
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书


 History
History
 E 2500 - 2000 BC
E 2500 - 2000 BC

 History
History
 F 2000 - 1500 BC
F 2000 - 1500 BC

 History
History
 G 1500 - 1000 BC
G 1500 - 1000 BC

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC
 Mesopotamian civilization
Mesopotamian civilization

 Civilization
Civilization
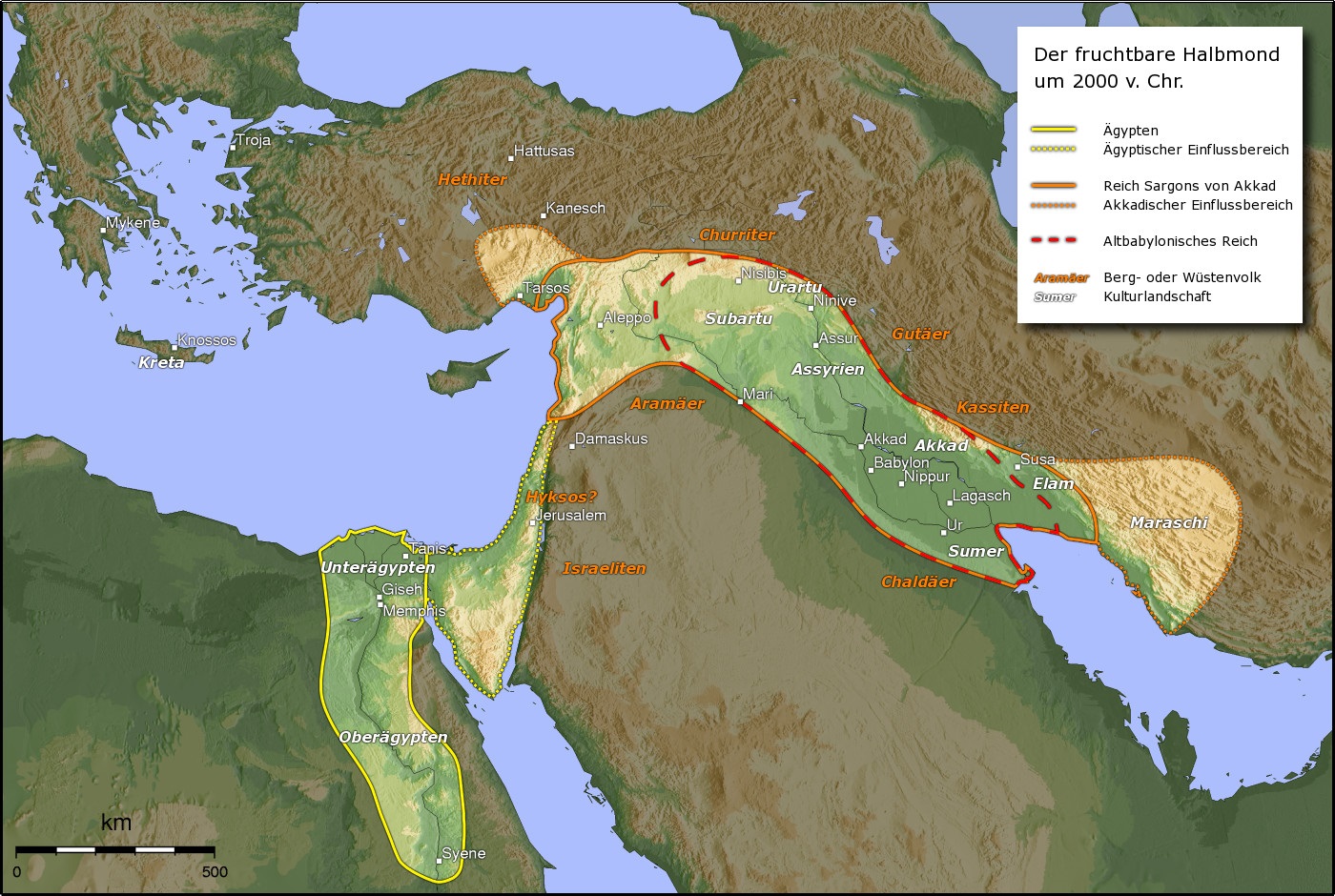
Das Reich Elam (sumerisch NIM.MAKI, akkadisch KURElammatum; griechisch Ἐλυμαία Elymaía oder Ἐλυμαΐς Elymaḯs) mit der Hauptstadt Susa (bzw. Schusim) lag östlich des Tigris in einem Gebiet, das heute Chusistan (im heutigen Iran) genannt wird. In seiner wechselvollen Geschichte – zwischen 3000 und 640 v. Chr. – wurde es immer wieder von den Mächten des Zweistromlandes (Sumerer, Akkader, Babylonier, Assyrer) erobert und fiel seinerseits häufig in Mesopotamien ein.
Der Landesname Elam entstammt der griechischen Bezeichnung Elymaía, die wiederum dem hebräischen Wort Elam entlehnt wurde. Die Eigenbezeichnung war Haltamti oder Hatamti und bedeutet „Land der Könige, Fürstenland“.
埃兰(英语:Elam),又译以拦、厄蓝或伊勒姆,是亚洲西南部的古老君主制城邦国家,位于今天伊朗的西南部,波斯湾北部,底格里斯河东部,现为伊朗的胡齐斯坦及伊拉姆省。埃兰是伊朗的最早文明,起源于伊朗高原以外的埃兰地区。一般认为埃兰国名出自境内哈尔答第城邦(意谓“神的国家”)。此名在《圣经》广为流传,故沿用至今。公元前三千年以前,在底格里斯河东岸建国,以善战的人民著称,圣经记载是诺亚儿子闪的儿孙及其后裔。
埃兰地区曾有许多君主制城邦国,其中最重要的有阿万(Awan)、苏萨、西马什(Simash)、安善(Anshan)等。
埃兰历史可以分为三个时期:古埃兰时期、中埃兰时期与新埃兰时期。
エラム (Elam) は古代オリエントで栄えた国家、または地方の名。紀元前3200年頃から紀元前539年までの間、複数の古代世界の列強国を出現させた。
エラムと呼ばれたのは、メソポタミアの東、現代のフーゼスターンなどを含むイラン高原南西部のザグロス山脈沿いの地域である。エラム人自身は自らをハルタミ (Haltami) と呼び、土地を指す際にはハルタムティ(Haltamti、後に訛ってアタムティAtamti)と呼んだ。シュメール語のエラムはこれの転訛したものである[1]。メソポタミアという古代文明世界の中心地に隣接したために、その文化的影響を強く受けたが、砂漠や湿地帯によって交通が困難であったために、政治的にはイラン高原地帯との関わりが深かった。エラム人は系統不明の言語エラム語を話す人々であり、メソポタミアでウルク古拙文字(楔形文字の元になったと考えられている絵文字)が発明されてから程なく、エラムでも原エラム文字と呼ばれる絵文字が発明された。この原エラム文字で書かれた文章は現在のアフガニスタンに近い地域からも見つかっており、エラム文化はイラン高原各地に影響を与えていたと考えられる。また、ほぼ同時代にエラム楔形文字も使われているが、それらの関係は全く解明されていない。メソポタミアの王朝はたびたびエラムに侵入して、これを支配下に置いた。一方でエラム人もメソポタミアへの介入を繰り返し、バビロニアの王朝をいくつも滅ぼしている。紀元前2000年紀に入ると、エラム人も楔形文字を使って記録を残すようになり、多くの情報がわかる。エラムの歴史で中心的役割を果たした都市はアンシャン、そしてスサである。スサを中心とした地方はギリシア人たちにはスシアナとよばれた。エラム人の残した文化や政治制度は、メディアやペルシアに大きな影響を及ぼした。
エラム人は、オリエントのほかの地域とは異なる独特の相続制度を持っていた。即ち、王位は親子ではなく、まず兄弟によって相続されていくのである。この相続制度はかなり後の時代にまで継承され、異民族の侵入によっても基本的に変化しなかった。
Elam (/ˈiːləm/; Elamite: ????? haltamti; Sumerian: ??? NIM.MAki; Hebrew: עֵילָם ʿÊlām) was an ancient Pre-Iranian civilization centered in the far west and southwest of what is now modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq. The modern name Elam stems from the Sumerian transliteration elam(a), along with the later Akkadian elamtu, and the Elamite haltamti. Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East.[1] In classical literature Elam was also known as Susiana (US: /ˌsuːʒiˈænə/ UK: /ˌsuːziˈɑːnə/; Ancient Greek: Σουσιανή Sousiānḗ), a name derived from its capital Susa.[2]
Elam was part of the early urbanization during the Chalcolithic period (Copper Age). The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Sumerian history, where slightly earlier records have been found.[3][4] In the Old Elamite period (Middle Bronze Age), Elam consisted of kingdoms on the Iranian plateau, centered in Anshan, and from the mid-2nd millennium BC, it was centered in Susa in the Khuzestan lowlands.[5] Its culture played a crucial role during the Persian Achaemenid dynasty that succeeded Elam, when the Elamite language remained among those in official use. Elamite is generally considered a language isolate unrelated to the much later arriving Persian and Iranic languages. In accordance with geographical and archaeological matches, some historians argue that the Elamites comprise a large portion of the ancestors of the modern day Lurs,[6][7] whose language, Luri, split from Middle Persian.
