öffnet. Der Sankt-Lorenz-Strom bildet zunächst die Grenze zwischen der kanadischen Provinz Ontario und dem US-Bundesstaat New York und durchquert dann die Provinz Québec. Das Einzugsgebiet des Stromes umfasst im Wesentlichen das Gebiet der Großen Seen, womit die Gesamtlänge des Flusssystems 2900 Kilometer erreicht.
セントローレンス川(セントローレンスがわ、英: St. Lawrence River、仏: Fleuve Saint-Laurent)は、北米大陸の五大湖と大西洋を結んでカナダ東部を東北に流れる河川である。水源である五大湖を含めれば世界第2位の水量となる。サンローラン川ともいわれる。
セントローレンス川はオンタリオ湖から始まり、ガナノクエ、ブロックビル、モリスタウン、オグゼンズバーグ、マシーナ、コーンウォール、モントリオール、トロワリヴィエール、ケベック・シティーを通り、世界でも最大級の三角江であるセントローレンス湾へと注ぐ。上流部はカナダのオンタリオ州とアメリカ合衆国のニューヨーク州を隔てる国境を形成し、その後はケベック州内を流れる。ケベック・シティー付近から潮汐がある。
オンタリオ湖の流出部からの長さは1,197kmで、もっとも遠い水源からでは3,058kmになる。五大湖も含む流域面積は1,344,200km×102であり、うち839,200 km×102がカナダ、505,000 km×102がアメリカ合衆国である。流域にはカナダのオンタリオ州とケベック州、アメリカ合衆国のイリノイ州、インディアナ州、ミネソタ州、ニューヨーク州、オハイオ州、ペンシルベニア州、バーモント州、ウィスコンシン州、ミシガン州が含まれる。
途中にはモントリオールの南のセントルイス湖、サラベリ・ド・ヴァレフィルドのセントフランシス湖 (Lake Saint Francis) やモントリオール東のサンピエール湖 (Lac Saint-Pierre) といった湖がある。また、アレクサンドリアベイおよびキングストン付近のサウザンド諸島、モントリオール島などを含むオシュラガ諸島 (Hochelaga Archipelago)、ケベックシティ付近のオルレアン島などの島がある。オンタリオ湖を出たところにあるサウザンドアイランズ地方はセントローレンス諸島国立公園として国立公園に指定されている。
支流にはシャンプレーン湖からのリシュリュー川やオタワ川、サグネ川、サン・フランソワ川 (Saint-François River) などがある。
The Saint Lawrence River (French: Fleuve Saint-Laurent; Tuscarora: Kahnawáʼkye;[3] Mohawk: Kaniatarowanenneh, meaning "big waterway") is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. The Saint Lawrence River flows in a roughly north-easterly direction, connecting the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean and forming the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin. It traverses the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is part of the international boundary between Ontario, Canada, and the U.S. state of New York. This river provides the basis for the commercial Saint Lawrence Seaway.
Le fleuve Saint-Laurent est un fleuve situé au nord-est de l'Amérique du Nord reliant les Grands Lacs à l'océan Atlantique. Il est le seul émissaire du bassin des Grands Lacs. Sur la première partie de son parcours, il marque la frontière entre le Canada et les États-Unis, plus précisément entre la province canadienne de l'Ontario et l'État américain de New York, avant de traverser la province de Québec, pour se jeter dans le golfe du Saint-Laurent, dans l'ouest de l'océan Atlantique. Long de 1 197 km, son estuaire est le plus grand sur Terre avec une largeur de 48 km et une longueur de 370 km. À lui seul, le Saint-Laurent draine environ 25 % des réserves d'eau douce de la planète.
Il San Lorenzo (in inglese Saint Lawrence River, in francese fleuve Saint-Laurent) è un grande fiume nordamericano.
Lungo quasi 1 150 km, la prima parte del suo corso, fino a poco prima di Montréal, delimita la frontiera fra Canada e Stati Uniti; dopo l'attraversamento dei Grandi Laghi, da esso collegati all'Oceano Atlantico, scorre invece in territorio canadese, attraversando le province di Ontario e Québec. Termina in un ampio estuario nell'Oceano Atlantico. La sua portata media è circa 9 volte quella del fiume Po.
