Die bronzezeitliche Indus-Kultur oder Indus-Zivilisation war eine der frühesten städtischen Zivilisationen. Sie entwickelte sich etwa in den Jahren 2800–1800 v. Chr. entlang des Indus im Nordwesten des indischen Subkontinents. Die Indus-Kultur erstreckte sich über fast das gesamte heutige Pakistan sowie Teile Indiens und Afghanistans, insgesamt umfasste sie 1.250.000 km² und damit eine größere Landfläche als das antike Ägypten und Mesopotamien zusammen. Sie war neben diesen eine der drei frühesten Zivilisationen der Welt.
Sie wird teilweise auch Harappa oder Harappa-Kultur genannt, nach Harappa, einem der Hauptausgrabungsplätze am Ravi. Eine weitere alternative Benennung dieser Kultur lautet Sindhu-Sarasvati-Zivilisation; hinter dieser Bezeichnung steht die Theorie, dass sie eine in der vedischen Literatur erwähnte Zivilisation sei. Möglicherweise ist sie auch mit dem sumerischen Meluha zu identifizieren.
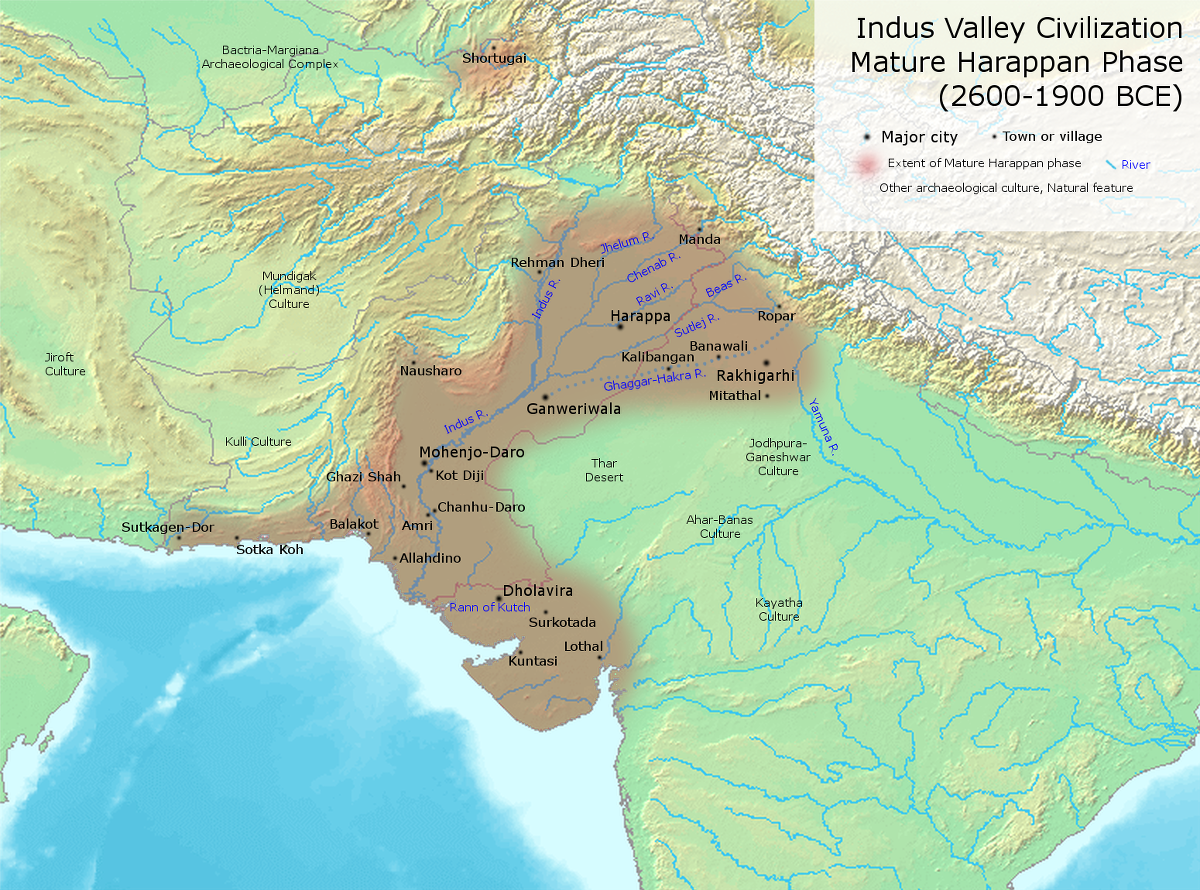
Bis heute sind über 1050 Fundorte identifiziert, hauptsächlich entlang des Indus. Zusätzlich gibt es Hinweise auf einen anderen großen Fluss östlich des Indus, der heute ausgetrocknet ist und der antike Ghaggra-Hakra oder Sarasvati gewesen sein könnte. Über 140 antike Städte und Siedlungen wurden an seinem Lauf gefunden. Die beiden größten urbanen Zentren der Harappa-Kultur waren wohl Harappa und Mohenjo-Daro, daneben gab es noch große Städte bei Dholavira, Ganweriwala, Lothal und Rakhigarhi. Zu ihrer Blütezeit zählte die Indus-Kultur vermutlich über fünf Millionen Menschen.
