
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River
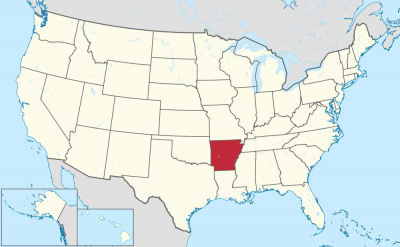


阿肯色州(英语:State of Arkansas /ˈɑːrkənsɔː/),是美国南部的一个州份,位处密西西比河中下游,北接密苏里州,西界俄克拉荷马州,南邻路易斯安那州,西南与得克萨斯州接壤,东隔密西西比河与田纳西州和密西西比州相望。其面积137,539平方公里,在五十个州内列第29位。2017年人口超过3百万,人口排名33。其首府是小石城。
该州的邮政缩写是AR。本州下辖共75个县,详见阿肯色州行政区划。
アーカンソー州(英: State of Arkansas [ˈɑrkənsɔː] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
地形的にはアメリカ内陸高原を構成するオザーク高原やワシタ山地(Ouachita Mountains)のある山岳地から、東部のミシシッピ川やアーカンソー・デルタのある低地まで多様である。
Arkansas (/ˈɑːrkənsɔː/)[c] is a state in the south central region of the United States, home to more than three million people as of 2018.[7][8] Its name is from the Osage language, of Siouan derivation; it denoted their related kin, the Quapaw people.[9] The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and the Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 33rd most populous of the 50 United States. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, located in the central portion of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, such as the Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area and Fort Smith metropolitan area, is a population, education, and economic center. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
The Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836.[10] Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and the state landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans as workers. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America during the Civil War.
On returning to the Union in 1868, the state continued to suffer due to its reliance on the large-scale plantation economy. Cotton continued as the leading commodity crop, although the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in terms of its economy and opportunities for residents.
White rural interests dominated the state's politics by disenfranchisement of African Americans and by refusal to reapportion the legislature. It was not until after the civil rights movement and federal intervention that more African Americans were able to vote. The Supreme Court overturned rural domination in the South and other states that had refused to reapportion their state legislatures, or retained rules based on geographic districts. In the landmark ruling of one man, one vote, it ruled that states had to organize both houses of their legislatures by districts that held approximately equal populations, and that these had to be redefined as necessary after each decade's census.
Following World War II, Arkansas began to diversify its economy. In the 21st century, its economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism; along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans and rice.
The culture of Arkansas is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state. Notable people from the state include politician and educational advocate William Fulbright; former president Bill Clinton, who also served as the 40th and 42nd governor of Arkansas; general Wesley Clark, former NATO Supreme Allied Commander; Walmart founder and magnate Sam Walton;[11] singer-songwriters Johnny Cash, Charlie Rich, Jimmy Driftwood, and Glen Campbell; actor-filmmaker Billy Bob Thornton; poet C. D. Wright; and physicist William L. McMillan, who was a pioneer in superconductor research.
L'Arkansas (prononcé : /aʁ.kɑ̃(n).sa(s)/3), les Arkansas (/aʁ.kɑ̃.sa/3), ou simplement les Arcs (/ɑɹk/4), (prononcé en anglais : /ˈɑɹkənsɔ/5), est un État du Sud des États-Unis. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Little Rock, située au centre du territoire. Avec une population de 2 915 918 habitants en 2010, estimée à 3 017 804 habitants en 2019, sur une superficie de 137 732 km2, l'État est le 32e plus peuplé et le 29e plus vaste du pays. L'Arkansas est entouré par six États : l'Oklahoma à l'ouest, le Missouri au nord, le Tennessee et le Mississippi à l'est, le Texas au sud-ouest et la Louisiane au sud. Il est divisé en 75 comtés. Surnommé The Natural State (« l'État naturel »), il présente des paysages variés : des chaînes montagneuses telles que les Monts Ozarks ou les Montagnes Ouachita ; au sud, des forêts denses nommées Timberlands de l'Arkansas (en) ; à l'est, les plaines du Mississippi et du delta de l'Arkansas (en).
Le nom de l'État provient du nom de la langue Sioux et désigne les Indiens Quapaw. Il forme un territoire dès 1819 et est admis dans l'Union le 15 juin 1836, dont il devient le 25e État. Esclavagiste, il repose sur l'économie de plantation (coton, riz) et se joint aux États confédérés durant la Guerre de Sécession (1861-1865). Après avoir réintégré l'Union, l'Arkansas connaît une crise due à l'effondrement des structures économiques et sociales antérieures. Les intérêts des Blancs ruraux dominent la vie politique locale jusqu'au Mouvement des droits civiques, au milieu du XXe siècle. L'État demeure ségrégationniste jusqu'à la fin des années 1960. Il est aujourd'hui un territoire populaire, conservateur, dont l'ancrage républicain se confirme depuis les années 2000. Néanmoins, l'État demeure de tradition démocrate au niveau local et beaucoup d'électeurs se considèrent toujours Dixiecrats. La tradition conservatrice de cet État s'illustre par l'application de la peine de mort par injection létale et l'interdiction du mariage homosexuel à la suite d'un référendum.
L'Arkansas demeure un État à dominante agricole. En plus des plantations traditionnelles, il produit du soja, et tend à se spécialiser dans l'arboriculture et l'élevage de poulets. Les ressources en hydrocarbures ont également permis une industrialisation durant l'après-guerre, avec la création de papeteries, de scieries, d'usines métallurgiques (aluminium) et textiles. Durant les dernières décennies, l'Arkansas voit son économie se diversifier dans les services, accueillant des sièges sociaux de grandes entreprises (Walmart, Tyson Foods), ainsi que des aciéries et des constructeurs aéronautiques. En outre, des personnalités comme le sénateur J. William Fulbright, le chanteur de country Johnny Cash ou l'ancien président Bill Clinton en sont originaires.
L'Arkansas (pronuncia italianizzata, AFI: /arˈkansas/[2]; in inglese , /ˈɑrkənsɔː/) è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, la cui capitale è Little Rock. Confina a nord con il Missouri, a est con il Tennessee e il Mississippi, a sud con la Louisiana e il Texas, e ad ovest con l'Oklahoma.
Il nome dello Stato deriva dalla parola Akansa (termine utilizzato dai nativi Algonchini per indicare i nativi Quapaw), modificata nella pronuncia attuale dai francesi del XVII secolo.[3]
Arkansas es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Little Rock.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Suroeste. Limita al norte con Misuri al este con el río Mississippi que lo separa de Tennessee y Mississippi, al sur con Louisiana, al suroeste con Texas y al oeste con Oklahoma. Fue admitido en la Unión el 15 de junio de 1836, como el estado número 25.