El río San Lorenzo (en francés, fleuve Saint-Laurent; en inglés, Saint Lawrence River; en tuscarora, Kahnawáˀkye;2 en mohawk, Kaniatarowanenneh, que significa «gran vía navegable») es uno de los principales ríos de Norteamérica, el colector de los Grandes Lagos que conecta con el océano Atlántico, en el golfo de San Lorenzo. En su primer tramo forma la frontera natural entre Estados Unidos y Canadá, bordeando el oeste de la provincia de Ontario, y luego se adentra en Quebec atravesándolo totalmente. Pertenece al sistema lacustre de Lawrence.
El San Lorenzo es un gran río que discurre por las latitudes medias del continente. Nace en el lago Ontario, junto a Kingston, para luego pasar por las ciudades de Brockville y Cornwall (en la provincia de Ontario); y Montreal, Trois-Rivières y la ciudad de Quebec (en la de Quebec). Desemboca en el Atlántico después de atravesar el homónimo estuario de San Lorenzo, el estuario más grande del mundo, tras un recorrido de más de 3000 km (3058 km, siendo el 2º río más largo de Canadá y uno de los 25 ríos más largos del mundo). Si se hace caso omiso de sus fuentes en los Grandes Lagos, el río San Lorenzo, desde la salida del lago Ontario, tiene una longitud de 1197 km. Su respaldera más lejana es la del río North,3
- Río Saint Louis4 en el lago Seven Beaver, en la cordillera Mesabi en Hibbing, Minnesota, la fuente más lejana del lago Superior.
El río forma parte del sistema fluvial del San Lorenzo, que estaría formado por la siguiente sucesión de ríos y lagos: río North – río Saint Louis – lago Superior – río St. Marys – lago Hurón – río Sainte-Claire – lago Sainte-Claire – río Detroit – lago Erie – río Niagara – lago Ontario- río San Lorenzo – estuario de San Lorenzo). El río forma parte también de la vía navegable de los Grandes Lagos.
Su cuenca hidrográfica —una buena parte del continente norteamericano, que incluye toda la región de los Grandes Lagos, el mayor sistema de lagos de agua dulce del mundo y que supone casi el 25 % de las reservas mundiales totales de agua dulce— drena un área de 1 344 200 km², de los que 839 200 km² se encuentran en Canadá y 505 000 km² en Estados Unidos. La cuenca comprende parte de las provincias canadiense de Ontario y Quebec y de los estados de Illinois, Indiana, Míchigan, Minnesota, Nueva York, Ohio, Pensilvania, Vermont y Wisconsin. El caudal medio en la boca es 9.850 m³/s.1
Река́ Свято́го Лавре́нтия (фр. fleuve Saint-Laurent, англ. Saint Lawrence River, тускарора Kahnawáʼkye[2], могаук. Kaniatarowanenneh, в переводе — «большой водный путь») — крупная водная артерия в Северной Америке, протекающая по территории США и Канады и соединяющая Великие озёра с Атлантическим океаном.


 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

加拿大横贯公路 (英语:Trans-Canada Highway,法语:Route Transcanadienne),又称横加公路,是一个自西向东横贯加拿大全部十个省的公路系统。主线西起不列颠哥伦比亚省的省会维多利亚,东至纽芬兰和拉布拉多省的省会圣约翰斯,全长8,030公里[3]。系统另有数条支线,例如连接温尼伯和夏洛特皇后群岛的耶洛黑德公路。
《加拿大横贯公路法案》 (Trans-Canada Highway Act)在1948年获议会通过[4]。工程于1950年开始,[5]1962年启用,1971年完工。
由于加拿大国内公路系统的建造和管理都是由各省政府负责(而非联邦政府),横加公路系统中的干线编号亦因省而异。横加公路沿线设有绿底白枫叶的标记以作识别。
有别于美国的州际公路系统,横加公路并未全线达致高速公路标准,部分路段更只是双线行车。
トランスカナダハイウェイ(英語:Trans-Canada Highway、フランス語:Route transcanadienne)はカナダを東西に横断する幹線道路網。日本語では「カナダ大陸横断高速道路」と書かれることもある。
カナダの太平洋岸から大西洋岸まですべての州(準州は含まない)を通る。1948年のトランスカナダハイウェイ法にて制定され、1962年に供用開始、1970年に完成した。緑地に白のメイプルリーフ標識で表される。略称はTCH。
アメリカ合衆国の州間高速道路網と違い、トランスカナダハイウェイは交差点が点在する区間や片側一車線の対面通行の区間も多く、アメリカのUSハイウェイ道路網や日本の国道のように一般道路に割り当てられている区間も多い。
The Trans-Canada Highway (French: Route Transcanadienne; abbreviated as TCH or T-Can[3]) is a transcontinental federal-provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada from the Pacific Ocean on the west to the Atlantic on the east. The main route spans 7,821 km (4,860 mi) across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world.[4] The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces.
