
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Brazil
Brazil
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS


 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Men
4x400 m Men
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 Geography
Geography
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2017 London
2017 London
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1991 Tokyo
1991 Tokyo




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

 Science and technology
Science and technology

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 The first industrial revolution and its leaders and followers
The first industrial revolution and its leaders and followers



Das Vereinigte Königreich von Großbritannien und Nordirland (englisch ), kurz Vereinigtes Königreich (englisch [juːˌnaɪ̯.tʰɪd ˈkʰɪŋ.dəm], internationale Abkürzung: UK oder GB), ist ein auf den Britischen Inseln vor der Nordwestküste Kontinentaleuropas gelegener europäischer Staat und bildet den größten Inselstaat Europas.
Das Vereinigte Königreich ist eine Union aus den vier Landesteilen England, Wales, Schottland und Nordirland. Im täglichen Sprachgebrauch wird es auch schlicht als Großbritannien oder England bezeichnet. Jedoch stellt England in der eigentlichen Bedeutung nur den größten Landesteil dar, während Großbritannien die Hauptinsel der Britischen Inseln mit den Landesteilen England, Schottland und Wales bezeichnet.
Mit rund 66,4 Millionen Einwohnern[6] steht das Vereinigte Königreich unter den bevölkerungsreichsten Staaten Europas nach Russland und Deutschland an dritter Stelle. Es ist Gründungsmitglied der NATO sowie der Vereinten Nationen. Es ist Atommacht, ständiges Mitglied des UN-Sicherheitsrates und einer der G7-Staaten. Von 1973 bis 2020 war es Mitglied der EWG bzw. später der Europäischen Union.
大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国(英语:United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland),国际间的标准简称为联合王国(英语:United Kingdom,缩写作UK)或者不列颠(英语:Britain),汉字文化圈通称“英国”[注 5][9][10](中文早期亦称“英联王国”[注 6]),是本土位于西欧并具有海外领地[注 7]的主权国家。英国位于欧洲大陆西北面,由大不列颠岛、爱尔兰岛东北部分及一系列较小岛屿组成[11]。英国和另一国家唯一的陆上国境线位于北爱尔兰,和爱尔兰共和国相邻[注 8]。英国由大西洋所环绕,东为北海,南为英吉利海峡,西南偏南为凯尔特海,与爱尔兰隔爱尔兰海相望。该国总面积达243,610平方千米(94,060平方英里),为世界面积第80大的主权国家及欧洲面积第11大的主权国家,人口约6636万,为全球第21名及欧洲第3名。
英国为君主立宪制国家,采用议会制进行管辖[12][13]。其首都伦敦为全球城市A++级别城市和国际金融中心,大都会区人口达1380万,为欧洲第三大[14]。现任英国君主为女王伊丽莎白二世,1952年2月6日即位。英国由四个构成国组成,分别为英格兰、苏格兰、威尔士和北爱尔兰[15],其中后三者在权力下放体系之下,各自拥有一定的权力[16][17][18]。三地首府分别为爱丁堡、加的夫和贝尔法斯特。附近的马恩岛、根西行政区及泽西行政区并非联合王国的一部分,而为皇家属地,英国政府负责其国防及外交事务[19]。
英国的构成国之间的关系在历史上经历了一系列的发展。英格兰王国通过1535年和1542年的联合法令将威尔士纳入领土。1707年联合法令使英格兰王国和苏格兰王国共组大不列颠王国,1801年大不列颠王国和爱尔兰王国共组大不列颠及爱尔兰联合王国。1922年爱尔兰中南部26个郡(面积占整个爱尔兰的约六分之五)脱离英国组成爱尔兰自由邦(当今爱尔兰的前身),最终造就了当今的大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国[注 9]。大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国亦有14块海外领地[20],为往日帝国的遗留部分。大英帝国在1921年达到其巅峰,拥有全球22%的领土,是有史以来面积最大的帝国。英国在语言、文化和法律体系上对其前殖民地保留了一定的影响,因而吸引许多以前英联邦的移民前来居住。
英国为发达国家,以名义GDP为量度是世界第五大经济体,以购买力平价为量度是世界第九大经济体。英国是世界首个工业化国家,工业革命使英国人的生产力大大提高,商业与财富极大的增长,更凭借著工业时代的船坚炮利,1763年—1945年英国为世界第一强国,其鼎盛时期的19世纪还被称作英国的世纪[21][22],当今英国仍是世界强国之一,在经济、文化、军事、科技、教育和政治上均有全球性的显著影响力[23][24]。英国为国际公认的有核国家,其军事开支位列全球第五[25][26]。1945年以来英国即为联合国安全理事会常任理事国。1973年—2020年英国是欧洲联盟(EU)及其前身欧洲经济共同体(EEC)的成员国。英国还是英联邦、欧洲委员会、七国财长峰会、七国集团、二十国集团、北大西洋公约组织、经济合作与发展组织和世界贸易组织成员国。
グレートブリテン及び北アイルランド連合王国(グレートブリテンおよびきたアイルランドれんごうおうこく、英: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland: UK)は、ヨーロッパ大陸の北西岸に位置し、グレートブリテン島・アイルランド島北東部・その他多くの島々から成る立憲君主制国家。首都はロンドン。日本語における通称の一例としてイギリス、英国(えいこく)がある(→#国名)。
イングランド、ウェールズ、スコットランド、北アイルランドという歴史的経緯に基づく4つの「カントリー(国)」が、同君連合型の単一の主権国家を形成している[1]。しかし、政治制度上は単一国家の代表的なモデルであり、連邦国家ではない。
国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国の一国(五大国)であり、G7・G20に参加する。GDPは世界10位以内に位置する巨大な市場を持ち、ヨーロッパにおける四つの大国「ビッグ4」の一国である。ウィーン体制が成立した1815年以来、世界で最も影響力のある国家を指す列強の一つに数えられる。また、民主主義、立憲君主制など近代国家の基本的な諸制度が発祥した国でもある。
イギリスの擬人化としてはジョン・ブル、ブリタニアが知られる。
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK or U.K.)[14] or Britain,[note 10] is a sovereign country located off the northwestern coast of the European mainland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the northeastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands.[15] Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland. Otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south and the Celtic Sea to the southwest, giving it the 12th-longest coastline in the world. The Irish Sea separates Great Britain and Ireland. The total area of the United Kingdom is 94,000 square miles (240,000 km2).
The United Kingdom is a unitary parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy.[note 11][16][17] The monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who has reigned since 1952, making her the world's longest-serving current head of state.[18] The United Kingdom's capital is London, a global city and financial centre with an urban area population of 10.3 million.[19]
The United Kingdom consists of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[20] Their capitals are London, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast, respectively. Apart from England, the countries have their own devolved governments,[21] each with varying powers.[22][23] Other major cities include Birmingham, Glasgow, Leeds, Liverpool, and Manchester.
