什叶派(阿拉伯语:شيعة,Shīʿah,英语:Shia,/ˈʃiːə/),来自阿拉伯语:شيعة علي(Shīʻatu ʻAlī,Shia-ne-Ali)的缩写,原意为阿里的追随者,与逊尼派并列为伊斯兰教的两大主要教派之一。什叶派与逊尼派各门派中的主要不同不在于教义问题,主要在于谁是穆罕默德“真正接班人”。在历史上曾出现过“穆阿维耶什叶”、“奥斯曼什叶”和“阿里什叶”等,目前则专指认为穆罕默德的继任者是阿里·本·阿比·塔利卜(穆罕默德堂弟及女婿)的人,逊尼派则认为穆罕默德的继任者是他的岳父阿布·伯克尔。
Die Schia (arabisch الشيعة asch-schīʿa, DMG aš-šīʿa ‚Anhängerschaft, Partei, Gruppe‘), im Deutschen auch Schiitentum oder Schiismus genannt, ist nach dem Sunnitentum die zweitgrößte religiöse Strömung innerhalb des Islams. Heute wird der Begriff häufig in verallgemeinernder Weise für die Zwölferschia verwendet, die die zahlenmäßig größte Gruppe innerhalb der Schia darstellt, allerdings umfasst die Schia noch zahlreiche andere Gruppierungen.
シーア派(アラビア語:الشيعة、ラテン文字転写:ash-Shīʻa(h))は、イスラム教の二大宗派の一つで、2番目の勢力を持つ。最大勢力であるもう一方はスンナ派(スンニ派)である。
7世紀のカリフであったアリー[1]とその子孫のみが、預言者の代理たる資格を持ち、「イスラム共同体(ウンマ))」の「指導者(イマーム)」の職務を後継する権利を持つと主張する。
Shia Islam or Shi'ism is one of the two main branches of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor and the Imam (leader) after him,[1] most notably at the event of Ghadir Khumm, but was prevented from the caliphate as a result of the incident of Saqifah. This view primarily contrasts with that of Sunni Islam, whose adherents believe that Muhammad did not appoint a successor and consider Abu Bakr, who was appointed caliph by a group of Muslims at Saqifah, to be the first rightful caliph after Muhammad.[2] A person observing Shia Islam is called a Shi'ite.
Shia Islam is based on Muhammad's hadith (Ghadir Khumm).[3][4] Shia consider Ali to have been divinely appointed as the successor to Muhammad, and as the first Imam. The Shia also extend this Imammah to Muhammad's family, the Ahl al-Bayt ("the people/family of the House"),[5] and some individuals among his descendants, known as Imams, who they believe possess special spiritual and political authority over the community, infallibility and other divinely ordained traits.[6] Although there are many Shia subsects, modern Shia Islam has been divided into two main groupings: Twelvers and Ismailis, with Twelver Shia being the largest and most influential group among Shia.[7][8][9]
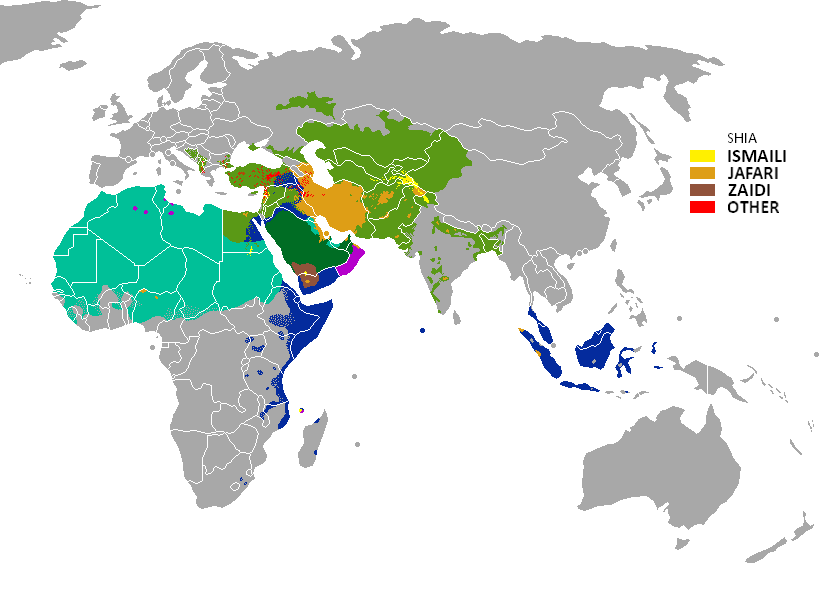
Il regroupe environ 10 à 15 % des musulmans. La première communauté chiite vit en Iran, où elle constitue 90 % de la population du pays, et environ 40 % de la population chiite mondiale2,3,4. Le reste des musulmans chiites se répartit principalement en Irak, en Azerbaïdjan, au Pakistan, en Inde, à Bahreïn et au Liban.
L’Islam sciita (in arabo: شيعة, shiʿa «partito, fazione», sottinteso «di ʿAli e dei suoi discendenti») è il principale ramo minoritario dell'Islam (intorno al 15% ai primi del XXI secolo).
Se da un lato essa presenta la maggioranza della popolazione in Iran, Iraq, Azerbaigian e Bahrein, dall'altro in Libano e in Yemen essa costituisce una forte e significativa minoranza, con quasi un terzo della popolazione di fede sciita.
In Egitto invece, in Siria, in Turchia, in Afghanistan, in India, in Qatar, in Kuwait, in Pakistan, nell'Asia Centrale ex-sovietica, nell'Africa islamica a sud del Sahara, lo sciismo vanta percentuali assai minori (tra il 5% e il 10%), come è il caso della stessa Arabia Saudita, col suo scarso 4-5% all'incirca. Anche all'interno dello sciismo (come nel sunnismo e nel kharigismo) ci sono i sufi e coloro che rifiutano l'approccio sufico considerato troppo libero.
El chiismo o islam chií (o chía, en árabe, شيعة (šīʿa)) constituye una de las principales ramas del islam junto al sunismo. Es el nombre tradicional por el que se conoce a la escuela de jurisprudencia islámica Ya'farita. El chiismo es profesado por alrededor del 15 % de los 1600 millones de musulmanes existentes en el mundo.2
Шии́ты (араб. شيعة; [шӣ‘а] — приверженцы, последователи) — направление ислама, объединяющее различные общины, признавшие Али ибн Абу Талиба и его потомков единственно законными наследниками и духовными преемниками пророка Мухаммеда[1]. В узком смысле понятие, как правило, означает шиитов-двунадесятников, преобладающее направление в шиизме, которое преимущественно распространено в Иране, Азербайджане, Бахрейне, Ираке и Ливане, а также в Йемене, Афганистане, Турции, Сирии, Кувейте, Пакистане, ОАЭ.




 History
History
 Religion
Religion



