法兰克王国(拉丁语:Regnum Francorum;法语:royaume des Francs;意为“法兰克人的王国”)是5世纪至9世纪在西欧和中欧的一个王国,其疆域与罗马帝国在西欧的疆域基本相同。
法兰克王国是一个多民族国家,其人民主要由民族大迁徙过程中从日耳曼尼亚迁入的民族组成。
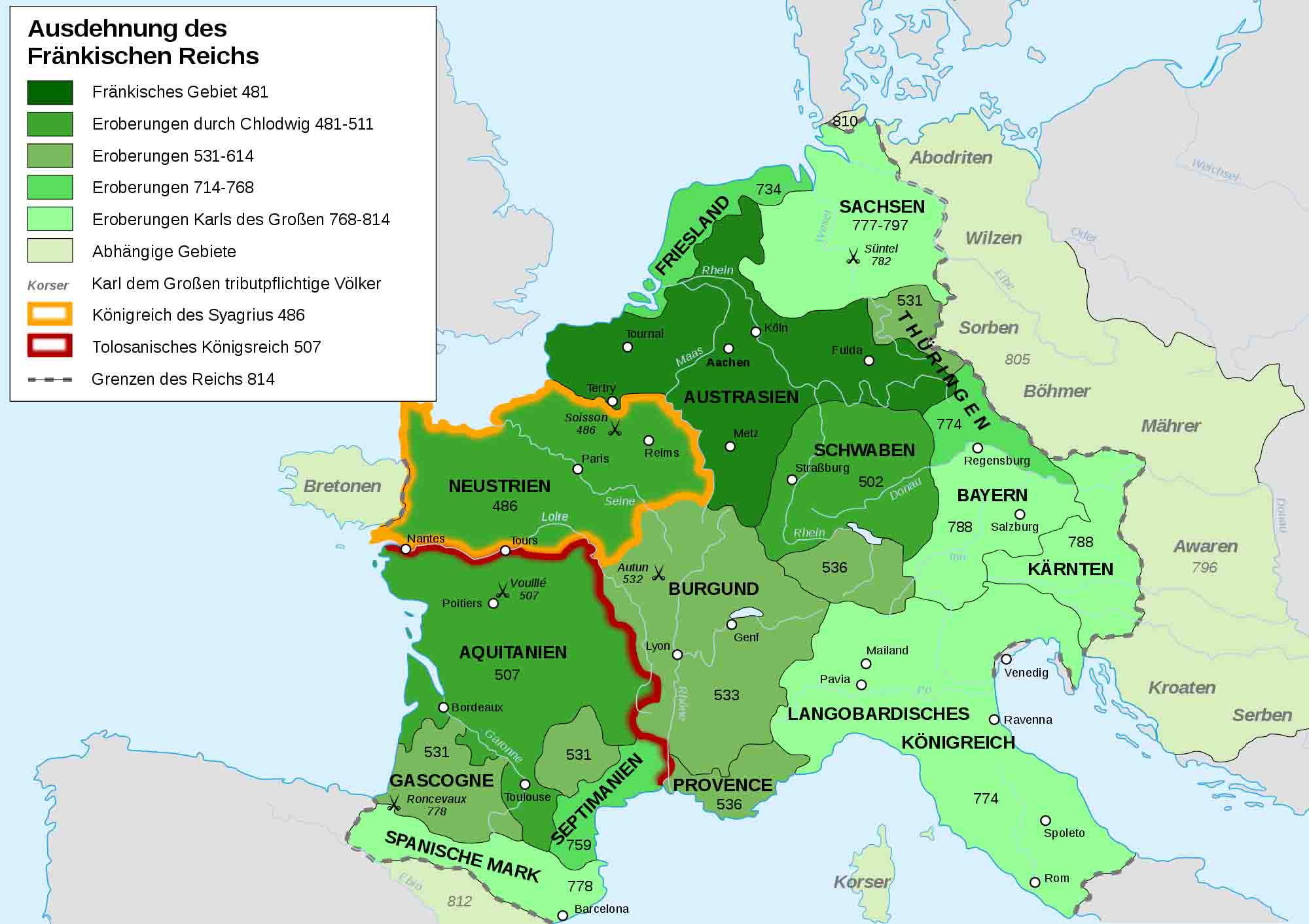
罗马帝国灭亡后,法兰克王国在其存在的三个世纪中成为中欧最重要的国家,它当时是中欧的大国。在它瓦解后它的组成部分逐渐演变成今天的法国、德国和其它一些小国家。统治法兰克王国的国王出自墨洛温王朝和卡洛林王朝,查理大帝统治时期它达到了其顶峰。
Das Fränkische Reich oder Frankenreich, das zwischen dem 5. und 9. Jahrhundert bestand und sich im Wesentlichen aus dem römischen Gallien und angrenzenden rechtsrheinisch-germanischen Siedlungsgebieten gebildet hatte, war der bedeutendste Nachfolgestaat des 476 untergegangenen Weströmischen Reiches und die historisch wichtigste Reichsbildung in Europa seit der Antike.[1]
Das Reich der Franken ging auf mehrere westgermanische Kriegerverbände der Völkerwanderungszeit zurück. Nach dem Untergang Westroms stieg es im Frühmittelalter unter den Dynastien der Merowinger und der Karolinger in drei Jahrhunderten zu einer Großmacht auf, die weite Teile West-, Mittel- und Südeuropas beherrschte. Als Hausmeier der merowingischen Könige übten die Karolinger bereits seit dem späten 7. Jahrhundert die tatsächliche politische Macht aus, bevor sie im Jahr 751 selbst die Königswürde übernahmen. Den Höhepunkt seiner Macht und Ausdehnung erreichte das Frankenreich unter der Herrschaft Karls des Großen (768–814). Nachdem es im 9. Jahrhundert geteilt worden war, entwickelten sich aus der östlichen Reichshälfte das Heilige Römische Reich, aus der westlichen das spätere Königreich Frankreich.