Throughout much of Canada, there are at least two routes designated as part of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). For example, in the western provinces, both the main Trans-Canada route and the Yellowhead Highway are part of the Trans-Canada system. Although the TCH, being strictly a transcontinental route, does not enter any of Canada's three northern territories or run to the Canada–US border, the Trans-Canada Highway forms part of Canada's overall National Highway System (NHS), providing connections to the Northwest Territories, Yukon and the border, although the NHS (apart from the TCH sections) is unsigned.[5]
La route Transcanadienne est un système de voies routières à régime fédéral-provincial qui relie les dix provinces du Canada. Ce réseau n'est pas une simple route, car il est à certains endroits composé de deux, voire trois routes parallèles. Par exemple, dans l'ouest du pays, la Route Yellowhead est une branche de la Transcanadienne parallèle à la route originale. La construction de la route fut décidée en 1948, débuta en 1950 pour se terminer en 1970. La route fut inaugurée en 1962. Elle fait actuellement 7 821 kilomètres de long, s'étendant d'un océan à l'autre, du Pacifique à l'Atlantique. Elle est la route « nationale » la plus longue du monde. Il faut préciser que le Canada n'a pas de système routier national, car les routes sont de compétence provinciale. Toutefois, l'entretien de la Transcanadienne est financé par le gouvernement fédéral qui, chaque année, octroie de l'argent aux provinces.
Contrairement au système Interstate des États-Unis, la route Transcanadienne n'est pas toujours une autoroute ou même une route à 4 voies divisées. En 2000, le gouvernement de Jean Chrétien a étudié la possibilité de financer la transformation de la Transcanadienne en autoroute à 4 voies à la grandeur du pays. Finalement, cette idée fut abandonnée car certaines portions de la route ne sont pas assez achalandées pour justifier ce projet. Les provinces ont préféré investir dans des axes routiers plus achalandés et plus commerciaux, comme les liaisons avec les États-Unis. Malgré cela, certaines sections ont été ou seront transformées en autoroute, comme la Route 185 du Québec qui deviendra l'Autoroute 85. Un autre exemple est la Route 2 du Nouveau-Brunswick. Au milieu des années 1980, cette route de plus de 500 km était à deux voies et souvent à accès non limité. En 1987, le gouvernement de la province lança le projet de transformation de la route en autoroute à 4 voies à chaussées séparées. La transformation se termina 20 ans plus tard, à l'automne 2007.
Étant donné que les routes relèvent des provinces, la numérotation de la Transcanadienne relève de celles-ci. Les provinces de l'Ouest (Colombie-Britannique, Alberta, Saskatchewan et Manitoba) ont harmonisé leurs numéros de routes, ainsi l'axe principal de la Transcanadienne, l'axe sud, est appelé Route 1. L'axe nord, la Route Yellowhead, pour sa part est désignée Route 16. Dans l'est du pays, la situation est complètement différente, le numéro de la route change à chaque frontière provinciale. Ceci est dû au fait que la Transcanadienne est composée de sections de routes importantes qui existaient avant son introduction. Il est peu probable que la route ait un jour une désignation uniforme à la grandeur du pays. Ceci serait incompatible avec le système de numérotation des provinces, comme celui du Québec qui est basé sur la géographie (voir Routes provinciales du Québec).
L'autostrada Transcanadese (TCH) (in inglese: Trans-Canada Highway; in francese: Route Transcanadienne) è un sistema di autostrade misto a strade di giurisdizione federale e provinciale che unisce le dieci province del Canada.