Aparte de la frontera este que forma el río Misisipi, por su territorio discurre en dirección este el río Arkansas. El nombre del estado deriva de la palabra kansas (el término con que los indios algonquinos designaban a los indios quapaw), tal como la pronunciaban los franceses en el siglo XVII.3 La geografía diversa del estado parte de las regiones montañosas del Ozark y las montañas de Ouachita, que componen las tierras altas del interior de los EE. UU., a la tierra densamente boscosa en el sur conocida como el Arkansas Timberlands, hasta las tierras bajas del este a lo largo del río Misssissippi y el delta de Arkansas. Conocido como «el estado natural», las diversas regiones de Arkansas ofrecen a los residentes y turistas una variedad de oportunidades de recreación al aire libre.
Арканза́с[1][2] (также Арка́нзас[3]; англ. Arkansas, [ˈɑːrkənsɔː] ![]() слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
Официальное прозвище — «Естественный штат» (англ. Natural State).
Слово «арканзас» является алгонкинским экзонимом сиуского племени куапо.




アイオワ州(英: State of Iowa [ˈaɪəwə, ˈaɪ.oʊə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国中西部に位置し、「アメリカのハートランド(中心地)」と呼ばれる州である。1846年12月28日にアメリカ合衆国29番目の州となった。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第26位、人口では第30位である。州都かつ人口最大の都市はデモインである。「アイオワ」という名前はヨーロッパ人がこの地域に探検に入った時代に、数多く住んでいたインディアン部族の中のアイオワ族から採られた[1]。その意味は、インディアン部族のスー族の言葉で「眠たがり」という意味である。アイオワ州法によって、アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙の前哨戦である大統領候補指名党員選挙を、全国に先駆けて行うことが定められている。したがって、アイオワ州党員選挙は大統領選挙の初戦としての位置付けにあり、大統領選挙の際には世界的に注目される。なお、アイオワ州党員選挙にて敗北した候補者が大統領に就任した例は少なく、「アイオワを制する者が大統領選挙を制する」とも言われている。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国中西部に位置し、「アメリカのハートランド(中心地)」と呼ばれる州である。1846年12月28日にアメリカ合衆国29番目の州となった。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第26位、人口では第30位である。州都かつ人口最大の都市はデモインである。「アイオワ」という名前はヨーロッパ人がこの地域に探検に入った時代に、数多く住んでいたインディアン部族の中のアイオワ族から採られた[1]。その意味は、インディアン部族のスー族の言葉で「眠たがり」という意味である。アイオワ州法によって、アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙の前哨戦である大統領候補指名党員選挙を、全国に先駆けて行うことが定められている。したがって、アイオワ州党員選挙は大統領選挙の初戦としての位置付けにあり、大統領選挙の際には世界的に注目される。なお、アイオワ州党員選挙にて敗北した候補者が大統領に就任した例は少なく、「アイオワを制する者が大統領選挙を制する」とも言われている。
アイオワ州となった地域はフランスのヌーベルフランスと呼ばれた植民地に属していた。アメリカ合衆国によるルイジアナ買収後、開拓者が農業に基づく経済の基礎を作り、「コーンベルト」と呼ばれる地域の中心になった[2]。「世界の食糧の首都」と呼ばれることも多い[3]。20世紀の後半に農業経済から、先進的製造、加工、金融、バイオテクノロジー、再生可能エネルギーなど多様な経済分野に移行してきた[3][4]。生活するには安全な州として位置づけられてきている[5]。
Iowa (/ˈaɪəwə/ (![]() listen))[5][6][7] is a state in the Midwestern United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north.
listen))[5][6][7] is a state in the Midwestern United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north.
In colonial times, Iowa was a part of French Louisiana and Spanish Louisiana; its state flag is patterned after the flag of France. After the Louisiana Purchase, people laid the foundation for an agriculture-based economy in the heart of the Corn Belt.[8]
In the latter half of the 20th century, Iowa's agricultural economy made the transition to a diversified economy of advanced manufacturing, processing, financial services, information technology, biotechnology, and green energy production.[9][10] Iowa is the 26th most extensive in land area and the 30th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. The state's capital, most populous city, and largest metropolitan area fully located within the state is Des Moines. A portion of the larger Omaha, Nebraska, metropolitan area extends into three counties of southwest Iowa.[11] Iowa has been listed as one of the safest U.S. states to live in.[12]
L'Iowa (prononcé en français : /i.jo.wa/, en anglais : /ˈaɪ.ə.wə/) est un État du Midwest des États-Unis, parfois appelé The American Heartland (« le cœur américain »). Il est bordé au nord par le Minnesota, par le Wisconsin et l'Illinois à l'est, par le Missouri au sud et par le Nebraska et le Dakota du Sud à l'ouest2. Ses frontières à l'est et l'ouest sont formées par des rivières, respectivement le Mississippi, d'une part, et le Missouri et la Big Sioux, de l'autre. Son surnom officiel est The Hawkeye State depuis 1838, soit 8 ans avant qu'il ne devienne officiellement un État au sein de l'Union. En 2019, sa population s'élève à 3 155 070 habitants3.
À l'époque coloniale, l'Iowa fait partie de la Louisiane française et de la Louisiane espagnole. Son drapeau est inspiré directement de celui de la France. Après la vente de la Louisiane par Napoléon, les colons décident de fonder l'économie de l'État sur l'agriculture, de sorte que l'Iowa devient, plus tard, une partie de la Corn Belt. Dans la seconde moitié du XXe siècle, l'économie de l'Iowa, jusqu'alors monopolisée par l'agriculture, se diversifie avec l'arrivée des industries techniquement avancées, des services financiers, de la biotechnologie et de la production d'énergies renouvelables.
L'Iowa est le 20e État le plus étendu du pays et le 30e plus peuplé. Sa capitale, qui est aussi la ville la plus peuplée de l'État, est Des Moines. L'Iowa est répertorié, en 2009, comme l'un des États les plus sûrs des États-Unis. Il est également le premier État à voter lors des primaires présidentielles avec le caucus de l'Iowa.
L'Iowa (in inglese: [ˈaɪ.əwɒ]) è il 29º stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America, essendo entrato nell'Unione il 28 dicembre 1846. Il nome ufficiale dello stato è "Stato dell'Iowa" (State of Iowa), la sua capitale è Des Moines.
Il nome dello Stato deriva da quello di una tribù di nativi americani di ceppo Sioux, gli Iowa appunto, che abitarono queste terre fino al 1836, quando volontariamente le cedettero agli Stati Uniti e si ritirarono nell'Oklahoma.
Iowa es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Des Moines. Está ubicado en la región Medio Oeste del país, división Centro Noroeste, limitando al norte con Minesota, al este con el río Misisipi que lo separa de Wisconsin (al noreste) e Illinois (al sureste), al sur con Misuri, al oeste con el río Misuri que lo separa de Nebraska, y al noroeste con el río Big Sioux que lo separa de Dakota del Sur. Fue admitido en la Unión el 28 de diciembre de 1846, como el estado número 29.
