German — Chinese

 *Track and field athletics
4x400 m Woman
*Track and field athletics
4x400 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
4x100 m Woman
*Track and field athletics
4x100 m Woman
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit

 History
M 1500 - 2000 AD
History
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
N 2000 - 2100 AD
History
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
2005 Helsinki
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
1999 Seville
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
1999 Seville
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
1993 Stuttgart
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
1993 Stuttgart




 Military, defense and equipment
Nuclear Weapon
Military, defense and equipment
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Party and government
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
BRICS
Party and government
BRICS
 Russia
Russia
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations Security Council
United Nations
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb
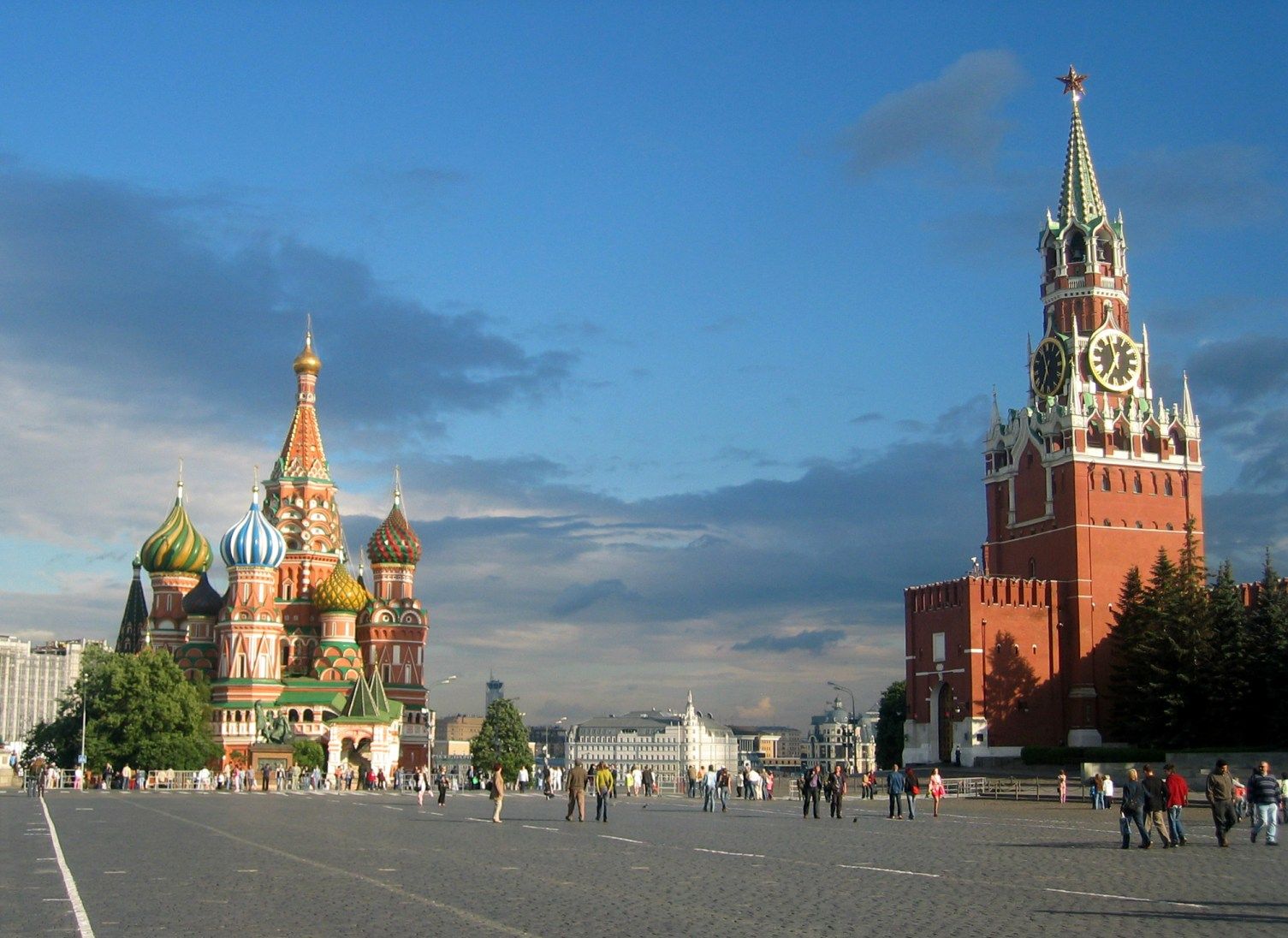
俄罗斯联邦[9](俄语:Российская Федерация,缩写为РФ),通称俄罗斯(Россия)[10],是位于欧亚大陆北部的联邦共和国,国土横跨欧亚两大洲,为世界上土地面积最大的国家,拥有1709万平方公里的面积,占地球陆地面积八分之一[11][12];它也是世界上第九大人口国家,拥有1.4亿人口,77%居住于其较为发达的欧洲部分。俄罗斯国土覆盖整个亚洲北部及东欧大部,横跨11个时区,涵盖广泛的环境和地形。拥有全世界最大的森林储备和含有约世界四分之一的淡水的湖泊[13]。俄罗斯有十四个陆上邻国(从西北方向起逆时针序):挪威、芬兰、爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚、立陶宛、波兰、白俄罗斯、乌克兰、格鲁吉亚、阿塞拜疆、哈萨克斯坦、中国、蒙古和朝鲜(其中立陶宛和波兰仅与俄罗斯外飞地加里宁格勒州接壤),另外与阿布哈兹和南奥塞梯两个只有俄罗斯承认的非联合国会员国接壤。同时,俄罗斯还与日本、美国、加拿大、格陵兰(丹麦)、冰岛、瑞典、土耳其隔海相望。俄罗斯北部和东部分别为北冰洋和太平洋包围,西北和西南则分别可经由波罗的海和黑海通往大西洋。
