(Quelle: VideoFromSpace)
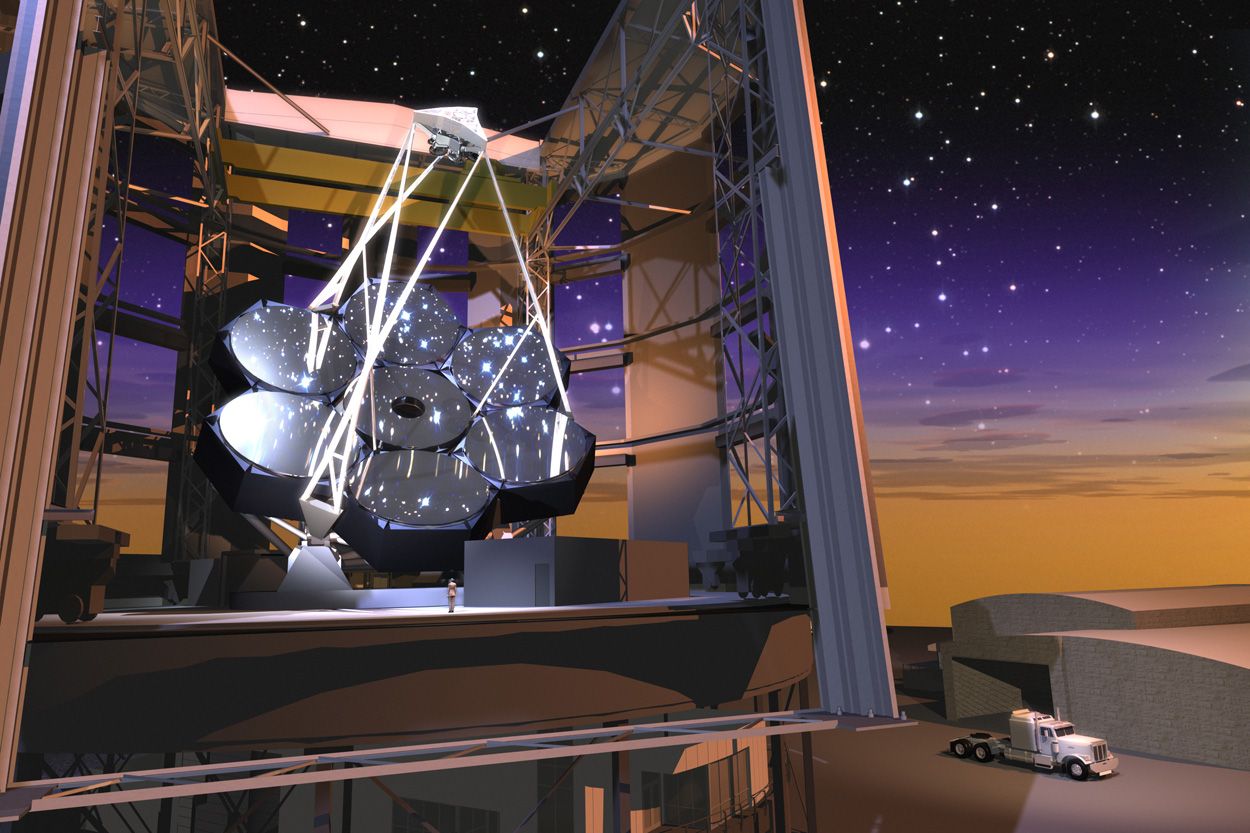
The Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) is a ground-based extremely large telescope under construction, planned for completion in 2025.[1] It will consist of seven 8.4 m (27.6 ft) diameter primary segments,[2] that will observe optical and near infrared (320–25000 nm[3]) light, with the resolving power of a 24.5 m (80.4 ft) primary mirror and collecting area equivalent to a 22.0 m (72.2 ft) one,[4] which is about 368 square meters.[5] (7×8.365 m) The telescope is expected to have the resolving power 10 times greater than the Hubble Space Telescope, and will be the largest optical observatory in the world, at the time of its first light. As of December 2015, four mirrors have been cast and the construction of the summit facility has begun.[6][7]
A total of seven primary mirrors are planned, but it will begin operation with four.[8][9] The $1 billion project is US-led in partnership with Australia, Brazil, and South Korea, with Chile as the host country.
Le télescope géant Magellan (en anglais Giant Magellan Telescope, en abrégé GMT) est un projet de télescope terrestre dont la livraison est prévue pour 20223 . Il sera constitué de sept miroirs primaires de 8,4 m de diamètre4, avec la résolution spatiale d'un miroir primaire de 24,5 m de diamètre et une surface collectrice équivalente à celle d'un miroir de 21,4 m5, ce qui en fait un des trois télescopes extrêmement grands. Ce télescope a une surface collectrice quatre fois supérieure au plus grand télescope actuel (2010).
Il Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) è un telescopio di elevate prestazioni in fase di costruzione, la cui ultimazione è prevista entro il 2025.[5]
Sarà costituito da sette telescopi riflettori di 8,4 metri di diametro, installati presso l'Osservatorio di Las Campanas, in Cile.
Il nome è stato scelto per analogia coi due Telescopi Magellano già operativi a Las Campanas.
Il primo specchio, realizzato presso l'Osservatorio Steward, in Arizona, è stato ultimato in autunno 2012[6] e dislocato in un sito temporaneo in attesa del trasporto a Las Campas a settembre 2017[7].
El Telescopio Gigante de Magallanes (TGM o GMT en inglés) es un proyecto de telescopio terrestre de grandes dimensiones planeado para completarse en 2020. Se compondrá de siete segmentos primarios de 8,4 metros de diámetro, con el poder de resolución de un espejo primario de 24,5 metros de diámetro y la superficie de recolección de 22 metros. Se espera que tenga más de 5-10 veces la capacidad de captación de luz de los instrumentos existentes. Ya se han producido cuatro de los siete espejos y la cima de la montaña está preparada para la construcción. El astrónomo jefe encargado del proyecto es Mark M. Phillips.
Гигантский Магелланов телескоп (англ. Giant Magellan Telescope; ГМТ) — наземный телескоп, строительство которого намечено завершить в 2022 году[2]. Телескоп начнёт производить первые измерения в 2024 году, а полностью функциональным станет в 2026.
В качестве собирающего свет элемента будет использоваться система из семи первичных зеркал диаметром 8,4 м[3] и весом 20 тонн каждое[4]. Суммарная апертура телескопа будет соответствовать телескопу с зеркалом диаметром 24,5 м[5]. Ожидается, что телескоп вчетверо превысит способность собирать свет по сравнению с крупнейшими на данный момент. ГМТ будет иметь разрешающую способность в 10 раз выше, чем у телескопа Хаббла. Благодаря ГМТ астрономы смогут открывать экзопланеты и получать их спектры, изучать свойства неуловимых тёмной материи и тёмной энергии.




 History
History


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Science and technology
Science and technology


