
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Germany
Germany

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
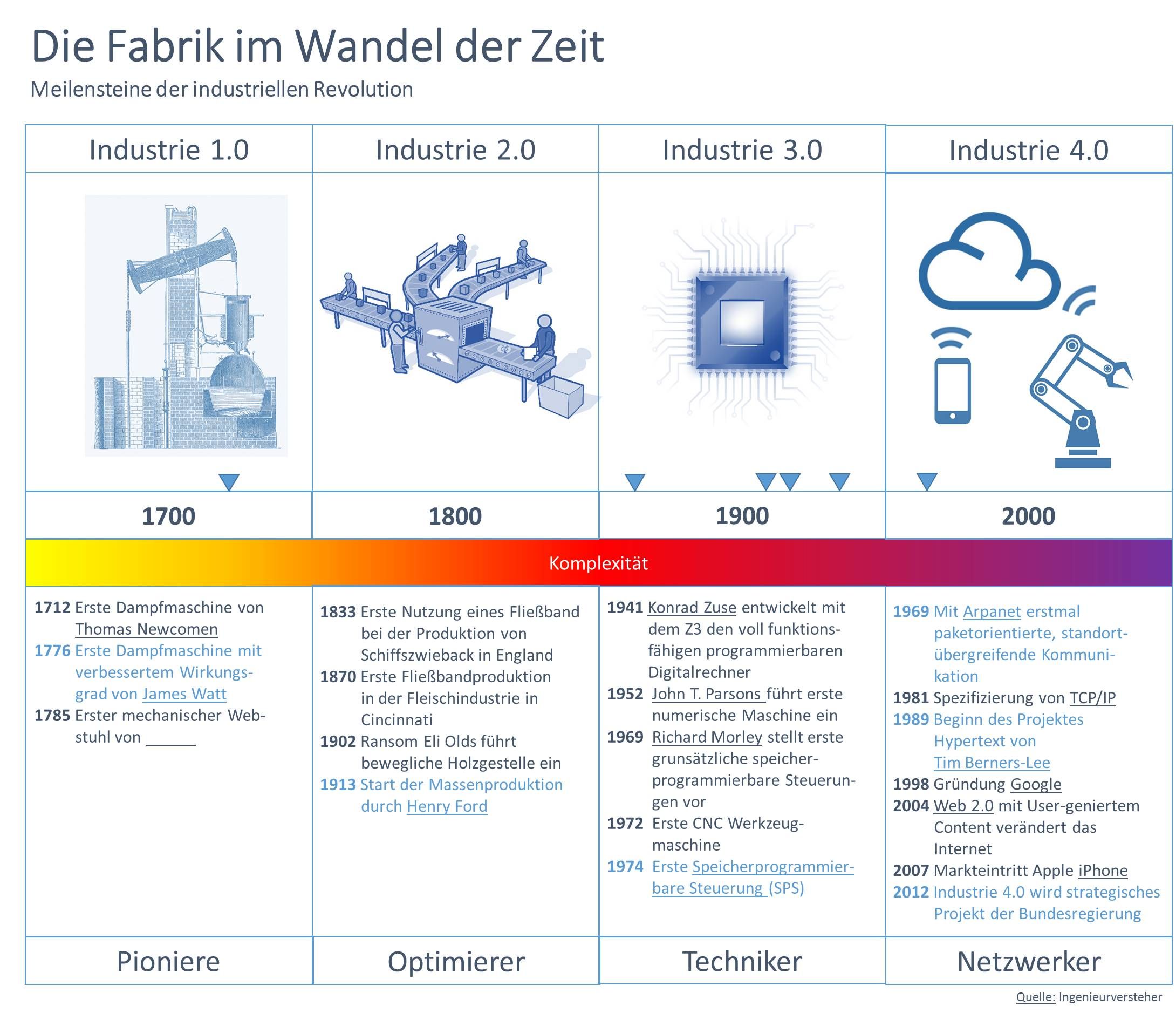
工业4.0(英语:Industry 4.0、德语:Industrie 4.0),或称生产力4.0,是一个德国政府提出的高科技计划[1]。又称为第四次工业革命、2013年德国联邦教育及研究部和联邦经济及科技部将其纳入《高技术战略2020》的十大未来项目,投资预计达2亿欧元,用来提升制造业的计算机化、数字化和智能化[2]。德国机械及制造商协会(VDMA)等设立了“工业4.0平台”;德国电气电子及信息技术协会发布了德国首个工业4.0标准化路线图。
所谓的4.0目标与以前不同,并不是单单创造新的工业技术,而是着重在将现有的工业相关的技术、销售与产品体验统合起来,是创建具有适应性、资源效率和人因工程学的智能工厂,并在商业流程及价值流程中集成客户以及商业伙伴[3][4],提供完善的售后服务。其技术基础是智能集成感控系统及物联网[5]。这样的架构虽然还在摸索,但如果得以陆续成真并应用,最终将能建构出一个有感知意识的新型智能工业世界,能透过分析各种大数据, 直接生成一个充分满足客户的相关解决方案产品(需求定制),更可利用计算机预测,例如天气预测、公共交通、市场调查数据等等,及时精准生产或调度现有资 源、减少多余成本与浪费等等(供应端优化),需要注意的是工业只是这个智能世界的一个部件,需要以“工业如何适应智能网络下的未来生活”去理解才不会搞混 工业的种种概念。
第四次工业革命可以实现的时间,各方说法不一;德国电气电子及信息技术协会的会员中只有四分之一认为2020年前会有大规模的实施[6],而工业通信标准、安全性和人员培训都是较大的问题。
Industrie 4.0 ist die Bezeichnung für ein Zukunftsprojekt zur umfassenden Digitalisierung der industriellen Produktion, um sie für die Zukunft besser zu rüsten. Der Begriff geht zurück auf die Forschungsunion der deutschen Bundesregierung und ein gleichnamiges Projekt in der Hightech-Strategie der Bundesregierung; zudem bezeichnet er eine Forschungsplattform.[1][2][3] Die industrielle Produktion soll mit moderner Informations- und Kommunikationstechnik verzahnt werden.[4] Technische Grundlage hierfür sind intelligente und digital vernetzte Systeme. Mit ihrer Hilfe soll weitestgehend selbstorganisierte Produktion möglich werden: Menschen, Maschinen, Anlagen, Logistik und Produkte kommunizieren und kooperieren in der Industrie 4.0 direkt miteinander.[4] Durch die Vernetzung soll es möglich werden, nicht mehr nur einen Produktionsschritt, sondern eine ganze Wertschöpfungskette zu optimieren. Das Netz soll zudem alle Phasen des Lebenszyklus des Produktes einschließen – von der Idee eines Produkts über die Entwicklung, Fertigung, Nutzung und Wartung bis zum Recycling.[4]
インダストリー4.0(独: Industrie 4.0、英: Industry 4.0)は、ドイツ連邦教育科学省が勧奨して、2011年にドイツ工学アカデミーが発表したドイツ政府が推進する製造業のデジタル化・コンピューター化を目指すコンセプト、国家的戦略的プロジェクトである[1][2][3]。IoTの普及についてトップダウンで国家プロジェクトとした世界初の事例となる[1]。
「インダストリー4.0」を日本語に直訳した場合には、「第四次産業革命」の意味合いもあるが、「IoTやAIを用いることによる製造業の革新」という一般的な意味の第四次産業革命とドイツの国家プロジェクトとしてのインダストリー4.0とでは意味合いが異なることもある[4]。
Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing[1][2][3][4] and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 is commonly referred to as the fourth industrial revolution.[5]
Industry 4.0 fosters what has been called a "smart factory". Within modular structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and with humans in real-time both internally and across organizational services offered and used by participants of the value chain.[1]
Le concept d’industrie 4.0 ou industrie du futur correspond à une nouvelle façon d’organiser les moyens de production. Cette nouvelle industrie s'affirme comme la convergence du monde virtuel, de la conception numérique, de la gestion (finance et marketing) avec les produits et objets du monde réel. Les grandes promesses de cette quatrième révolution industrielle sont de séduire les consommateurs avec des produits uniques et personnalisés, et malgré de faibles volumes de fabrication, de maintenir des gains. Ces mêmes consommateurs peuvent ainsi communiquer avec les machines durant les phases de réalisation, ce type de production s'appelle la « Smart Product ». Selon ce principe, dans le contexte de l’automatisation industrielle, cela se caractérise par la mise en œuvre de capteurs qui sont les éléments de base des système d'acquisition et de contrôle de données (SCADA). Ils permettent de transformer des grandeurs physiques (température, pression, position, concentration, autres…) en signaux, le plus souvent électriques, qui renseignent sur ces grandeurs. Ces capteurs permettent aux robots d'une chaîne de production de dialoguer et d'adapter l'outil de production aux différents besoins, de manière non exhaustive, les maintenances, les besoins des marchés ou les modifications des clients.
Outre les aspects technologiques, cette quatrième révolution industrielle influe sur différents aspects de nos sociétés modernes. De nouveaux enjeux apparaissent au travers de cette nouvelle manière de produire. L'industrie 4.0 touche évidemment l'aspect économique mais a également des impacts sociaux, politiques ou environnementaux. Il pose la question de l'emploi de millions de salariés à travers le monde. En effet, l'accompagnement des salariés actuels et la formation des futurs salariés sont à prendre en compte. Il semble difficile d'envisager que des millions de travailleurs se retrouvent sans emploi. Plus généralement, il est nécessaire de réfléchir à la place de l'humain dans cette industrie 4.0.