俄罗斯历史始于欧洲的东斯拉夫民族,聚集区域自公元3世纪至8世纪逐渐扩大[14]。在9世纪,源自北欧的瓦良格人武士精英建立了基辅罗斯这个中世纪国家并开始统治。公元988年,国家从拜占庭帝国采纳了东正教会,随后由此开始,千年拜占庭与斯拉夫文化的融合成为了今日的俄罗斯文化[15]。基辅罗斯最终解散分化为众多公国,被蒙古人逐一击破,并均在13世纪成为了金帐汗国的一部分。莫斯科大公自14世纪起逐渐崛起并统一周边俄罗斯诸侯国,在15世纪成功从金帐汗国独立,且成为了基辅罗斯文化和政治的继承者。16世纪起伊凡四世自称沙皇,自诩“第三罗马”。在18世纪,俄罗斯沙皇国通过征服、吞并和探索而扩张。彼得一世称帝成立了俄罗斯帝国,最终成为史上领土第三大帝国,疆域最大曾自中欧的波兰连绵至北美的阿拉斯加[16][17]。
1917年俄国革命后,俄罗斯苏维埃联邦社会主义共和国成为了世界上第一个宪法意义上的社会主义国家[18],并成为随后成立的苏维埃社会主义共和国联盟的主体和其最大的加盟共和国。二战时期,苏联为同盟国的胜利扮演了决定性的角色。在战后其崛起成为公认的超级大国,并在冷战时期与美国互相竞争。苏联时期产生了20世纪的许多最重要的科技成就,其中包括世界第一颗人造地球卫星,以及首次将人类送入太空。在1990年,苏联为世界上第二大经济体[19],且拥有世界上最多的常备军人以及最多的大规模杀伤性武器库存。1991年苏联解体后,包括俄罗斯在内的15个共和国从原苏联独立;身为原苏联最大的加盟共和国,俄罗斯通过修宪改制为俄罗斯联邦,成为原苏联的唯一法理继承国家,政体采用联邦制、民主共和制及半总统制。
截至2015年,俄罗斯根据国民生产总值为世界第13大经济体,根据购买力平价为世界第六大经济体。俄罗斯拥有世界上最大储量的矿产和能源资源[20],是世界上最大的石油和天然气输出国[21][22]。俄罗斯为世界大国之一,为认定的拥核国家,联合国安理会常任理事国,G20、欧洲理事会、亚太经合组织、上合组织、欧安组织、世贸组织和金砖国家成员。它也是独联体、集体安全条约组织的领导者和欧亚经济联盟创始成员。俄罗斯亦是世界八大工业国之一。
Russland (russisch Россия [rɐˈsʲijə] , Transkription Rossija) bzw. die Russische Föderation (oder der russischen Bezeichnung entsprechend Russländische Föderation; russisch Российская Федерация, , Transkription Rossijskaja Federazija)[9] ist ein souveräner, föderativer Staat im nordöstlichen Eurasien und mit etwa 17 Millionen Quadratkilometern flächenmäßig der größte Staat der Erde. Russland umfasst mehr als ein Achtel der bewohnten Landmasse der Erde und steht mit 144 Millionen Einwohnern (2017) an 9. Stelle der bevölkerungsreichsten Länder; es ist zugleich eines der am dünnsten besiedelten. Der europäische Teil des Staatsgebiets ist viel dichter besiedelt und verstädtert als der über dreimal so große asiatische Teil: Etwa 77 % der Bevölkerung (110 Millionen Einwohner) leben westlich des Urals. Die Hauptstadt Moskau ist eine der größten Städte und Metropolregionen der Welt; als weiteres wichtiges Zentrum gilt Sankt Petersburg, das zwischen 1712 und 1918 Hauptstadt war und eine Brücke für Kunst und Kultur aus Westeuropa bildete.