Si contende il titolo di autostrada più lunga del mondo con l'autostrada Trans-Siberiana e la Highway 1 dell'Australia. È una delle più lunghe autostrade nazionali del mondo, con una rotta principale che si estende per 8.030 km (4.990 miglia)[1]. Il sistema venne approvato grazie al Trans-Canada Highway Act del 1948,[2] e vide l'inizio della costruzione nel 1950.[3] Ufficialmente l'autostrada venne aperta nel 1962, e venne completata nel 1971. Il sistema di autostrade è riconoscibile per il logo verde su bianco a forma di foglia d'acero (maple leaf) che marca gli accessi, e i numeri delle strade. La Trans-Canada Highway viene spesso abbreviata come TCH.
Attraverso il Canada, vi sono almeno due percorsi designati come facenti parte della Trans-Canada Highway. Ad esempio, nelle province occidentali, sia la Trans-Canada route principale che la Yellowhead Highway formano parte del sistema della Trans-Canada.
La Carretera Transcanadiense (en inglés: Trans-Canada Highway, en francés: Route Transcanadienne) es un sistema vial de carreteras federal-provincial que enlaza las diez provincias de Canadá. Esta carretera es, después de la Australia's Highway 1 y de la Carretera transiberiana, la tercera autopista nacional más larga del mundo, ya que su ruta principal atraviesa 7821 kilómetros. El sistema fue aprobado mediante la Ley de la Carretera Transcanadiense de 1948 (Trans-Canada Highway Act of 1948), si bien la construcción no comenzó hasta 1950. Fue abierta al tráfico oficialmente en 1962 y terminada en 1971.
Atraviesa algunas de las principales ciudades del país como son Vancouver, Calgary, Montreal, Winnipeg, Ottawa, Quebec, Victoria y Edmonton.
Транскана́дское шоссе́ (англ. Trans-Canada Highway, TCH, фр. Route Transcanadienne) — федерально-провинциальная сеть автомобильных дорог, соединяющая десять провинций Канады. Вместе с Транссибирским шоссе и австралийским шоссе 1 оно является одной из самых длинных в мире национальных скоростных автострад: длина магистрали составляет 8030 км. Сеть была одобрена Законом о Трансканадском шоссе 1948 г., а строительство началось в 1950 г. Официально шоссе было открыто в 1962 г., а завершено в 1971 г. Эта сеть автомобильных дорог отличается от других шоссе легко узнаваемыми бело-зелёными дорожными указателями с кленовым листом.
На протяжении всей Канады существует не менее двух трасс, считающихся частью Трансканадского шоссе. Например, в западных провинциях частью трансканадской сети являются Трансканадская магистраль и Йеллоухедское шоссе.
加拿大横贯公路 (英语:Trans-Canada Highway,法语:Route Transcanadienne),又称横加公路,是一个自西向东横贯加拿大全部十个省的公路系统。主线西起不列颠哥伦比亚省的省会维多利亚,东至纽芬兰和拉布拉多省的省会圣约翰斯,全长8,030公里[3]。系统另有数条支线,例如连接温尼伯和夏洛特皇后群岛的耶洛黑德公路。
《加拿大横贯公路法案》 (Trans-Canada Highway Act)在1948年获议会通过[4]。工程于1950年开始,[5]1962年启用,1971年完工。
由于加拿大国内公路系统的建造和管理都是由各省政府负责(而非联邦政府),横加公路系统中的干线编号亦因省而异。横加公路沿线设有绿底白枫叶的标记以作识别。
有别于美国的州际公路系统,横加公路并未全线达致高速公路标准,部分路段更只是双线行车。
Der Trans-Canada Highway (TCH; frz. Route Transcanadienne) ist die einzige Bundesstraße (Federal Highway) Kanadas, die mit einigen Verzweigungen ein Verbindungssystem durch zehn Provinzen des Landes bildet. Mit über 7000 km stellt der TCH sowohl die einzige durchgehende transkontinentale Straßenverbindung Kanadas als auch die drittlängste Straßenverbindung der Welt dar. Die „Transsibirische Straße“ in Russland und der Highway 1 in Australien sind länger als der TCH. Der Yellowhead Highway bildet den nördlichen Zweig des TCH in den westlichen Provinzen. Der Trans-Canada Highway wurde zwar schon 1962 eröffnet, aber erst 1970 fertiggestellt. Zwischenzeitlich ist er größtenteils vierspurig und kreuzungsfrei ausgebaut.