L'Élam est un ancien pays occupant la partie sud-ouest du plateau Iranien, autour des actuelles provinces du Khouzistan et du Fars, qui correspondent à ses deux principales régions, celle de Suse et celle d'Anshan/Anzan. Le pays élamite, attesté par des textes allant de la fin du IVe millénaire av. J.‑C. au Ier millénaire ap. J.-C., recouvrit des réalités géographiques et politiques qui différent pendant sa longue histoire. Il fut parfois divisé en plusieurs entités politiques, surtout jusqu'au IIIe millénaire av. J.‑C., mais aussi plusieurs fois par la suite, et il connut par contre des phases d'unification, sous l'impulsion de puissantes dynasties (notamment les Sukkalmah, Igehalkides, Shutrukides), surtout au IIe millénaire av. J.‑C. À partir du Ier millénaire av. J.‑C., l'Élam se réduit à sa partie occidentale, autour de la Susiane, la partie orientale étant occupée par les Perses, qui lui donnèrent le nom qu'elle a gardé depuis (Perse/Fars). Le pays élamite perdit son autonomie politique après son combat contre l'Assyrie et sa conquête par les Perses, même s'il semble avoir revécu plusieurs siècles plus tard, à travers le royaume d'Élymaïde. Des survivances de cet ancien pays et de son peuple semblent encore attestées jusqu'au début du IIe millénaire ap. J.-C.
L'histoire de l'Élam est difficilement dissociable de celle de la Mésopotamie voisine, qui exerça sur ces territoires une forte influence. Les sources mésopotamiennes sont essentielles pour redécouvrir la civilisation élamite, complétées par celles provenant de sites de la région, avant tout de Suse. Elles laissent apparaître un ensemble de régions hétérogènes présentant des originalités culturelles (perceptibles dans le culte religieux et l'art), mais beaucoup d'aspects restent obscurs en l'état actuel des connaissances scientifiques (par exemple l'organisation politique, les activités de production, la mythologie).
Elam è il nome convenzionale con cui si fa riferimento ad una civiltà sviluppatasi dal III al I millennio a.C. nell'area corrispondente all'attuale Iran occidentale, nelle regioni del Khuzistan e del Fars. I due centri di riferimento furono Susa, nell'estensione sud-orientale del bassopiano mesopotamico, e Anshan, identificato con il sito di Tall-i Malyan, nella piana di Marvdasht (a nord-est di Shiraz), la stessa in cui più tardi fu costruita Persepoli.
Elam (en elamita antiguo Haltamti;1 akkadio Elamtu; persa antiguo Hujiyā; persa moderno تمدن عیلام ―‘cultura de Elam’―), se situaba al este de Sumeria y Acad, en el actual suroeste de Irán. Los elamitas llamaban a su país Haltamti (en elamita tardío, Atamti), del cual sus vecinos acadios adaptaron como Elamtu. El alto Elam fue posteriormente más y más identificado por su baja capital, Susa, y geógrafos posteriores a Ptolomeo la llamaron Susiana. El término del antiguo persa Hujiyā sobrevive en el topónimo Juzestán, que es la provincia junto con la de Lorestán en la que se sitúan los restos del antiguo Elam. En diversos períodos existieron diversos imperios elamitas y en otros momentos estuvieron sometidos a imperios vecinos.
Excavaciones realizadas en Susa han proporcionado numerosos documentos escritos con caracteres cuneiformes que permiten reconstruir la más antigua historia y religión de los elamitas. El idioma elamita ―según se ha establecido a partir de los registros cuneiformes― no está relacionado con los cuatro grupos lingüísticos vecinos: camito-semítico, sumerio e indoeuropeo (en concreto, del grupo iranio temprano). Algunos expertos creen que la lengua de los elamitas está emparentada con las actuales lenguas drávidas del sur de la India (ver lenguas elamo-drávidas).23 Sin embargo, aun es oscura la relación de los elamitas con otras naciones conocidas.
Элам (также Елам[1]; шум. Ним, аккад. Эламту, самоназвание — Haltamti) — историческая область и древнее государство (3 тысячелетие — сер. VI в. до н. э.) на юго-западе современного Ирана (провинции Хузестан и Лурестан).