フランク王国(フランクおうこく、フランス語: Royaumes francs、ドイツ語: Fränkisches Reich)は、5世紀後半にゲルマン人の部族、フランク人によって建てられた王国。カール1世(大帝)の時代(8世紀後半から9世紀前半)には、現在のフランス・イタリア北部・ドイツ西部・オランダ・ベルギー・ルクセンブルク・スイス・オーストリアおよびスロベニアに相当する地域を支配し、イベリア半島とイタリア半島南部、ブリテン諸島を除く西ヨーロッパのほぼ全域に勢力を及ぼした。カール1世以降のフランク王国は、しばしば「フランク帝国」「カロリング帝国」などとも呼ばれる。
この王国はキリスト教を受容し、その国家運営は教会の聖職者たちが多くを担った。また、歴代の王はローマ・カトリック教会と密接な関係を構築し、即位の際には教皇によって聖別された。これらのことから、西ヨーロッパにおけるキリスト教の普及とキリスト教文化の発展に重要な役割を果たした。
フランク王国はメロヴィング朝とカロリング朝と言う二つの王朝によって統治された。その領土は、成立時より王族による分割相続が行われていたため、国内は恒常的に複数の地域(分王国)に分裂しており、統一されている期間は寧ろ例外であった。ルートヴィヒ1世(敬虔王、ルイ1世とも)の死後の843年に結ばれたヴェルダン条約による分割が最後の分割となり、フランク王国は東・中・西の3王国に分割された。その後、西フランクはフランス王国、東フランクは神聖ローマ帝国の母体となり、中フランクはイタリア王国を形成した。
このようにフランク王国は政治的枠組み、宗教など多くの面において中世ヨーロッパ社会の原型を構築した。
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks (Latin: Regnum Francorum), or Frankish Empire was the largest post-Roman Barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. It is the predecessor of the modern states of France and Germany. After the Treaty of Verdun in 843, West Francia became the predecessor of France, and East Francia became that of Germany. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era until its partitioning in 843.
The core Frankish territories inside the former Western Roman Empire were close to the Rhine and Maas rivers in the north. After a period where small kingdoms inter-acted with the remaining Gallo-Roman institutions to their south, a single kingdom uniting them was founded by Clovis I who was crowned King of the Franks in 496. His dynasty, the Merovingian dynasty, was eventually replaced by the Carolingian dynasty. Under the nearly continuous campaigns of Pepin of Herstal, Charles Martel, Pepin the Short, Charlemagne, and Louis the Pious—father, son, grandson, great-grandson and great-great-grandson—the greatest expansion of the Frankish empire was secured by the early 9th century, by this point dubbed as the Carolingian Empire.
During the Carolingian and Merovingian dynasties the Frankish realm was one large kingdom polity subdivided into several smaller kingdoms, often effectively independent. The geography and number of subkingdoms varied over time, but a basic split between eastern and western domains persisted. The eastern kingdom was initially called Austrasia, centred on the Rhine and Meuse, and expanding eastwards into central Europe. It evolved into a German kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire. The western kingdom Neustria was founded in Northern Roman Gaul, and as the original kingdom of the Merovingians it came over time to be referred to as Francia, now France, although in other contexts western Europe generally could still be described as "Frankish". In Germany there are prominent other places named after the Franks such as the region of Franconia, the city of Frankfurt, and Frankenstein Castle.
Les royaumes francs sont les différents royaumes barbares qui se sont succédé ou ont cohabité en Europe occidentale (France, Belgique, Pays-Bas, Allemagne) après le déclin de l'Empire romain d'Occident et la conquête de ces territoires par les Francs au cours du Ve siècle.
Ces royaumes, formant ensemble une entité appelée le royaume des Francs (Regnum Francorum en latin), perdurent pendant tout le haut Moyen Âge, du Ve au IXe siècle1.
À partir de 911, sous Charles III le Simple, le plus occidental des royaumes francs, issu du partage de Verdun en 843 et que certains historiens qualifient de Francie occidentale, revendique seul de façon continue l'héritage du royaume des Francs de Clovis et Charlemagne par la titulature permanente de ses rois se proclamant tous rois des Francs.
Ce royaume des Francs où, dès le VIIe siècle, le terme « Franc » a perdu toute connotation ethnique du fait des mariages mixtes entre Gallo-Romains et Francs et de l'enrôlement dans l'armée de non-Germains2 conserve ainsi seul le nom de Francia ou France (dans des actes officiels, sous les règnes de Charles II le Chauve et Louis II le Bègue3 puis sous le règne de Louis IV4).
La fédération des royaumes francs par Clovis Ier en 492, donnant naissance (en théorie) à un seul et unique royaume des Francs, peut être considérée comme la première réalité politique de ce qui deviendra la France3.
Il Regno franco o Regno dei Franchi (Regnum Francorum in latino) fu l'entità statale costituita dai Franchi tra il 420 (stanziamento dei Franchi Sali di Faramondo a ovest del Reno, secondo la tradizione riportata da Gregorio di Tours) e l'800 (trasformazione del regno nell'Impero carolingio con Carlo Magno) in un'ampia area dell'Europa occidentale, oggi compresa tra Francia, Belgio, Paesi Bassi, Lussemburgo e Germania, e in seguito ulteriormente espansa verso sud e verso est. Il regno era ripartito in due grandi regioni, Neustria e Austrasia, e fu governato da due dinastie: i Merovingi (420-751) e i Carolingi (751-800), anche se questi detenevano il potere reale già dalla fine del VII secolo, in qualità di maestri di palazzo.
Reino de los francos, Regnum francorum, también conocido (aunque menos usualmente) como Francia (palabra latina que no se refiere a la actual Francia), o simplemente Reino Franco, son las denominaciones historiográficas del reino germánico de los francos que traspasaron el limes (frontera) del Imperio romano en el siglo V aprovechando la decadencia de la autoridad romana en las Galias, durante la denominada época de las invasiones.
De entre todas las tribus en que se dividían los francos, fueron los salios, encabezados por Clovis o Clodoveo I, los que lograron eliminar toda competencia y aseguraron el dominio de sus líderes, convertidos en dinastía merovingia. Desde su establecimiento inicial en el norte de la actual Francia, se extendieron sobre la mayor parte de las antiguas diócesis romanas denominadas Diocesis Viennensis y Diocesis Galliarum, previamente ocupadas por los reinos germánicos de visigodos (reino visigodo de Tolosa) y burgundios (reino burgundio), y sobre territorio de germanos no romanizados, como alamanes, turingios o bávaros. Ese conjunto territorial se extendía sobre los actuales Bélgica, Luxemburgo y Suiza, la casi totalidad de los actuales Países Bajos, Francia y Austria y la parte occidental de la actual Alemania.
Con la dinastía carolingia (que sustituye a los merovingios en el siglo VIII), y especialmente a partir de la coronación imperial de Carlomagno en el año 800, la denomación historiográfica habitual del Reino Franco pasa a ser Imperio carolingio.
Фра́нкское госуда́рство (короле́вство; фр. royaumes francs, лат. regnum (imperium) Francorum), реже Франкия (лат. Francia) — условное название государства в Западной и Центральной Европе c V по IX века, которое образовалось на территории Западной Римской империи одновременно с другими варварскими королевствами. Эта территория была населена франками начиная с III столетия. Вследствие непрерывных военных походов майордома франков Карла Мартелла, его сына Пипина Короткого, а также внука Карла Великого, территория империи франков к началу IX века достигла самых больших размеров в период своего существования.
Вследствие традиции разделять наследство между сыновьями, территория франков только условно управлялась как единое государство; фактически же она была разделена на несколько подчинённых королевств (regna). Количество и расположение королевств менялось с течением времени, и изначально Франкией называлось только одно королевство, а именно Австразия, располагавшееся в северной части Европы на реках Рейн и Маас; тем не менее, иногда в это понятие включали и королевство Нейстрия, находившееся севернее реки Луара и западнее реки Сена. С течением времени применение названия Франкия смещалось в направлении Парижа, установившись в результате над областью бассейна реки Сены, окружавшей Париж (в наши дни известной под именем Иль-де-Франс) и давшей своё имя всему королевству Франция.