トランスカナダハイウェイ(英語:Trans-Canada Highway、フランス語:Route transcanadienne)はカナダを東西に横断する幹線道路網。日本語では「カナダ大陸横断高速道路」と書かれることもある。
カナダの太平洋岸から大西洋岸まですべての州(準州は含まない)を通る。1948年のトランスカナダハイウェイ法にて制定され、1962年に供用開始、1970年に完成した。緑地に白のメイプルリーフ標識で表される。略称はTCH。
アメリカ合衆国の州間高速道路網と違い、トランスカナダハイウェイは交差点が点在する区間や片側一車線の対面通行の区間も多く、アメリカのUSハイウェイ道路網や日本の国道のように一般道路に割り当てられている区間も多い。
The Trans-Canada Highway (French: Route Transcanadienne; abbreviated as TCH or T-Can[3]) is a transcontinental federal-provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada from the Pacific Ocean on the west to the Atlantic on the east. The main route spans 7,821 km (4,860 mi) across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world.[4] The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces.
Throughout much of Canada, there are at least two routes designated as part of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). For example, in the western provinces, both the main Trans-Canada route and the Yellowhead Highway are part of the Trans-Canada system. Although the TCH, being strictly a transcontinental route, does not enter any of Canada's three northern territories or run to the Canada–US border, the Trans-Canada Highway forms part of Canada's overall National Highway System (NHS), providing connections to the Northwest Territories, Yukon and the border, although the NHS (apart from the TCH sections) is unsigned.[5]
La route Transcanadienne est un système de voies routières à régime fédéral-provincial qui relie les dix provinces du Canada. Ce réseau n'est pas une simple route, car il est à certains endroits composé de deux, voire trois routes parallèles. Par exemple, dans l'ouest du pays, la Route Yellowhead est une branche de la Transcanadienne parallèle à la route originale. La construction de la route fut décidée en 1948, débuta en 1950 pour se terminer en 1970. La route fut inaugurée en 1962. Elle fait actuellement 7 821 kilomètres de long, s'étendant d'un océan à l'autre, du Pacifique à l'Atlantique. Elle est la route « nationale » la plus longue du monde. Il faut préciser que le Canada n'a pas de système routier national, car les routes sont de compétence provinciale. Toutefois, l'entretien de la Transcanadienne est financé par le gouvernement fédéral qui, chaque année, octroie de l'argent aux provinces.
Contrairement au système Interstate des États-Unis, la route Transcanadienne n'est pas toujours une autoroute ou même une route à 4 voies divisées. En 2000, le gouvernement de Jean Chrétien a étudié la possibilité de financer la transformation de la Transcanadienne en autoroute à 4 voies à la grandeur du pays. Finalement, cette idée fut abandonnée car certaines portions de la route ne sont pas assez achalandées pour justifier ce projet. Les provinces ont préféré investir dans des axes routiers plus achalandés et plus commerciaux, comme les liaisons avec les États-Unis. Malgré cela, certaines sections ont été ou seront transformées en autoroute, comme la Route 185 du Québec qui deviendra l'Autoroute 85. Un autre exemple est la Route 2 du Nouveau-Brunswick. Au milieu des années 1980, cette route de plus de 500 km était à deux voies et souvent à accès non limité. En 1987, le gouvernement de la province lança le projet de transformation de la route en autoroute à 4 voies à chaussées séparées. La transformation se termina 20 ans plus tard, à l'automne 2007.
Étant donné que les routes relèvent des provinces, la numérotation de la Transcanadienne relève de celles-ci. Les provinces de l'Ouest (Colombie-Britannique, Alberta, Saskatchewan et Manitoba) ont harmonisé leurs numéros de routes, ainsi l'axe principal de la Transcanadienne, l'axe sud, est appelé Route 1. L'axe nord, la Route Yellowhead, pour sa part est désignée Route 16. Dans l'est du pays, la situation est complètement différente, le numéro de la route change à chaque frontière provinciale. Ceci est dû au fait que la Transcanadienne est composée de sections de routes importantes qui existaient avant son introduction. Il est peu probable que la route ait un jour une désignation uniforme à la grandeur du pays. Ceci serait incompatible avec le système de numérotation des provinces, comme celui du Québec qui est basé sur la géographie (voir Routes provinciales du Québec).