El 92 por ciento de la población del estado son blancos, y el mayor grupo étnico de Iowa son los alemanes, que componen el 35,7% de la población del estado. Sus principales fuentes de renta son la manufactura, la agricultura y el turismo. Es el mayor productor de soja y etanol de los Estados Unidos, y posee el mayor rebaño porcino del país.
El nombre del estado proviene del pueblo nativo americano Iowa que habitaba la región. Los primeros europeos que exploraron la región fueron los franceses Louis Jolliet y Jacques Marquette en 1673, quienes describieron la región como verde y fértil. Los primeros colonos blancos se instalaron en la región en junio de 1833. El 28 de diciembre de 1846, Iowa se convirtió en el 29º estado de la Unión.
Айова[2] (англ. Iowa, /ˈaɪəwə/)[3] (варианты ударения: А́йова[4] и Айо́ва[5]) — 29-й по счёту штат[6] США, расположенный на Среднем Западе в области, называемой «Сердце Америки». Айова является частью бывшей французской колонии «Новая Франция», перешедшей к США в результате Луизианской покупки. Поселенцами был заложен фундамент сельскохозяйственной экономики штата, расположенного в центре кукурузного пояса США[7]. Штат иногда называют продовольственной столицей мира[8].
Название штата позаимствовано от наименования племени айова, одного из индейских племён, проживавших на территории штата до прихода европейских поселенцев[9].
Во второй половине XX века в Айове был осуществлён переход от сельскохозяйственной к многоотраслевой экономике, включающей передовые производственные, обрабатывающие, финансовые услуги, информационные технологии, биотехнологии и экологически чистое производство энергии[10][11]. Занимает 26-е место по территории в США и 30-е по численности населения. Столица и крупнейший город штата — Де-Мойн. Айова относится к числу самых безопасных штатов страны[12].


 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
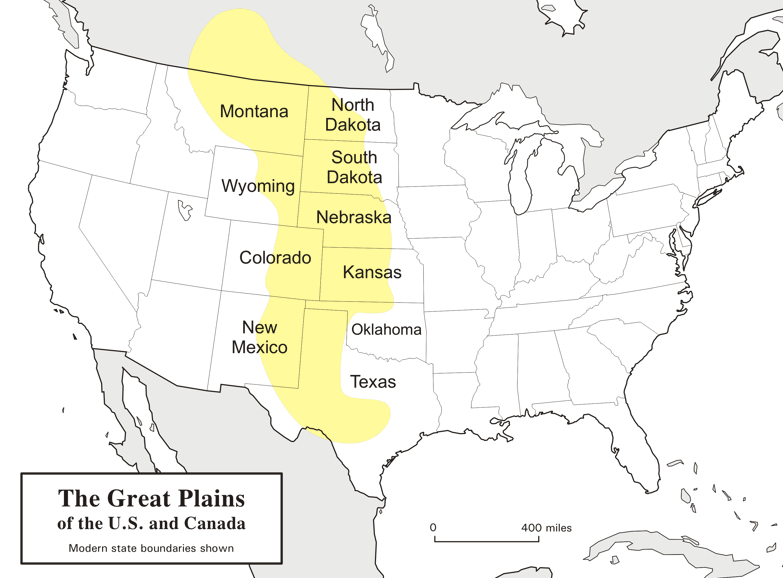
Die Great Plains (deutsch „Große Ebenen“) sind ein trockenes Gebiet östlich der Rocky Mountains in Nordamerika. Naturräumlich sind sie die klassischen Kurzgras-Prärien des amerikanischen Westens, heute werden sie intensiv landwirtschaftlich genutzt. Sie reichen von den kanadischen Prärieprovinzen (Alberta, Saskatchewan und Manitoba) bis nach Texas; manchmal wird auch ein kleiner Teil Mexikos dazu gezählt.
Die Great Plains umfassen (je nach Grenzziehung) eine Fläche von knapp 2 Millionen Quadratkilometern und erstrecken sich insgesamt etwa auf einer maximalen Breite von über 750 km und einer Länge von fast 3000 km. Während sie an den Rocky Mountains noch über 1800 m hoch sind, fallen sie nach Osten auf ca. 500 m ab. Damit sind sie insgesamt als Hochebene zu betrachten, die sich als „Piedmont-Plateau“, zum Teil in Schichtstufen ansteigend, vor dem Gebirge ausbreitet.
Man kann die Great Plains in zwei klimatische Regionen unterteilen, da man westlich des 100. Längengrades einen spärlichen Niederschlagsdurchschnitt vorfindet (weniger als 500 mm pro Jahr), wohingegen die östliche Region ein vergleichsweise humides Klima hat. Entsprechend dominiert im Westen die Viehwirtschaft und im Osten der Getreideanbau.
大平原(英语:Great Plains),多称北美大平原、北美大草原,是北美洲中部一块广袤的平原地区,大致位于密西西比河以西、洛基山脉以东、格兰德河以北。自然植被以草为主。
大平原东西长800千米,南北长3,200千米。另根据内布拉斯加-林肯大学大平原研究中心的定义,其总面积约130万平方千米。大平原主要包括了美国的科罗拉多州、堪萨斯州、蒙大拿州、内布拉斯加州、新墨西哥州 、北达科他州、俄克拉荷马州、南达科他州、得克萨斯州和怀俄明州,以及加拿大的草原三省(艾伯塔省、曼尼托巴省和萨斯喀彻温省)还有墨西哥的一小部分。

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA
 United States
United States

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
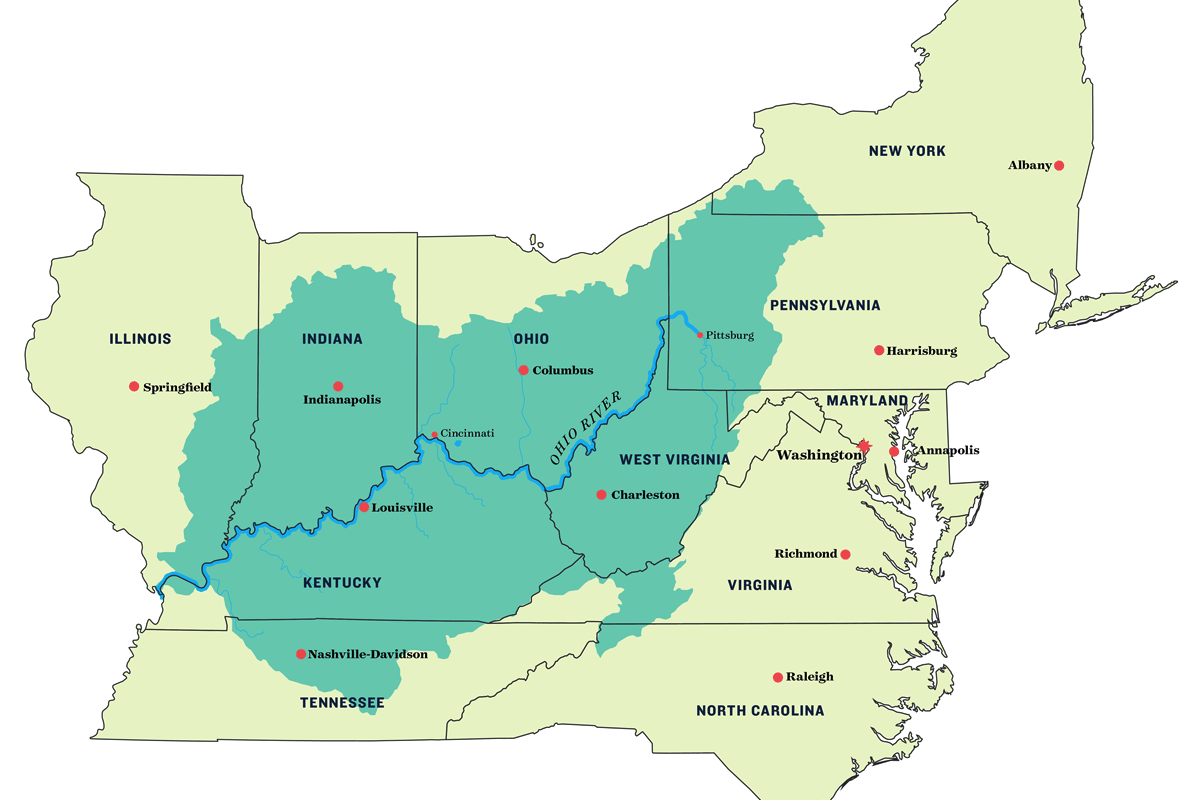
Der Ohio (Irokesisch: Ohi:yo' bzw. Uhíyu' – „guter Fluss“, englisch Ohio River) ist der größte linke Nebenfluss des Mississippi. Er entsteht durch die Vereinigung der beiden Flüsse Allegheny (Hauptquellfluss) und Monongahela in Pittsburgh. Nahe der Stadt Cairo mündet der Ohio in den bis dahin sogenannten Oberen Mississippi (Upper Mississippi). Der Ohio ist auf seiner gesamten Länge von 1579 km schiffbar.