Il termine Industria 4.0 (o in inglese Industry 4.0) indica una tendenza dell'automazione industriale che integra alcune nuove tecnologie produttive per migliorare le condizioni di lavoro e aumentare la produttività e la qualità produttiva degli impianti.
El concepto "'Industria 4.0'" (también señalado o referenciado como Revolución industrial 4.0,1o Industria inteligente,2 o Ciberindustria del futuro)3 corresponde a una nueva manera de organizar los medios de producción.
El objetivo que pretende alcanzarse es la puesta en marcha de un gran número de «fábricas inteligentes» (en inglés: «smart factories») capaces de una mayor adaptabilidad a las necesidades y a los procesos de producción, así como a una asignación más eficiente de los recursos, abriendo así la vía a una nueva revolución industrial o Revolución industrial 4.0.4
Las bases tecnológicas en que se apoya esta orientación, entre otras son las siguientes: (1) Internet de las cosas ; (2) Sistemas ciberfísicos (3) Cultura maker (Cultura Hágalo usted mismo) ; (4) Fábrica 4.0…56 Sin embargo, la Industria 4.0 no se reduce exclusivamente a los cuatro puntos recién citados, pues es mucho más que eso. La Industria 4.0 es consistente con la llamada Cuarta Revolución Industrial, enfatizando y acentuando la idea de una creciente y adecuada digitalización y coordinación cooperativa en todas las unidades productivas de la economía.7
Industria 4.0 es un concepto nuevo, que también recibe otras denominaciones o subdenominaciones tales como:8 « Ciberusina »,9 « Ciberfábrica »,10 « Usina digital », « Industria digital »,11 « Fabricación avanzada »,1213 « Futurprod »,14 « Integrated Industry »,15 « Smart-Industries »,161718 « Intelligent Manufacturing System ».19
Este concepto de Industria 4.0 que aquí se presenta no es una realidad ya consolidada y experimentada, sino un nuevo hito en el desarrollo industrial que podría marcar importantes cambios sociales en los próximos años, haciendo un uso intensivo de Internet y de las tecnologías punta, con el fin primordial de desarrollar plantas industriales y generadores de energía más inteligentes y más respetuosos con el medio ambiente, y con cadenas de producción mucho mejor comunicadas entre sí y con los mercados de oferta y demanda.4


 IT-Times
IT-Times


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 *IT security and data protection policy
*IT security and data protection policy


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 *Government
*Government

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 *eHealth
*eHealth


 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Bretagne
Bretagne

 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France


 IT-Times
IT-Times


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence

 Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Universität Paris-Saclay
Universität Paris-Saclay

- centre de recherche Bordeaux - Sud-Ouest (situé à Talence) ;
- centre de recherche Grenoble - Rhône-Alpes (situé à Montbonnot-Saint-Martin, sur le parc technologique Inovallée) ;
- centre de recherche Lille - Nord Europe (situé à Villeneuve-d'Ascq, sur le parc scientifique de la Haute Borne) ;
- centre de recherche de Lyon (situé à Villeurbanne, sur le campus de la Doua) ;
- centre de recherche Nancy - Grand Est (situé à Villers-lès-Nancy, à la frontière de Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy) ;
- centre de recherche de Paris (situé rue Simone-Iff à Paris 12e) ;
- centre de recherche Rennes - Bretagne Atlantique (situé sur le Campus de Beaulieu) ;
- centre de recherche Saclay - Île-de-France (situé à Palaiseau) ;
- centre de recherche Sophia Antipolis - Méditerranée (situé à Biot).



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology

 California-CA
California-CA


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 FPGA
FPGA


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Processing Units - CPU, GPU, NPU, APU, TPU, VPU, FPGA, QPU, IPU, PIC
Processing Units - CPU, GPU, NPU, APU, TPU, VPU, FPGA, QPU, IPU, PIC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 IC
IC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Motherboard
Motherboard


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Semiconductor technology
Semiconductor technology


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Internet of Things
Internet of Things


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Games industry
Games industry


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PCI-SIG
PCI-SIG


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 MCU
MCU


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
 Partner of the Paris 2024 organizing committee
Partner of the Paris 2024 organizing committee

 Companies
Companies
 *Big semiconductor manufacturer
*Big semiconductor manufacturer
 United States
United States

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Global Innovators
Global Innovators

Intel Corporation (von englisch Integrated electronics, deutsch integrierte Elektronik; NASDAQ-Küzel INTC) ist ein US-amerikanischer Halbleiterhersteller mit Hauptsitz im kalifornischen Santa Clara (Silicon Valley).
英特尔(英语:Intel Corporation)是世界上第二大的半导体公司[5],也是首家推出x86架构中央处理器(CPU)的公司,总部位于美国加利福尼亚州圣克拉拉。由罗伯特·诺伊斯、高登·摩尔、安迪·葛洛夫,以“集成电子”(Integrated Electronics)之名在1968年7月18日共同创办公司,将高阶芯片设计能力与领导业界的制造能力结合在一起。英特尔也有开发主板芯片组、网卡、闪存、绘图芯片(GPU),与对通信与运算相关的产品等。“Intel Inside”的广告标语,Pentium系列处理器以及与微软组成的“Wintel”联盟在1990年代间非常成功地打响英特尔的品牌名号。

智能制造(英语:Smart manufacturing)[1]是指引入电脑整合制造以及数字信息技术的制造业。智能工厂就是典型的智能制造。智能制造中有可互操作的系统、智能自动化机器人、强大的网络安全以及联网的传感器。
Smart manufacturing[1] is a broad category of manufacturing that employs computer-integrated manufacturing, high levels of adaptability and rapid design changes, digital information technology, and more flexible technical workforce training.[2] Other goals sometimes include fast changes in production levels based on demand,[3][1] optimization of the supply chain,[3] efficient production and recyclability.[4] In this concept, as smart factory has interoperable systems, multi-scale dynamic modelling and simulation, intelligent automation, strong cyber security, and networked sensors.
The broad definition of smart manufacturing covers many different technologies. Some of the key technologies in the smart manufacturing movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices and services, and advanced robotics.[

Interdisziplinarität (lateinisch inter ‚zwischen‘, disciplina ‚Unterweisung‘, ‚Lehre‘, ‚Ordnung‘, ‚Disziplin‘) bezeichnet die kooperative Nutzung und Weiterentwicklung von Ansätzen, Denkweisen oder Methoden[1] verschiedener wissenschaftlicher Fachrichtungen.
科际整合(英语:Interdisciplinarity),或译跨学科、交叉学科、学科间研究、学科交叉等,指的是两个或多个学科相互合作,在同一个目标下进行的学术活动。科际整合的项目通常源于对单一学科无法、或是无意对某些重要问题进行研究的认识。


知识蒸馏(knowledge distillation)是人工智能领域的一项模型训练技术。该技术透过类似于教师—学生的方式,令规模较小、结构较为简单的人工智能模型从已经经过充足训练的大型、复杂模型身上学习其掌握的知识。该技术可以让小型简单模型快速有效学习到大型复杂模型透过漫长训练才能得到的结果,从而改善模型的效率、减少运算开销,因此亦被称为模型蒸馏(model distillation)。
In machine learning, knowledge distillation or model distillation is the process of transferring knowledge from a large model to a smaller one. While large models (such as very deep neural networks or ensembles of many models) have more knowledge capacity than small models, this capacity might not be fully utilized. It can be just as computationally expensive to evaluate a model even if it utilizes little of its knowledge capacity. Knowledge distillation transfers knowledge from a large model to a smaller one without loss of validity. As smaller models are less expensive to evaluate, they can be deployed on less powerful hardware (such as a mobile device).
Model distillation is not to be confused with model compression, which describes methods to decrease the size of a large model itself, without training a new model. Model compression generally preserves the architecture and the nominal parameter count of the model, while decreasing the bits-per-parameter.
Knowledge distillation has been successfully used in several applications of machine learning such as object detection, acoustic models, and natural language processing. Recently, it has also been introduced to graph neural networks applicable to non-grid data.

 Education and Research
Education and Research

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 *Important disciplines
*Important disciplines

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Big Data
Big Data


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing

 Important disciplines
Important disciplines

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts

Künstliche Intelligenz (KI, auch artifizielle Intelligenz, AI, A. I., englisch artificial intelligence, AI) ist ein Teilgebiet der Informatik, welches sich mit der Automatisierung intelligenten Verhaltens befasst. Der Begriff ist insofern nicht eindeutig abgrenzbar, als es bereits an einer genauen Definition von Intelligenz mangelt. Dennoch wird er in Forschung und Entwicklung verwendet.
Im Allgemeinen bezeichnet künstliche Intelligenz oder KI den Versuch, eine menschenähnliche Intelligenz nachzubilden, d. h., einen Computer zu bauen oder so zu programmieren, dass er eigenständig Probleme bearbeiten kann. Oftmals wird damit aber auch, besonders bei Computerspielen, eine nachgeahmte Intelligenz bezeichnet, womit durch meist einfache Algorithmen ein intelligentes Verhalten simuliert werden soll.
人工智能(英语:Artificial Intelligence, AI)亦称机器智能,是指由人工制造出来的系统所表现出来的智能。通常人工智能是指通过普通电脑实现的智能。该词同时也指研究这样的智能系统是否能够实现,以及如何实现的科学领域。
一般教材中的定义领域是“智能主体(intelligent agent)的研究与设计”[1],智能主体是指一个可以观察周遭环境并作出行动以达致目标的系统。[2]约翰·麦卡锡于1955年的定义是[3]“制造智能机器的科学与工程。”[4]
人工智能的研究是高度技术性和专业的,各分支领域都是深入且各不相通的,因而涉及范围极广。[5]
人工智能的研究可以分为几个技术问题。其分支领域主要集中在解决具体问题,其中之一是,如何使用各种不同的工具完成特定的应用程序。AI的核心问题包括推理、知识、规划、学习、交流、感知、移动和操作物体的能力等。[6]强人工智能目前仍然是该领域的长远目标。[7]目前比较流行的方法包括统计方法,计算智能和传统意义的AI。目前有大量的工具应用了人工智能,其中包括搜索和数学优化、逻辑推演。而基于仿生学、认知心理学,以及基于概率论和经济学的算法等等也在逐步探索当中。


LLaMA(英语:Large Language Model Meta AI)是Meta AI公司于2023年2月发布的大型语言模型。它训练了各种模型,这些模型的参数从70亿到650亿不等。LLaMA的开发人员报告说,LLaMA运行的130亿参数模型在大多数NLP基准测试中的性能超过了更大的、具有1750亿参数的GPT-3提供的模型,且LLaMA的模型可以与PaLM和Chinchilla等最先进的模型竞争[3]。
Das LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) von Meta ist ein sogenanntes Großes Sprachmodell, das von Meta AI am 24. Februar 2023 veröffentlicht wurde.[1] Es ist ein generatives Sprachmodell, das in der Lage ist, menschenähnlichen Text zu erzeugen, Sprachen zu übersetzen, verschiedene Arten kreativer Inhalte zu schreiben und Fragen informativ zu beantworten.[2][3][4]


 Law
Law