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 G 1500 - 1000 BC
G 1500 - 1000 BC

 History
History
 E 2500 - 2000 BC
E 2500 - 2000 BC

 History
History
 F 2000 - 1500 BC
F 2000 - 1500 BC
 Syria
Syria

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Civilization
Civilization

Palmyra (arabisch تدمر Tadmur; aramäisch ܬܕܡܘܪܬܐ Tedmurtā; hebräisch תדמור Tadmor), gegenwärtig auch Tadmor genannt, ist eine antike Oasenstadt im heutigen Gouvernement Homs in Syrien. Sie liegt auf dem Gebiet der modernen Stadt Tadmor, die vor dem Bürgerkrieg etwa 51.000 Einwohner hatte.
Die ersten archäologischen Funde stammten aus der Jungsteinzeit. Die erste schriftliche Erwähnung der Stadt selbst erfolgte in altorientalischer Zeit: Sie wurde in den Annalen mehrerer assyrischer Könige und im Alten Testament erwähnt. Palmyra war später Teil des Seleukidenreiches und erlebte seine Blütezeit nach der Annexion durch das Römische Reich im 1. Jahrhundert n. Chr.
Palmyra verfügte über eine gewisse Autonomie innerhalb des Römischen Reiches und wurde Teil der Provinz Syria. Die Metropole besaß einen eigenen Senat, der für öffentliche Arbeiten und die lokale Miliz zuständig war, und ein unabhängiges Steuersystem. Im 3. Jahrhundert wurde sie zur colonia erhoben. In der Zeit der Reichskrise des 3. Jahrhunderts gewann die Stadt stark an politischer Bedeutung und wurde 270 kurzzeitig unabhängig. Das Reich der Stadt stellte einen bedeutenden Machtfaktor im Vorderen Orient dar. Palmyra wurde jedoch 272 von römischen Truppen wieder erobert und die Stadt 273 nach einer gescheiterten zweiten Rebellion weitgehend zerstört.
Palmyra lag an einer wichtigen Karawanenstraße in Syrien, auf halber Strecke von Damaskus über die römische Oase Al-Dumair und weiter über das Kastell Resafa bis zum Euphrat. Inmitten der syrischen Wüste spenden zwei Quellen Wasser, mit dem die noch immer erhaltenen Palmengärten im Süden und Osten der Stadt bewässert werden. Der Reichtum der Stadt ermöglichte die Errichtung von monumentalen Bauprojekten. Im dritten Jahrhundert war die Stadt eine wohlhabende Metropole und zu einem regionalen Zentrum des Nahen Ostens aufgestiegen. Die Palmyrer gehörten zu den renommierten Händlern, etablierten Stationen entlang der Seidenstraße und betrieben im gesamten Reich Handel. Die Sozialstruktur der Stadt war tribal und ihre Bewohner sprachen mit dem Palmyrenischen Dialekt des Aramäischen eine eigene Sprache. Griechisch wurde für kommerzielle und diplomatische Zwecke verwendet. Die Kultur von Palmyra, die durch die Römer, Griechen und Perser beeinflusst wurde, ist in der Region einzigartig. Die Einwohner verehrten lokale Gottheiten und mesopotamische und arabische Götter.
Die Stadt gehört seit der Vertreibung der Osmanen 1918 zu Syrien als eigenständigem Staat. Sie beherbergt heute unverwechselbare Kunst und Architektur und wurde 1980 zum UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe erklärt.Palmyra (/ˌpɑːlˈmaɪrə/; Palmyrene: ![]() Tadmor; Arabic: تَدْمُر Tadmur) is an ancient Semitic city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early second millennium BC. Palmyra changed hands on a number of occasions between different empires before becoming a subject of the Roman Empire in the first century AD.
Tadmor; Arabic: تَدْمُر Tadmur) is an ancient Semitic city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early second millennium BC. Palmyra changed hands on a number of occasions between different empires before becoming a subject of the Roman Empire in the first century AD.
The city grew wealthy from trade caravans; the Palmyrenes became renowned as merchants who established colonies along the Silk Road and operated throughout the Roman Empire. Palmyra's wealth enabled the construction of monumental projects, such as the Great Colonnade, the Temple of Bel, and the distinctive tower tombs. Ethnically, the Palmyrenes combined elements of Amorites, Arameans, and Arabs. The city's social structure was tribal, and its inhabitants spoke Palmyrene (a dialect of Aramaic), while using Greek for commercial and diplomatic purposes. Greco-Roman culture influenced the culture of Palmyra, which produced distinctive art and architecture that combined eastern and western traditions. The city's inhabitants worshiped local Semitic deities, Mesopotamian and Arab gods.
By the third century AD Palmyra had become a prosperous regional center. It reached the apex of its power in the 260s, when the Palmyrene King Odaenathus defeated Persian Emperor Shapur I. The king was succeeded by regent Queen Zenobia, who rebelled against Rome and established the Palmyrene Empire. In 273, Roman emperor Aurelian destroyed the city, which was later restored by Diocletian at a reduced size. The Palmyrenes converted to Christianity during the fourth century and to Islam in the centuries following the conquest by the 7th-century Rashidun Caliphate, after which the Palmyrene and Greek languages were replaced by Arabic.
Before AD 273, Palmyra enjoyed autonomy and was attached to the Roman province of Syria, having its political organization influenced by the Greek city-state model during the first two centuries AD. The city became a Roman colonia during the third century, leading to the incorporation of Roman governing institutions, before becoming a monarchy in 260. Following its destruction in 273, Palmyra became a minor center under the Byzantines and later empires. Its destruction by the Timurids in 1400 reduced it to a small village. Under French Mandatory rule in 1932, the inhabitants were moved into the new village of Tadmur, and the ancient site became available for excavations.
Palmyre (Παλμύρα / Palmúra en grec ancien, تدمر / tadmor en arabe) est une oasis du désert de Syrie, à 210 km au nord-est de Damas, où se situe un site historique très riche en ruines archéologiques, et la ville moderne de Tadmor.
Le site est classé patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO depuis 1980, puis classé « en péril » pendant la guerre civile syrienne.
Palmira (in palmireno ![]() ; in arabo: تدمر), chiamata anche la Sposa del Deserto, fu in tempi antichi una delle più importanti città della Siria.
; in arabo: تدمر), chiamata anche la Sposa del Deserto, fu in tempi antichi una delle più importanti città della Siria.
Palmira (en árabe تدمر Tadmor1 o Tadmir) fue una antigua ciudad situada en el desierto de Siria, en la actual provincia de Homs a 3 km de la moderna ciudad de Tedmor2 o Tadmir, (versión árabe de la misma palabra aramea "palmira", que significa "ciudad de los árboles de dátil"). En la actualidad sólo persisten sus amplias ruinas que son foco de una abundante actividad turística internacional. La antigua Palmira fue la capital del Imperio de Palmira bajo el efímero reinado de la reina Zenobia, entre los años 268 - 272.
Palmira fue elegida como Patrimonio de la Humanidad en 1980. El 20 de junio de 2013, la Unesco incluyó a todos los sitios sirios en la lista del Patrimonio de la Humanidad en peligro para alertar sobre los riesgos a los que están expuestos debido a la Guerra Civil Siria.3