Der Ohio entwässert den größten Teil des Ostens der Vereinigten Staaten. Das Einzugsgebiet umfasst 14 Bundesstaaten, darunter die meisten südlichen Staaten an der Ostküste. An seiner Mündung führt der Ohio rund ein Drittel mehr Wasser als der Mississippi und ist damit hydrologisch der Hauptfluss des Mississippi-Flusssystems.
俄亥俄河(英语:Ohio River)是美国东部的一条河流,是密西西比河最东的支流。发源于匹兹堡,初向西北流,在宾夕法尼亚州、西维吉尼亚州和俄亥俄州的边界以下转向西南方,并流经肯塔基州北界(同时是印地安那州和伊利诺伊州南界),在肯塔基州与田纳西河汇合,最后在开罗与密西西比河汇合。全长1,579公里,流域面积490,603平方公里。



Kentucky (engl. Aussprache [kənˈtʰʌki]) (offiziell The Commonwealth of Kentucky) ist ein Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Der Name des Staates ist shawnesischer oder irokesischer Herkunft, möglicherweise aus dem Wyandotischen, mit der Bedeutung „Wiese“, „Aue“, „Flur“. Im Senecaischen, ebenfalls einer irokesischen Sprache, bedeutet das Wort geda’geh „auf dem Feld“.[1] Den Beinamen Bluegrass State, womit die von März bis April blaugrün blühenden Grasweiden gemeint sind, trägt Kentucky als verbreitete Umschreibung.
Kentucky war zunächst ein Teil Virginias und trat 1792 als 15. Staat den Vereinigten Staaten bei. Im Sezessionskrieg versuchte Kentucky anfangs neutral zu bleiben, dann standen Einwohner des Staates auf beiden Seiten, wie z. B. Abraham Lincoln als Präsident der Union und Jefferson Davis als Präsident der Konföderation. Das United States Census Bureau zählt Kentucky heute jedoch eindeutig zu den Südstaaten.
Neben den Bundesstaaten Virginia, Pennsylvania und Massachusetts führt Kentucky den amtlichen Namen „Commonwealth of Kentucky“ im Gegensatz zu der sonst üblichen Gliedstaaten-Bezeichnung als „State“.
肯塔基州(英语:Commonwealth of Kentucky)是美国中东部的一个州,正式名称为肯塔基邦,面积104,749平方公里,在全国排名37。2005年人口4,041,769人,全国排名第26位。
肯塔基州在美国革命时属弗吉尼亚州一部分,称肯塔基县。1792年肯塔基脱离弗吉尼亚州,成为美国的第十五个州。肯塔基州以纯种马和威士忌闻名。另外快餐连锁企业肯德基(Kentucky Fried Chicken)也以肯塔基州为发源地。
ケンタッキー州(英: Commonwealth of Kentucky)は、アメリカ合衆国中東部にある州(コモンウェルス)である。州都はフランクフォートで、最大都市はルイビルである。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第37位、人口では第26位である。元はバージニア州の一部だった。1792年にアメリカ合衆国15番目の州に昇格した。
他の主要な都市にレキシントンがある。また、オハイオ州の大都市、シンシナティの大都市圏の一部はケンタッキー州北部にまたがっており、北ケンタッキー地域と呼ばれる。
Kentucky (UK: /kɛnˈtʌki/ ken-TUK-ee, US: /kən-/ (![]() listen) kən-),[4] officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a U.S. state in the Southern region of the country. It was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process.[5] Kentucky is the 37th most extensive and the 26th most populous of the 50 United States.
listen) kən-),[4] officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a U.S. state in the Southern region of the country. It was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process.[5] Kentucky is the 37th most extensive and the 26th most populous of the 50 United States.
The bluegrass region in the central part of the state contains the state's capital, Frankfort, as well as its two largest cities, Louisville and Lexington. Together they comprise more than 20% of the state's population.[3] Kentucky shares borders with Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia and Virginia to the east, Tennessee to the south, and Missouri to the west.
Kentucky is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state.[6] It is home to the world's longest cave system: Mammoth Cave National Park, as well as one of the greatest lengths of navigable waterways and streams in the contiguous United States and the two largest man-made lakes east of the Mississippi River. The state is also known for horse racing, bourbon, moonshine, coal, "My Old Kentucky Home" historic state park, automobile manufacturing, tobacco, bluegrass music, college basketball, Kentucky Fried Chicken, and the Kentucky colonel.