Diese frühe indische Kultur kannte bereits Architektur und eine regelmäßige Städteplanung einschließlich gepflasterter Straßen mit Straßenablauf (Gullys). Sie entwickelte zum ersten Mal in der Geschichte der Menschheit den gebrannten Ziegel mit den perfekten, noch heute gebräuchlichen Proportionen 1:2:4, der als Einhandziegel in allen Richtungen beliebig addierbar ist.
Möglicherweise besaß sie auch eine Schrift; ob aber die sogenannte Indus-Schrift tatsächlich eine Schrift ist, wird in Fachkreisen bisher kontrovers diskutiert.
古印度文明時期,也称哈拉帕文明(harappa)时期,是指世界四大文明之一的古印度,約公元前2300年至前1300年之時期。
印度河流域文明发生晚于两河流域文明、尼罗河流域文明,但早于商朝。考古专家在印度河流域发现摩亨约达罗和哈拉帕两个古代城市遗址,发现了大量石器、青铜器、印章和农作物遗迹,估计城市人口都在4万以上。
两个城市的中心都有一个人工堆成的土墩,作用未知,考古学家猜测这可能是城市的中心。城市建筑以卫城为中心呈网格状分布,有市政建筑、市场、作坊、储存区、民居和神庙。每座民居都围着一个院子建成,有几个房间、一间厕所和一口水井。建筑用基本材料是从烧木头的窑里制出的土砖。在摩亨佐-达罗的卫城上建造了一个大浴池,有私人浴池、会所等。
印度河流域的农民种植大麦、小麦、棉花、瓜和椰枣。他们还驯养大象和水牛在田里干活。这一地区有许多手艺精湛的制陶人,他们用陶轮制作陶器,这在当时是一项崭新的技术。哈拉帕人使用石器,并用青铜制作刀、武器、碗和雕像。他们建立了发达的废物处理系统,包括有盖板的排水系统和倒垃圾的斜槽。
遗址中有许多天秤和砝码,说明他们有一套度量衡制度好配合其繁荣的商业贸易。而印度河流域文明更证明与古美索不达米亚,阿富汗,缅甸甚至和古中国都有商业往来。
印度河文明持续了800年,尚未有人知道它是如何结束的,但是有几种说法:河水泛滥、瘟疫、贸易或经济或国内秩序崩溃等等。
インダス文明(インダスぶんめい、Indus Valley civilization)は、インド・パキスタン・アフガニスタンのインダス川および並行して流れていたとされるガッガル・ハークラー川周辺に栄えた文明である。これら各国の先史文明でもある(インドの歴史、アフガニスタンの歴史も参照)。崩壊の原因となったという説のあった川の名前にちなんでインダス文明、最初に発見された遺跡にちなんでハラッパー文明とも呼ばれる[1]。
狭義のインダス文明は、紀元前2600年から紀元前1800年の間を指す。インダス文明の遺跡は、東西1500km、南北1800kmに分布し、遺跡の数は約2600におよぶ。そのうち発掘調査が行われた遺跡は、2010年時点でインド96、パキスタン47、アフガニスタン4の合計147となっている[2]。
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE.[1] Along with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia it was one of three early civilisations of the Old World, and of the three, the most widespread, extending from what today is northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India.[2][note 1] It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial, mostly monsoon-fed, rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the seasonal Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.[1][3] Aridification of this region during the 3rd millennium BCE may have been the initial spur for the urbanisation associated with the civilisation, but eventually also reduced the water supply enough to cause the civilisation's demise, and to scatter its population eastward.[4][5][3][6]
The civilisation's cities were noted for their urban planning, baked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, clusters of large non-residential buildings, and new techniques in handicraft (carnelian products, seal carving) and metallurgy (copper, bronze, lead, and tin). [7] Its large urban centres of Mohenjo-daro and Harappa very likely grew to containing between 30,000 and 60,000 individuals,[8][note 2] and the civilisation itself during its florescence may have contained between one and five million individuals.[9][note 3]
The Indus civilisation is also known as the Harappan Civilisation, after its type site, Harappa, the first of its sites to be excavated in the 1920s in what was then the Punjab province of British India and now is Pakistan.[10][note 4] The discovery of Harappa and soon afterwards Mohenjo-Daro was the culmination of work beginning in 1861 with the founding of the Archaeological Survey of India during the British Raj.[11] There were however also earlier and later cultures often called Early Harappan and Late Harappan in the same area; for this reason, the Harappan civilisation is sometimes called the Mature Harappan' culture to distinguish it from these cultures. By 2002, over 1,000 Mature Harappan cities and settlements had been reported, of which just under a hundred had been excavated,[12][note 5][13][14][note 6] mainly in the general region of the Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra Rivers and their tributaries; however, there are only five major urban sites at the peak of the settlement hierarchy:[15][note 7] Harappa, Mohenjo-daro (UNESCO World Heritage Site), Dholavira, Ganeriwala in Cholistan and Rakhigarhi.[16][note 8] The early Harappan cultures were preceded by local Neolithic agricultural villages, from which the river plains were populated.[17][18]
The Harappan language is not directly attested, and its affiliation is uncertain since the Indus script is still undeciphered.[19] A relationship with the Dravidian or Elamo-Dravidian language family is favoured by a section of scholars.[20][21]
La civilisation de la vallée de l'Indus (vers 2600 av. J.-C. – vers 1900 av. J.-C.), ou civilisation harappéenne, du nom de la ville antique de Harappa, est une civilisation de l'Âge du bronze, dont le territoire s'étendait autour de la vallée du fleuve Indus, dans l'ouest du sous-continent indien (le Pakistan moderne et ses alentours). Les raisons de son émergence, de sa prospérité rayonnante durant sept siècles, puis de son déclin brutal, sont mal connues et restent débattues, ainsi que son influence, probable, sur la culture hindoue antique.
Oubliée jusqu’à sa découverte dans les années 1920, la civilisation de l’Indus se classe, avec celles de la Mésopotamie et de l’Égypte antique, comme l’une des toutes premières civilisations de l'histoire, celles-ci étant définies par l'apparition de villes, puis de l’écriture.
Si la civilisation de l’Indus n’est pas considérée comme la première civilisation antique, la Mésopotamie et l’Égypte ayant développé des villes un peu plus tôt, elle est par contre celle qui connait à son époque la plus grande extension géographique. À ce jour, sur les 1 052 sites qui ont été découverts, plus de 140 se trouvent sur les rives du cours d'eau saisonnier Ghaggar-Hakra. D’après certaines hypothèses, ce système hydrographique, autrefois permanent, arrosait la principale zone de production agricole de la civilisation de l’Indus.
La plupart des autres sites se situent le long de la vallée de l’Indus et de ses affluents, mais on en trouve aussi à l’ouest, jusqu’à la frontière de l’Iran, à l’est jusqu’à Delhi, au sud jusque dans le Maharashtra, et au nord jusqu’à l’Himalaya. Parmi ces sites, on compte de nombreuses villes comme Dholavira, Ganweriwala, Mehrgarh, Harappa, Lothal, Mohenjo-daro et Rakhigarhi. À son apogée, sa population pourrait avoir dépassé cinq millions de personnes.
Malgré toutes ses réalisations, cette civilisation est très mal connue. Son existence même a été oubliée jusqu’au XXe siècle. Son écriture reste indéchiffrée et on ne sait pas si elle a un lien quelconque avec l’écriture brahmi, ce qui semble peu probable au regard des connaissances actuelles. Parmi les mystères que cette civilisation recèle, trois questions au moins sont fondamentales :
- formait-elle un État ou un ensemble de cités-états ?
- quels étaient ses moyens de subsistance ?
- quelles sont les causes de sa disparition soudaine et dramatique, à partir du XIXe siècle av. J.-C. ?
La langue utilisée par ses membres et le nom qu’ils se donnaient restent à ce jour inconnus.
La civiltà della valle dell'Indo (c. 3300–1500 a.C., fiorita 2600–1900 a.C.) fu una civiltà antica, estesa geograficamente soprattutto lungo il fiume Indo nel subcontinente indiano, ma anche lungo il Sarasvati, un fiume dell'India ormai prosciugato.
Nel mondo anglosassone viene citata come "civiltà dell'Indo-Sarasvati", in riferimento alla civiltà descritta nei Veda e che si sarebbe sviluppata lungo i due fiumi. È anche conosciuta come "civiltà di Harappa", dal primo sito conosciuto, scoperto nel 1857, ma scavato soltanto dagli anni venti del Novecento.
La cultura del valle del Indo fue una civilización de la Edad del Bronce, que se desarrolló desde c. 3300 a. C. hasta 1300 a. C. a lo largo del valle del río Indo, en Afganistán, Pakistán y el noroeste de la India. Abarcaba cerca de un centenar de asentamientos y dos ciudades importantes: Harappa y Mohenjo-Daro, ambos sitios en Pakistán. En conjunto comprendía el área más extensa de todas las civilizaciones antiguas, más de un millón de kilómetros cuadrados, y atravesó varios periodos, siendo su máximo esplendor entre el 2600 y el 1900 a. C.