Theben (altägyptisch im Neuen Reich Waset, sonst auch: Niut oder Niut-reset) war eine am Nil liegende altägyptische Stadt in Oberägypten. Homer nannte es das hunderttorige Theben in seiner Ilias (9. Gesang, V. 3. Gesang); das griechische Theben in Böotien nannte er dagegen siebentorig in der Odyssee (11. Gesang, V. 2. Gesang).
An der Stelle Thebens war zu Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts nur noch ein ausgedehntes Ruinenfeld zu beiden Seiten des Nils vorhanden. Das Tempel- und Stadtgebiet lag in einer Schwemmebene, die durch wiederkehrende künstliche Aufschüttungen immer weiter anwuchs. Als Schutzmaßnahme gegen die Nilflut erfolgte zusätzlich der Bau von Deichanlagen, die insbesondere die Tempelanlagen schützen sollten. Heute befindet sich in einem Teil von Theben-Ost eines der touristischen Zentren Ägyptens, die Stadt Luxor. Seit 1979 ist Theben in die UNESCO-Liste des Weltkulturerbes eingetragen.
Von den Griechen der Ptolemäerzeit ist der Name Θῆβαι Thēbai (Theben) überliefert, aber auch die Bezeichnung Διὸς Πόλις Μεγάλη Diòs Pólis Megálē ‚große Stadt des Zeus‘, woraus in der Zeit des Römischen Reiches die Benennungen Thebae beziehungsweise Diospolis Magna abgeleitet wurden. Das Gebiet von Theben umfasste spätestens seit dem Neuen Reich beide Nilseiten; es gliedert sich in Theben-Ost und Theben-West. Daneben existierte als weiterer Ort das nördliche „unterägyptische Theben“ in Tell el-Balamun.
底比斯(希腊语:Θῆβαι)是上埃及古城,古埃及名称为瓦塞特,意为权杖之城。濒临尼罗河,位于今埃及中部,即今天的卢克索附近。作为皇室居地和宗教膜拜的宗教中心,它从公元前22世纪中期到公元前18世纪曾繁荣一时。它的建筑遗迹包括许多辉煌的庙宇和帝王谷附近的法老陵墓。
在古王国时期,底比斯只是一个寂寂无名的小型商道中心。它作为通往西奈半岛和彭特的水路及通往努比亚的陆路的枢纽。但正因为这个优势,第十一王朝法老曼图霍特普二世决定把首都定在底比斯,并在底比斯为阿蒙神大兴土木,兴建很多神庙,底比斯从此成为古埃及的圣地。
根据历史年表,底比斯可以算是埃及的九朝古都。自十一王朝第一位国王塞赫塔尼-安特夫(Sehertani Antef,前2120-前2118年)决定迁都至此并开始建设,以后在此建都的王朝有:十二王朝(前1991)、十三王朝(前1785)、十六王朝(前1622)、十八王朝(前1580)、十九王朝(前1314)、二十王朝(前1200)、二十一王朝(前1085)、和二十五王朝(前716)。
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt

 Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt

 History
History
 B 5000 - 4000 BC
B 5000 - 4000 BC

 History
History
 D 3000 - 2500 BC
D 3000 - 2500 BC

 History
History
 E 2500 - 2000 BC
E 2500 - 2000 BC

 History
History
 F 2000 - 1500 BC
F 2000 - 1500 BC

 History
History
 G 1500 - 1000 BC
G 1500 - 1000 BC

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Civilization
Civilization

Altes Ägypten ist die allgemeine Bezeichnung für das Land Ägypten im Altertum. Der ägyptische Name lautete Kemet und bedeutet „schwarzes Land“. Kemet bezeichnet das Delta des Nils und geht auf den schwarzen Schlamm zurück, der nach der jährlichen Nilschwemme zurückblieb und eine fruchtbare Ernte garantierte. Eine andere Bezeichnung für das Land des Altertums war Ta meri (T3 mrj), was mit „geliebtes Land“ übersetzt wird.[1]
古埃及(阿拉伯语:مصر القديمة)是位于非洲东北部尼罗河中下游地区的一段时间跨度近3000年的古代文明,开始于公元前32世纪左右时美尼斯统一上下埃及建立第一王朝,终止于公元前343年波斯再次征服埃及,虽然之后古埃及文化还有少量延续,但到公元以后的时代,古埃及已经彻底被异族文明所取代,在连象形文字也被人们遗忘后,古代史前社会留给后人的是宏伟的建筑与无数谜团,1798年,拿破仑远征埃及,发现罗塞塔石碑,1822年法国学者商博良解读象形文字成功,埃及学才诞生,古埃及文明才重见天日。直到今日都还不断被挖掘出来。
古埃及的居民是由北非的土著居民和来自西亚的游牧民族塞姆人融合形成的多文化圈。约公元前6000年,因为地球轨道的运转规律性变化、间冰期的高峰过去等客观气候因素,北非茂密的草原开始退缩,人们放弃游牧而开始寻求固定的水源以耕作,即尼罗河河谷一带,公元前4千年后半期,此地逐渐形成国家,至公元前343年为止,共经历前王朝、早王朝、古王国、第一中间期、中王国、第二中间期、新王国、第三中间期、后王朝9个时期31个王朝的统治(参见“古埃及历史”一节)。其中古埃及在十八王朝时(公元前15世纪)达到鼎盛,南部尼罗河河谷地带的上埃及的领域由现在的苏丹到埃塞俄比亚,而北部三角洲地区的下埃及除了现在的埃及和部分利比亚以外,其东部边界越过西奈半岛直达迦南平原。[1]
在社会制度方面,古埃及有自己的文字系统,完善的行政体系和多神信仰的宗教系统,其统治者称为法老,因此古埃及又称为法老时代或法老埃及[2]。古埃及的国土紧密分布在尼罗河周围的狭长地带,是典型的水力帝国[来源请求]。古埃及跟很多文明一样,具有保存遗体的丧葬习俗,透过这些木乃伊的研究能一窥当时人们的日常生活,对古埃及的研究在学术界已经形成一门专门的学科,称为“埃及学”。
エジプトは不毛の砂漠地帯であるが、毎年春のナイル川の増水で水に覆われる地域には河土が運ばれて堆積し、農耕や灌漑が可能になる。この氾濫原だけが居住に適しており、主な活動はナイル河畔で行われた。ナイル川の恩恵を受ける地域はケメト(黒い大地)と呼ばれ、ケメトはエジプトそのものを指す言葉として周囲に広がるデシェレト(赤い大地、ナイル川の恩恵を受けない荒地)と対比される概念だった。このケメトの範囲の幅は非常に狭く、ナイル川の本流・支流から数kmの範囲にとどまっていた。しかしながら川の周囲にのみ人が集住しているということは交通においては非常に便利であり、川船を使って国内のどの地域にも素早い移動が可能であった。この利便性は、ナイル河畔に住む人々の交流を盛んにし、統一国家を建国し維持する基盤となった。
ナイル川本流からナイル川の上流は谷合でありナイル川1本だけが流れ、下流はデルタ地帯(ナイル川デルタ)が広がっている。最初に上流地域(上エジプト)と下流地域(下エジプト)[1]でそれぞれ違った文化が発展した後に統一されたため、ファラオ(王)の称号の中に「上下エジプト王」という部分が残り、古代エジプト人も自国のことを「二つの国」と呼んでいた。
毎年のナイル川の氾濫を正確に予測する必要から天文観測が行われ、太陽暦が作られた。太陽とシリウス星が同時に昇る頃、ナイル川は氾濫したという。また、氾濫が収まった後に農地を元通り配分するため、測量術、幾何学、天文学が発達した。ヒエログリフから派生したワディ・エル・ホル文字と原シナイ文字(原カナン文字)は世界の殆どのアルファベットの起源となったされる。
エジプト文明と並ぶ最初期における農耕文明の一つであるメソポタミア文明が、民族移動の交差点にあたり終始異民族の侵入を被り支配民族が代わったのと比べ、地理的に孤立した位置にあったエジプトは比較的安定しており、部族社会が城壁を廻らせて成立する都市国家の痕跡は今の所発見されていない。
Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient North Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in the place that is now the country Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology)[1] with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes (often identified with Narmer).[2] The history of ancient Egypt occurred as a series of stable kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.
Egypt reached the pinnacle of its power in the New Kingdom, ruling much of Nubia and a sizable portion of the Near East, after which it entered a period of slow decline. During the course of its history Egypt was invaded or conquered by a number of foreign powers, including the Hyksos, the Libyans, the Nubians, the Assyrians, the Achaemenid Persians, and the Macedonians under the command of Alexander the Great. The Greek Ptolemaic Kingdom, formed in the aftermath of Alexander's death, ruled Egypt until 30 BC, when, under Cleopatra, it fell to the Roman Empire and became a Roman province.[3]
The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River valley for agriculture. The predictable flooding and controlled irrigation of the fertile valley produced surplus crops, which supported a more dense population, and social development and culture. With resources to spare, the administration sponsored mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions, the early development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military intended to assert Egyptian dominance. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a pharaoh, who ensured the cooperation and unity of the Egyptian people in the context of an elaborate system of religious beliefs.[4][5]
The many achievements of the ancient Egyptians include the quarrying, surveying and construction techniques that supported the building of monumental pyramids, temples, and obelisks; a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems and agricultural production techniques, the first known planked boats,[6] Egyptian faience and glass technology, new forms of literature, and the earliest known peace treaty, made with the Hittites.[7] Ancient Egypt has left a lasting legacy. Its art and architecture were widely copied, and its antiquities carried off to far corners of the world. Its monumental ruins have inspired the imaginations of travelers and writers for centuries. A new-found respect for antiquities and excavations in the early modern period by Europeans and Egyptians led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy.[8]
L'Égypte antique est une ancienne civilisation du nord-est de l'Afrique, concentrée le long du cours inférieur du Nil, dans ce qui constitue aujourd'hui l'Égypte.
La civilisation de l'Égypte antique prend forme autour de -31501 avec l'unification politique de la Haute-Égypte au sud et de la Basse-Égypte au nord sous le règne du premier roi et se développe sur plus de trois millénaires2. Son histoire est parsemée d'une série de périodes stables politiquement, entrecoupées de plusieurs périodes intermédiaires, plus troublées. L'Égypte antique atteint son apogée sous le Nouvel Empire puis entre dans une période de lent déclin. Le pays subit les assauts répétés de puissances étrangères dans cette période tardive et le règne des pharaons prend officiellement fin en -30 où l'Empire romain conquiert l'Égypte pour en faire une province3.
Le succès de la civilisation égyptienne antique découle en partie de sa capacité à s'adapter aux conditions de la vallée du Nil. L'inondation prévisible du fleuve et le contrôle de l'irrigation de la vallée produit des récoltes excédentaires qui alimentent le développement social et culturel du pays. Ce surplus agricole donne à l'administration les moyens de financer l'exploitation minière de la vallée et des régions voisines du désert. Le développement rapide d'un système d'écriture indépendant, l'organisation de constructions collectives et de projets agricoles, les relations commerciales avec les pays voisins et une armée solide permettent à l'Égypte d'affirmer sa domination sur la région. Toutes ces activités sont organisées par une bureaucratie de scribes, de dirigeants religieux et d'administrateurs sous le contrôle du pharaon qui assure l'unité du peuple égyptien dans le cadre d'un système complexe de croyances religieuses4,5.
Les nombreuses réalisations des Égyptiens de l'Antiquité comprennent l'extraction minière, l'arpentage et les techniques de construction qui facilitent la construction de pyramides monumentales, de temples et d'obélisques. On compte également à leur crédit le développement des mathématiques, de la médecine, de l'irrigation et de la production agricole, la construction des premiers navires connus, la faïence égyptienne, de nouvelles formes de littérature6. Du rassemblement des tribus primitives qui créent le premier royaume pharaonique jusqu'à son absorption au Ier siècle av. J.-C., l'Égypte antique est le théâtre d'évènements majeurs qui influencent assurément la culture et l'imaginaire des peuples lui ayant succédé. Son art et son architecture sont largement copiés et ses antiquités sont disséminées aux quatre coins du monde. Un regain d'intérêt pour la période antique au début de l'époque moderne conduit à de nombreuses investigations scientifiques de la civilisation égyptienne, notamment par des fouilles, et à une meilleure appréciation de son héritage culturel, pour l'Égypte et le monde7.
Con Antico Egitto si intende la civiltà sviluppatasi lungo la Valle del Nilo a partire dalle cateratte, a sud e al confine con l’attuale Sudan[N 1], alla foce, al delta, nel Mar Mediterraneo, per un’estensione complessiva di circa 1000 km. Benché il territorio fosse molto più vasto, comprendendo gran parte anche del Deserto Libico-Nubiano, gli insediamenti umani, fin dai tempi più remoti, si svilupparono solo nella stretta fascia verdeggiante a ridosso delle rive del fiume larga, in alcuni punti anche solo poche centinaia di metri.
Fin dal 3500 a.C., di pari passo con l'avvento dell'agricoltura, in particolare la coltivazione del grano, dell’orzo e del lino, si ha contezza di insediamenti umani specie lungo le rive del Nilo[1]. Le piene annuali del fiume, infatti, favorivano la coltivazione anche con più raccolti annui grazie ai sedimenti, particolarmente fertili (Limo), che il fiume, nel suo ritirarsi, lasciava sul terreno. Ciò comportò, fin dai tempi più remoti, conseguentemente, la necessità di controllare, incanalare e conservare le acque onde garantire il costante approvvigionamento, vuoi per il sostentamento umano, vuoi per quello del bestiame e delle piantagioni.
Non è da escludersi che proprio la complessa necessità di dover far fronte alle esigenze connesse con la gestione dell’agricoltura, e segnatamente, delle acque nilotiche, abbia favorito proprio il formarsi delle prime comunità su territori parziali tuttavia ben differenziati e politicamente e geograficamente individuabili. Tali entità, normalmente individuate con il termine greco di nomoi, ben presto si costituirono in due distinte entità geo-politiche più complesse. Tale l’importanza del fiume Nilo, che attraversava tutto il paese, che anche le denominazioni di tali due macro-aree fanno riferimento al fiume: considerando che le sorgenti del Nilo, benché all'epoca non note, dovevano essere a sud, tale sarà l’Alto Egitto, mentre, di converso, l’area del delta, verso il Mediterraneo, sarà indicato come Basso Egitto[2].
Varie culture si susseguirono nella valle nilotica fin dal 3900 a.C. in quello che viene definito Periodo Predinastico. Un’entità embrionale di Stato può riconoscersi, invece, a partire dal 3200-3100 a.C. con la I dinastia e l’unificazione delle due macro-aree che resteranno, tuttavia, sempre distinte tanto che per tutta la storia del Paese i regnanti annovereranno tra i loro titoli quello di Signore delle Due Terre.
