斯拉夫語族是印欧语系的一个语族,產生於斯拉夫民族。可分為東斯拉夫語支、南斯拉夫語支及西斯拉夫語支,東斯拉夫語支及南斯拉夫語支使用西里爾字母,但有一例外,塞尔维亚语和克罗地亚语原是同一种语言,由于宗教的原因,塞尔维亚语用西里尔字母书写,克罗地亚语用拉丁字母书写,两种字母可以自由转写。波斯尼亚语和斯洛文尼亚语用拉丁字母书写(見塞尔维亚语、克罗地亚语和波斯尼亚语的比较),西斯拉夫語支使用拉丁字母。
Die slawischen Sprachen (auch slavisch) bilden einen Hauptzweig der indogermanischen Sprachen. Man unterscheidet gewöhnlich zwischen Ostslawisch, Westslawisch und Südslawisch.[1]
Etwa 300 Millionen Menschen sprechen eine der rund 20 slawischen Sprachen als Muttersprache; 400 Millionen inklusive Zweitsprechern. Die mit Abstand sprecherreichste slawische Sprache ist das Russische mit rund 145 Millionen Muttersprachlern. Weitere bedeutende slawische Sprachen sind Polnisch und Ukrainisch (jeweils etwa 50 Millionen Sprecher). Fast alle größeren slawischen Sprachen sind Nationalsprachen ihrer Länder.
Die Wissenschaft von den slawischen Sprachen, Literaturen und Kulturen heißt Slawistik.
スラヴ語派(スラヴごは)とは、インド・ヨーロッパ語族バルト・スラヴ語派の一派で、スラヴ系諸民族が話す言語の総称。かつては同民族の祖先スラヴ人に話される「スラヴ祖語」が存在したと想定されるが、スラヴ人の民族大移動の頃(5 - 6世紀)から分化が進み、次第に各語群が独自の特徴を明確にし始め、12世紀には単一言語としての統一は完全に失われた。
The Slavic languages (also called Slavonic languages) are the Indo-European languages spoken by the Slavic peoples. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.
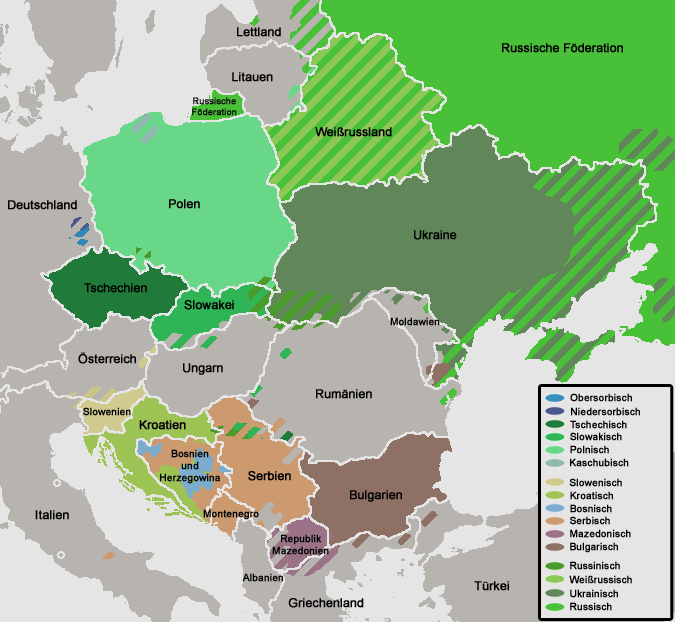
The Slavic languages are divided intro three subgroups: East, West, and South, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Of these, 10 have at least one million speakers and official status as the national languages of the countries in which they are predominantly spoken: Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian (of the East group), Polish, Czech and Slovak (of the West group) and Slovene, Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian and Bulgarian (of the South group).
The current geographic distribution of natively spoken Slavic languages covers Eastern Europe, the Balkans, Central Europe and all of the territory of Russia, which includes northern and north-central Asia. Furthermore, the diasporas of many Slavic peoples have established isolated minorities of speakers of their languages all over the world. The number of speakers of all Slavic languages together is estimated to be 315 million.[2][3][unreliable source?] Despite the large extent, the individual Slavic languages are considerably less differentiated than Germanic and Romance languages.
Les langues slaves sont des langues indo-européennes, du groupe balto-slave. Les langues slaves forment un groupe de langues important dont les locuteurs se situent majoritairement en Europe centrale, Balkans, Europe de l'Est, Sibérie, Extrême-Orient russe, Asie centrale.
Le lingue slave sono un gruppo di idiomi appartenenti alla famiglia delle lingue indoeuropee. Vengono, a volte, inserite nell'ipotetica sottofamiglia delle lingue balto-slave a causa di molteplici similitudini isoglottiche con le lingue baltiche, sebbene non vi siano altri tipi di legami tra i due gruppi. Alcuni studiosi non accettano questo accorpamento, in quanto i due gruppi si sono evoluti indipendentemente l'uno dall'altro[2].
Le lingue slave sono parlate da oltre 315 milioni di persone abitanti in Europa orientale, centro-orientale e balcanica[3], nonché da un folto gruppo di emigrati in tutto il mondo. Alcune lingue slave usano l'alfabeto latino con alcuni segni diacritici (sloveno, croato), altre quello cirillico (bulgaro, serbo), con variazioni minime tra una lingua e l'altra.
Sulla base delle lingue slave sono state create diverse lingue artificiali che possono essere comprese da coloro che parlano almeno una lingua slava.
Las lenguas eslavas son un conjunto de lenguas pertenecientes a la familia lingüística indoeuropea. Son habladas en gran parte de Europa Central, los Balcanes, Europa Oriental y el norte de Asia. El número total de hablantes ronda los 400 millones de personas.
En la escritura se usan los alfabetos cirílico y latino. Antiguamente, además se usaban los alfabetos glagolítico y el árabe.
Славя́нские языки́ — группа родственных языков индоевропейской семьи. Распространены в ряде стран Центральной и Восточной Европы и Северной Азии[3]. Общее число говорящих — более 400 млн человек[4][5][6][7], преимущественно славяне. Отличаются большой степенью близости друг к другу, которая обнаруживается в структуре слова, употреблении грамматических категорий, структуре предложения, семантике, системе регулярных звуковых соответствий, морфонологических чередованиях. Эта близость объясняется единством происхождения славянских языков и их длительными и интенсивными контактами между собой на уровне литературных языков и диалектов.
Длительное самостоятельное развитие славянских народов в разных этнических, географических и историко-культурных условиях, их контакты с различными этническими группами привели к появлению различий материального, функционального и типологического характера.




 History
History
 Literature
Literature