Die nächstgrößeren Millionenstädte Russlands sind Nowosibirsk in Sibirien, Jekaterinburg im Ural und Nischni Nowgorod an der Wolga. Weitere Großstadtregionen sind Tscheljabinsk, Ufa und Kasan.
Das heutige Russland entwickelte sich aus dem Großfürstentum Moskau, einem Teilfürstentum des früheren ostslawischen Reiches Kiewer Rus, zu einem über einhundert Ethnien zählenden Vielvölkerstaat, wobei ethnische Russen heute fast 80 Prozent der Bevölkerung ausmachen. Die föderale Gliederung Russlands besteht aus acht Föderationskreisen und 85 Föderationssubjekten.
Die Russische Föderation ist „Fortsetzerstaat“[10] der Sowjetunion in internationalen Organisationen, Atommacht und ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates. Nach der Erholung von der postkommunistischen Transformationskrise der 1990er Jahre wurde Russland die nach Kaufkraftparität sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt, zwischen Deutschland und Brasilien (Schätzung für 2016).[11]
Russlands Rohstoffreserven sind mit etwa 20 bis 30 % die wahrscheinlich größten der Welt,[12][13][14] mit erheblichen Vorkommen von Primärenergieträgern, vor allem Erdgas.
Russland gehört zu den anerkannten Nuklearmächten und besitzt das weltgrößte Arsenal an Massenvernichtungswaffen. Russland ist Großmacht und Regionalmacht und wird teilweise als potentielle Supermacht betrachtet.[15] Es ist ständiges Mitglied im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen, G 20-Mitglied, Mitglied des Europarates, der APEC, der Shanghaier Organisation für Zusammenarbeit (SCO), der OSCE, der WTO; es ist führendes Mitglied in der Gemeinschaft Unabhängiger Staaten (GUS), der Organisation des Vertrags über kollektive Sicherheit (OVKS) und der Eurasischen Wirtschaftsunion (mit Armenien, Kasachstan, Kirgisistan und Weißrussland).
Russland ist ein Schwellenland im Bereich des oberen mittleren Einkommens.[16] Im Human Development Index der Vereinten Nationen stand Russland 2016 mit 0,8 (von 1) auf Platz 49,[17] der Gini-Koeffizient lag bei 37,7.