La storia dell’Antico Egitto copre, complessivamente, circa 4000 anni, dal 3900 a.C. (con il Periodo Predinastico) al 342 a.C. (con il Periodo tardo) e comprende, dal 3200 a.C., trenta dinastie regnanti riconosciute archeo-storicamente. A queste debbono esserne aggiunte altre, dette di comodo, giacché riferite, di fatto, non a governi autoctoni, o comunque derivanti dal Paese, bensì frutto di invasioni o di raggiungimento del potere da parte di regnanti stranieri. Avremo perciò una XXXI dinastia, costituita da re persiani, una XXXII dinastia macedone, che annovera un solo sovrano, Alessandro Magno, e una XXXIII dinastia, meglio nota come Dinastia tolemaica, nata dallo smembramento dell’impero di Alessandro.
Anche molti imperatori romani, occupato l’Egitto, non disdegnarono di assumere il titolo di faraone con titolatura geroglifica.
El Antiguo Egipto fue una civilización que se originó a lo largo del cauce medio y bajo del río Nilo, y que alcanza tres épocas de esplendor faraónico en los periodos denominados Imperio Antiguo, Imperio Medio, e Imperio Nuevo. Alcanzaba desde el delta del Nilo en el norte, hasta Elefantina, en la primera catarata del Nilo, en el sur, llegando a tener influencia desde el Éufrates hasta Jebel Barkal, en la cuarta catarata del Nilo, en épocas de máxima expansión. Su territorio también abarcó, en distintos periodos, el desierto oriental y la línea costera del mar Rojo, la península del Sinaí, y un gran territorio occidental dominando los dispersos oasis. Históricamente, fue dividido en Alto y Bajo Egipto, al sur y al norte respectivamente.
La civilización egipcia se desarrolló durante más de 3000 años. Comenzó con la unificación de algunas ciudades del valle del Nilo,1 alrededor del año 3150 a. C.,2 y convencionalmente se da por terminado en el año 31 a. C., cuando el Imperio romano conquistó y absorbió el Egipto ptolemaico, que desaparece como Estado.3 Este acontecimiento no representó el primer período de dominación extranjera, pero fue el que condujo a una transformación gradual en la vida política y religiosa del valle del Nilo, marcando el final del desarrollo independiente de su cultura. Su identidad cultural había comenzado a diluirse paulatinamente tras las conquistas de los reyes de Babilonia (siglo VI a. C.) y Macedonia (siglo IV a. C.), desapareciendo su religión con la llegada del cristianismo, en la época de Justiniano I, cuando en 535 fue prohibido el culto a la diosa Isis, en el templo de File.
Egipto tiene una combinación única de características geográficas, situada en el África nororiental y confinada por Libia, Sudán, el mar Rojo y el mar Mediterráneo. El río Nilo fue la clave para el éxito de la civilización egipcia, ya que éste permitía el aprovechamiento de los recursos y ofrecía una significativa ventaja sobre otros oponentes: el légamo fértil depositado a lo largo de los bancos del Nilo tras las inundaciones anuales significó para los egipcios el practicar una forma de agricultura menos laboriosa que en otras zonas, liberando a la población para dedicar más tiempo y recursos al desarrollo cultural, tecnológico y artístico.
La vida se ordenaba en torno al desarrollo de un sistema de escritura y de una literatura independientes, así como en un cuidadoso control estatal sobre los recursos naturales y humanos, caracterizado sobre todo por la irrigación de la fértil cuenca del Nilo y la explotación minera del valle y de las regiones desérticas circundantes, la organización de proyectos colectivos como las grandes obras públicas, el comercio con las regiones vecinas de África del este y central y con las del Mediterráneo oriental y, finalmente, por un poderío militar capaz de derrotar a cualquier enemigo, y que mantuvieron una hegemonía imperial y la dominación territorial de civilizaciones vecinas en diversos períodos. La motivación y la organización de estas actividades estaba encomendada a una burocracia de élite sociopolítica y económica, los escribas, bajo el control del Faraón, un personaje semidivino, perteneciente a una sucesión de dinastías, que garantizaba la cooperación y la unidad del pueblo egipcio en el contexto de un elaborado sistema de creencias religiosas.45
Los muchos logros de los egipcios incluyen la extracción minera, la topografía y las técnicas de construcción que facilitaron el levantamiento de monumentales pirámides, templos y obeliscos, unos procedimientos matemáticos, una práctica médica eficaz, métodos de riego y técnicas de producción agrícola, las primeras naves conocidas,6 la tecnología del vidrio y de la fayenza, las nuevas formas de la literatura y el tratado de paz más antiguo conocido, firmado con los hititas.7 Egipto dejó un legado duradero, su arte y arquitectura fueron ampliamente copiados, y sus antigüedades se llevaron a los rincones más lejanos del mundo. Sus ruinas monumentales han inspirado la imaginación de los viajeros y escritores desde hace siglos. Un nuevo respeto por las antigüedades y excavaciones en la época moderna han llevado a la investigación científica de la civilización egipcia y a una mayor apreciación de su legado cultural.8
