

南达科他州(英语:State of South Dakota),简称南达州,是美国中西部平原上地势较高的一州,过去曾是美国印地安人苏族中拉科他族(Lakota)的聚落所在。南达科他州在1889年11月2日加入美国联邦,也是在同一天被命名的。
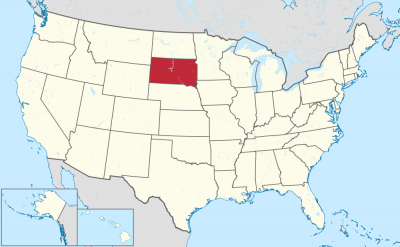
南达科他州的北边是北达科他州,南边是内布拉斯加州,东边则紧邻艾奥瓦州与明尼苏达州,西边是怀俄明州和蒙大拿州,它同时也是美国上被称为边疆带六州中的一州。
美国战舰南达科他号就是以此州命名的。
South Dakota (englische Aussprache [ˌsaʊ̯θ dəˈkʰoʊ̯ɾə], deutsch Süddakota) ist einer der nordwestlichen Prärie-Bundesstaaten der Vereinigten Staaten. Er umfasst 199.731 km². Im Westen befinden sich die Black Hills, östlich davon die Badlands und im Osten des Staates das Coteau des Prairies. Die größte Stadt ist Sioux Falls, die Hauptstadt ist Pierre. South Dakota beheimatet mehrere Indianerreservate, insbesondere der Lakota. Der Staat hat innerhalb der USA nach Alaska und New Mexico den dritthöchsten Bevölkerungsanteil von Indianern.[2]
Der Name Dakota leitet sich von der indianischen Ethnie der Dakota ab, die vor der Unterwerfung durch die Weißen in diesem Gebiet lebte. Spitzname von South Dakota ist The Mount Rushmore State.
サウスダコタ州(英: State of South Dakota [ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の中西部にある州である。グレートプレーンズ(大平原)にあり、南西部はハイプレーンズと呼ばれる標高の高い平原地帯である。州の北はノースダコタ州に、東側はミネソタ州とアイオワ州に、西側はモンタナ州とワイオミング州に、南側はネブラスカ州に接している。州の中央にはミズーリ川が南北に流れているので、その東側と西側には地理的にも社会的にもはっきりとした特徴があり、州民は「イーストリバー」「ウェストリバー」と呼んでいる[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の中西部にある州である。グレートプレーンズ(大平原)にあり、南西部はハイプレーンズと呼ばれる標高の高い平原地帯である。州の北はノースダコタ州に、東側はミネソタ州とアイオワ州に、西側はモンタナ州とワイオミング州に、南側はネブラスカ州に接している。州の中央にはミズーリ川が南北に流れているので、その東側と西側には地理的にも社会的にもはっきりとした特徴があり、州民は「イーストリバー」「ウェストリバー」と呼んでいる[2]。
州都はピア市であり、人口最大の都市は、ミネソタ州、アイオワ州との州境に近いスーフォールズ市である。「ダコタ」という名前はインディアン部族のダコタ族(スー族)の言葉「ダコタ(仲間)」に由来する。面積ではアメリカ合衆国50州の中で第17位だが、人口では第46位、人口密度も第46位と過疎である。19世紀後半にできたダコタ準州の南側半分であり、1889年11月2日に40番目の州に昇格した。
州内東側には州民の大半が住んでおり、その肥沃な土壌で様々な農作物が栽培されている。西側は牧畜業が盛んであり、その経済は観光業と防衛費に依存している。州南西部にはブラックヒルズと呼ばれる低木の松に覆われた山脈があり、スー族の聖地である。ここには4人の大統領の顔のモニュメントで有名な観光地ラシュモア山国立記念公園がある。他にもバッドランズ国立公園、クレイジー・ホース記念碑、ウインドケーブ国立公園、ジュエルケーブ国定記念物、カスター州立公園、また歴史ある町のデッドウッドなどが、訪れる人の多い観光地である。ウォール・ドラッグストアなど、民間主導で運営されている観光地・名所も少なくない。はっきりとした四季のある大陸性気候であり、雨量は東部で中程度、西部でやや少ない亜乾燥気候である。生態系は北アメリカ草原に典型的な様相を示している。
自然が豊富で多くの観光客が訪れる州という華やかな面がある一方、ゴールドラッシュ期にはインディアンと白人との激しい抗争が繰り返された州でもある。全米で最も経済的に貧しい地域がある州であり、現在でも、インディアン居留地の貧困は、サウスダコタ州が抱える大きな問題として残っている。
South Dakota (/- dəˈkoʊtə/ (![]() listen)) is a U.S. state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population and historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the seventeenth largest by area, but the fifth smallest by population and the 5th least densely populated of the 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. It was either the 39th or 40th state admitted to the union. Before signing the statehood papers, President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the papers so that no one could tell which became a state first.[8] Pierre is the state capital and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 187,200,[9] is South Dakota's largest city.
listen)) is a U.S. state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population and historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the seventeenth largest by area, but the fifth smallest by population and the 5th least densely populated of the 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. It was either the 39th or 40th state admitted to the union. Before signing the statehood papers, President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the papers so that no one could tell which became a state first.[8] Pierre is the state capital and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 187,200,[9] is South Dakota's largest city.
South Dakota is bordered by the states of North Dakota (to the north), Minnesota (to the east), Iowa (to the southeast), Nebraska (to the south), Wyoming (to the west), and Montana (to the northwest). The state is bisected by the Missouri River, dividing South Dakota into two geographically and socially distinct halves, known to residents as "East River" and "West River".[10]
Eastern South Dakota is home to most of the state's population, and the area's fertile soil is used to grow a variety of crops. West of the Missouri River, ranching is the predominant agricultural activity, and the economy is more dependent on tourism and defense spending. Most of the Native American reservations are in West River. The Black Hills, a group of low pine-covered mountains sacred to the Sioux, are in the southwest part of the state. Mount Rushmore, a major tourist destination, is there. South Dakota has a temperate continental climate, with four distinct seasons and precipitation ranging from moderate in the east to semi-arid in the west. The state's ecology features species typical of a North American grassland biome.
Humans have inhabited the area for several millennia, with the Sioux becoming dominant by the early 19th century. In the late 19th century, European-American settlement intensified after a gold rush in the Black Hills and the construction of railroads from the east. Encroaching miners and settlers triggered a number of Indian wars, ending with the Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890. Key events in the 20th century included the Dust Bowl and Great Depression, increased federal spending during the 1940s and 1950s for agriculture and defense, and an industrialization of agriculture that has reduced family farming.
While several Democrats have represented South Dakota for multiple terms in both chambers of Congress, the state government is largely controlled by the Republican Party, whose nominees have carried South Dakota in each of the last 13 presidential elections. Historically dominated by an agricultural economy and a rural lifestyle, South Dakota has recently sought to diversify its economy in areas to attract and retain residents. South Dakota's history and rural character still strongly influence the state's culture.
Le Dakota du Sud /dakɔta dy syd/3 Écouter (en anglais : South Dakota /ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə/4 Écouter) est un État du Nord des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest par le Wyoming et le Montana, au nord par le Dakota du Nord, à l'est par le Minnesota et l'Iowa et au sud par le Nebraska. État situé dans l'ouest des plaines du Midwest, il possède un climat continental. Il compte 814 180 habitants en 2010 (soit le 46e État américain au regard de la population). Sa capitale est Pierre et sa plus grande ville Sioux Falls, avec environ 154 000 habitants.
Le Dakota du Sud est coupé en deux par la rivière Missouri : à l'est de la rivière se trouvent la plupart des habitants et les exploitations agricoles, tandis qu'à l'ouest prédominent l'élevage et le tourisme. Le mont Rushmore, les Black Hills et les parcs nationaux de l'État sont des destinations appréciées.
Le Dakota du Sud est traditionnellement dirigé par des élus du Parti républicain. Si la ruralité influence grandement la culture de l'État, il a, ces dernières décennies, diversifié son économie afin d'attirer et de fixer de nouveaux habitants, ce qui a permis une augmentation modérée de la population ; le Dakota du Sud se trouve cependant confronté à l'exode rural et à de fortes disparités économiques, notamment entre les centres urbains et les réserves amérindiennes.
Il Dakota del Sud (AFI: [daˈkɔta][3]; in inglese , [ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə]) è uno stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America, situato nelle alte pianure del Midwest. Prende il nome dalla tribù di Nativi Americani Lakota (Sioux) e venne ammesso nell'Unione il 2 novembre 1889, assieme al Dakota del Nord, quando in precedenza, dal 2 marzo 1861 era stato costituito il Territorio del Dakota[4].
Costituito da 66 contee, la capitale è Pierre e confina a nord con il Dakota del Nord, a sud con il Nebraska, ad est con Iowa e Minnesota, ad ovest con Wyoming e Montana. L'unità navale USS South Dakota prese questo nome in onore dello Stato.
Dakota del Sur (en inglés, South Dakota) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Pierre y su ciudad más poblada, Sioux Falls. Está ubicado en la región Medio Oeste del país, división Centro Noroeste, limitando al norte con Dakota del Norte, al este con Minnesota, al sureste con el río Big Sioux que lo separa de Iowa, al sur con Nebraska, al oeste con Montana y al noroeste con Wyoming. Con 814 180 habs. en 2010 es el quinto estado menos poblado —por delante de Alaska, Dakota del Norte, Vermont y Wyoming, el menos poblado— y con 4,1 hab/km², el quinto menos densamente poblado, por delante de Dakota del Norte, Montana, Wyoming y Alaska, el menos densamente poblado. Fue admitido en la Unión el 2 de noviembre de 1889, como el estado número 40.
Su nombre proviene de las tribus amerindias lakota y dakota (sioux). Alberga el Monte Rushmore (Colinas Negras) donde están esculpidos los bustos de cuatro Presidentes de los Estados Unidos. Esta enorme escultura es una de las atracciones turísticas más conocidas del mundo, y que da al estado el sobrenombre de The Mount Rushmore State.
Su territorio está dividida por el río Misuri, que lo separa en dos mitades social y económicamente distintas, conocidas por los residentes como "este del río" y "oeste del río". La agricultura ha sido históricamente su principal fuente de riqueza. Es uno de los líderes nacionales en la producción de trigo. Posee, también, una de las mayores cabañas de ganado bovino del país. Dominado por una economía basada en la agricultura, ha procurado diversificarse para atraer y mantener a sus residentes. Sigue siendo sin embargo mayoritariamente rural, con una de las densidades de población más bajas del país.1
La región que forma actualmente Dakota del Sur fue una de las últimas zonas de Estados Unidos continental en ser explorada y asentada por los estadounidenses. En 1858, el gobierno federal crearía el Territorio de Dakota, que incluyó las actuales Dakotas, hasta entonces parte del de Minnesota. Estuvo escasamente poblado hasta el siglo XIX, cuando lo atravesaron las primeras líneas ferroviarias, lo que incentivó la agricultura. Inicialmente, solo algunos pocos latifundistas dominaban la economía del territorio. Sin embargo, el éxito de estos latifundistas y los ferrocarriles atrajeron a miles de personas a la región. El 2 de noviembre de 1889, el Territorio de Dakota fue dividido en las actuales Dakota del Norte y Dakota del Sur, y ambas fueron elevadas a la categoría de estados, incorporándose a la Unión.
Ю́жная Дако́та[1][2] (англ. South Dakota, МФА: /ˌsɑʊθ dəˈkoʊtə/ ![]() слушать) — штат, расположенный на Среднем Западе США. Назван в честь индейских племён Лакота и Дакота (Сиу). Южная Дакота стала штатом 2 ноября 1889 года (одновременно с Северной Дакотой). Столица штата — город Пирр, крупнейший город — Су-Фолс.
слушать) — штат, расположенный на Среднем Западе США. Назван в честь индейских племён Лакота и Дакота (Сиу). Южная Дакота стала штатом 2 ноября 1889 года (одновременно с Северной Дакотой). Столица штата — город Пирр, крупнейший город — Су-Фолс.




 Geography
Geography