The nearby Isle of Man, Bailiwick of Guernsey and Bailiwick of Jersey are not part of the UK, being Crown dependencies with the British Government responsible for defence and international representation.[24] The medieval conquest and subsequent annexation of Wales by the Kingdom of England, followed by the union between England and Scotland in 1707 to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, and the union in 1801 of Great Britain with the Kingdom of Ireland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Five-sixths of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present formulation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The UK's name was adopted in 1927 to reflect the change.[note 12] There are fourteen British Overseas Territories,[25] the remnants of the British Empire which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world's landmass and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and political systems of many of its former colonies.[26][27][28][29][30] The United Kingdom has the world's sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the ninth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). It has a high-income economy and a very high human development index rating, ranking 14th in the world. It was the world's first industrialised country and the world's foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries.[31][32] The UK remains a great power, with considerable economic, cultural, military, scientific and political influence internationally.[33][34] It is a recognised nuclear weapons state and is sixth in military expenditure in the world.[35] It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a leading member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the G20, NATO, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Interpol and the World Trade Organization (WTO). It was a member of the European Union (EU) and its predecessor, the European Economic Community (EEC), for 47 years, between 1 January 1973 and withdrawal on 31 January 2020.
Le Royaume-Uni (prononcé en français : /ʁwajom‿yni/a Écouter), en forme longue le Royaume-Uni de Grande-Bretagne et d'Irlande du Nordb (en anglais : United Kingdom /juːˌnaɪtɪd ˈkɪŋdəm/c Écouter et United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland)d, est un pays d'Europe de l'Ouest, ou selon certaines définitions, d'Europe du Nord, dont le territoire comprend l'île de Grande-Bretagne et la partie nord de l'île d'Irlande, ainsi que de nombreuses petites îles autour de l'archipel. Le territoire du Royaume-Uni partage une frontière terrestre avec la république d'Irlande, et est entouré par l'océan Atlantique au nord, la mer du Nord à l'est, la Manche au sud, la mer Celtique au sud-sud-ouest, la mer d'Irlande au sud-ouest et les mers intérieures de la côte ouest de l'Écosse au nord-ouest. Le Royaume-Uni couvre une superficie de 246 690 km2, faisant de lui le 80e plus grand pays du monde, et le 11e d'Europe. Il est le 22e pays plus peuplé du monde, avec une population estimée à 65,1 millions d'habitants. Le Royaume-Uni est une monarchie constitutionnelle7 ; il possède un système parlementaire de gouvernance8,3. Sa capitale est Londres, une ville mondiale et la première place financière au monde.
Le Royaume-Uni est composé de quatre nations constitutives : l'Angleterre, l'Écosse, le pays de Galles et l'Irlande du Nord. Les trois dernières ont des administrations dévolues9, chacune avec des pouvoirs variés10, basés dans leurs capitales régionales, respectivement Édimbourg, Cardiff et Belfast. Les bailliages de Guernesey, de Jersey et l'île de Man sont des dépendances de la Couronne et ne sont donc pas rattachés au pays11. De plus, le pays comprend quatorze territoires d'outre-mer12, disséminés sur plusieurs océans. Le Royaume-Uni est né en 1707, lorsque les royaumes d'Angleterre et d'Écosse s'unifièrent pour former le royaume de Grande-Bretagne, qui s'agrandit en 1801 en s'unifiant avec le royaume d'Irlande pour former le Royaume-Uni de Grande-Bretagne et d'Irlande. En 1922, l'Irlande du Sud fit sécession du Royaume-Uni, donnant naissance à l'État d'Irlande, amenant au nom officiel et actuel de « Royaume-Uni de Grande-Bretagne et d'Irlande du Nord ». Les territoires d'outre-mer, anciennement des colonies, sont les vestiges de l'Empire britannique, qui, jusqu'à la seconde moitié du XXe siècle, était le plus vaste empire colonial de l'histoire.
L'influence britannique peut être observée dans la langue, la culture, le système politique et juridique des anciennes colonies. Le Royaume-Uni est un pays développé. Il est en 2018 la cinquième puissance mondiale par son PIB nominal13 et la neuvième puissance en termes de PIB à parité de pouvoir d'achat. Berceau de la révolution industrielle, le pays fut la première puissance mondiale durant la majeure partie du XIXe siècle14,15. Le Royaume-Uni reste une grande puissance, avec une influence internationale considérable sur le plan économique, politique, culturel, militaire et scientifique16,17. Il est également une puissance nucléaire reconnue avec le sixième budget de la défense le plus élevé18. Le Royaume-Uni est membre du Commonwealth, du Conseil de l'Europe, du G7, du G20, de l'OTAN, de l'OCDE, de l'OMC, et membre permanent du Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies depuis 1946. Le Royaume-Uni a adhéré le 1er janvier 1973 à la CEE, devenue Union Européenne, puis en est sorti le 1er février 2020 à la suite de la victoire du «