Le Kentucky /kɑ̃n̪.ty.ki/ ou /kɛn̪.tə.ki/ (prononcé en anglais /kənˈtʌki/) est un État (officiellement, un Commonwealth, comme seulement trois autres États parmi les cinquante) des États-Unis, à la limite du Midwest et du Sud profond. Il est bordé au nord par l'Illinois, l'Indiana et l'Ohio, à l'est par la Virginie-Occidentale et la Virginie, au sud par le Tennessee et à l'ouest par le Missouri.
Faisant initialement partie de la Virginie, le Kentucky devient en 1792 le 15e État à rejoindre l'Union. Il est le 37e État par sa superficie et le 26e État par sa population parmi les 50 États américains.
Le Kentucky est connu comme le « Bluegrass State » (État de l'herbe bleue), un surnom dû à l'« herbe bleue » que l'on trouve dans de nombreux pâturages de son sol fertile. Une des principales régions du Kentucky est la Bluegrass region, dans le centre de l'État, où se trouvent les deux principales villes, Louisville et Lexington. Le Kentucky présente divers environnements et d'abondantes ressources dont le plus long réseau de grottes du monde au parc national de Mammoth Cave, le plus long système de voies navigables des États-Unis contigus et les deux plus grand lacs artificiels à l'est du Mississippi.
Le Kentucky est aussi connu pour ses courses de chevaux, ses distilleries de bourbon et son alcool de contrebande (Kentucky Moonshine), son charbon, son tabac, sa construction automobile, la musique bluegrass, le site historique My Old Kentucky Home, le basket universitaire et la société Kentucky Fried Chicken.
Il Commonwealth del Kentucky (abbreviazione comune: Kentucky in inglese , [kɨnˈtʌki]; denominazione ufficiale in lingua inglese: Commonwealth of Kentucky; soprannome: Bluegrass State) è uno stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America. La capitale è Frankfort. Confina ad ovest con il Missouri, a nord con l'Ohio, l'Illinois e l'Indiana, a sud con il Tennessee e ad est con Virginia e Virginia Occidentale.
Le origini del nome non sono chiare, ma si ipotizza che derivi da un termine irochese, col significato di “prateria”, “campo”, ma anche “terra del domani” o “fiume di sangue”[2].
Kentucky, oficialmente mancomunidad de Kentucky (en inglés Commonwealth of Kentucky), es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Frankfort y su ciudad más poblada, Louisville.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Sureste. Limita al norte con el río Ohio que lo separa de Illinois (al noroeste), Indiana y Ohio, al noreste con los ríos Big Sandy y Tug Fork que lo separan de Virginia Occidental, al sureste con Virginia, al sur con Tennessee y al oeste con el río Misisipi que lo separa de Misuri. Fue admitido en la Unión el 1 de junio de 1792, como el estado número 15.
Aunque el centro de su actividad económica son la manufactura de productos industrializados y el turismo, buena parte del estado es predominantemente rural, con la agricultura como principal fuente de ingresos.
Anteriormente, se creía que el origen del nombre del estado venía de una palabra amerindia, que significa «terreno de caza oscuro y sangriento», porque las tribus nativas que vivían en la región cazaban dentro de los densos bosques del estado, y porque a menudo estas tribus luchaban entre sí en estos bosques.3 Sin embargo, actualmente se cree que la palabra Kentucky pueda ser atribuida a numerosos idiomas indígenas, con varios significados posibles. Algunos de estos significados son «tierra del mañana», «tierra de caña y pavos» y «pradera».45 La región donde está localizada actualmente Kentucky fue colonizada originalmente por pobladores de la colonia británica de Pensilvania en 1774, pero pasó a ser controlada por Virginia durante la Guerra de Independencia de 1776, y se convirtió en el decimoquinto estado estadounidense en formar parte de la Unión, el 1 de junio de 1792.
Kentucky es una tierra con ambientes diversos y recursos abundantes. Posee el sistema de cuevas más largo del mundo,6 la mayor longitud de corrientes y canales navegables de los Estados Unidos continentales (sin Alaska y Hawái), los dos lagos artificiales más grandes al este del río Misisipi y el yacimiento de carbón más productivo del país. Kentucky es mundialmente conocido por sus caballos purasangre, las carreras de caballos (especialmente el Derby de Kentucky), las destilerías de bourbon, la música bluegrass, el tabaco y sus equipos de baloncesto universitario.
Кенту́кки[1][2] (англ. Kentucky, американское произношение: [kənˈtʌki] (![]() слушать)), официально — Содру́жество Кенту́кки (англ. Commonwealth of Kentucky) — штат[3] в восточной части США, входит в число так называемых штатов Юго-Восточного Центра. Население 4 369 356 человек (2011; 26-е место среди штатов). Столица — Франкфорт. Крупнейший город — Луисвилл, другие крупные города — Лексингтон-Файетт, Оуэнсборо, Боулинг-Грин, Хопкинсвилл.
слушать)), официально — Содру́жество Кенту́кки (англ. Commonwealth of Kentucky) — штат[3] в восточной части США, входит в число так называемых штатов Юго-Восточного Центра. Население 4 369 356 человек (2011; 26-е место среди штатов). Столица — Франкфорт. Крупнейший город — Луисвилл, другие крупные города — Лексингтон-Файетт, Оуэнсборо, Боулинг-Грин, Хопкинсвилл.
Официальные девизы штата — «Вместе мы выстоим, порознь — падём» (англ. United We Stand, Divided We Fall) и «Возблагодарим Господа» (лат. Deo Gratiam Habeamus). Официальное прозвище — «Штат мятлика» (англ. Bluegrass State).
Название Кентукки происходит от индейского названия одноимённой реки[4][источник не указан 2120 дней], насчёт значения которого до сих пор сохраняются разногласия. По одной из версий, выражение означает «Тёмная и кровавая территория охоты». Предлагаются также варианты «Завтрашняя страна», «Земля лугов» и т. д.

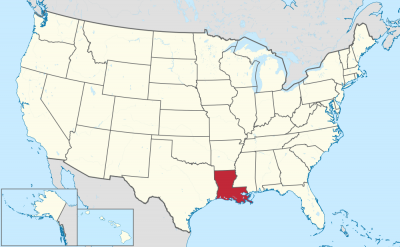


ルイジアナ州(英: State of Louisiana)は、アメリカ合衆国南部の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第31位、人口では第25位である。 州都はバトンルージュ市、最大の都市はニューオーリンズ市である。元フランス領であったが、1812年、アメリカ合衆国の州になった。民法には大陸法の影響が色濃く残っている。また州の下の行政区画として、他州で用いられるカウンティ(county、郡)のかわりにパリッシュ(parish、キリスト教の小教区を意味したが、現在は行政小教区 civil parishで、日本語ではカウンティ相当として「郡」と訳している)が用いられるのもフランス植民地時代の影響である。パリッシュがカウンティ相当として使われるのはアメリカではルイジアナ州のみである。
州内幾つかの都市圏では、多文化、多言語の遺産が残っており、18世紀に領域を支配したフランス(本国およびアカディア)やスペイン(ヌエバ・エスパーニャ)の混合文化に強く影響され、また先住民であるインディアンや、西アフリカから奴隷として連れてこられたアフリカ系アメリカ人の文化の影響も見られる。19世紀初めにアメリカ合衆国の領土となり、アングロサクソン系のアメリカ人が流入して州に昇格する前に、アメリカ合衆国の他州とは幾分異なった文化が形成され、今日に繋がっている。
Louisiana (/luˌiːziˈænə/ (![]() listen), /ˌluːzi-/ (
listen), /ˌluːzi-/ (![]() listen))[a] is a state in the Deep South region of the South Central United States. It is the 19th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties. The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans.
listen))[a] is a state in the Deep South region of the South Central United States. It is the 19th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties. The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans.
Much of the state's lands were formed from sediment washed down the Mississippi River, leaving enormous deltas and vast areas of coastal marsh and swamp.[citation needed] These contain a rich southern biota; typical examples include birds such as ibis and egrets. There are also many species of tree frogs, and fish such as sturgeon and paddlefish. In more elevated areas, fire is a natural process in the landscape and has produced extensive areas of longleaf pine forest and wet savannas. These support an exceptionally large number of plant species, including many species of terrestrial orchids and carnivorous plants.[citation needed] Louisiana has more Native American tribes than any other southern state, including four that are federally recognized, ten that are state recognized, and four that have not received recognition.[9]
Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th-century French, Italian, Haitian, Spanish, French Canadian, Native American, and African cultures that they are considered to be exceptional in the U.S. Before the American purchase of the territory in 1803, the present-day State of Louisiana had been both a French colony and for a brief period a Spanish one. In addition, colonists imported numerous African people as slaves in the 18th century. Many came from peoples of the same region of West Africa, thus concentrating their culture. In the post-Civil War environment, Anglo-Americans increased the pressure for Anglicization, and in 1921, English was for a time made the sole language of instruction in Louisiana schools before a policy of multilingualism was revived in 1974.[10][11] There has never been an official language in Louisiana, and the state constitution enumerates "the right of the people to preserve, foster, and promote their respective historic, linguistic, and cultural origins".[10]
Like other states in the Deep South region, Louisiana frequently ranks low in terms of health, education, and development, and high in measures of poverty.[12][13][14] In 2018, Louisiana was ranked as the least healthy state in the country, with high levels of drug-related deaths and excessive alcohol consumption, while it has had the highest homicide rate in the United States since at least the 1990s.[15][16][17]
La Louisiane (en anglais : Louisiana, /luˌi.ziˈæ.nə/4 Écouter ; en créole louisianais : Lwizyàn) est un État du Sud des États-Unis, entouré à l'ouest par le Texas, au nord par l'Arkansas, à l'est par le Mississippi et au sud par le golfe du Mexique. C'est le 31e État américain par sa superficie et le 25e par sa population. Sa capitale est Baton Rouge et sa plus grande ville est La Nouvelle-Orléans.
En 2019, sa population s'élève à 4 648 794 habitants5.
C'est le seul État américain dont les subdivisions politiques sont dénommées paroisses et non comtés ou boroughs (en Alaska).
La Louisiana (in italiano Luisiana[2][3], anticamente Lugiana) è uno stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America. Confina con Texas, Arkansas e Mississippi, mentre a sud è bagnata dal Golfo del Messico. La capitale è Baton Rouge, mentre la città più grande e famosa è New Orleans. Lo Stato ha due lingue ufficiali: inglese e francese.
Luisiana5 (en inglés: Louisiana) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Baton Rouge y su ciudad más poblada, Nueva Orleans. Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Suroeste. Limita al norte con Arkansas, al este con los ríos Misisipi y Pearl, que lo separan de Misisipi, al sur con el golfo de México (océano Atlántico) y al oeste con Texas (la mayor parte de esta frontera la forma el río Sabine). Fue admitido en la Unión el 30 de abril de 1812, como el estado número 18.
Otras ciudades importantes son Lafayette y Shreveport. Luisiana es el único estado del país cuyas subdivisiones políticas se denominan parroquias, que son los gobiernos locales equivalentes a los condados de los demás estados. La parroquia más poblada es la parroquia de East Baton Rouge, y la más grande por área es la parroquia de Plaquemines.
Algunos entornos urbanos de Luisiana ostentan un patrimonio multicultural y multilingüe, mostrando una intensa mezcla de la cultura francesa (especialmente del s. XVIII), la española, la indoamericana (como la nación Caddo) y culturas africanas; todo este mosaico étnico está considerado como algo excepcional en los EE. UU.
El actual estado de Luisiana fue un territorio bajo dominio español (Luisiana española) y luego una colonia francesa (Luisiana francesa).
Su patrón de desarrollo incluyó la importación de numerosos esclavos africanos en el siglo XVII, muchos de ellos capturados y llevados a la Luisiana desde la misma región del África Occidental, concentrando así su cultura. Después de la Guerra de secesión, los angloamericanos aumentaron la presión para la anglificación, y en 1915 el idioma inglés se hizo el único idioma oficial del estado. Pese a todo, el estado de Luisiana tiene más tribus indoamericanas que cualquier otro estado del sur, entre ellas, cuatro que son reconocidas por el gobierno federal, diez reconocidas por el estado y cuatro que aún no han recibido reconocimiento.
Луизиа́на[1][2] (англ. Louisiana; фр. Louisiane; исп. Luisiana) — штат[3] на юге США, 18-й штат, вошедший в Союз. Столица — Батон-Руж, крупнейший город — Новый Орлеан. Общая площадь 135 382 км² (31 место в США), в том числе на сушу приходится 113 721 км². Население 4 574 836 человек (25 место в США). Официальное прозвище Луизианы — «Штат пеликанов». Названа в честь французского короля Людовика XIV (во французском произношении Луи).
В прошлом Луизианой называлась обширная территория вблизи побережья Мексиканского залива, контролировавшаяся французами (см. Новая Франция). После Луизианской покупки южная часть этой территории составила штат с одноименным названием.

Memphis ist die zweitgrößte Stadt im US-Bundesstaat Tennessee und County-Sitz des Shelby County. Die Stadt liegt im äußersten Südwesten Tennessees am Ostufer des Mississippi River und hat etwa 653.000 Einwohner (Stand: 2016).
Die Stadt ist eine der Metropolen der klassischen Südstaaten. Nachdem Memphis bis in den Sezessionskrieg und die 1870er hinein floriert hatte, suchten mehrere Katastrophen die Stadt heim. In jüngster Zeit verdankt sie ihren wirtschaftlichen Aufschwung vor allem der Transportfirma FedEx, die mit Abstand größter Arbeitgeber der Stadt ist.
Die Stadt ist ein wichtiger Ort sowohl für die Entwicklung des Blues und des Souls als auch für die des Rock ’n’ Rolls. Elvis Presley lebte in Memphis, viele Größen der Rockmusik begannen ihre Karriere dort. Die Beale Street ist eines der Zentren des Blues.
孟菲斯(英语:Memphis)是美国田纳西州谢尔比县的一座城市,也是谢尔比县县治。根据2006年的人口预估,孟菲斯的总人口为68万0768人,是田纳西州最大的城市,在美国东南部排名第二、次于佛罗里达州杰克逊维尔,也是全国第17大城市[2]。孟菲斯都会区是田纳西州次于纳什维尔都会区的第二大都会区,包含在邻近密西西比州和阿肯色州的部分地区,总人口为126万0581人。在包含诺克斯维尔、查特怒加、和纳什维尔的田纳西州四大城市里,孟菲斯是人口最多但也是最年轻的。孟菲斯位于密西西比河岸边、下契卡索陡岸(Chickasaw Bluff)上,狼河(Wolf River)的河口。其联外机场孟菲斯国际机场是世界第二大货运机场。



地形上,密苏里州境内大部分都是平缓的平原与丘陵,密苏里河与密西西比河分别流经该州的西境与东境。密苏里州是个内陆州,其位置非常接近美国的地理中心点(在西边的堪萨斯州境内)。
行政区位上,密苏里州北边与艾奥瓦州相邻,西边由北到南分别是内布拉斯加州、堪萨斯州与俄克拉荷马州,南邻阿肯色州,东边由北至南则分别是伊利诺伊州、肯塔基州与田纳西州。 进入美国中西部地区的知名建筑圣路易拱门即位于该州圣路易斯市。
ミズーリ州(英: State of Missouri 発音: [mɪˈzuəri] (![]() 音声ファイル), [məˈzɜrə] (
音声ファイル), [məˈzɜrə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国中西部[1]のミシシッピ川沿いにある内陸の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第21位、人口では第18位である。前身のミズーリ準州から1821年8月10日に合衆国24番目の州に昇格した。現在は観光が州のおもな産業の一つとなっている。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国中西部[1]のミシシッピ川沿いにある内陸の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第21位、人口では第18位である。前身のミズーリ準州から1821年8月10日に合衆国24番目の州に昇格した。現在は観光が州のおもな産業の一つとなっている。
州都はジェファーソンシティ市である。同州を代表する都市はイリノイ州との州境にあるセントルイス市と、カンザス州との州境にあるカンザスシティ市であり、ともに都市圏人口200万人以上の大都市である。ほかの主要都市には、スプリングフィールド市、インディペンデンス市、コロンビア市などがある。とりわけミシシッピ川に面するセントルイス市は、開拓時代より西部への玄関口として発展し、現在では中西部きっての観光都市である。
また、ミシシッピ川沿いにある多数の町は、ヨーロッパからの移民の影響を強く受けており、現在でも当時の教会や町並みが多く残っている。特にセントジェネビーブや、そこから1時間ほどの場所にあるケープジラードなどはフランス系移民の影響が強く、大きな教会や狭い街路など美しい町並みが見られ、知られざる観光地である。
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern United States.[5] With more than six million residents, it is the 18th-most populous state of the country. The largest urban areas are St. Louis, Kansas City, Springfield and Columbia; the capital is Jefferson City. The state is the 21st-most extensive in area. Missouri is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee (via the Mississippi River) to the east, Arkansas to the south and Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska to the west. In the south are the Ozarks, a forested highland, providing timber, minerals and recreation. The Missouri River, after which the state is named, flows through the center of the state into the Mississippi River, which makes up Missouri's eastern border.
Humans have inhabited the land now known as Missouri for at least 12,000 years. The Mississippian culture built cities and mounds, before declining in the 14th century. When European explorers arrived in the 17th century, they encountered the Osage and Missouria nations. The French established Louisiana, a part of New France, founding Ste. Genevieve in 1735 and St. Louis in 1764. After a brief period of Spanish rule, the United States acquired the Louisiana Purchase in 1803. Americans from the Upland South, including enslaved African Americans, rushed into the new Missouri Territory. Missouri was admitted as a slave state as part of the Missouri Compromise. Many from Virginia, Kentucky and Tennessee settled in the Boonslick area of Mid-Missouri. Soon after, heavy German immigration formed the Missouri Rhineland.
Missouri played a central role in the westward expansion of the United States, as memorialized by the Gateway Arch. The Pony Express, Oregon Trail, Santa Fe Trail and California Trail all began in Missouri.[6] As a border state, Missouri's role in the American Civil War was complex and there were many conflicts within. After the war, both Greater St. Louis and the Kansas City metropolitan area became centers of industrialization and business. Today the state is divided into 114 counties and the independent city of St. Louis.
Missouri's culture blends elements from the Midwestern and Southern United States. The musical styles of ragtime, Kansas City jazz and St. Louis blues developed in Missouri. The well-known Kansas City-style barbecue and lesser-known St. Louis-style barbecue, can be found across the state and beyond. Missouri is also a major center of beer brewing; Anheuser-Busch is the largest producer in the world. Missouri wine is produced in the Missouri Rhineland and Ozarks. Missouri's alcohol laws are among the most permissive in the United States.[7] Outside of the state's major cities, popular tourist destinations include the Lake of the Ozarks, Table Rock Lake and Branson.
Well-known Missourians include Chuck Berry, Sheryl Crow, Walt Disney, Edwin Hubble, Nelly, Brad Pitt, Harry S. Truman, and Mark Twain. Some of the largest companies based in the state include Cerner, Express Scripts, Monsanto, Emerson Electric, Edward Jones, H&R Block, Wells Fargo Advisors, and O'Reilly Auto Parts. Universities in Missouri include the University of Missouri and the top-ranked Washington University in St. Louis.[8] Missouri has been called the "Mother of the West" and the "Cave State", but its most famous nickname is the "Show Me State".[9]
Le Missouri (en anglais : /mɨˈzɝi/ ou /məˈzɝə/) est un État du Midwest des États-Unis, juste à l'ouest du fleuve Mississippi qui marque sa frontière orientale. Le Missouri est bordé à l'ouest par le Kansas, au nord par l'Iowa, au nord-ouest par le Nebraska, à l'est par l'Illinois, au sud-est par le Kentucky et le Tennessee, au sud par l'Arkansas et au sud-ouest par l'Oklahoma. Il tient son nom de la rivière Missouri, le plus important affluent du Mississippi et qui traverse l'État d'ouest en est.
Ses deux plus grandes villes sont Kansas City (qui partage son agglomération avec le Kansas) et Saint-Louis (qui partage son agglomération avec l'Illinois). La capitale de l'État est Jefferson City.
Il Missouri (AFI: /misˈsuri/[2]; in inglese , /mɨˈzʊəri/), italianizzato in Missuri[3], è uno stato federato del Midwest (talvolta viene considerato anche come Stato del Sud) degli Stati Uniti d'America. La capitale è Jefferson City, la città più grande è Kansas City, mentre l'area metropolitana più estesa è quella di Saint Louis. Attraverso lo Stato scorre il fiume Missouri fino a pochi chilometri a nord di Saint Louis dove sbocca nel fiume Mississippi che delinea i confini fra il Missouri e gli stati di Illinois, Kentucky e Tennessee.
Misuri21 (en inglés, Missouri) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Jefferson City y su ciudad más poblada, Kansas City. Se ubica en la región del Medio Oeste del país, división Centro Noroeste, limitando al norte con Iowa, al este con el río Misisipi que lo separa de Illinois, Kentucky y Tennessee, al sur con Arkansas, al suroeste con Oklahoma, al oeste con Kansas (la parte más septentrional de esta frontera está delimitada por el río Misuri) y al noroeste con el río Misuri que lo separa de Nebraska. Fue admitido en la Unión el 10 de agosto de 1821, como el estado número 24.
El apodo del estado es la Puerta al Oeste, o el Estado Muéstreme (Show-me State), en referencia a una expresión de un representante político del estado. La abreviatura del Servicio Postal de los Estados Unidos para Misuri es MO y la rama principal de la universidad estatal pública está localizada en Columbia. El río Misuri y el Misisipi son los dos ríos principales que fluyen por este estado. Misuri recibe su nombre del nombre dado a los missouria un grupo de lengua siux que fueron llamados ouemessourita (wimihsoorita3 'los que han tallado canoas'), por los miami-illinois (que eran algonquinos). Los buques de guerra USS Missouri fueron nombrados así en honor de este estado. En la cubierta del USS Missouri (BB-63) se firmó la rendición de Japón al finalizar la Segunda Guerra Mundial.
Миссу́ри[1][2] (англ. Missouri, МФА: [mɨˈzʊəri]) — штат[3] на Среднем Западе США, 24-й штат в составе федерации, 21-й штат по площади и 18-й по населению (население 6 021 988 человек). Штат объединяет 114 обычных округов и 1 городской округ — Сент-Луис. Столица — город Джефферсон-Сити. Крупнейшими городами являются — Сент-Луис, Канзас-Сити, Спрингфилд и Колумбия[4]. Официальное прозвище — «Штат „Покажи-ка мне“».

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD
 United States
United States
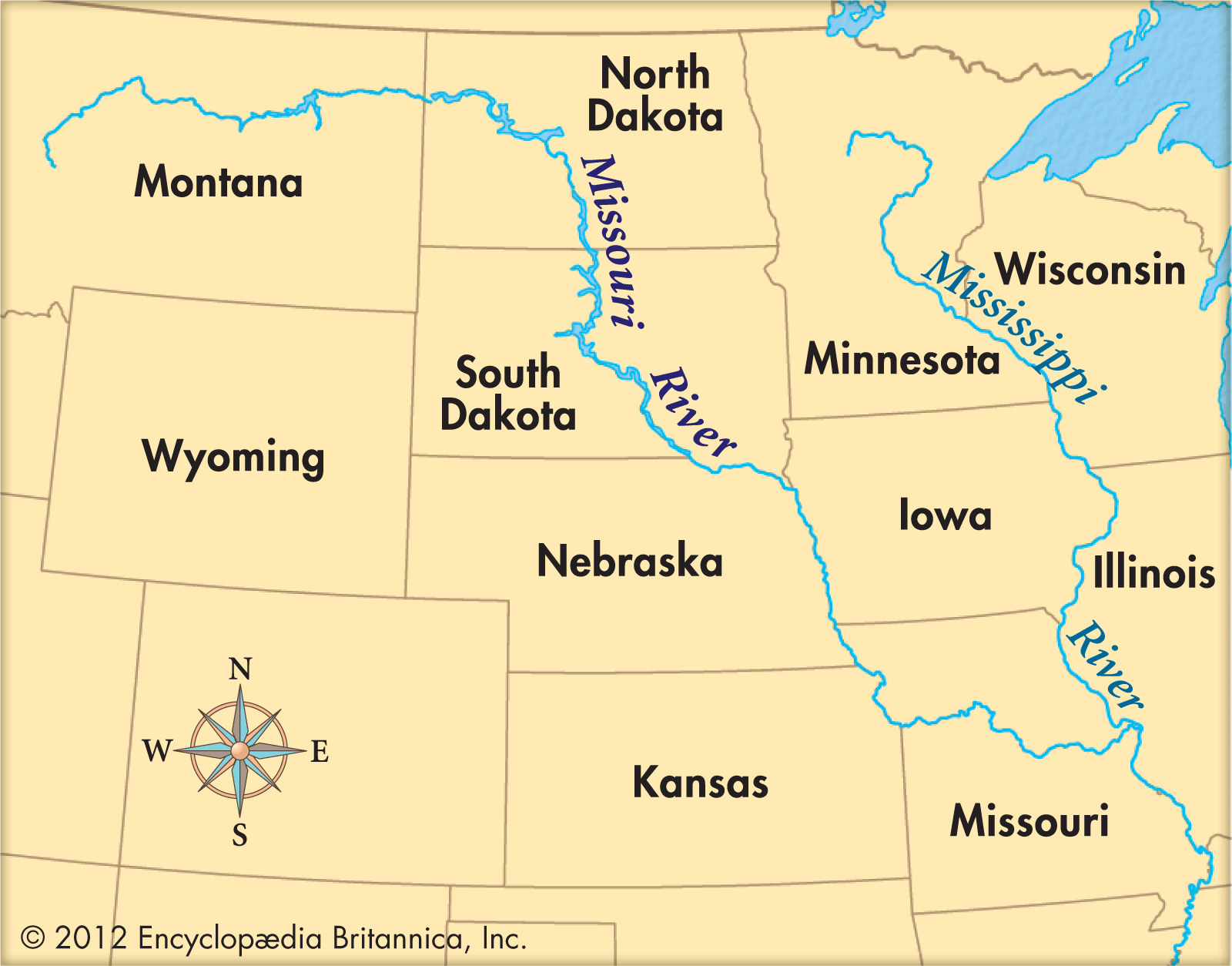
Der Missouri River [mɪˈzʊɹɪˌɹɪvɚ], der wegen seines hohen Schlammanteils auch den Spitznamen „Big Muddy“ trägt, ist mit 4087 Kilometern[1] der längste Nebenfluss des Mississippi River und der längste Fluss der USA, denn er ist länger als der Strom, in den er mündet.
Mit diesem Strom bildet der Missouri als Missouri-Mississippi das längste Flusssystem in Nordamerika und das viertlängste der Erde.
密苏里河(英语:Missouri River),美国主要河流之一,北美洲最长河流,在汇入密西西比河前,长3,767公里,流域面积逾130万平方公里。
 Geography
Geography
 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN
 International cities
International cities

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA
 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN