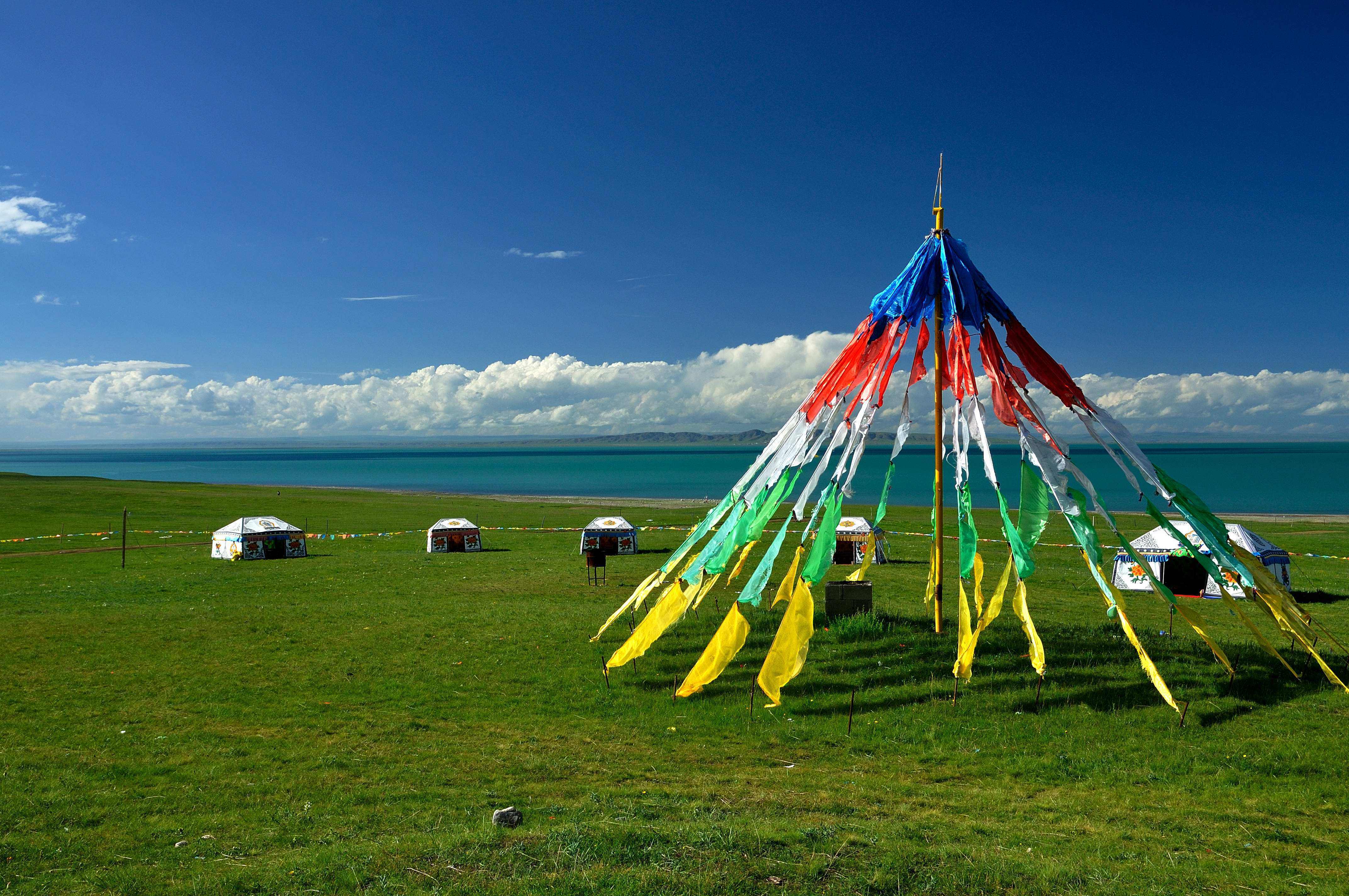
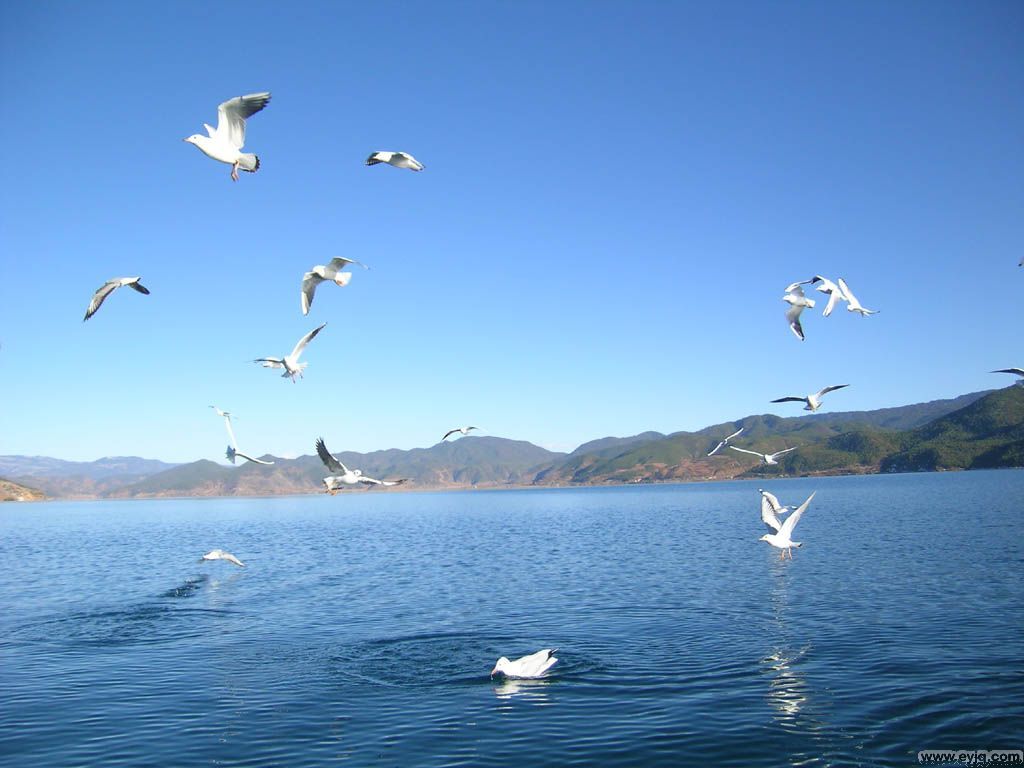
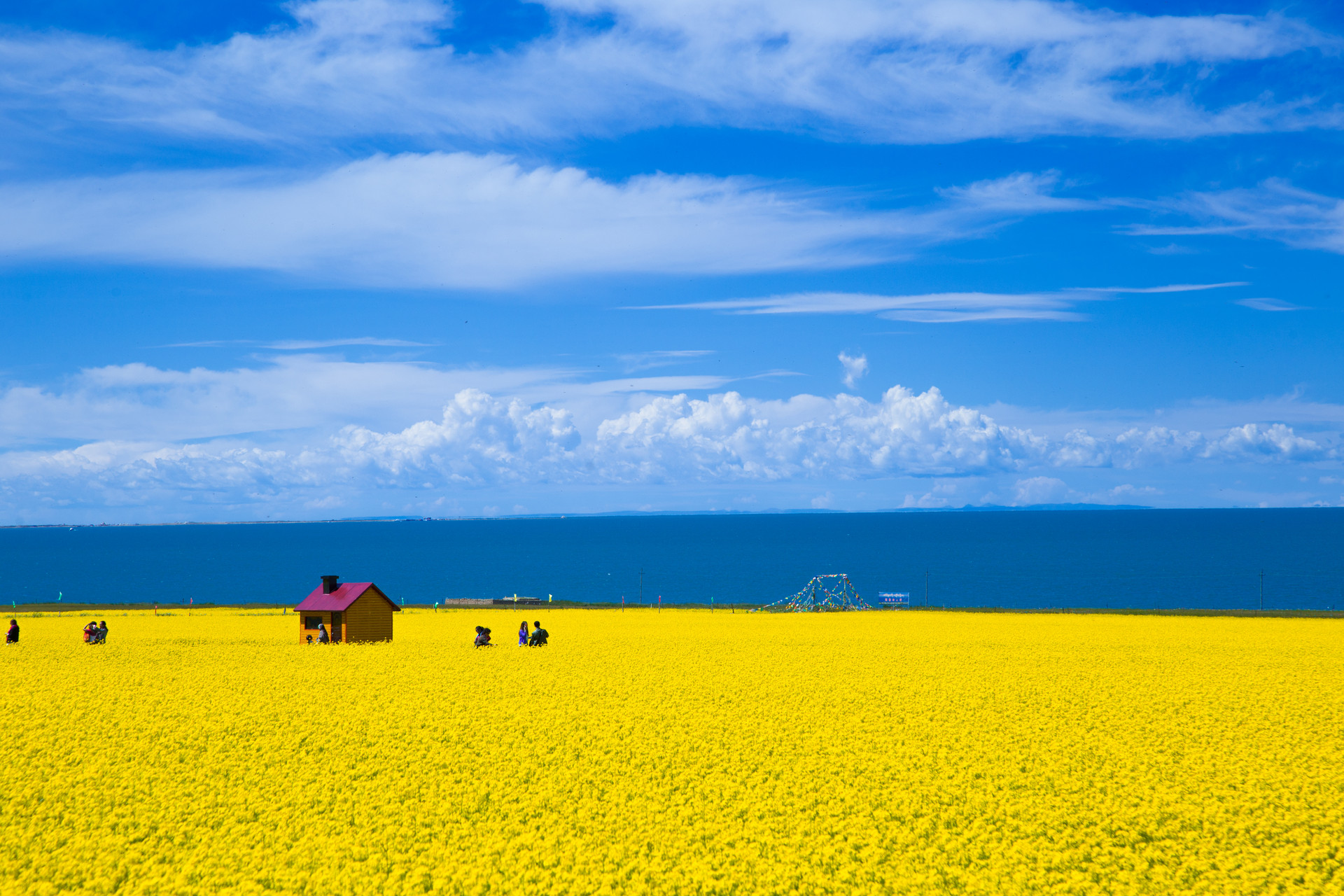
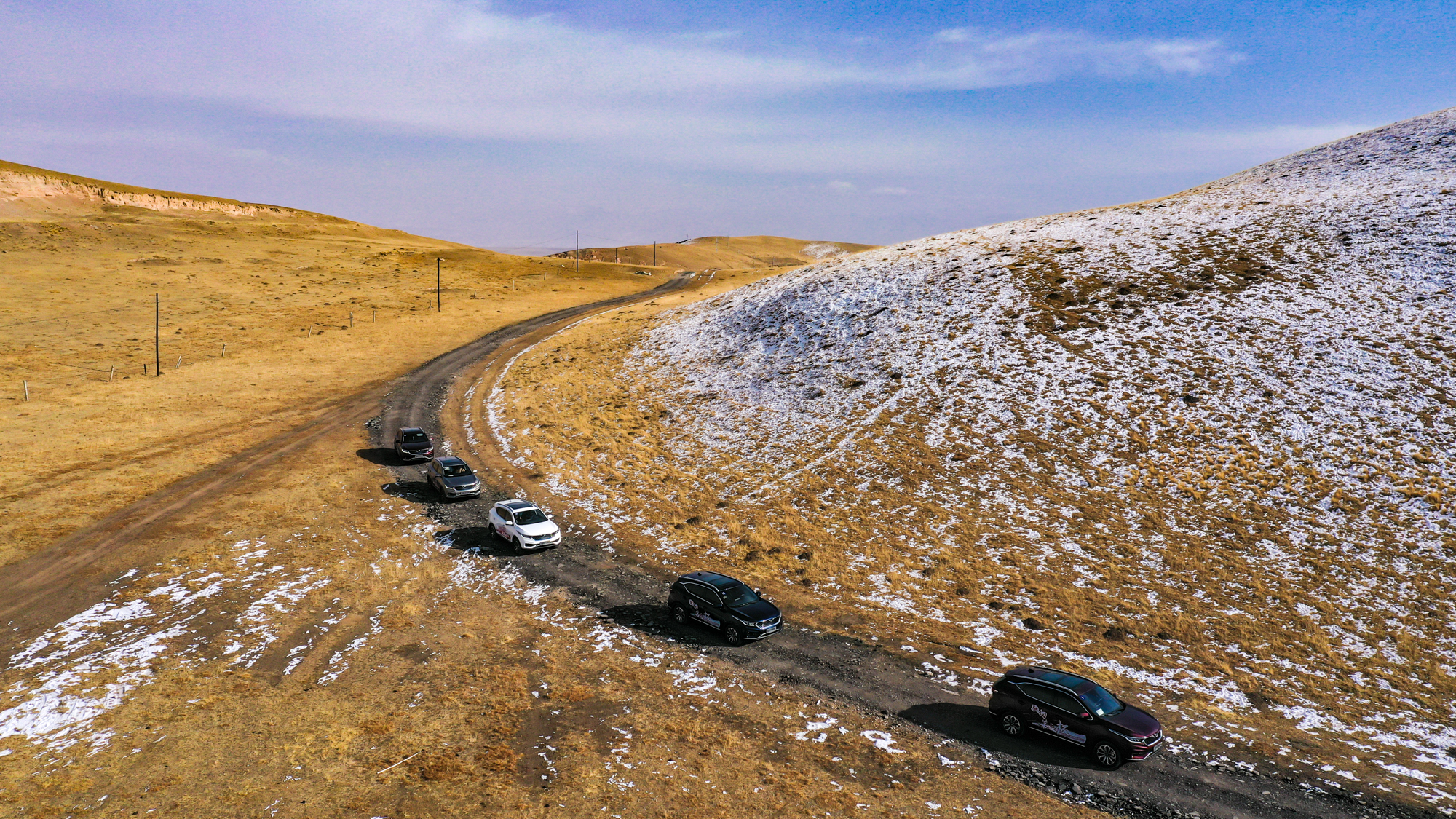
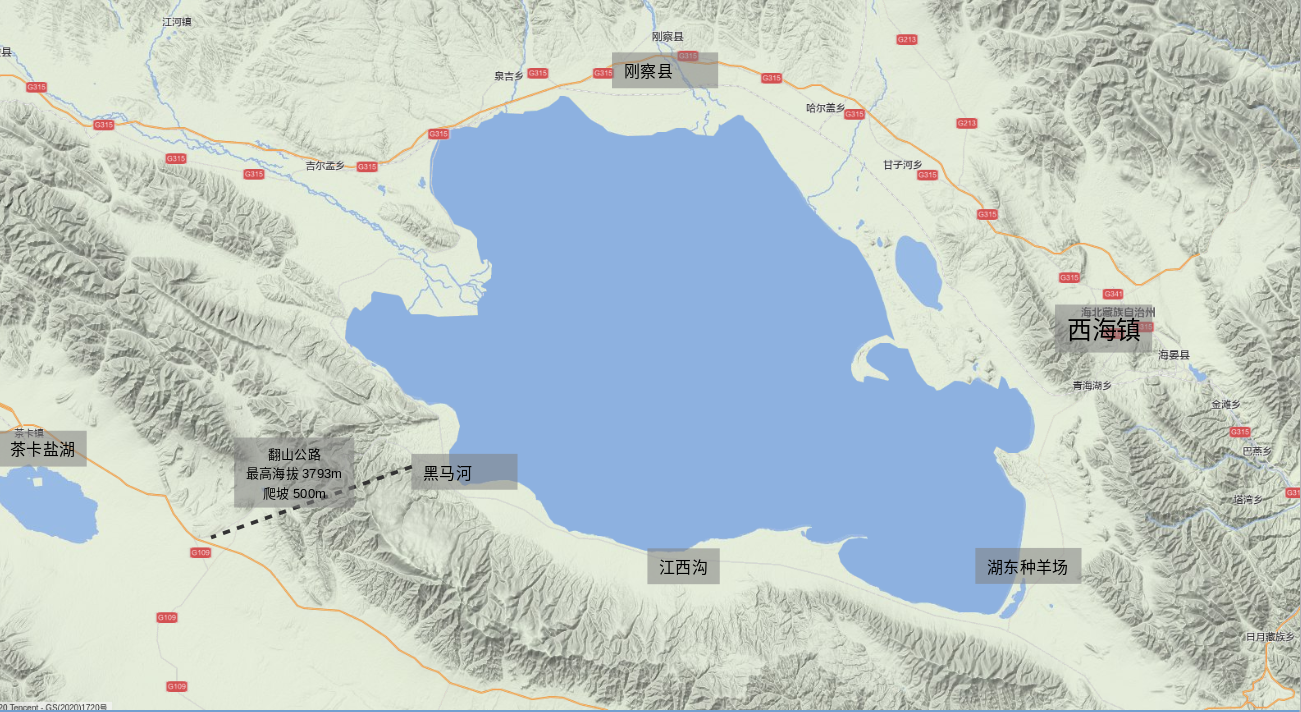
青海湖(藏语:མཚོ་སྔོན་པོ་,藏语拼音:Co Ngoinbo,威利:mtsho-sngon-po,THL:Tso Ngönpo,音错温布,藏语“青色的海”之意;蒙古语:Köke naɣur,音库库淖尔)。意均为蓝湖、青湖;古称西海、鲜水、鲜海、卑禾羌海。位于中国青海省内青藏高原的东北部,是中国最大的湖泊,也是中国最大的咸水湖、内流湖,早期面积4236.6平方公里,有时因人为及气候因素而极遽减小但也有扩大情况,环湖周长360多公里。湖水平均深约21米多,最大水深为32.8米,蓄水量1050亿立方米,湖面海拔3260米。湖水盐度为1.24%(一般海水含盐量为3.5%)。[1]
Der Qinghai-See ist der grösste Salzwassersee in China und liegt westlich der Provinzhauptstadt Xining in einer Senke des tibetischen Plateaus.
Der See ist berühmt für seine Fauna, vor allem für seinen Fisch- und Vogelreichtum. Zugvögel machen hier einen Zwischenstopp auf ihren Reisen.Am nordöstlichen Ufer befindet sich die „Vogelinsel“, welche ein Zufluchtsort für die zahlreichen Vogelarten auf ihren Wegen durch Asien darstellt. Der See hat eine Fläche von 5,694 km² und einen Umfang von 360km, trotzdem bleibt er im Winter oft für drei Monate gefroren. 23 Flüsse und Bäche fliessen in ihn herein.
Das internationale Radrennen „Tour of Qinghai Lake“ findet jährlich im Juli statt. Mehr als 100 Fahrer und 20 Teams nehmen an diesem Anlass über circa 1344km teil. Sie werden einen Teil dieser Strecke abfahren.(Quelle:www.amazing-china.de/de/latest/mountainbike-tour-qinghai-tibet-plateau.html)
Der Qinghai-See (chinesisch 青海湖, Pinyin Qīnghǎi Hú, tib. མཚོ་སྔོན་པོ། Wylie mtsho sngon po), im Mongolischen auch als Koko-nor bekannt, ist einer der größten abflusslosen Salzseen der Erde. Der chinesische Name des Sees Qīnghǎi Hú bedeutet etwa „See des türkisfarbenen Meers“, wobei das Zeichen qīng – 青 im Chinesischen ohne Kontext sowohl die Farben „Blaugrün“, „Grünblau“ „Türkis“ als auch „Schwarz“ bedeutet kann. (siehe Grün und Blau in verschiedenen Sprachen)[5][6][7] Das Zeichen hǎi – 海 bedeutet „Meer“[8][9] und hú – 湖 bedeutet „See – Binnensee“.[10][11]
青海湖(せいかいこ、チンハイフー)は、中華人民共和国青海省(チベット・アムド地方)にある湖。「チンハイこ」とも読まれる。モンゴル語ではココ・ノール(ᠬᠥᠬᠡ
ᠨᠠᠭᠤᠷ Хөхнуур/Köke naɣur「青い湖」の意)[1]、チベット語ではツォ・ゴンポ(མཚོ་སྔོན་; mtsho sngon po)またはツォ・ティショル・ギャルモ(མཚོ་ཁྲི་ཤོར་རྒྱལ་མོ་; mtsho khri shor rgyal mo)と呼称される。
Qinghai Lake or Ch'inghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuated in size, shrinking over much of the 20th century but increasing since 2004. It had a surface area of 4,317 km2 (1,667 sq mi), an average depth of 21 m (69 ft), and a maximum depth of 25.5 m (84 ft) in 2008.
Le lac Qinghai [tɕʰiŋ.xaɪ] (chinois : 青海湖 ; pinyin : ; EFEO Thsing-haï, littéralement : « lac de la mer bleue »), historiquement connu sous son nom mongol, translittéré autrefois de différentes formes se rapprochant Kokonor, (mongol : ᠬᠥᠬᠡ
ᠨᠠᠭᠤᠷ, translittération VPMC : qoqe naɣur ; mongol cyrillique : Хөх нуур, translittération MNS : khökh nuur, littéralement : « lac Bleu ») et également appelé Tso Ngönpo (tibétain : མཚོ་སྔོན་པོ་, Wylie : mtsho-sngon-po, pinyin tibétain : Co Ngoinbo, THL : Tso Ngönpo), est le plus grand lac de Chine.
Il est situé pour sa rive sud dans le xian de Gonghe de la préfecture autonome tibétaine de Hainan et pour sa rive nord dans les Xians de Haiyan et de Gangca de la préfecture autonome tibétaine de Haibei de la province éponyme de Qinghai, dont la capitale, Xining, est située à environ 180 km à l'est du lac.
Il lago Qinghai («lago azzurro»; in cinese 青海湖: (pinyin) Qinghai Hu o (romanizzazione Wade-Giles) Ch'ing-hai Hu; in tibetano མཚོ་སྔོན་པོ: Tso Ngömpo), noto anche come Koko Nor, è un lago della provincia del Qinghai (Cina centro-occidentale). Questo specchio d'acqua, il più grande lago di montagna privo di emissario dell'Asia centrale, è situato in una depressione dei monti Qilian; giace a circa 3200 m di altezza sul livello del mare.
El lago Qinghai (Pinyin: lago Kokonor, Koko Nor o Tso Ngonpo, en mongol, Хөх нуур) es el mayor lago de China.
El lago Qinghai recibe las aguas de 23 ríos y arroyos, y se encuentra situado a 3.205 m por encima del nivel del mar, en una depresión de la meseta Tibetana.
La zona del lago fue tradicionalmente una zona fronteriza entre los pueblos mongoles y tibetanos, por lo que el lago fue conocido en Occidente por su nombre de origen mongol Kokonor. En mongol moderno, este nombre se escribe Хөх нуур (Höhnuur) y significa lago azul. Las versiones tibetana y manchú del nombre tienen el mismo significado. El nombre en chino Qinghai (青海, pinyin: Qīnghǎi) significa literalmente "mar azul" y da nombre a la provincia de Qinghai. La superficie del lago es de 5.694 km², pero se ha reducido en los últimos años (hasta 4.635 km², según algunas fuentes), y tiene 360 km de perímetro. A pesar de su alta salinidad, presenta una abundancia de especies marinas, como el pez comestible huángyú (湟鱼).El lago Qinghai se encuentra en la provincia noroccidental de Qinghai, a la que da nombre, concretamente en la división entre las dos prefecturas autónomas tibetanas de Hainan y Haibei. Es el punto de encuentro de varias rutas migratorias de aves en Asia. Muchas especies hacen parada en el lago Qinghai en sus migraciones estacionales. Debido a esta característica del lago, este ha sido un centro de atención en las medidas de seguimiento de la propagación del virus H5N1 de la gripe aviaria, ya que una aparición del virus en el lago podría extenderlo con suma facilidad por Asia y Europa. De hecho, se han identificado casos aislados de H5N1 en el lago.
Al nordeste del lago se encuentran las «islas de los pájaros» (isla del Cormorán e isla del Huevo), que han sido reservas de aves de la Zona de Protección Natural del Lago de Qinghai desde 1997. Durante el invierno la superficie del lago permanece helada durante un máximo de tres meses.
Кукуно́р (Цинха́й)[1] (кит. упр. 青海湖, палл. Цинхай ху, монг. Хөх нуур) — второе по размерам бессточное горное солёное озеро Центральной Азии после озера Иссык-Куль. Расположено в провинции Цинхай на западе Китая. Длина — около 105 км, ширина — до 65 км, площадь — около 4200 км²[2], наибольшая известная глубина — 38 м, расположено на высоте 3205 м и занимает центральную часть Кукунорской равнины.