Das Regierungssystem Russlands wird von Politikwissenschaftlern entsprechend dem Wortlaut der Verfassung meist formal als Verbindung präsidentieller und parlamentarischer Formen eingeordnet; die Verfassungswirklichkeit des politischen Systems entspricht jedoch eher den Modellen defekter Demokratien oder der Postdemokratie, zumal der Präsident fast autokratische Macht ausübt.[18][19][20] Für die politische Ordnung wird in Russland gelegentlich von offizieller Seite der Begriff „Gelenkte Demokratie“ im affirmativen Sinne gebraucht.[21]
Die Annexion der Krim im März 2014 belastet die Beziehungen zwischen Russland und dem Westen. Der russischen Regierung wird vorgeworfen, die europäische Friedensordnung zu verletzen.[22]
Das Land war 2016 mit 69,9 Mrd. Dollar für 4,1 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit im internationalen Vergleich hinter den Vereinigten Staaten mit 611 Mrd. Dollar (36 %) und China mit 215 Mrd. Dollar (13 %) auf Platz 3, gefolgt von Saudi-Arabien und Indien.[23][24]
ロシア連邦(ロシアれんぽう、ロシア語: Российская Федерация:英語名 Russian Federation)、またはロシア (Россия) は、ユーラシア大陸北部にある共和制及び連邦制国家。
地理的にロシアの国境は、北西から南東へ、ノルウェー、フィンランド、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニアおよびポーランド(ともにカリーニングラード州と隣接)、ベラルーシ、ウクライナ、ジョージア、アゼルバイジャン、カザフスタン、中華人民共和国、モンゴル国、朝鮮民主主義人民共和国と接する。海上境界線としては、日本とはオホーツク海・宗谷海峡・根室海峡・珸瑤瑁水道、アメリカ合衆国とはベーリング海峡でアラスカ州と接する。ロシアの面積は17,075,400km2で世界最大であり、地球上の居住地域の8分の1を占める。2012年時点で、ロシアの人口は1億4300万人で世界第9位である[3]。国土は北アジア全体および東ヨーロッパの大部分に広がることに伴い、ロシアは11の標準時を有し、広範な環境および地形を包含する。
ロシアの歴史は、3世紀から8世紀までの間にヨーロッパで認識され始めた東スラヴ人の歴史に始まる[4]。9世紀、ヴァリャーグの戦士の精鋭およびその子孫により設立及び統治されて、キエフ大公国の中世国家が誕生した。988年、東ローマ帝国から正教会を導入し、次の千年紀のロシア文化を特徴付ける東ローマ帝国およびスラブ人の文化の統合が始まった[5]。キエフ大公国は最終的には多くの国に分裂し、キエフ大公国の領土の大部分はモンゴルに制圧され、遊牧国家ジョチ・ウルスの属国になった[6]。モスクワ大公国は次第に周辺のロシアの公国を再統合し、ジョチ・ウルスからの独立を獲得し、キエフ大公国の文化的および政治的な遺産を支配するようになった。18世紀までにモスクワ大公国は、王朝による征服・併合、シェレホフ提督による探検を通じ、史上第3位の大帝国であるロシア帝国となり、版図がポーランドから北米のアラスカまで広がった[7][8]。
しかし帝国は国土に見合う開発資金を国内で捻出することができなかった。サンクトペテルブルクの貿易為替銀行にドイツ銀行を参加させたが、露仏同盟を結んで以来国際金融市場から外資が雪崩れ込むようになった。
ロシア革命後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国がソビエト連邦最大かつ指導的な構成国となり、世界初の憲法上の社会主義国および広く認められた超大国となり[9]、第二次世界大戦において連合国の勝利に決定的な役割を果たした[10][11]。ソビエト時代には、世界初の人工衛星および世界初の有人宇宙飛行を含む20世紀の最も重要な複数の技術的偉業を経験した。1991年のソ連崩壊後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国は自らをロシア連邦として再構成し、連邦国家の継続的な法人格として認識されている。ソ連政府は国民にあまねく賃貸住宅を配分していたが、それらを建設するだけで巨額の財政負担となっており、財政再建中のロシア連邦がリフォームすることなどかなわず、無償で住民が物件を取得できるようにしてしまい急激な私有化を進めた[12]。私有化されていないものは地方自治体への譲渡が進んで、人口減少社会となる中、若者向けに低家賃で貸し出されている[12]。
1996年11月、ロシアは第一回だけで10億ドルのユーロ債を起債した[13]。それまでの累積ユーロ債発行額は160億ドルほどに達した[13]。1997年、第一回サンクトペテルブルク国際経済会議が開かれた。1998年、ロシア財政危機。1999年、ロスチャイルド代理人のアルフレッド・ハルトマン博士が資金洗浄の国内捜査線上で名前をとりあげられた。
2003年、ミハイル・ホドルコフスキーが脱税などの罪で逮捕・起訴され、ユコスの社長を辞任した。シブネフチとの合併が取り消されるなどして株価が乱高下し、内部者取引が横行した。2005年でロシアの住宅私有化率は63%に達し[12]、国際的な不動産価格の下落へつながっていった。2007年、ホドルコフスキーを除くユコス株主らは、ロシア政府がユコスを破綻させたとしてハーグの常設仲裁裁判所へ提訴した(ユコス破綻事件)。2010年6月26日、政府側のロスネフチに賠償命令が出た。7月27日、内部者取引と株価操作を取り締まる法案がようやく批准された[14]。これは翌年から施行された。
2014年ウクライナ騒乱が2月に起きてVTBが態度を硬化させた。7月、ユコス破綻事件で政府は19億ユーロの賠償金支払いを命じられていたが、12月に欧州人権裁判所が政府の上訴を棄却した[15]。2016年4月、ハーグ地区裁判所が、ロシア政府に株主らへ500億ドルの賠償金支払いを命じた常設仲裁裁判所の判決を棄却した[16]。
2014年時点で、ロシアの経済は名目GDPで世界第9位かつ購買力平価で世界第6位であった[17]。ロシアの豊富な鉱物およびエネルギー資源は世界最大の埋蔵量であり[18]、世界最大の原油生産国および世界最大の天然ガス生産国の一つである。ロシアは核保有を認められた5大国の一つであり、世界最大の大量破壊兵器保有量がある。ロシアは列強および国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、独立国家共同体の指導国であるだけでなく、G20、欧州評議会、アジア太平洋経済協力、上海協力機構、ユーラシア経済共同体、欧州安全保障協力機構 (OSCE)、世界貿易機関 (WTO) 加盟国である。
Russia (Russian: Росси́я, tr. Rossiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijə]), officially the Russian Federation[12] (Russian: Росси́йская Федера́ция, tr. Rossiyskaya Federatsiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijskəjə fʲɪdʲɪˈratsɨjə]), is a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and North Asia.[13] At 17,125,200 square kilometres (6,612,100 sq mi),[14] Russia is the largest country in the world by area, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area,[15][16][17] and the ninth most populous, with about 146.77 million people as of 2019, excluding Crimea.[8] About 77% of the population live in the western, European part of the country. Russia's capital, Moscow, is the largest metropolitan area in Europe proper[18] and one of the largest cities in the world; other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod. Extending across the entirety of Northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia spans eleven time zones and incorporates a wide range of environments and landforms. From northwest to southeast, Russia shares land borders with Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland (both with Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and North Korea. It shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk and the U.S. state of Alaska across the Bering Strait. However, Russia recognises two more countries that border it, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, both of which are internationally recognized as parts of Georgia.