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Silk road
Silk road

 States of Asia
States of Asia
Die Republik Korea (kor. 대한민국, 大韓民國, [ˈtɛ̝ːɦa̠nminɡuk̚], Daehan Minguk), teilweise Südkorea genannt, liegt in Ostasien und nimmt den südlichen Teil der Koreanischen Halbinsel ein. Die einzige Landgrenze, mit 243 km Länge, besteht faktisch die Grenze zum nördlichen Nachbarn Nordkorea. Die beiden Nachfolgestaaten Chōsens wurden 1948 im aufkommenden Kalten Krieg gegründet; der folgende Koreakrieg zementierte die Teilung Koreas. Der Norden wurde sozialistisch und autokratisch, während im kapitalistischen, diplomatisch nach Westen orientierten Südkorea mit der Zeit eine parlamentarische Demokratie etabliert werden konnte. Im Westen grenzt Südkorea an das Gelbe (in Südkorea: Westmeer), im Süden an das Ostchinesische und im Osten an das Japanische Meer (in Südkorea: Ostmeer).
Mit rund 51,5 Millionen Einwohnern zählt Südkorea zu den dicht besiedelten Staaten und zu den 30 bevölkerungsreichsten Staaten der Erde. Etwa die Hälfte der Einwohner lebt im Großraum der Hauptstadt Seoul, einer Weltstadt mit der viertgrößten Wirtschaft weltweit. Über zwei Millionen Menschen leben jeweils in den Städten Busan, Incheon und Daegu.
„Das Wunder am Han-Fluss“, wie die Zeit des rapiden Wirtschaftsaufschwungs ab 1962 genannt wird, machte Südkorea schnell von einem armen Agrarland zu einem modernen Industriestaat. Man spricht auch von einem Tigerstaat. In der Produktion von Schiffen und elektronischen Produkten wie Halbleitern, Mikrochips, Flachbildschirmen und Computern hat die südkoreanische Industrie eine marktbeherrschende Stellung erreicht. Auch dadurch nimmt die kulturelle Bedeutung des Landes zu, was etwa in der Koreanischen Welle Ausdruck findet. Das Land ist Mitgliedsstaat der Vereinten Nationen, der G20, der OECD, der APEC und ASEAN+3.
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Woman
4x400 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1993 Stuttgart
1993 Stuttgart