Al igual que las civilizaciones de Mesopotamia y Egipto, dependía de su río. Como el Nilo, el Indo se desbordaba todos los años, inundando extensas zonas y depositando sedimentos fértiles. Este inmenso potencial agrícola fue la base sobre la cual se desarrolló el urbanismo en torno al río Indo.
Con las culturas prehistóricas del valle del Indo se prepara el primer capítulo de la historia de la India. Se trata de un largo periodo prehistórico, probado por testimonios líticos. Por otra parte, se pueden encontrar vestigios prehistóricos hasta el I milenio a. C., es decir, hasta un tiempo en que la península ya había entrado en la historia. En sentido estricto, las culturas del Indo pertenecen a la prehistoria ya que solamente han dejado restos arqueológicos sin documentos literarios, pero para apreciar la historia india hace falta tomar en consideración estas culturas urbanas prearias.
И́ндская или Хара́ппская цивилизация — третья[* 1] по времени появления древневосточная цивилизация бронзы[1], после египетской и месопотамской. Из всех трёх она занимала наибольшую площадь, превосходя в 2 раза суммарную площадь двух остальных[2][3]. Индская цивилизация относительно быстро пришла в упадок, пережив расцвет между 2600—1900 годами до нашей эры, см. Засуха 2200 года до н. э..
Хараппская цивилизация развивалась в долине реки Инд в 3300—1300 годах до нашей эры[4]. Наиболее значительные центры — Ракхигархи (350 га), Мохенджо-Даро (300 га)[5], Хараппа (150 га), Лотхал (60 га) и Дхолавира — 47 гектаров.[6]. Население в годы расцвета составляло около 5 миллионов человек и состояло из эламито-дравидов, без примеси индоевропейцев[7]. Зрелый период развития Индской цивилизации шёл с 2600 до 1900 лет до нашей эры. Простиралась на территориях нынешних Афганистана, Пакистана и Северо-Западной Индии.
В шумерских текстах хараппская цивилизация предположительно носила название «Мелухха»[8].
В течение III-го тысячелетия до нашей эры началась аридизация — постепенное истощение водных ресурсов региона, где находилось государство. Возможной причиной аридизации археологи называют возросшую урбанизацию в регионе и постепенное осушение почв и рек. В итоге это могло привести к упадку государства. При этом, после упадка, население ушло на Восток.
Первые данные о существовании доарийской цивилизации в западной Индии опубликовал в XIX веке Александр Каннингем. Окончательно существование индской цивилизации было установлено в 1921—1922 годах экспедицией во главе с Джоном Маршаллом.
На пике развития индская цивилизация имела население свыше 5 миллионов человек. Жители долины реки Инд разработали ряд новых ремёсел — обработку сердолика, обработку кости, металлургию бронзы, меди, свинца и олова. Города хараппской цивилизации отличаются чётким планированием построек. Строительный материал — обожжённый кирпич из глины. Освоены и использовались сложные дренажные системы, системы водоснабжения и целые кластеры крупных нежилых зданий.
При раскопках городов были найдены как детские игрушки, так и небольшое количество оружия, что указывает на не сильную милитаризацию государства и относительно мирные периоды существования. Ставка в развитии была сделана на торговлю с далёкими землями, дальше чем Вавилон, Шумер и южная Месопотамия. На развитую торговлю указывают многочисленные печати, украшенные животными и мифическими существами.
Названия «цивилизация Инд» и «цивилизация Хараппы» — равнозначны в археологической литературе[источник не указан 150 дней], хотя термин «Хараппа» может ввести в заблуждение, так как это обозначение дано по названию современного городка Хараппа, где располагается хронологически первая археологическая площадка, раскопанная еще в 1920-е годы. Вскоре был обнаружен и исследован Мохенджо-Даро, что привело к сенсационным открытиям. Данные памятники относятся к зрелому этапу хараппской цивилизации и отличаются от предшествующих и последующих культур, называемых ранней хараппской и поздней хараппской культурами. Ранней хараппской культуре предшествовали местные неолитические поселения сельскохозяйственного типа.
К 2008 году было найдено 1 022 города и поселения, главным образом в районе рек Инд и Гхаггар-Хакра и их притоков. Из них 406 объектов найдены на территории нынешнего Пакистана и 616 в Индии. Раскопаны и изучены — 96 объектов. Среди этих 96 объектов значатся крупные городские центры, в том числе Хараппа, Мохенджо-Даро (объект Всемирного наследия Юнеско), Дхолавира, Ганеривала[en], Ракхигархи.
Язык государства не имеет точной идентификации, его генеалогическая принадлежность пока не ясна. Связи хараппского языка и дравидийских и эламо-дравидийских языков изучены недостаточно.[9]






