Das Kaspische Meer, auch Kaspisee genannt[2] (aserbaidschanisch Xəzər dənizi, kasachisch Каспий теңізі, persisch دریای خزر / دریای مازندران, DMG Daryā-ye Ḫazar / Daryā-ye Māzandarān, russisch Каспийское море, turkmenisch Kaspi deňzi), ist der größte See der Erde. Der Salzsee ist ein endorheisches Gewässer, das heißt ohne natürliche Verbindung zu den Ozeanen.
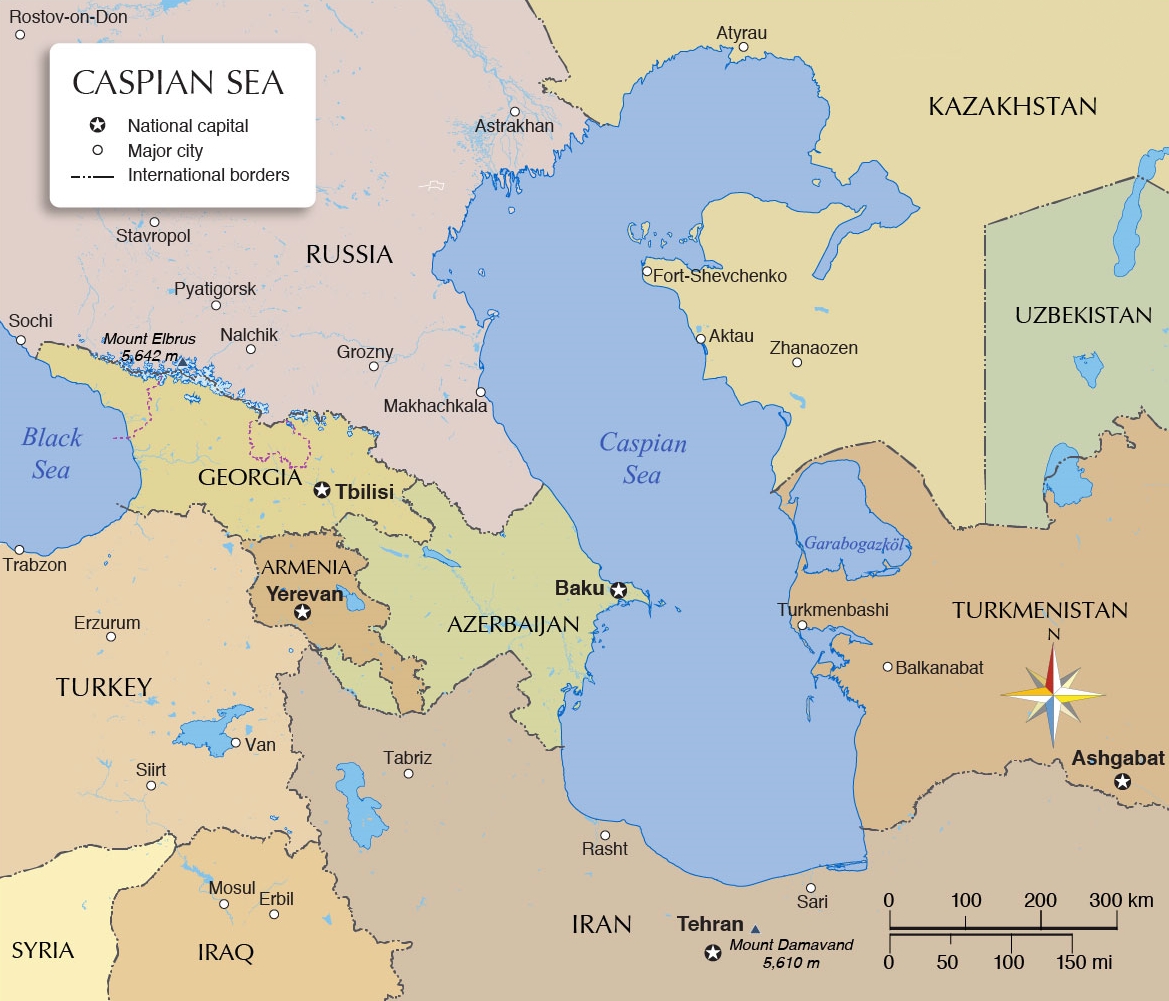
Das Kaspische Meer liegt innerhalb der großen Aralo-Kaspischen Niederung in West-Asien und im äußersten Osteuropa. Im Norden grenzt es an Russland und Kasachstan, im Osten an Turkmenistan, im Süden an den Iran und im Westen an Aserbaidschan.
里海(阿塞拜疆语:Xəzər dənizi,波斯语:دریای مازندران/دریای خزر,俄语:Каспийское море,哈萨克语:Каспий теңізі,土库曼语:Hazar deňizi)位于欧亚交界,是世界上最大的湖泊及封闭内陆水体。[2][3]里海的面积有371,000平方公里(不包括卡腊博加兹哥耳湾),体积为78,200立方公里,湖面比海平面低27米(89英尺),最深处有1,025米(3,360英尺),平均深度为187米(610英尺)[4],南部的海床低至海平面以下1,023米(3,356英尺),这是仅次于贝加尔湖(-1,180米或-3,870英尺),地球上第二低的自然凹陷。从北向南的长度近1,200公里(750英里),平均宽度为320公里(200英里)。
里海是咸水湖,盐度大约为1.2%,为平均海水盐度的三分之一。[5]沿海地区的古代居民将里海视为海洋,这可能是因为其湖水盐度高和面积广大的缘故。里海是内流湖,没有流出口;由多个国家环抱,西北有俄罗斯,西面是阿塞拜疆,南面是伊朗,东南是土库曼,东北为哈萨克。里海也是海迹湖,原本为古地中海的一部分。
里海有相当多种鱼类,以鱼子酱和石油工业而负有盛名。石油工业的污染,以及流入里海的河流之上所建的水坝,对湖内的生物有负面的影响。广阔而且内流的里海呈南北走向长方形的形状,主要淡水由窝瓦河,从比较浅的北端流入,在它中部和南部有两个深的盆地,导致里海在不同的深度在温度、盐度和生态方面会有差异。
カスピ海(カスピかい、ロシア語: Каспийское море、英語: Caspian Sea)は、ユーラシア大陸の中央アジアと東ヨーロッパの境界にある塩湖。世界最大の湖である。2018年締結の沿岸5か国の協定によって「海」と定義されている(「国際紛争」の項目参照)。カスピの名は古代に南西岸にいたカス族あるいはカスピ族に由来する。カスピ海に近い現在のイラン・ガズヴィーン州都ガズヴィーンは同じ語源であると言われる。現代のペルシア語では一般に「ハザール海」دریای خزرと呼ばれるが、これは7世紀から10世紀にカスピ海からコーカサスや黒海にかけて栄えたハザール王国に由来する(現代ペルシア語では、カスピ海南岸のイランの地名から「マーザンダラーン海」دریای مازندرانとも呼ばれる)。また、トルコ語でも同様の名でHazar Deniziと呼ばれる[2][3]。中国語では現在に至るまで「裏海」(りかい)と呼ばれる。
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. As an endorheic basin, it is located between Europe and Asia, east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, and north of the Iranian Plateau of Western Asia. The sea has a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi) (excluding the detached lagoon of Garabogazköl) and a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/l), about a third of the salinity of most seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the west, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.
The Caspian Sea spreads out over nearly 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) from north to south, with an average width of 320 km (200 mi). It covers a region of around 386,400 km2 (149,200 sq mi) and its surface is about 27 m (89 ft) below sea level. Its main freshwater inflow, Europe's longest river, the Volga, enters at the shallow north end. Two deep basins occupy its central and southern areas. These lead to horizontal differences in temperature, salinity, and ecology. The seabed in the southern part reaches as low as 1,023 m (3,356 ft) below sea level, which is the second lowest natural depression on Earth after Lake Baikal (−1,180 m or −3,870 ft). The ancient inhabitants of its coast perceived the Caspian Sea as an ocean, probably because of its saltiness and large size.
The Caspian Sea is home to a wide range of species and may be best known for its caviar and oil industries. Pollution from the oil industry and dams on rivers draining into the Caspian Sea have had negative effects on the organisms living in the sea.
La mer Caspienne est une vaste étendue d'eau située en Asie occidentale, principalement alimentée par la Volga, issue de la fermeture d’une mer océanique ancienne, l'océan ou mer Paratéthys. Bien qu'il s'agisse, d'un point de vue strictement juridique, d'un lac2, on la qualifie couramment de plus grande mer fermée du monde. Elle est bordée au nord et à l’est par les steppes de l’Asie centrale, à l’ouest et au sud par des chaînes issues de l’orogénèse himalayo-alpine : respectivement Caucase et Elbourz. Les pays riverains sont (dans le sens des aiguilles d'une montre) : le Kazakhstan au nord-est, le Turkménistan au sud-est, l’Iran au sud, l’Azerbaïdjan au sud-ouest, et la Russie au nord-ouest (avec le Daghestan, la Kalmoukie et l’oblast d'Astrakhan). Son niveau varie selon les années, mais de 1995 à 2017 il diminue rapidement (−6,72 cm/an en moyenne, soit −1,5 m en 20 ans) principalement à cause d'une évaporation accrue par le réchauffement climatique, et cette tendance devrait se poursuivre3.
Il mar Caspio (درياى خزر daryā-ye xazar in Persiano, kaz. Каспий теңізі Kaspij Tengizi, turkm. Hazar deňizi) è un bacino endoreico situato a 28 metri sotto il livello del mare (depressione caspica), fra Russia, Kazakistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaigian e il nord dell'Iran: lungo 1 200 km, con una larghezza media di 310 km, una superficie di 371 000 km², un volume di 78 200 km³ ed una profondità massima di 1 025 metri nella parte meridionale (a nord la profondità non supera i 6 metri), tre sono i fiumi maggiori che sfociano nel mar Caspio: Volga, Ural e Kura.
Mar Caspio (en ruso, Каспи́йское мо́ре) es un lago de agua salobre que se extiende entre Europa y Asia. Su superficie es de 371 000 km², su profundidad media es de 170 m, la máxima es de 995 m y es el lago más extenso del mundo. Sus dimensiones son 1210 km en dirección norte-sur y de 210 km a 436 km en dirección este-oeste.1
Ocupa la parte occidental de la depresión uralocáspica, que forma parte de la mayor cuenca endorreica de la Tierra, estando su superficie 28 m bajo el nivel del mar.
Está fundamentalmente alimentado por el río Volga y por otros menos caudalosos como el Ural, el Emba y el Kurá.2
Каспи́йское мо́ре[1] (Ка́спий[1][2], от лат. Caspium mare или др.-греч. Κασπία θάλασσα, Kaspía thálassa) — крупнейший на Земле замкнутый водоём[3], который может классифицироваться как самое большое бессточное озеро либо как море — из-за своих размеров, а также из-за того, что его ложе сложено земной корой океанического типа. Расположено на стыке Европы и Азии. Вода в Каспии солоноватая, — от 0,05 ‰ близ устья Волги до 11—13 ‰ на юго-востоке. Уровень воды подвержен колебаниям, согласно данным 2009 года составлял 27,16 м ниже уровня моря[4]. Площадь Каспийского моря в настоящее время — примерно 371 000 км², максимальная глубина — 1025 м.