Древний Еги́пет (от др.-греч. Αἴγυπτος и лат. Aegyptus), самоназвание Та-кемет, Та-мери, Та-уи и др. (транслит. егип. tA-kmt, tA-mrj, tA-wy), Ке́ми (копт. Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ) — название исторического региона и культуры значительной цивилизации Древнего мира, существовавшей на северо-востоке Африки вдоль нижнего течения реки Нил. История Древнего Египта составляет около 40 веков и подразделяется исследователями на додинастический период (относится к финалу доисторического периода, краткий обзор которого также приводится в статье), династический период (основной этап существования египетской цивилизации протяжённостью около 27 веков), эллинистический период (синтез с греко-македонской культурой под властью династии Птолемеев), римский период (в составе древнеримского государства, как одна из важнейших провинций Римской империи). Временные границы существования древнеегипетской культуры, принятые исследователями, охватывают период с середины IV тысячелетия до н. э. до IV век н. э. Византийско-коптский период (в составе Византии) хотя и относится уже к раннему средневековью, при этом также иногда рассматривается в рамках изучения Древнего Египта. Временные границы начинаются с IV века и заканчиваются арабским завоеванием в VII веке.
Возвышение древнеегипетской цивилизации в большой степени было результатом её способности адаптироваться к условиям речной долины и дельты Нила. Регулярные ежегодные разливы, удобряющие почву плодородным илом, а также организация ирригационной системы земледелия позволяли производить зерновые культуры в избыточном количестве, обеспечивавшем социальное и культурное развитие. Концентрация людских и материальных ресурсов в руках администрации способствовала созданию и поддержанию сложной сети каналов, появлению регулярной армии и расширению торговли, а с постепенным развитием горнодобывающего дела, полевой геодезии и строительных технологий давала возможность организовывать коллективные возведения монументальных сооружений. Принуждающей и организующей силой в Древнем Египте был хорошо развитый государственный аппарат, состоявший из жрецов, писцов и администраторов во главе с фараоном, который часто обожествлялся в сложной системе религиозных верований с развитым культом погребальных обрядов.
Древний Египет оставил огромное культурное наследие для мировой цивилизации, произведения его искусства ещё в древности вывозились в различные уголки мира и широко копировались мастерами других стран. Своеобразные архитектурные формы — величественные пирамиды, храмы, дворцы и обелиски вдохновляли воображение путешественников и исследователей в течение многих столетий. Египетскими мастерами создавались прекрасные настенные росписи и статуи, были освоены способы производства стекла и фаянса, поэтами и писателями созданы новые формы в литературе. В числе научных достижений древних египтян было создание оригинальной системы письма, математика, практическая медицина, астрономические наблюдения и возникший на их основе календарь. Интерес к памятникам, артефактам и археологическим раскопкам в Древнем Египте, возникший на рубеже XVIII—XIX веков, привёл к созданию науки египтологии и возникновению направлений искус
Die Erste Zwischenzeit umfasst die Zeit von 2216–2025 v. Chr. im Alten Ägypten. Nach der 6. Dynastie zerfällt Ägypten und unter den neu entstandenen Herrschaftsgebieten gelangen zwei Städte zu besonderem Einfluss: Theben und Herakleopolis.
Den Herakleopoliten, die in Unterägypten leben, gelingt es, abtrünnige Gebiete unter Kontrolle zu bringen. Der Thebaner Mentuhotep II. schafft es, nach seinem Aufstieg um 2025 v. Chr., Unter- und Oberägypten wieder zu vereinigen. Nubien wird bis Wawat zurückerobert.
Als Mittleres Reich wird der von etwa 2137 bis 1781 v. Chr. bestehende Staat im alten Ägypten bezeichnet.
Für den Beginn der Datierung des Mittleren Reichs wird die Wiedervereinigung des Reiches unter Mentuhotep II. in der Mitte der 11. Dynastie angegeben. Trotzdem wird hier die komplette 11. Dynastie besprochen.
Durch den Zerfall des geeinten Ägypten zu Beginn der Ersten Zwischenzeit war die Macht auf einige Kleinkönige verteilt. Allerdings bildete sich am Ende der 10. Dynastie deren Vormachtstellung in Herakleopolis deutlich heraus. Zeitgleich wuchs die Macht im Süden, als sich in Theben die 11. Dynastie etablierte.
Das Mittlere Reich wird oftmals auch als feudale Epoche bezeichnet. Tatsächlich gibt es kaum eine andere Periode in der ägyptischen Geschichte, in der man so viele Denkmäler auch in den abgelegensten Provinzen findet.
Das Mittlere Reich kann deutlich in zwei Abschnitte unterteilt werden:
- Das frühe Mittlere Reich (bis etwa Sesostris II.) ist noch stark von den Traditionen der Ersten Zwischenzeit geprägt. Die Pyramiden und Teile der Kunst orientieren sich am Alten Reich.
- Das späte Mittlere Reich (ab Sesostris III. bis in die 13. Dynastie) ist durch eine Zentralisierung des Landes gekennzeichnet. Das Herrscherbild zeigt nicht länger einen jungen idealisierten König (Pharao), sondern einen weisen, von Lebenserfahrung gekennzeichneten Herrscher. Die Sprache des Mittleren Reiches galt für die folgenden Epochen als klassisch.
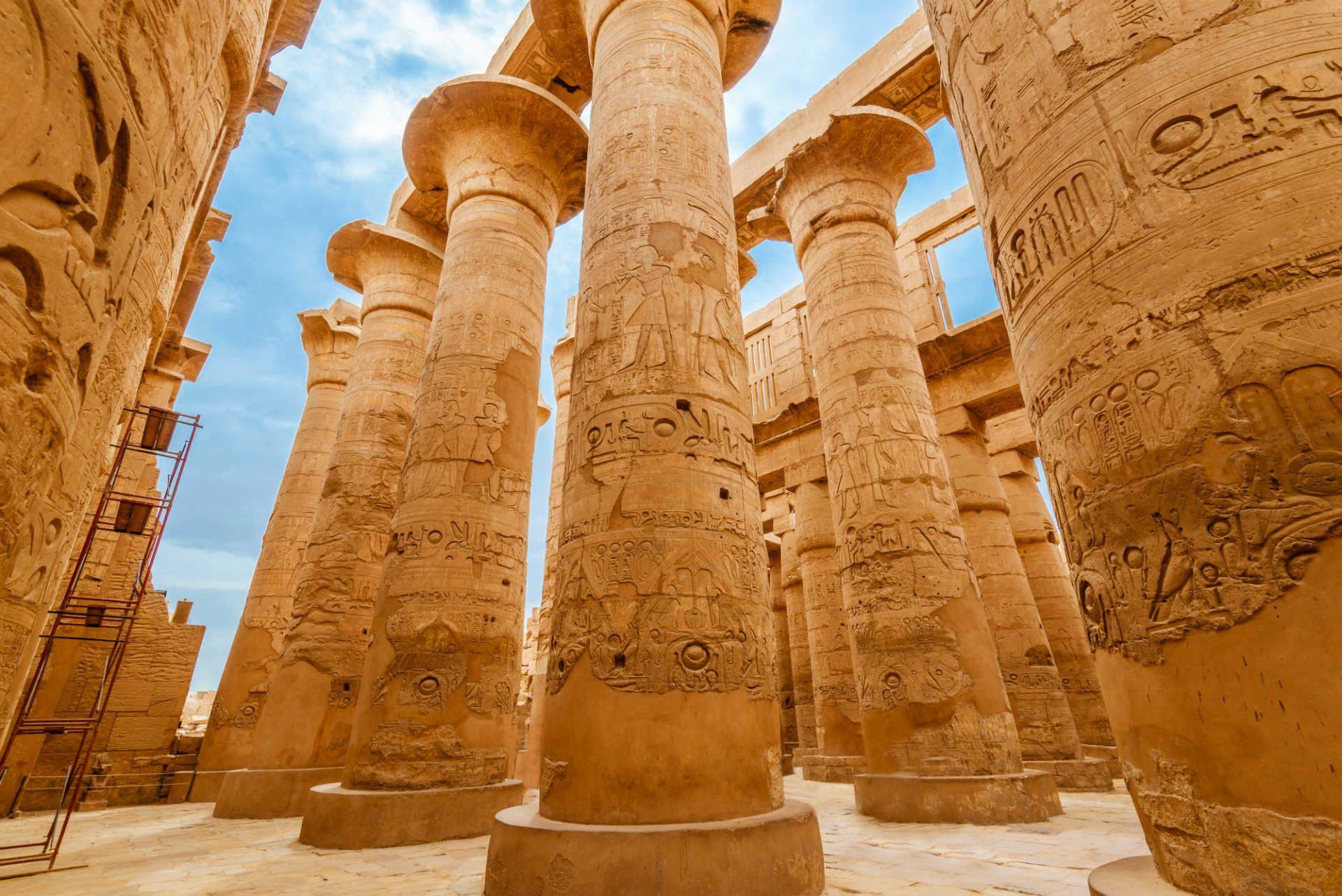






Die Karnak-Tempel liegen als größte Tempelanlage von Ägypten in Karnak, einem Dorf etwa 2,5 Kilometer nördlich von Luxor und direkt am östlichen Nilufer. Die ältesten heute noch sichtbaren Baureste des Tempels stammen aus der 12. Dynastie unter Sesostris I.[1] Bis in die römische Kaiserzeit wurde die Tempelanlage immer wieder erweitert und umgebaut.
Die Tempelanlage steht seit 1979 zusammen mit dem Luxor-Tempel und der thebanischen Nekropole auf der Weltkulturerbeliste der UNESCO.
卡纳克(Karnak)神庙是底比斯最为古老的庙宇,在尼罗河东岸的卢克索镇北4千米处,该神庙经很长时间陆续建造起来,由砖墙隔成三部分。其中中间的部分保存得最完好,也是面积最大的一部分,占地约有30公顷,也是献给太阳神阿蒙的。
 Architecture
Architecture
 Art
Art
 Literature
Literature