The East Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD.[19] Founded and ruled by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, the medieval state of Rus arose in the 9th century. In 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire,[20] beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium.[20] Rus' ultimately disintegrated into a number of smaller states; most of the Rus' lands were overrun by the Mongol invasion and became tributaries of the nomadic Golden Horde in the 13th century.[21] The Grand Duchy of Moscow gradually reunified the surrounding Russian principalities and achieved independence from the Golden Horde. By the 18th century, the nation had greatly expanded through conquest, annexation, and exploration to become the Russian Empire, which was the third largest empire in history, stretching from Poland on the west to Alaska on the east.[22][23]
Following the Russian Revolution, the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic became the largest and leading constituent of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, the world's first constitutionally socialist state.[24] The Soviet Union played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World War II,[25][26] and emerged as a recognized superpower and rival to the United States during the Cold War. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements of the 20th century, including the world's first human-made satellite and the launching of the first humans in space. By the end of 1990, the Soviet Union had the world's second largest economy, largest standing military in the world and the largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.[27][28][29] Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, twelve independent republics emerged from the USSR: Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and the Baltic states regained independence: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania; the Russian SFSR reconstituted itself as the Russian Federation and is recognized as the continuing legal personality and a successor of the Soviet Union.[30] It is governed as a federal semi-presidential republic.
Russia's economy ranks as the twelfth largest by nominal GDP and sixth largest by purchasing power parity in 2015.[31] Russia's extensive mineral and energy resources are the largest such reserves in the world,[32] making it one of the leading producers of oil and natural gas globally.[33][34] The country is one of the five recognized nuclear weapons states and possesses the largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.[35] Russia is a great power as well as a regional power and has been characterised as a potential superpower. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and an active global partner of ASEAN,[36][37][38] as well as a member of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the G20, the Council of Europe, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), and the World Trade Organization (WTO), as well as being the leading member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) and one of the five members of the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU), along with Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
La Russie, en forme longue la fédération de Russiea (en russe : Россия, Rossiab ; [forme longue] Российская Федерация, Rossiïskaïa Federatsiïac), est un État fédéral transcontinental dont le territoire est le plus vaste de la planète.
Sa population est estimée à 146,88 millions d’habitants en 20181. Le pays est à cheval sur l’Asie du Nord (74,7 % de sa superficie) et sur l’Europe (25,3 % de sa superficie, mais 78 % de ses habitants sont en Europe6). Son territoire s'étend d’ouest en est (de Kaliningrad à Vladivostok) sur plus de 9 000 km pour une superficie de dix-sept millions de kilomètres carrés (17 000 000 km2) et compte onze fuseaux horaires7. Sa capitale est Moscou, sa langue officielle le russe et sa monnaie le rouble. Bien qu’entourée de nombreuses mers et de deux océans, la Russie est caractérisée par un climat continental avec des milieux froids et hostiles sur la majeure partie du territoire.
La Russie dispose de ressources minières (houille, fer, nickel, diamant, etc.) et énergétiques (pétrole, gaz naturel, hydroélectricité) abondantes qui en font l’un des principaux producteurs et exportateurs mondiaux. Elle se dote, à l'époque de l’URSS, d'une industrie lourde puissante (aciéries, raffineries, industrie chimique, etc.). Les secteurs liés à l’armement, au nucléaire et à l’aérospatiale sont également fortement développés, ce qui a permis au pays de jouer un rôle pionnier dans la conquête de l'espace.
La république socialiste fédérative soviétique de Russie (RSFSR) fut la plus importante des quinze républiques de l’Union des républiques socialistes soviétiques, dont elle constituait le noyau historique.
Fin 1991, l’URSS éclate en quinze États indépendants souverains, dont la Russie, qui a hérité des trois quarts du territoire de l’ancienne superpuissance, de plus de la moitié de sa population, des deux tiers de son industrie et de la moitié de sa production agricole. La Russie occupe aussi dans la continuité sa place dans les institutions internationales, dont le siège permanent au Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies, et a également assumé le passif financier de l’URSS. La Russie est aussi fondatrice de la Communauté des États indépendants (CEI) qui rassemble neuf des quinze ex-républiques soviétiques.
Elle demeure une fédération constituée de 85 sujets disposant d’une autonomie politique et économique variable. Le découpage, tenant compte entre autres de la présence de minorités, existait déjà dans l’ancienne URSS.
Après la fin du système soviétique au début des années 1990, le pays a graduellement adopté une économie de marché et un régime parlementaire pluraliste. Aspirant à suivre la mondialisation, la Russie se considère par ailleurs comme étant le pont entre l'Europe et l'Asie. Aujourd'hui, la Russie fait partie des BRICS aux côtés de la Chine, de l'Inde, de l'Afrique du Sud et du Brésil. Elle est actuellement douzième puissance mondiale en 2017 en matière de PIB à valeur nominale8 et sixième en parité de pouvoir d'achat9. En devenant la première capitalisation boursière européenne10, le géant gazier Gazprom devient le symbole de cette expansion russe11, au même titre que le leader mondial de l'aluminium Rusal. Avec la chute du rouble (liée aux réactions internationales à la suite de la crise de Crimée) et du pétrole en 2014, le PIB de la Russie est retombé en 2015 au niveau de celui de 2006, ce qui fait un PIB nominal par habitant d'un peu plus de 9 000 $12.
La Russia (in russo: Россия?, traslitterato: Rossija, ) o la Federazione Russa (in russo: Российская Федерация?, traslitterato: Rossijskaja Federacija, ) è uno Stato transcontinentale che si estende tra l'Europa e l'Asia ed è il più vasto Stato del mondo, con una superficie di circa 17 098 242 km² (per più della metà disabitato).[5]
Confina con Norvegia, Finlandia, Estonia, Lettonia, Lituania, Polonia, Bielorussia, Ucraina, Georgia e territori contesi di Ossezia del Sud e Abcasia, Azerbaigian, Kazakistan, Cina, Corea del Nord e Mongolia; assieme alla Cina, è lo Stato al mondo con il maggior numero di Stati limitrofi (14), mentre, considerando anche i due Stati con ridotto riconoscimento internazionale di Abcasia e Ossezia del Sud (entrambi riconosciuti dalla Russia), gli Stati confinanti con la Russia diventano 16. Essa possiede, inoltre, confini marittimi con il Giappone (attraverso il mare di Ochotsk) e gli Stati Uniti (attraverso lo stretto di Bering). È bagnata a Nord-Ovest dal mar Baltico nel golfo di Finlandia, a Nord dal mar Glaciale Artico, a Est dall'oceano Pacifico e a Sud dal mar Nero e dal mar Caspio. Comprende anche l'exclave dell'Oblast' di Kaliningrad, compresa tra mar Baltico, Polonia e Lituania. Nel 2016 contava circa 144 milioni di abitanti, ha come capitale Mosca ed è tradizionalmente suddivisa tra Russia europea e asiatica dalla catena montuosa degli Urali.
Come principale successore dell'Unione Sovietica, la Russia ha mantenuto il seggio di membro permanente nel Consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni Unite. Resta ancora secondo alcuni accademici una grande potenza, tra i protagonisti della storia del XX secolo, sia nel secondo conflitto mondiale, sia nel secondo dopoguerra, con la guerra fredda e l'opposizione attraverso il blocco sovietico al cosiddetto blocco occidentale, che annoverava anche l'altra superpotenza, gli Stati Uniti. È uno Stato con una forte influenza politica all'interno della Comunità degli Stati Indipendenti, che comprende tutte le ex-Repubbliche dell'Unione Sovietica tranne le tre repubbliche baltiche, il Turkmenistan, la Georgia (uscita nel 2008) e l'Ucraina (uscita come membro osservatore nel 2014). È inoltre uno degli Stati fondatori dell'Unione eurasiatica, che comprende, oltre la Russia, la Bielorussia, l'Armenia e il Kazakistan e vede il Tagikistan e l'Uzbekistan come Stati osservatori.
Nei primi anni del XXI secolo l'economia ha presentato tassi di crescita tra i più elevati a livello globale, tanto che la Russia è considerata uno dei cinque Paesi cui ci si riferisce con l'acronimo BRICS.[6] La crisi finanziaria internazionale si è fatta però sentire duramente a partire dall'autunno 2008, mettendo in dubbio molte delle certezze acquisite in un decennio di espansione[7]. Il 18 marzo 2014, in seguito all'esito di un referendum che vide la schiacciante vittoria dei favorevoli all'annessione alla Russia ed era stato indetto dalle forze politiche della Repubblica autonoma di Crimea che si era proclamata unilateralmente indipendente dall'Ucraina in data 11 marzo 2014, è cominciato l'iter amministrativo di integrazione della penisola di Crimea (compresa quindi anche la città autonoma di Sebastopoli) come nuovo soggetto federale della Federazione Russa, sebbene l'occupazione non sia riconosciuta dall'ONU.
Rusia (en ruso: Россия, romanización: Rossíya)n. 1 o formalmenten. 2 Federación de Rusian. 1 (en ruso: Российская Федерация, romanización: Rossíyskaya Federátsiya) es el país más extenso del mundo. La Federación de Rusia cuenta con una superficie de 17 098 242 km2,1 equivalente a la novena parte de la tierra firme del planeta, y con gran variedad de relieve y de ecosistemas. Su capital es la ciudad federal de Moscú.
Esta república semipresidencialista, formada por ochenta y tres sujetos federales, es el noveno país por población al tener 146 804 372 habitantes7. Ocupa toda el Asia del Norte y alrededor del 40 % de Europa (principalmente Europa Oriental),n. 3 y es un país transcontinental. En Rusia hay once zonas horarias, desde UTC+2 hasta UTC+12.n. 4 Rusia tiene las mayores reservas de recursos energéticos y minerales del mundo aún sin explotar, y es considerada la mayor superpotencia energética. Posee las mayores reservas de recursos forestales y la cuarta parte del agua dulce sin congelar del mundo.
Rusia es el país que limita con mayor número de países, un total de dieciséis,n. 5 y el que tiene las fronteras más extensas. Limita con los siguientes países (empezando por el noroeste y siguiendo el sentido antihorario): Noruega, Finlandia, Estonia, Letonia, Bielorrusia, Lituania,n. 6 Polonia,n. 6 Ucrania,n. 7 Georgia,n. 8 Azerbaiyán, Kazajistán, República Popular China, Mongolia y Corea del Norte. Tiene límites de aguas territoriales con varios de los anteriores, con Japón y con los Estados Unidos (en concreto, con el estado de Alaska). Limita también con los estados de reconocimiento limitado Abjasia, Osetia del Sur y la Unión de Repúblicas Populares (Nueva Rusia). Las costas de Rusia están bañadas por el océano Ártico, el norte del Océano Pacífico y mares interiores como el Báltico, el Negro y el Caspio.