L'autostrada Transcanadese (TCH) (in inglese: Trans-Canada Highway; in francese: Route Transcanadienne) è un sistema di autostrade misto a strade di giurisdizione federale e provinciale che unisce le dieci province del Canada.
Si contende il titolo di autostrada più lunga del mondo con l'autostrada Trans-Siberiana e la Highway 1 dell'Australia. È una delle più lunghe autostrade nazionali del mondo, con una rotta principale che si estende per 8.030 km (4.990 miglia)[1]. Il sistema venne approvato grazie al Trans-Canada Highway Act del 1948,[2] e vide l'inizio della costruzione nel 1950.[3] Ufficialmente l'autostrada venne aperta nel 1962, e venne completata nel 1971. Il sistema di autostrade è riconoscibile per il logo verde su bianco a forma di foglia d'acero (maple leaf) che marca gli accessi, e i numeri delle strade. La Trans-Canada Highway viene spesso abbreviata come TCH.
Attraverso il Canada, vi sono almeno due percorsi designati come facenti parte della Trans-Canada Highway. Ad esempio, nelle province occidentali, sia la Trans-Canada route principale che la Yellowhead Highway formano parte del sistema della Trans-Canada.
La Carretera Transcanadiense (en inglés: Trans-Canada Highway, en francés: Route Transcanadienne) es un sistema vial de carreteras federal-provincial que enlaza las diez provincias de Canadá. Esta carretera es, después de la Australia's Highway 1 y de la Carretera transiberiana, la tercera autopista nacional más larga del mundo, ya que su ruta principal atraviesa 7821 kilómetros. El sistema fue aprobado mediante la Ley de la Carretera Transcanadiense de 1948 (Trans-Canada Highway Act of 1948), si bien la construcción no comenzó hasta 1950. Fue abierta al tráfico oficialmente en 1962 y terminada en 1971.
Atraviesa algunas de las principales ciudades del país como son Vancouver, Calgary, Montreal, Winnipeg, Ottawa, Quebec, Victoria y Edmonton.
Транскана́дское шоссе́ (англ. Trans-Canada Highway, TCH, фр. Route Transcanadienne) — федерально-провинциальная сеть автомобильных дорог, соединяющая десять провинций Канады. Вместе с Транссибирским шоссе и австралийским шоссе 1 оно является одной из самых длинных в мире национальных скоростных автострад: длина магистрали составляет 8030 км. Сеть была одобрена Законом о Трансканадском шоссе 1948 г., а строительство началось в 1950 г. Официально шоссе было открыто в 1962 г., а завершено в 1971 г. Эта сеть автомобильных дорог отличается от других шоссе легко узнаваемыми бело-зелёными дорожными указателями с кленовым листом.
На протяжении всей Канады существует не менее двух трасс, считающихся частью Трансканадского шоссе. Например, в западных провинциях частью трансканадской сети являются Трансканадская магистраль и Йеллоухедское шоссе.



Ungava Bay (französisch Baie d'Ungava;[1] Inuktitut: ᐅᖓᕙ ᑲᖏᖅᓗᒃ / ungava kangiqluk) ist eine Bucht im Norden der kanadischen Labrador-Halbinsel.
Die Bucht und alle in ihr liegenden Inseln gehören administrativ zur Region Qikiqtaaluk des Territoriums Nunavut, während ihre Festlandküste zur Region Nunavik (Verwaltungsregion Nord-du-Québec) der Provinz Québec gehört.
昂加瓦湾是加拿大的海湾,位于该国东北部哈得逊海峡,长320公里、宽260公里,面积50,000平方公里,每年平均降雨量400至450毫米,最大水深300米。
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 Universities in Canada
Universities in Canada

 Architecture
Architecture
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Sport
Sport
 Geography
Geography
 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Climate
Climate
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 United Nations
United Nations
 Nunavut-NU
Nunavut-NU
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink