
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Indien
Indien



1947年印巴分治以前,印度河仅次于恒河,为该地区的文化和商业中心地带。该河流上源为狮泉河(森格藏布),它发源于冈底斯山脉冈仁波齐峰东北方向的切日阿弄拉山口西侧,源头位于中国西藏阿里地区革吉县境内,源头溪流名为邦果贡[1]。从喜马拉雅山脉朝西北方向流入克什米尔,调头向南流入巴基斯坦,在信德省的卡拉奇附近流进阿拉伯海。河流总长度3180公里,流域面积100万1549平方公里[1]。印度河文明为世界上最早进入农业文明和定居社会主要文明之一,后来因为约二百年的干旱而灭亡[2]。
印度河每年的流量约有207立方公里,是世界流量第二十一名的河流。赞斯卡河是位在拉达克的左岸支流,在进入平原后,印度河的左岸支流是潘季纳德河(五河),其五条主要支流分别是杰赫勒姆河、奇纳布河、拉维河、比亚斯河及萨特莱杰河。印度河的主要右岸支流有什约克河、吉尔吉特河、喀布尔河、库拉姆河及古马尔河及。印度河的沿岸有温带森林、平原及干旱乡村等不同的生态系统。
印度河形成了印度河三角洲,在古印度的《梨俱吠陀》中称为Sapta Sindhu,在伊朗人的波斯古经中称做Hapta Hindu,两者都是“七河”的意思。波斯王大流士曾在公元前510年派西拉克斯探索印度河。
The Indus River (called Sindhū in Sanskrit with derived names in most Indic languages)[1][2] is one of the longest rivers in Asia. It flows through China (western Tibet), India (Ladakh) and Pakistan.[3] Originating in the Tibetan Plateau in the vicinity of Lake Manasarovar, the river runs a course through the Ladakh region of India,[a] towards Gilgit-Baltistan and then flows in a southerly direction along the entire length of Pakistan to merge into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi in Sindh.[4] It is the longest river of Pakistan.[5]
The river has a total drainage area exceeding 1,165,000 km2 (450,000 sq mi). Its estimated annual flow stands at around 243 km3 (58 cu mi), twice that of the Nile River and three times that of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers combined, making it one of the largest rivers in the world in terms of annual flow.[6] The Zanskar is its left bank tributary in Ladakh. In the plains, its left bank tributary is the Panjnad which itself has five major tributaries, namely, the Chenab, Jhelum, the Ravi, the Beas, and the Sutlej. Its principal right bank tributaries are the Shyok, the Gilgit, the Kabul, the Gomal, and the Kurram. Beginning in a mountain spring and fed with glaciers and rivers in the Himalayan, Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, the river supports ecosystems of temperate forests, plains and arid countryside.
The northern part of the Indus Valley, with its tributaries, forms the Punjab region, while the lower course of the river is known as Sindh and ends in a large delta. The river has historically been important to many cultures of the region. The 3rd millennium BC saw the rise of a major urban civilization of the Bronze Age. During the 2nd millennium BC, the Punjab region was mentioned in the hymns of the Hindu Rigveda as Sapta Sindhu and the Zoroastrian Avesta as Hapta Hindu (both terms meaning "seven rivers"). Early historical kingdoms that arose in the Indus Valley include Gandhāra, and the Ror dynasty of Sauvīra. The Indus River came into the knowledge of the West early in the Classical Period, when King Darius of Persia sent his Greek subject Scylax of Caryanda to explore the river, c. 515 BC.
L’Indus (connu sous le nom de Sindh ou Sindhu dans l’Antiquité, et de Senge Khabab en tibétain « qui sort de la bouche du lion » au niveau de sa source) est un fleuve d'Asie qui a donné son nom à l’Inde1. Il coule depuis l’Himalaya en direction du sud-ouest et se jette dans la mer d'Arabie. L’Indus fait partie des sept rivières sacrées de l'Inde.
L'Indo è il più lungo e importante fiume del Pakistan. È il più lungo fiume del subcontinente indiano e il terzo più grande dell'Asia intera in termini di portata annua.
La sorgente dell'Indo si trova in Tibet tra monti Kailâs o Gangri. Il fiume prende il suo nome a partire dalla confluenza dei torrenti Sengge e Gar, che scendono dall'Himalaya raccogliendo le acque delle catene del Nganglong Kangri e del Gangdise Shan. L'Indo passa in seguito verso nord-ovest attraverso il Kashmir, a sud della catena del Karakorum, poi gradualmente gira verso sud, lasciando le colline tra Peshawar e Rawalpindi. In quest'area una diga forma il lago artificiale di Tarbela. A partire dalla sua confluenza con il fiume Kaboul, l'Indo diventa navigabile.
Il resto del suo tragitto verso il mare si svolge quindi nelle pianure del Panjab e del Sindh, e il fiume prende allora un corso molto lento. Attraversa Hyderabad poi si getta nel mare Arabico con un grande delta di 7770 km² che si estende su 200 km di costa, a sud-est di Karachi, ora considerata come una delle regioni ecologiche più importanti del mondo.El río Indo es un río asiático que discurre por el subcontinente indio, uno de los más largos del continente, el más importante de Pakistán y de los principales de la India (y que también recorre en su curso alto China). Originario de la meseta tibetana del oeste de China, en la Región Autónoma del Tíbet, el río discurre a través del distrito de Ladakh de Jammu y Cachemira y luego entra en Pakistán a través de Gilgit-Baltistán; sigue después desde el norte del país en dirección sur cruzando a lo largo todo Pakistán, hasta desembocar en el mar Arábigo, cerca de la ciudad portuaria de Karachi en Sind.
La longitud total del río es de 3.180 km, siendo el río más largo de Pakistán. Drena una gran cuenca de más de 1.165.000 km² y tiene un caudal anual estimado en unos 207 km³, lo que lo convierten en el 21º más caudaloso del mundo. Comenzando en las alturas del mundo con glaciares, el río alimenta el ecosistema de los bosques templados, llanuras y paisajes áridos. Junto con los ríos Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej, Beas y dos afluentes desde la Jaiber Pajtunjuá y Afganistán, el Indo forma el delta del Indo de Pakistán, mencionado en el Rig-veda (el texto más antiguo de la India, de mediados del II milenio a. C.) como Sapta Sindhu y en el texto iranio Zend Avesta como Hapta Hindu (significando ambos términos, ‘siete ríos’).
El río Indo proporciona los recursos hídricos clave para la economía de Pakistán —especialmente el granero de la provincia de Panyab, que representa la mayor parte de la producción agrícola de la nación, y de Sindh. El Indo también soporta muchas industrias pesadas y constituye el principal suministro de agua potable en Pakistán. Los cinco ríos que dan nombre al Panyab son el Jhelum, Chenab, el Ravi, el Beas y el Sutlej.
Antes de la división en 1947 de la antigua India en los modernos estados de la India y Pakistán, el Indo era el segundo río en importancia de la región, después del río Ganges, tanto en términos culturales como comerciales. En la actualidad el río también da nombre a la provincia pakistaní de Sind.
El río ha sido una fuente de asombro durante el periodo clásico. El rey Darío I de Persia envió a Escílax de Carianda a explorar el Indo entre los años 519 y 512 a. C., descendiéndolo hasta llegar al mar. Llamado Hindós o Indós por los griegos y luego Indus por los autores latinos, fue siempre conocido en Occidente por su nombre latinizado que también dio nombre a la India (Bharat).
Инд (тиб. སེང་གེ།་གཙང་པོ Sênggê Zangbo, кит. 印度河 Yìndù Hé, хинди सिन्धु नदी, з.-пандж. دریاۓ سندھ Sindh, пушту اباسين Abāsin, синдхи سنڌوندي Sindhu, урду دریائے سندھ) — крупная река в Южной Азии, берёт начало на территории Китая в Гималаях и протекает большей частью по территории северо-западной Индии и Пакистана. Исток находится на Тибетском нагорье, устье — на севере Аравийского моря[1], недалеко от города Карачи. Длина Инда — 3180 км, площадь бассейна 960 000[2] км². (980 тыс. км² в БСЭ[3]). Средний расход воды — 6600 м³/с.[источник не указан 1256 дней]
Названия: санскр. सिन्धु (Sindhu IAST); урду سندھ (Sindh); синдхи سندھو (Sindhu); в.-пандж. سندھ (Sindh IAST); авест. Hindu; пушту اباسين (Абба-Син «отец рек»); перс. هند («Hind»); тиб. སེངགེ་ཆུ («Lion River»); кит. упр. 印度河, пиньинь Yìndù Hé; греч. Ινδός (Индос).
Инд (Синдху) — одна из главных рек ведийского Семиречья.

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 E 2500 - 2000 vor Christus
E 2500 - 2000 vor Christus

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 F 2000 - 1500 vor Christus
F 2000 - 1500 vor Christus

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 G 1500 - 1000 vor Christus
G 1500 - 1000 vor Christus
 Geschichte Indiens
Geschichte Indiens
 Indien
Indien
 Pakistan
Pakistan

 Zivilisation
Zivilisation

Die bronzezeitliche Indus-Kultur oder Indus-Zivilisation war eine der frühesten städtischen Zivilisationen. Sie entwickelte sich etwa in den Jahren 2800–1800 v. Chr. entlang des Indus im Nordwesten des indischen Subkontinents. Die Indus-Kultur erstreckte sich über fast das gesamte heutige Pakistan sowie Teile Indiens und Afghanistans, insgesamt umfasste sie 1.250.000 km² und damit eine größere Landfläche als das antike Ägypten und Mesopotamien zusammen. Sie war neben diesen eine der drei frühesten Zivilisationen der Welt.
Sie wird teilweise auch Harappa oder Harappa-Kultur genannt, nach Harappa, einem der Hauptausgrabungsplätze am Ravi. Eine weitere alternative Benennung dieser Kultur lautet Sindhu-Sarasvati-Zivilisation; hinter dieser Bezeichnung steht die Theorie, dass sie eine in der vedischen Literatur erwähnte Zivilisation sei. Möglicherweise ist sie auch mit dem sumerischen Meluha zu identifizieren.
Bis heute sind über 1050 Fundorte identifiziert, hauptsächlich entlang des Indus. Zusätzlich gibt es Hinweise auf einen anderen großen Fluss östlich des Indus, der heute ausgetrocknet ist und der antike Ghaggra-Hakra oder Sarasvati gewesen sein könnte. Über 140 antike Städte und Siedlungen wurden an seinem Lauf gefunden. Die beiden größten urbanen Zentren der Harappa-Kultur waren wohl Harappa und Mohenjo-Daro, daneben gab es noch große Städte bei Dholavira, Ganweriwala, Lothal und Rakhigarhi. Zu ihrer Blütezeit zählte die Indus-Kultur vermutlich über fünf Millionen Menschen.
Diese frühe indische Kultur kannte bereits Architektur und eine regelmäßige Städteplanung einschließlich gepflasterter Straßen mit Straßenablauf (Gullys). Sie entwickelte zum ersten Mal in der Geschichte der Menschheit den gebrannten Ziegel mit den perfekten, noch heute gebräuchlichen Proportionen 1:2:4, der als Einhandziegel in allen Richtungen beliebig addierbar ist.
Möglicherweise besaß sie auch eine Schrift; ob aber die sogenannte Indus-Schrift tatsächlich eine Schrift ist, wird in Fachkreisen bisher kontrovers diskutiert.
印度河流域文明(IVC) ,也称哈拉帕文明(harappa)、印度河谷文明(英语:Indus Valley Civilization),是一个南亚青铜时代约公元前3300年至前1300年之时期的古代文明,鼎盛于公元前2600到公元前1900间[1][a]。因起源于印度河和萨拉斯瓦蒂河流域,有时也称之为文明摇篮之一的古印度印萨两河文明[2][b]。
因印度河古文明兴盛于印度河沿岸盆地,故虽名古印度文明,但地理上大致主要是包括在今天的巴基斯坦的整个纵深长度;不过,印度西北和巴基斯坦东部的一部分季风性季节性河流沿岸也包含在内[1][3]。印度河谷文明最著名的特点是其独特的城市规划、烧制砖建房屋、供水系统、成群的大型非住宅建筑、进步的手工艺制造和冶金(铜、青铜、铅、锡)工艺[4]。摩亨佐-达罗和哈拉帕非常有可能一度发展到独自容纳30000至60000名居民的规模[5][c],而在其鼎盛时期整个文明可能包含了1至5百万人口[6][d]。
公元前3世纪逐渐严重的全新世干旱化[7]导致了印度河谷的土壤退化;这首先加快了该文明人口的城镇化,但最终减少的季风性降水使得印度河流域文明陷入困境,其人口不得不向东、南方向的地区迁徙[8][9]。
印度河流域文明发源晚于两河流域文明、尼罗河流域文明,但早于商朝。 考古专家在印度河、萨拉斯瓦蒂河流域发现摩亨佐-达罗和哈拉帕两个古代城市遗址,发现了大量石器、青铜器、印章和农作物遗迹,估计城市人口都在4万以上。
两个城市的中心都有一个人工堆成的土墩,作用未知,考古学家猜测这可能是城市的中心。城市建筑以卫城为中心呈网格状分布,有市政建筑、市场、作坊、储存区、民居和神庙。每座民居都围着一个院子建成,有几个房间、一间厕所和一口水井。建筑用基本材料是从烧木头的窑里制出的土砖。在摩亨佐-达罗的卫城上建造了一个浴池,有私人浴池、会所等。
印度河流域的农民种植大麦、小麦、棉花、瓜和椰枣。他们还驯养大象和水牛在田里工作。这一地区有许多手艺精湛的制陶人,他们也用陶轮制作陶器,这是产生于两河流域苏美尔人的技术。哈拉帕人使用石器,并用青铜制作刀、武器、碗和雕像。他们建立了发达的废物处理系统,包括有盖板的排水系统和倒垃圾的斜槽。
遗址中有许多天秤和砝码,说明他们有一套度量衡制度好配合其繁荣的商业贸易。而印度河流域文明更证明与两河流域文明,阿富汗,缅甸甚至和古中国都有商业往来。
印度河文明持续了800年,目前尚不得知其结束的原因,但是有几种假说:外族入侵、地震、气候变化导致的干旱或是人为的生态灾难,这些假说都可能解释一部分导致其经济和文明秩序崩溃的原因。
インダス文明(インダスぶんめい、Indus Valley civilization)は、インド・パキスタン・アフガニスタンのインダス川および並行して流れていたとされるガッガル・ハークラー川周辺に栄えた文明である。これら各国の先史文明でもある(インドの歴史、アフガニスタンの歴史も参照)。崩壊の原因となったという説のあった川の名前にちなんでインダス文明、最初に発見された遺跡にちなんでハラッパー文明とも呼ばれる[1]。
狭義のインダス文明は、紀元前2600年から紀元前1800年の間を指す。インダス文明の遺跡は、東西1500km、南北1800kmに分布し、遺跡の数は約2600におよぶ。そのうち発掘調査が行われた遺跡は、2010年時点でインド96、パキスタン47、アフガニスタン4の合計147となっている[2]。
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE.[1] Along with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia it was one of three early civilisations of the Old World, and of the three, the most widespread, extending from what today is northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India.[2][note 1] It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial, mostly monsoon-fed, rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the seasonal Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.[1][3] Aridification of this region during the 3rd millennium BCE may have been the initial spur for the urbanisation associated with the civilisation, but eventually also reduced the water supply enough to cause the civilisation's demise, and to scatter its population eastward.[4][5][3][6]
The civilisation's cities were noted for their urban planning, baked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, clusters of large non-residential buildings, and new techniques in handicraft (carnelian products, seal carving) and metallurgy (copper, bronze, lead, and tin). [7] Its large urban centres of Mohenjo-daro and Harappa very likely grew to containing between 30,000 and 60,000 individuals,[8][note 2] and the civilisation itself during its florescence may have contained between one and five million individuals.[9][note 3]
The Indus civilisation is also known as the Harappan Civilisation, after its type site, Harappa, the first of its sites to be excavated in the 1920s in what was then the Punjab province of British India and now is Pakistan.[10][note 4] The discovery of Harappa and soon afterwards Mohenjo-Daro was the culmination of work beginning in 1861 with the founding of the Archaeological Survey of India during the British Raj.[11] There were however also earlier and later cultures often called Early Harappan and Late Harappan in the same area; for this reason, the Harappan civilisation is sometimes called the Mature Harappan' culture to distinguish it from these cultures. By 2002, over 1,000 Mature Harappan cities and settlements had been reported, of which just under a hundred had been excavated,[12][note 5][13][14][note 6] mainly in the general region of the Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra Rivers and their tributaries; however, there are only five major urban sites at the peak of the settlement hierarchy:[15][note 7] Harappa, Mohenjo-daro (UNESCO World Heritage Site), Dholavira, Ganeriwala in Cholistan and Rakhigarhi.[16][note 8] The early Harappan cultures were preceded by local Neolithic agricultural villages, from which the river plains were populated.[17][18]
The Harappan language is not directly attested, and its affiliation is uncertain since the Indus script is still undeciphered.[19] A relationship with the Dravidian or Elamo-Dravidian language family is favoured by a section of scholars.[20][21]
La civilisation de la vallée de l'Indus (vers 2600 av. J.-C. – vers 1900 av. J.-C.), ou civilisation harappéenne, du nom de la ville antique de Harappa, est une civilisation de l'Âge du bronze, dont le territoire s'étendait autour de la vallée du fleuve Indus, dans l'ouest du sous-continent indien (le Pakistan moderne et ses alentours). Les raisons de son émergence, de sa prospérité rayonnante durant sept siècles, puis de son déclin brutal, sont mal connues et restent débattues, ainsi que son influence, probable, sur la culture hindoue antique.
Oubliée jusqu’à sa découverte dans les années 1920, la civilisation de l’Indus se classe, avec celles de la Mésopotamie et de l’Égypte antique, comme l’une des toutes premières civilisations de l'histoire, celles-ci étant définies par l'apparition de villes, puis de l’écriture.