La historia de Rusia comienza con los eslavos orientales. Los eslavos emergieron como un grupo reconocible en Europa entre los siglos III y VIII.7 Fundado y dirigido por una clase guerrera noble de vikingos y sus descendientes, el primer estado de los eslavos orientales, la Rus de Kiev, surgió en el siglo IX y en el año 988 adoptó el cristianismo procedente del Imperio bizantino. Comenzó entonces una síntesis de las culturas bizantina y eslava que definiría la rusa durante el siguiente milenio.8 Más tarde, la Rus de Kiev se desintegró en muchos pequeños estados feudales, de los cuales el más poderoso fue el Principado de Moscú, que se convirtió en la fuerza principal en el proceso de la reunificación rusa y la lucha por la independencia contra la Horda de Oro. Moscú reunificó gradualmente los principados rusos circundantes y comenzó a dominar en el legado cultural y político de la Rus de Kiev. En el siglo XVIII, el país se expandió mediante la conquista, la anexión y la exploración hasta convertirse en el tercer imperio más grande de la historia, el ruso, al extenderse desde Polonia, en poniente, hasta el Océano Pacífico y Alaska.
Rusia ha tenido poder y mucha influencia en el mundo: primero, en los tiempos del Imperio Ruso; después, como el país dominante de la Unión Soviética (URSS), el primero y el más grande de los estado socialistas constitucionalmente establecidos y una superpotencia reconocida como tal; y, actualmente, como la Federación de Rusia. Tiene una larga tradición de calidad en todos los aspectos de las artes y de las ciencias.7 La Federación Rusa se fundó en 1991, al disolverse la Unión Soviética, y es reconocida como la heredera de la personalidad legal de ésta.9 Su economía tiene uno de los mayores crecimientos del mundo. Es el octavo país por PIB nominal y el sexto por PIB (PPA), con el tercer presupuesto militar más grande del mundo. Es uno de los cinco países con armas nucleares reconocidos y posee el mayor arsenal de armas de destrucción masiva del mundo.10 Rusia es miembro permanente del Consejo de Seguridad de Naciones Unidas, miembro del G20, del APEC y de la OCS, y tiene mucha influencia en los países que fueron repúblicas soviéticas, particularmente en la Comunidad de Estados Independientes (CEI).
Росси́я, официально также Росси́йская Федера́ция[e] (РФ[f]) — государство в Восточной Европе и Северной Азии. Территория России в рамках её конституционного устройства[c] составляет 17 125 191[5] км²; население страны (в пределах её заявленной территории[c]) составляет 146 793 744[6] чел. (2019). Занимает первое место в мире по территории, шестое — по объёму ВВП по ППС и девятое — по численности населения.
Столица — Москва. Государственный язык — русский.
Президентско-парламентская республика[2] с федеративным устройством. С 7 мая 2012 года пост Президента занимает Владимир Путин. C 8 мая 2012 года пост Председателя Правительства занимает Дмитрий Медведев.
В состав Российской Федерации входят 85 субъектов[c], 46 из которых именуются областями, 22[c] — республиками, 9 — краями, 3[c] — городами федерального значения, 4 — автономными округами и 1 — автономной областью. Всего в стране около 157 тысяч населённых пунктов[15].
Россия граничит с шестнадцатью государствами (больше, чем любая другая страна в мире), а также двумя частично признанными государствами.
Россия — многонациональное государство, отличающееся большим этнокультурным многообразием[16]. Бо́льшая часть населения (около 75 %) относит себя к православию[17], что делает Россию страной с самым многочисленным православным населением в мире.
Ядерная держава[18][19][20]; одна из ведущих промышленных[21][22] и космических держав мира[23]. Россия занимает 1-е место в рейтинге самых образованных стран мира [24]; Русский язык — язык мирового значения, один из шести официальных и рабочих языков ООН, ЮНЕСКО и других международных организаций. Россия является постоянным членом Совета безопасности ООН с правом вето; одна из современных великих держав мира[25].
После распада СССР в конце 1991 года Российская Федерация была признана международным сообществом как государство-продолжатель СССР[26] в вопросах ядерного потенциала, внешнего долга, государственной собственности за рубежом, а также членства в Совете Безопасности ООН[27]. Россия состоит в ряде международных организаций: ООН, ОБСЕ, Совете Европы, ЕАЭС, СНГ, ОЧЭС, ОДКБ, ГКМЧП, ВОИС, ММО, ВТО, ЮНВТО, ВФП, ШОС, АТЭС, БРИКС, КООМЕТ, МОК, МЭК, ISO, EUREKA, IRENA, G20 и других.
По данным Всемирного банка, объём ВВП по ППС за 2017 год составил 3,817 трлн долларов (25 532 долларов на человека), по данным МВФ - 4,008 трлн долларов. Денежная единица — российский рубль.