Si la civilisation de l’Indus n’est pas considérée comme la première civilisation antique, la Mésopotamie et l’Égypte ayant développé des villes un peu plus tôt, elle est par contre celle qui connait à son époque la plus grande extension géographique. À ce jour, sur les 1 052 sites qui ont été découverts, plus de 140 se trouvent sur les rives du cours d'eau saisonnier Ghaggar-Hakra. D’après certaines hypothèses, ce système hydrographique, autrefois permanent, arrosait la principale zone de production agricole de la civilisation de l’Indus.
La plupart des autres sites se situent le long de la vallée de l’Indus et de ses affluents, mais on en trouve aussi à l’ouest, jusqu’à la frontière de l’Iran, à l’est jusqu’à Delhi, au sud jusque dans le Maharashtra, et au nord jusqu’à l’Himalaya. Parmi ces sites, on compte de nombreuses villes comme Dholavira, Ganweriwala, Mehrgarh, Harappa, Lothal, Mohenjo-daro et Rakhigarhi. À son apogée, sa population pourrait avoir dépassé cinq millions de personnes.
Malgré toutes ses réalisations, cette civilisation est très mal connue. Son existence même a été oubliée jusqu’au XXe siècle. Son écriture reste indéchiffrée et on ne sait pas si elle a un lien quelconque avec l’écriture brahmi, ce qui semble peu probable au regard des connaissances actuelles. Parmi les mystères que cette civilisation recèle, trois questions au moins sont fondamentales :
- formait-elle un État ou un ensemble de cités-états ?
- quels étaient ses moyens de subsistance ?
- quelles sont les causes de sa disparition soudaine et dramatique, à partir du XIXe siècle av. J.-C. ?
La langue utilisée par ses membres et le nom qu’ils se donnaient restent à ce jour inconnus.
La civiltà della valle dell'Indo (c. 3300–1500 a.C., fiorita 2600–1900 a.C.) fu una civiltà antica, estesa geograficamente soprattutto lungo il fiume Indo nel subcontinente indiano, ma anche lungo il Sarasvati, un fiume dell'India ormai prosciugato.
Nel mondo anglosassone viene citata come "civiltà dell'Indo-Sarasvati", in riferimento alla civiltà descritta nei Veda e che si sarebbe sviluppata lungo i due fiumi. È anche conosciuta come "civiltà di Harappa", dal primo sito conosciuto, scoperto nel 1857, ma scavato soltanto dagli anni venti del Novecento.
La cultura del valle del Indo fue una civilización de la Edad del Bronce, que se desarrolló desde c. 3300 a. C. hasta 1300 a. C. a lo largo del valle del río Indo, en Afganistán, Pakistán y el noroeste de la India. Abarcaba cerca de un centenar de asentamientos y dos ciudades importantes: Harappa y Mohenjo-Daro, ambos sitios en Pakistán. En conjunto comprendía el área más extensa de todas las civilizaciones antiguas, más de un millón de kilómetros cuadrados, y atravesó varios periodos, siendo su máximo esplendor entre el 2600 y el 1900 a. C.
Al igual que las civilizaciones de Mesopotamia y Egipto, dependía de su río. Como el Nilo, el Indo se desbordaba todos los años, inundando extensas zonas y depositando sedimentos fértiles. Este inmenso potencial agrícola fue la base sobre la cual se desarrolló el urbanismo en torno al río Indo.
Con las culturas prehistóricas del valle del Indo se prepara el primer capítulo de la historia de la India. Se trata de un largo periodo prehistórico, probado por testimonios líticos. Por otra parte, se pueden encontrar vestigios prehistóricos hasta el I milenio a. C., es decir, hasta un tiempo en que la península ya había entrado en la historia. En sentido estricto, las culturas del Indo pertenecen a la prehistoria ya que solamente han dejado restos arqueológicos sin documentos literarios, pero para apreciar la historia india hace falta tomar en consideración estas culturas urbanas prearias.
И́ндская или Хара́ппская цивилизация — третья[* 1] по времени появления древневосточная цивилизация бронзы[1], после египетской и месопотамской. Из всех трёх она занимала наибольшую площадь, превосходя в 2 раза суммарную площадь двух остальных[2][3]. Индская цивилизация относительно быстро пришла в упадок, пережив расцвет между 2600—1900 годами до нашей эры, см. Засуха 2200 года до н. э..
Хараппская цивилизация развивалась в долине реки Инд в 3300—1300 годах до нашей эры[4]. Наиболее значительные центры — Ракхигархи (350 га), Мохенджо-Даро (300 га)[5], Хараппа (150 га), Лотхал (60 га) и Дхолавира — 47 гектаров.[6]. Население в годы расцвета составляло около 5 миллионов человек и состояло из эламито-дравидов, без примеси индоевропейцев[7]. Зрелый период развития Индской цивилизации шёл с 2600 до 1900 лет до нашей эры. Простиралась на территориях нынешних Афганистана, Пакистана и Северо-Западной Индии.
В шумерских текстах хараппская цивилизация предположительно носила название «Мелухха»[8].
В течение III-го тысячелетия до нашей эры началась аридизация — постепенное истощение водных ресурсов региона, где находилось государство. Возможной причиной аридизации археологи называют возросшую урбанизацию в регионе и постепенное осушение почв и рек. В итоге это могло привести к упадку государства. При этом, после упадка, население ушло на Восток.
Первые данные о существовании доарийской цивилизации в западной Индии опубликовал в XIX веке Александр Каннингем. Окончательно существование индской цивилизации было установлено в 1921—1922 годах экспедицией во главе с Джоном Маршаллом.
На пике развития индская цивилизация имела население свыше 5 миллионов человек. Жители долины реки Инд разработали ряд новых ремёсел — обработку сердолика, обработку кости, металлургию бронзы, меди, свинца и олова. Города хараппской цивилизации отличаются чётким планированием построек. Строительный материал — обожжённый кирпич из глины. Освоены и использовались сложные дренажные системы, системы водоснабжения и целые кластеры крупных нежилых зданий.
При раскопках городов были найдены как детские игрушки, так и небольшое количество оружия, что указывает на не сильную милитаризацию государства и относительно мирные периоды существования. Ставка в развитии была сделана на торговлю с далёкими землями, дальше чем Вавилон, Шумер и южная Месопотамия. На развитую торговлю указывают многочисленные печати, украшенные животными и мифическими существами.
Названия «цивилизация Инд» и «цивилизация Хараппы» — равнозначны в археологической литературе[источник не указан 150 дней], хотя термин «Хараппа» может ввести в заблуждение, так как это обозначение дано по названию современного городка Хараппа, где располагается хронологически первая археологическая площадка, раскопанная еще в 1920-е годы. Вскоре был обнаружен и исследован Мохенджо-Даро, что привело к сенсационным открытиям. Данные памятники относятся к зрелому этапу хараппской цивилизации и отличаются от предшествующих и последующих культур, называемых ранней хараппской и поздней хараппской культурами. Ранней хараппской культуре предшествовали местные неолитические поселения сельскохозяйственного типа.
К 2008 году было найдено 1 022 города и поселения, главным образом в районе рек Инд и Гхаггар-Хакра и их притоков. Из них 406 объектов найдены на территории нынешнего Пакистана и 616 в Индии. Раскопаны и изучены — 96 объектов. Среди этих 96 объектов значатся крупные городские центры, в том числе Хараппа, Мохенджо-Даро (объект Всемирного наследия Юнеско), Дхолавира, Ганеривала[en], Ракхигархи.
Язык государства не имеет точной идентификации, его генеалогическая принадлежность пока не ясна. Связи хараппского языка и дравидийских и эламо-дравидийских языков изучены недостаточно.[9]

 Energieressource
Energieressource

 Energieressource
Energieressource
 *Atomkraft
*Atomkraft

 Energieressource
Energieressource
 *Elektrische Energie
*Elektrische Energie

 Energieressource
Energieressource
 Kernkraftwerke
Kernkraftwerke
 Indien
Indien
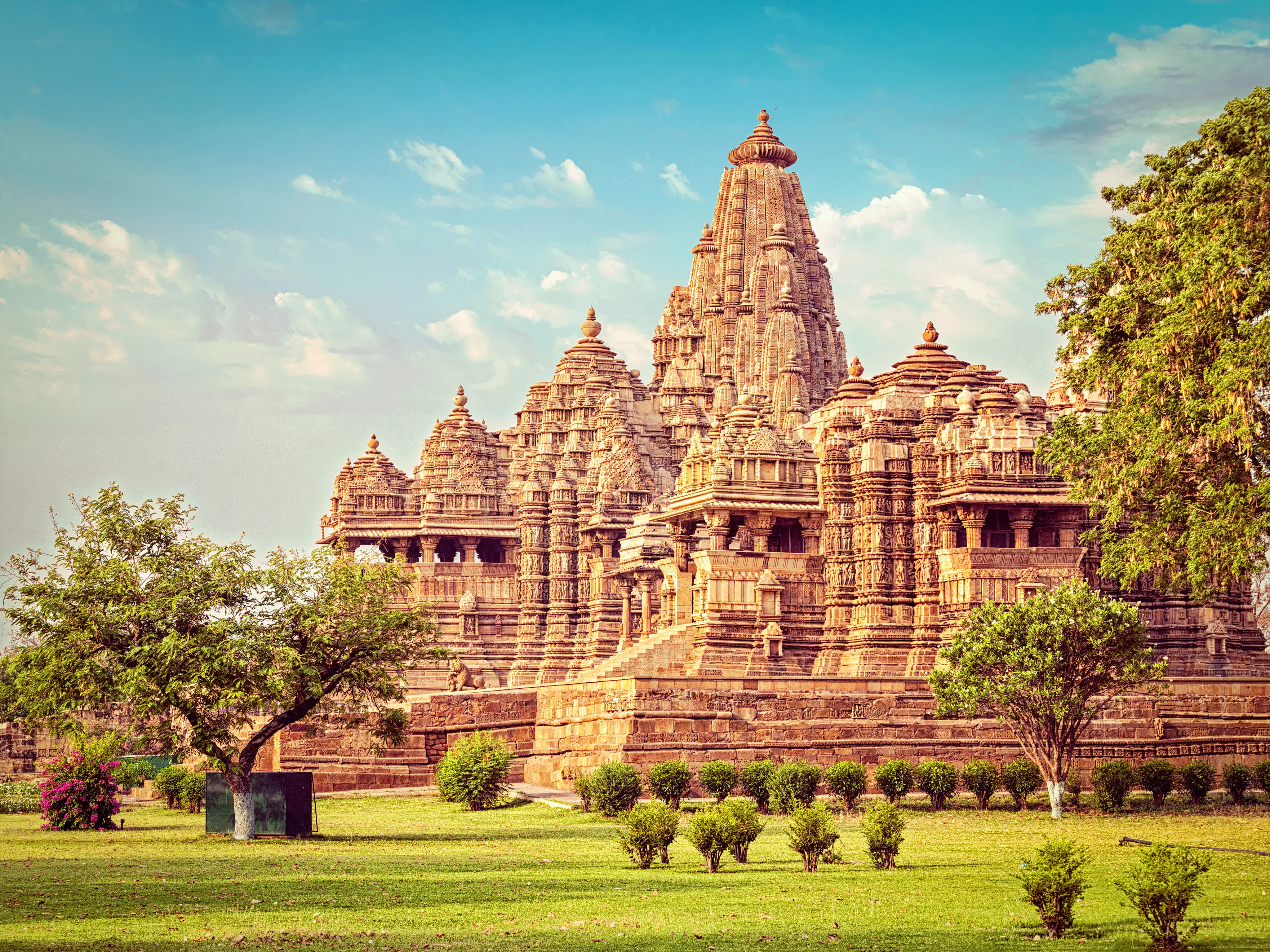






Die indische Architektur umfasst die Architektur des indischen Subkontinents mit den Staaten Indien, Pakistan, Bangladesch, Nepal und Sri Lanka vom Beginn der Indus-Kultur im 3. Jahrtausend v. Chr. bis heute. Sie spiegelt sowohl die ethnische und religiöse Vielfalt des indischen Subkontinents als auch dessen historische Entwicklung wider.
印度建筑包括印度次大陆(印度、巴基斯坦、孟加拉国、尼泊尔和斯里兰卡)从公元前三千年印度河文明开始至今的建筑。它反映了印度次大陆的民族和宗教多样性及其历史发展。
Allgemeines
Die ältesten Hindu Tempel, Bauten aus Holz und Lehm, haben die Jahrtausende nicht überlebt. Die späteren Steintempel versuchten jedoch, die Holztempel nachzuahmen. Ein Hindu Tempel war in der Regel die Stiftung eines Herrschers oder Angehörigen des Hofstaates. Er steht immer an einer "heiligen" Stelle. Meistens hat es eine Wasserstelle oder einen Garten in der Nähe und liegt außerhalb der Städte.
Der Hindutempel entwickelte sich als eine Synthese aus Architektur, Skulptur und Malerei. Oft wurden spezielle Hallen errichtet, in denen Musik- und Tanzveranstaltungen stattfanden. Alle Künste sollten den Wohnplatz der Götter attraktiv machen und die Legenden vor den einfachen Menschen präsentieren. ln den Shilpashastras (Bücher über die Baukunst) wurden der Grundriß und die Proportionen der Tempel genau beschrieben. (Quelle:http://www.indien-reise.com/)

Indien belegt mit einer Fläche von 3.287.263 km² Rang 7 in der Welt.
Den Süden prägt tropischer Monsun, während sich der Norden deutlich gemäßigter gibt.
Entlang des Ganges ist das Gelände überwiegend eben und steigt im Süden auf das Hochland von Dekkan, im Norden zu den Himalayas an. Der Kanchenjunga, mit einer Höhe von 8.598m der dritthöchste Berg der Welt, liegt auf der Grenze zu Nepal. Als Kontrast findet man im Westen Indiens die Wüsten.

印度考古研究所(Archaeological Survey of India),或译印度考古調查局,是印度文化部下属的一个政府部门,负责印度古迹的研究与保护。它由亚历山大·卡宁厄姆创立于1861年,亚历山大·卡宁厄姆本人也是其第一任所长[2]。
Der Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) in Neu-Delhi ist eine Abteilung des indischen Kulturministeriums, die für die archäologische Erforschung sowie Erhaltung des Kulturguts Indiens verantwortlich ist. Er hat seinen Hauptsitz im Dharohar Bhawan, 24 Tilak Marg, New Delhi 110001.
 Transport und Verkehr
Transport und Verkehr
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen
 Messe
Messe


 Luft- und Raumfahrt
Luft- und Raumfahrt
 Geographie
Geographie

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Architektur
Architektur
 Religion
Religion
 Kunst
Kunst
 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe
 Essen und Trinken
Essen und Trinken