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
 Russia
Russia
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb
Russland (russisch Россия [rɐˈsʲijə] , Transkription Rossija) bzw. die Russische Föderation (oder der russischen Bezeichnung entsprechend Russländische Föderation; russisch Российская Федерация, , Transkription Rossijskaja Federazija)[9] ist ein souveräner, föderativer Staat im nordöstlichen Eurasien und mit etwa 17 Millionen Quadratkilometern flächenmäßig der größte Staat der Erde. Russland umfasst mehr als ein Achtel der bewohnten Landmasse der Erde und steht mit 144 Millionen Einwohnern (2017) an 9. Stelle der bevölkerungsreichsten Länder; es ist zugleich eines der am dünnsten besiedelten. Der europäische Teil des Staatsgebiets ist viel dichter besiedelt und verstädtert als der über dreimal so große asiatische Teil: Etwa 77 % der Bevölkerung (110 Millionen Einwohner) leben westlich des Urals. Die Hauptstadt Moskau ist eine der größten Städte und Metropolregionen der Welt; als weiteres wichtiges Zentrum gilt Sankt Petersburg, das zwischen 1712 und 1918 Hauptstadt war und eine Brücke für Kunst und Kultur aus Westeuropa bildete.
Die nächstgrößeren Millionenstädte Russlands sind Nowosibirsk in Sibirien, Jekaterinburg im Ural und Nischni Nowgorod an der Wolga. Weitere Großstadtregionen sind Tscheljabinsk, Ufa und Kasan.
Das heutige Russland entwickelte sich aus dem Großfürstentum Moskau, einem Teilfürstentum des früheren ostslawischen Reiches Kiewer Rus, zu einem über einhundert Ethnien zählenden Vielvölkerstaat, wobei ethnische Russen heute fast 80 Prozent der Bevölkerung ausmachen. Die föderale Gliederung Russlands besteht aus acht Föderationskreisen und 85 Föderationssubjekten.
Die Russische Föderation ist „Fortsetzerstaat“[10] der Sowjetunion in internationalen Organisationen, Atommacht und ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates. Nach der Erholung von der postkommunistischen Transformationskrise der 1990er Jahre wurde Russland die nach Kaufkraftparität sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt, zwischen Deutschland und Brasilien (Schätzung für 2016).[11]
Russlands Rohstoffreserven sind mit etwa 20 bis 30 % die wahrscheinlich größten der Welt,[12][13][14] mit erheblichen Vorkommen von Primärenergieträgern, vor allem Erdgas.
Russland gehört zu den anerkannten Nuklearmächten und besitzt das weltgrößte Arsenal an Massenvernichtungswaffen. Russland ist Großmacht und Regionalmacht und wird teilweise als potentielle Supermacht betrachtet.[15] Es ist ständiges Mitglied im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen, G 20-Mitglied, Mitglied des Europarates, der APEC, der Shanghaier Organisation für Zusammenarbeit (SCO), der OSCE, der WTO; es ist führendes Mitglied in der Gemeinschaft Unabhängiger Staaten (GUS), der Organisation des Vertrags über kollektive Sicherheit (OVKS) und der Eurasischen Wirtschaftsunion (mit Armenien, Kasachstan, Kirgisistan und Weißrussland).
Russland ist ein Schwellenland im Bereich des oberen mittleren Einkommens.[16] Im Human Development Index der Vereinten Nationen stand Russland 2016 mit 0,8 (von 1) auf Platz 49,[17] der Gini-Koeffizient lag bei 37,7.
Das Regierungssystem Russlands wird von Politikwissenschaftlern entsprechend dem Wortlaut der Verfassung meist formal als Verbindung präsidentieller und parlamentarischer Formen eingeordnet; die Verfassungswirklichkeit des politischen Systems entspricht jedoch eher den Modellen defekter Demokratien oder der Postdemokratie, zumal der Präsident fast autokratische Macht ausübt.[18][19][20] Für die politische Ordnung wird in Russland gelegentlich von offizieller Seite der Begriff „Gelenkte Demokratie“ im affirmativen Sinne gebraucht.[21]
Die Annexion der Krim im März 2014 belastet die Beziehungen zwischen Russland und dem Westen. Der russischen Regierung wird vorgeworfen, die europäische Friedensordnung zu verletzen.[22]
Das Land war 2016 mit 69,9 Mrd. Dollar für 4,1 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit im internationalen Vergleich hinter den Vereinigten Staaten mit 611 Mrd. Dollar (36 %) und China mit 215 Mrd. Dollar (13 %) auf Platz 3, gefolgt von Saudi-Arabien und Indien.[23][24]
俄罗斯联邦[9](俄语:Российская Федерация,缩写为РФ),通称俄罗斯(Россия)[10],是位于欧亚大陆北部的联邦共和国,国土横跨欧亚两大洲,为世界上土地面积最大的国家,拥有1709万平方公里的面积,占地球陆地面积八分之一[11][12];它也是世界上第九大人口国家,拥有1.4亿人口,77%居住于其较为发达的欧洲部分。俄罗斯国土覆盖整个亚洲北部及东欧大部,横跨11个时区,涵盖广泛的环境和地形。拥有全世界最大的森林储备和含有约世界四分之一的淡水的湖泊[13]。俄罗斯有十四个陆上邻国(从西北方向起逆时针序):挪威、芬兰、爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚、立陶宛、波兰、白俄罗斯、乌克兰、格鲁吉亚、阿塞拜疆、哈萨克斯坦、中国、蒙古和朝鲜(其中立陶宛和波兰仅与俄罗斯外飞地加里宁格勒州接壤),另外与阿布哈兹和南奥塞梯两个只有俄罗斯承认的非联合国会员国接壤。同时,俄罗斯还与日本、美国、加拿大、格陵兰(丹麦)、冰岛、瑞典、土耳其隔海相望。俄罗斯北部和东部分别为北冰洋和太平洋包围,西北和西南则分别可经由波罗的海和黑海通往大西洋。
俄罗斯历史始于欧洲的东斯拉夫民族,聚集区域自公元3世纪至8世纪逐渐扩大[14]。在9世纪,源自北欧的瓦良格人武士精英建立了基辅罗斯这个中世纪国家并开始统治。公元988年,国家从拜占庭帝国采纳了东正教会,随后由此开始,千年拜占庭与斯拉夫文化的融合成为了今日的俄罗斯文化[15]。基辅罗斯最终解散分化为众多公国,被蒙古人逐一击破,并均在13世纪成为了金帐汗国的一部分。莫斯科大公自14世纪起逐渐崛起并统一周边俄罗斯诸侯国,在15世纪成功从金帐汗国独立,且成为了基辅罗斯文化和政治的继承者。16世纪起伊凡四世自称沙皇,自诩“第三罗马”。在18世纪,俄罗斯沙皇国通过征服、吞并和探索而扩张。彼得一世称帝成立了俄罗斯帝国,最终成为史上领土第三大帝国,疆域最大曾自中欧的波兰连绵至北美的阿拉斯加[16][17]。
1917年俄国革命后,俄罗斯苏维埃联邦社会主义共和国成为了世界上第一个宪法意义上的社会主义国家[18],并成为随后成立的苏维埃社会主义共和国联盟的主体和其最大的加盟共和国。二战时期,苏联为同盟国的胜利扮演了决定性的角色。在战后其崛起成为公认的超级大国,并在冷战时期与美国互相竞争。苏联时期产生了20世纪的许多最重要的科技成就,其中包括世界第一颗人造地球卫星,以及首次将人类送入太空。在1990年,苏联为世界上第二大经济体[19],且拥有世界上最多的常备军人以及最多的大规模杀伤性武器库存。1991年苏联解体后,包括俄罗斯在内的15个共和国从原苏联独立;身为原苏联最大的加盟共和国,俄罗斯通过修宪改制为俄罗斯联邦,成为原苏联的唯一法理继承国家,政体采用联邦制、民主共和制及半总统制。
截至2015年,俄罗斯根据国民生产总值为世界第13大经济体,根据购买力平价为世界第六大经济体。俄罗斯拥有世界上最大储量的矿产和能源资源[20],是世界上最大的石油和天然气输出国[21][22]。俄罗斯为世界大国之一,为认定的拥核国家,联合国安理会常任理事国,G20、欧洲理事会、亚太经合组织、上合组织、欧安组织、世贸组织和金砖国家成员。它也是独联体、集体安全条约组织的领导者和欧亚经济联盟创始成员。俄罗斯亦是世界八大工业国之一。
ロシア連邦(ロシアれんぽう、ロシア語: Российская Федерация:英語名 Russian Federation)、またはロシア (Россия) は、ユーラシア大陸北部にある共和制及び連邦制国家。
地理的にロシアの国境は、北西から南東へ、ノルウェー、フィンランド、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニアおよびポーランド(ともにカリーニングラード州と隣接)、ベラルーシ、ウクライナ、ジョージア、アゼルバイジャン、カザフスタン、中華人民共和国、モンゴル国、朝鮮民主主義人民共和国と接する。海上境界線としては、日本とはオホーツク海・宗谷海峡・根室海峡・珸瑤瑁水道、アメリカ合衆国とはベーリング海峡でアラスカ州と接する。ロシアの面積は17,075,400km2で世界最大であり、地球上の居住地域の8分の1を占める。2012年時点で、ロシアの人口は1億4300万人で世界第9位である[3]。国土は北アジア全体および東ヨーロッパの大部分に広がることに伴い、ロシアは11の標準時を有し、広範な環境および地形を包含する。
ロシアの歴史は、3世紀から8世紀までの間にヨーロッパで認識され始めた東スラヴ人の歴史に始まる[4]。9世紀、ヴァリャーグの戦士の精鋭およびその子孫により設立及び統治されて、キエフ大公国の中世国家が誕生した。988年、東ローマ帝国から正教会を導入し、次の千年紀のロシア文化を特徴付ける東ローマ帝国およびスラブ人の文化の統合が始まった[5]。キエフ大公国は最終的には多くの国に分裂し、キエフ大公国の領土の大部分はモンゴルに制圧され、遊牧国家ジョチ・ウルスの属国になった[6]。モスクワ大公国は次第に周辺のロシアの公国を再統合し、ジョチ・ウルスからの独立を獲得し、キエフ大公国の文化的および政治的な遺産を支配するようになった。18世紀までにモスクワ大公国は、王朝による征服・併合、シェレホフ提督による探検を通じ、史上第3位の大帝国であるロシア帝国となり、版図がポーランドから北米のアラスカまで広がった[7][8]。
しかし帝国は国土に見合う開発資金を国内で捻出することができなかった。サンクトペテルブルクの貿易為替銀行にドイツ銀行を参加させたが、露仏同盟を結んで以来国際金融市場から外資が雪崩れ込むようになった。
ロシア革命後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国がソビエト連邦最大かつ指導的な構成国となり、世界初の憲法上の社会主義国および広く認められた超大国となり[9]、第二次世界大戦において連合国の勝利に決定的な役割を果たした[10][11]。ソビエト時代には、世界初の人工衛星および世界初の有人宇宙飛行を含む20世紀の最も重要な複数の技術的偉業を経験した。1991年のソ連崩壊後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国は自らをロシア連邦として再構成し、連邦国家の継続的な法人格として認識されている。ソ連政府は国民にあまねく賃貸住宅を配分していたが、それらを建設するだけで巨額の財政負担となっており、財政再建中のロシア連邦がリフォームすることなどかなわず、無償で住民が物件を取得できるようにしてしまい急激な私有化を進めた[12]。私有化されていないものは地方自治体への譲渡が進んで、人口減少社会となる中、若者向けに低家賃で貸し出されている[12]。
1996年11月、ロシアは第一回だけで10億ドルのユーロ債を起債した[13]。それまでの累積ユーロ債発行額は160億ドルほどに達した[13]。1997年、第一回サンクトペテルブルク国際経済会議が開かれた。1998年、ロシア財政危機。1999年、ロスチャイルド代理人のアルフレッド・ハルトマン博士が資金洗浄の国内捜査線上で名前をとりあげられた。
2003年、ミハイル・ホドルコフスキーが脱税などの罪で逮捕・起訴され、ユコスの社長を辞任した。シブネフチとの合併が取り消されるなどして株価が乱高下し、内部者取引が横行した。2005年でロシアの住宅私有化率は63%に達し[12]、国際的な不動産価格の下落へつながっていった。2007年、ホドルコフスキーを除くユコス株主らは、ロシア政府がユコスを破綻させたとしてハーグの常設仲裁裁判所へ提訴した(ユコス破綻事件)。2010年6月26日、政府側のロスネフチに賠償命令が出た。7月27日、内部者取引と株価操作を取り締まる法案がようやく批准された[14]。これは翌年から施行された。
2014年ウクライナ騒乱が2月に起きてVTBが態度を硬化させた。7月、ユコス破綻事件で政府は19億ユーロの賠償金支払いを命じられていたが、12月に欧州人権裁判所が政府の上訴を棄却した[15]。2016年4月、ハーグ地区裁判所が、ロシア政府に株主らへ500億ドルの賠償金支払いを命じた常設仲裁裁判所の判決を棄却した[16]。
2014年時点で、ロシアの経済は名目GDPで世界第9位かつ購買力平価で世界第6位であった[17]。ロシアの豊富な鉱物およびエネルギー資源は世界最大の埋蔵量であり[18]、世界最大の原油生産国および世界最大の天然ガス生産国の一つである。ロシアは核保有を認められた5大国の一つであり、世界最大の大量破壊兵器保有量がある。ロシアは列強および国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、独立国家共同体の指導国であるだけでなく、G20、欧州評議会、アジア太平洋経済協力、上海協力機構、ユーラシア経済共同体、欧州安全保障協力機構 (OSCE)、世界貿易機関 (WTO) 加盟国である。
Russia (Russian: Росси́я, tr. Rossiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijə]), officially the Russian Federation[12] (Russian: Росси́йская Федера́ция, tr. Rossiyskaya Federatsiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijskəjə fʲɪdʲɪˈratsɨjə]), is a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and North Asia.[13] At 17,125,200 square kilometres (6,612,100 sq mi),[14] Russia is the largest country in the world by area, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area,[15][16][17] and the ninth most populous, with about 146.77 million people as of 2019, excluding Crimea.[8] About 77% of the population live in the western, European part of the country. Russia's capital, Moscow, is the largest metropolitan area in Europe proper[18] and one of the largest cities in the world; other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod. Extending across the entirety of Northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia spans eleven time zones and incorporates a wide range of environments and landforms. From northwest to southeast, Russia shares land borders with Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland (both with Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and North Korea. It shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk and the U.S. state of Alaska across the Bering Strait. However, Russia recognises two more countries that border it, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, both of which are internationally recognized as parts of Georgia.
The East Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD.[19] Founded and ruled by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, the medieval state of Rus arose in the 9th century. In 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire,[20] beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium.[20] Rus' ultimately disintegrated into a number of smaller states; most of the Rus
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 England
England

 European Union
European Union
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Mexico
Mexico

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Turkey
Turkey
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

Die G20 (Abkürzung für Gruppe der zwanzig wichtigsten Industrie- und Schwellenländer) ist ein seit 1999 bestehender informeller Zusammenschluss aus 19 Staaten und der Europäischen Union. Sie soll als Forum für die Kooperation und Konsultation in Fragen des internationalen Finanzsystems dienen.
An den Treffen der G20 nehmen die Staats- und Regierungschefs der G20 Länder, die Finanzminister und Zentralbankchefs der G8 und elf weiterer Staaten, darunter die O-5, sowie die EU-Präsidentschaft (wenn diese zu diesem Zeitpunkt nicht von einem G8-Staat geführt wird), der Präsident der Europäischen Zentralbank, der Geschäftsführende Direktor (Managing Director) des Internationalen Währungsfonds, der Vorsitzende des Internationalen Währungs- und Finanzausschusses (IMFC), der Präsident der Weltbank und der Vorsitzende des Development Committees von Weltbank und Internationalem Währungsfonds teil.
20国集团(G20)是一个国际经济合作论坛,于1999年9月25日由八国集团的财长在华盛顿宣布成立,属于布雷顿森林体系框架内非正式对话的一种机制,由原八国集团以及其余十二个重要经济体组成。该组织的宗旨是为推动已工业化的发达国家和新兴市场国家之间就实质性问题进行开放及有建设性的讨论和研究,以寻求合作并促进国际金融稳定和经济的持续增长,按照以往惯例,国际货币基金组织与世界银行列席该组织的会议。20国集团成员涵盖面广,代表性强,该集团的GDP占全球经济的90%,贸易额占全球的80%,因此已取代G8成为全球经济合作的主要论坛。 二十国集团(英语:Group of Twenty,缩写:G20)是一个国际经济合作论坛,于1999年12月16日在德国柏林成立,属于布雷顿森林体系框架内对话的一种机制,由七国集团(加拿大、美国、英国、法国、德国、意大利、日本),金砖五国(巴西、俄罗斯、印度、中国、南非),七个重要经济体(墨西哥、阿根廷、土耳其、沙特阿拉伯、韩国、印度尼西亚、澳大利亚),以及欧洲联盟组成。按照惯例,国际货币基金组织与世界银行列席该组织的会议。
G20(ジートゥエンティ)は、"Group of Twenty"の略で、主要国首脳会議(G7)に参加する7か国、EU、ロシア、および新興国11か国の計20か国・地域からなるグループである。
構成国・地域は、アメリカ合衆国、イギリス、フランス、ドイツ、日本、イタリア、カナダ、EU、ロシア、中華人民共和国、インド、ブラジル、メキシコ、南アフリカ共和国、オーストラリア、大韓民国、インドネシア、サウジアラビア、トルコ、アルゼンチンである。20か国・地域首脳会合(G20首脳会合)および20か国・地域財務大臣・中央銀行総裁会議(G20財務相・中央銀行総裁会議)を開催している。主要20か国・地域[1][2]とも言い、日本の放送局であるNHKでは、先進国会合であるG7と区別して、先進国に新興国を加えた主要20か国[3]と表現している。
The G20 (or Group of Twenty) is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability,[3] the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks[4], have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.[3]
Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank. Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 90%[5] of the gross world product (GWP), 80% of world trade (or, if excluding EU intra-trade, 75%), two-thirds of the world population,[2] and approximately half of the world land area.
With the G20 growing in stature[6] after its inaugural leaders' summit in 2008, its leaders announced on 25 September 2009 that the group would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.[7] Since its inception, the G20's membership policies have been criticized by some intellectuals,[8][9] and its summits have been a focus for major protests.[10][11]
The heads of the G20 nations held summits twice in 2009 and twice in 2010. Since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been held annually.[12]
Le Groupe des vingt (G20) est un groupe composé de dix-neuf pays et de l'Union européenne dont les ministres, les chefs des banques centrales et les chefs d'État se réunissent annuellement. Il a été créé en 1999, après la succession de crises financières dans les années 19901. Il vise à favoriser la concertation internationale, en intégrant le principe d'un dialogue élargi tenant compte du poids économique croissant pris par un certain nombre de pays. Le G20 représente 85 % du commerce mondial, les deux tiers de la population mondiale et plus de 90 % du produit mondial brut (somme des PIB de tous les pays du monde)1. Le 15 novembre 2008, pour la première fois de son histoire, les chefs d'État ou de gouvernement se sont réunis. Le G20 se décline sous trois formes : les G20 regroupant des chefs d'État et de gouvernement, les G20 finance regroupant les ministres des finances et les gouverneurs des banques centrales et, depuis les 20-21 avril 2010, des G20 sociaux, réunissant les ministres de l'emploi.
Il Gruppo dei 20 (o G20) è un forum dei leader, dei ministri delle finanze e dei governatori delle banche centrali, creato nel 1999, dopo una successione di crisi finanziarie per favorire l'internazionalità economica e la concertazione tenendo conto delle nuove economie in sviluppo. Di esso fanno parte i 19 paesi più industrializzati (quelli del G8 in primis) con l'eccezione di Spagna e Paesi Bassi (sono presenti invece Argentina e Sudafrica). È presente, inoltre, l'Unione europea.
Il G20 rappresenta i due terzi del commercio e della popolazione mondiale, oltre all'80% del PIL mondiale. Sono presenti anche alcune tra le maggiori organizzazioni internazionali.
El Grupo de los 20 (numerónimo: G-20) es un foro cuyos miembros permanentes son 19 países de todos los continentes (Alemania, Arabia Saudita, Argentina, Australia, Brasil, Canadá, China, Corea del Sur, Estados Unidos, Francia, India, Indonesia, Italia, Japón, México, Reino Unido, Rusia, Sudáfrica, Turquía y la Unión Europea).1
Es el principal espacio de deliberación política y económica del mundo.1 En conjunto las entidades políticas representadas en el G20 reúnen el 66 % de la población mundial y el 85 % del producto bruto mundial.1.
El G-20 cuenta además con 14 organizaciones internacionales socias, cuyas presidencias también integran el foro:2
- Mundiales (7): Naciones Unidas (ONU), Fondo Monetario Internacional (FMI), Banco Mundial, Consejo de Estabilidad Financiera (FSB), Organización Internacional del Trabajo (OIT), Organización Mundial de Comercio (OMC) y Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS)
- Regionales (7): Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN), Unión Africana, Nueva Alianza para el Desarrollo de África (NEPAD), Comunidad del Caribe (CARICOM), Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo (BID), Banco de Desarrollo de América Latina (CAF) y Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico (OCDE)
El G-20 surgió en dos etapas. Primero en 1999, como un grupo de segundo nivel de autoridades económicas y financieras, y luego como un grupo de primer nivel en 2008, como consecuencia de la crisis mundial que estalló ese año, al constituirse como Cumbre de Jefes de Estado, desplazando al G-8 y al G8+5 como foro de discusión de la economía mundial.3
La instancia más importante del G20 es la Cumbre de Jefes de Estado, denominada Cumbre de Líderes, que se reúne una vez por año.4 El G20 cuenta con dos instancias gubernamentales de segundo nivel, denominadas canales de trabajo: el Canal de Finanzas que reúne a los ministros de Finanzas y presidentes de bancos centrales y el Canal de Sherpas, para tratar los temas no económicos.4
Complementariamente el G-20 cuenta con grupos de participación de la sociedad civil, llamados grupos de afinidad: Business 20 (B20) para empresarios, Civil 20 (C20) para ONGs, Labour 20 (L20) para sindicatos, Science 20 (S20) para científicos, Think 20 (T20) para institutos de investigación, Women 20 (W20) para organizaciones feministas y Youth 20 (Y20) para organizaciones juveniles.4
En 2019 la cumbre se realizó en Osaka Japón, correspondiendo la presidencia del grupo a su primer ministro, Shinzō Abe.
Больша́я двадца́тка (также G20, G-20 , Группа двадцати; официально — англ. The Group of Twenty, major advanced and emerging economies[1]) — клуб правительств и глав центральных банков государств с наиболее развитой и развивающейся экономикой[2].
В совокупности, G20 представляет 85 % мирового валового национального продукта, 75 % мировой торговли (включая торговлю внутри ЕС) и две трети населения мира[2].
Европейский союз представлен председателем Европейской комиссии и председателем Европейского совета[3]. Кроме того, обычно на встречах G20 присутствуют представители различных международных организаций, среди которых Совет по финансовой стабильности, Международный валютный фонд, Всемирная торговая организация, Африканский Союз, АСЕАН, Организация Объединённых Наций и Всемирный банк[2].
Группа 20 была создана в ответ на азиатский финансовый кризис конца 1990-х[2] и растущее сознание того, что страны с развивающейся рыночной экономикой не были адекватно представлены в мировых экономических обсуждениях и принятии решений. Переход от «большой семёрки» к формату G20 был ускорен из опасения катастрофы глобальной экономики в общемировой экономический кризис 2008 года[4]. До 2008 года группа не проводила саммитов на высшем уровне, её основной формой деятельности были ежегодные встречи на уровне министров финансов и глав центробанков. На сегодняшний день саммиты G20 являются глобальным форумом для сотрудничества и консультаций по вопросам, относящимся к международной финансово-экономической систе.
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Men
4x400 m Men
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states
 France
France

 Geography
Geography
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

Frankreich ![]() [ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
[ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
Im 17. und 18. Jahrhundert hatte Frankreich eine europäische Führungsrolle und Vormachtstellung inne. Bedeutend war die politische und kulturelle Ausstrahlung: Die Hofhaltung Ludwigs XIV. wurde zum Vorbild absolutistischer Staaten in ganz Europa und die Französische Revolution mit der Erklärung der Menschen- und Bürgerrechte gab zusammen mit Okkupationen durch Napoleon Bonaparte in vielen Ländern den Auftakt zu der immer wieder von Rückschlägen unterbrochenen Entwicklung zur Demokratie. In Übersee baute Frankreich zweimal ein Kolonialreich auf. Das erste umfasste u. a. große Teile Nordamerikas und ging großenteils Mitte des 18. Jahrhunderts im Siebenjährigen Krieg verloren; das zweite mit Schwerpunkt in Afrika war im 19. und frühen 20. Jahrhundert das zweitgrößte der Welt. Im 21. Jahrhundert gilt Frankreich mit Deutschland als treibende Kraft der europäischen Integration.
Die Französische Republik wird in ihrer Verfassung als unteilbar, laizistisch, demokratisch und sozial erklärt.[7] Ihr Grundsatz lautet: „Regierung des Volkes durch das Volk und für das Volk“. Frankreich steht auf Rang 26 des Index der menschlichen Entwicklung (2019) der Vereinten Nationen.[8] Gemessen am nominalen Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist es die sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt.[5] Die Kaufkraft pro Einwohner betrug 2016 19.254 Euro (zum Vergleich: Deutschland 21.879 Euro, Großbritannien 21.141 Euro).[9] Lebensstandard, Bildungsgrad und durchschnittliche Lebenserwartung[10] gelten als hoch. Als meistbesuchtes Land der Welt empfängt Frankreich rund 83 Millionen ausländische Touristen pro Jahr.[11][12]
Frankreich unterhält die drittstärksten Streitkräfte innerhalb der NATO und das größte Heer der Europäischen Union. Es ist eines der fünf ständigen Mitglieder des UN-Sicherheitsrates und hatte 2010 als Atommacht die weltweit dritthöchste Anzahl an Kernwaffen.[13] Das Land ist Gründungsmitglied der Europäischen Union und der Vereinten Nationen, Mitglied der Frankophonie, der G7, der G20, der NATO, der Organisation für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (OECD), der Welthandelsorganisation (WTO) und der Lateinischen Union.
法兰西共和国(法语:République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]),通称法国(法语:France [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() 聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
今日之法国本土于铁器时代由高卢人(凯尔特人的一支)征服,前51年又由罗马帝国吞并。486年法兰克人(日耳曼人的一支)又征服此地,其于该地域建立的早期国家最终发展成为法兰西王国。法国至中世纪末期起成为欧洲大国,国力于19-20世纪时达致巅峰,建立了世界第二大殖民帝国,亦为20世纪人口最稠密的国家[来源请求],现今则是众多前殖民地的首选移民国[8]。在漫长的历史中,法国培养了不少对人类发展影响深远的著名哲学家、文学家与科学家,亦为文化大国,具有第四多的世界遗产[9]。
フランス共和国(フランスきょうわこく、フランス語: République française、通称:フランス、France)は、西ヨーロッパ、カリブ、太平洋およびインド洋に位置する共和制国家。首都はパリ。
フランス・メトロポリテーヌ(本土)は地中海からイギリス海峡及び北海へ、ライン川から大西洋へと広がる。この他世界各地に海外地域および領土を有する。
なお、フランス・メトロポリテーヌ周辺は北東がドイツとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東をスイスとイタリア、南にスペインと国境を接している。
フランスは国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、G7・G20、欧州評議会、世界貿易機関、経済協力開発機構、北大西洋条約機構、パリクラブおよびフランコフォニー国際機関における主要なメンバーである。国際政治においてはこれらの理由から、政治・経済・文化において強力な影響を及ぼす列強の一角に数えられており、ヨーロッパにおける「ビッグ4」の1つでもある。
核拡散防止条約により核兵器の保有を認められた5つの公式核保有国の1つであり、その他にアメリカ合衆国を除けば世界で唯一の原子力空母「シャルル・ド・ゴール」や原子力潜水艦を保有しており、強力な軍事力を持っている。
GDPは名目GDP世界第7位かつ購買力平価で世界第10位・ユーロ圏ではドイツに次ぐ第2位の経済力を有する国であり、高い人間開発指数を持つ先進国として知られる。数多くの世界遺産を抱えており、世界で最も観光客の多い国の1つである。
歴史的にはデカルト、モンテスキュー、ルソー、サルトルといった哲学者やマリ・キュリー、パストゥールといった科学者、モネ、セザンヌ、ゴーギャン、クールベ、ドラクロワといった芸術家の故国もしくは活躍の舞台であり、また百年戦争やフランス革命、ナポレオン戦争といった歴史的事象の主要な舞台であった。
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() ), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks arrived in 476 and formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987.
In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom in which the king's authority was barely felt. King Philip II achieved remarkable success in the strengthening of royal power and the expansion of his realm, defeating his rivals and doubling its size. By the end of his reign, the kingdom had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts for the French throne, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, various wars with rival powers, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world.[14] The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. But France once again emerged as Europe's dominant cultural, political and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War.[15] Inadequate economic policies, an inequitable taxation system as well as endless wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence), left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the absolute monarchy, replaced the Ancien Régime with one of history's first modern republics and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of European and world history. The collapse of the empire initiated a period of relative decline, in which France endured a tumultuous succession of governments until the founding of the French Third Republic during the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Subsequent decades saw a period of optimism, cultural and scientific flourishing, as well as economic prosperity known as the Belle Époque. France was one of the major participants of World War I, from which it emerged victorious at great human and economic cost. It was among the Allied powers of World War II, but was soon occupied by the Axis in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, the short-lived Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The current Fifth Republic was formed in 1958 by Charles de Gaulle. Algeria and most French colonies became independent in the 1960s, with the majority retaining close economic and military ties with France.
France retains its centuries-long status as a global centre of art, science and philosophy. It hosts the fifth-largest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites and is the world's leading tourist destination, receiving over 89 million foreign visitors in 2018.[16] France is a developed country with the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and ninth-largest by PPP; in terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[17] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy and human development.[18][19] It remains a great power in global affairs,[20] being one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. France is a founding and leading member of the European Union and the Eurozone,[21] as well as a key member of the Group of Seven, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and La Francophonie.
La France (Écouter), en forme longue depuis 1875 la République française (Écouter), est un État souverain transcontinental dont le territoire métropolitain est situé en Europe de l'Ouest et dont le territoire ultramarin est situé dans les océans Indien, Atlantique et Pacifique ainsi qu'en Amérique du Sud. Il s'agit de l'unique pays au monde à s'étendre sur treize fuseaux horaires. Le pays a des frontières terrestres avec la Belgique, le Luxembourg, l'Allemagne, la Suisse, l'Italie, l'Espagne et les deux principautés d'Andorre et de Monaco en Europe, auxquelles s'ajoutent les frontières terrestres avec le Brésil, le Suriname et les Pays-Bas aux Amériques. La France dispose d'importantes façades maritimes sur l'Atlantique, la Méditerranée, le Pacifique et l'océan Indien, lui permettant de bénéficier de la plus vaste zone économique exclusive du monde6.
La France est une république constitutionnelle unitaire ayant un régime semi-présidentiel. La devise de la République est depuis 1875 « Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité » et son drapeau est constitué des trois couleurs nationales : bleu, blanc, rouge. Son hymne national est La Marseillaise, chant patriotique hérité de la Révolution française. Son principe constitutif est la démocratie : le « gouvernement du peuple, par le peuple et pour le peuple ». Elle a pour capitale Paris et pour langue officielle le français depuis 1539, remplaçant le latin. Ses monnaies sont l'euro depuis 2002 dans la majeure partie du pays et le franc Pacifique dans ses territoires de l'océan Pacifique.
La France s'appelle ainsi depuis 1214, lorsque les troupes du roi Philippe Auguste battent celles de l’empereur germanique à Bouvines. La France tire son nom des
 African Union
African Union
 Alpha Condé
Alpha Condé
 African Union
African Union
 Bingu wa Mutharika
Bingu wa Mutharika
 African Union
African Union
 Denis Sassou Nguesso
Denis Sassou Nguesso
 African Union
African Union
 Hailemariam Desalegn
Hailemariam Desalegn
 African Union
African Union
 Idriss Déby
Idriss Déby
 African Union
African Union
 Jakaya Kikwete
Jakaya Kikwete
 African Union
African Union
 Joaquim Chissano
Joaquim Chissano
 African Union
African Union
 John Agyekum Kufuor
John Agyekum Kufuor
 African Union
African Union
 Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz
Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz
 African Union
African Union
 Muammar al-Gaddafi
Muammar al-Gaddafi
 African Union
African Union
 Olusegun Obasanjo
Olusegun Obasanjo
 African Union
African Union
 Robert Mugabe
Robert Mugabe
 African Union
African Union
 Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo
Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo
 African Union
African Union
 Thabo Mbeki
Thabo Mbeki
 African Union
African Union
 Thomas Boni Yayi
Thomas Boni Yayi
 African Union
African Union
 Paul Kagame
Paul Kagame
 African Union
African Union
 Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
 African Union
African Union
 Moussa Faki
Moussa Faki
 African Union
African Union
 Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma
Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma
 African Union
African Union
 Jean Ping
Jean Ping
 African Union
African Union
 Alpha Oumar Konaré
Alpha Oumar Konaré
 African Union
African Union
 Amara Essy
Amara Essy
 African Union
African Union
 Mohamed Ould Ghazouani
Mohamed Ould Ghazouani
 African Union
African Union
 Azali Assoumani
Azali Assoumani
 African Union
African Union
 Macky Sall
Macky Sall
 African Union
African Union
 Félix Tshisekedi
Félix Tshisekedi
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Angola
Angola
 Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Benin
Benin
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Demokratische Arabische Republik Sahara
Demokratische Arabische Republik Sahara
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia

 Geography
Geography
 Ghana
Ghana
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kenya
Kenya
 Comoros
Comoros
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Liberia
Liberia
 Libya
Libya
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Mali
Mali
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Republik Südsudan
Republik Südsudan
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Sambia
Sambia
 Sao Tome und Principe
Sao Tome und Principe
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Togo
Togo
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Uganda
Uganda

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic


Die Afrikanische Union (arabisch الاتحاد الأفريقي, DMG al-Ittiḥād al-Ifrīqī, englisch African Union, französisch Union africaine, portugiesisch União Africana)[2] ist eine Internationale Organisation, die 2002 die Nachfolge der Organisation für Afrikanische Einheit (OAU) angetreten hat und sich für Kooperation auf allen Gebieten einsetzen soll. Sie ist ein Zusammenschluss von anfangs 53 afrikanischen Staaten (Westsahara ist Mitglied der Afrikanischen Union, sein völkerrechtlicher Status allerdings umstritten).
Der Hauptsitz der Organisation befindet sich im äthiopischen Addis Abeba, das Panafrikanische Parlament im südafrikanischen Midrand. Mitgliedstaaten der AU sind alle international allgemein anerkannten afrikanischen Staaten, einschließlich Westsaharas. Geplant ist in der AU unter anderem ein Afrikanischer Gerichtshof. Marokko wurde am 30. Januar 2017 nach 33 Jahren Abwesenheit wieder in die Afrikanische Staatengemeinschaft aufgenommen.[3]
非洲联盟(法语:Union Africaine; 英语:African Union),简称非盟(UA或AU),是一个包涵了55个非洲国家的联盟,是属于集政治、经济和军事于一体的全非洲性政治实体。非洲联盟于未来有计划统一使用货币、联合防御力量、以及成立跨国家的机关,这包括一个管理非洲联盟的内阁政府。此联盟的主要目的是帮助发展及稳固非洲的民主、人权、以及能永续发展的经济,除此之外亦希望减少非洲内部的武装战乱及创造一个有效的共同市场,最终目标是建立“非洲合众国”。
前身是1963年在埃塞俄比亚首都亚的斯亚贝巴成立的“非洲统一组织”。2002年7月在南非改组。[6]2017年在第28届非盟首脑会议上,摩洛哥获得了54个成员国中的42国同意,时隔33年重新成为该组织成员国,至此非洲联盟已涵盖所有非洲主权国家。[7]
アフリカ連合(アフリカれんごう)は、アフリカの国家統合体。アフリカ統一機構 (OAU) が、2002年に発展改組して発足した[3]。エチオピアのアディスアベバに本部を置いている。
1963年に創設されたアフリカ統一機構は、モロッコを除くアフリカ大陸の53か国(当時)全てが加入する世界最大の地域統合であったが、「統一機構」という名とは裏腹に各国間の内政不干渉を原則としており、各国で頻発する内戦やクーデターといった危機に対して有効な手段をとることができておらず、機能不全に陥っていた[4]。また、各国間の経済統合なども遅々として進んでいなかった。こうした状況に一石を投じたのが、1991年に締結されたアブジャ条約である。この条約では、アフリカ各国は2028年までに大陸統一通貨「アフロ」を導入し、アフリカ経済共同体(AEC)を創設することが謳われた。これによりアフリカ大陸が経済統合の方向に向かう中、より一層のアフリカ大陸の統合を進めるために新しい機構の創設が求められるようになった。
こうしたなか、アフリカ統一機構により強い権限を持たせ、政治・経済的統合を進めて最終的に欧州連合的な形態にアフリカ大陸を持っていくことを目的として、旧統一機構をアフリカ連合へと改組することを提案したのが、リビアの元首だったムアンマル・アル=カッザーフィーであった。カッザーフィーは1997年以降急速にアラブからアフリカへと外交重心を転換させていたが、1999年9月のスルトにおけるOAU首脳会談においてAUへの移行がリビアによって正式提案された[5]。この提案は各国に受け入れられ、アフリカ統一機構からアフリカ連合への移行のため、2000年7月のロメOAU首脳会議でアフリカ連合制定法(アフリカ連合を創設するための条約)が採択され、各国の批准を待って、2001年に発効した[6]。2002年7月のダーバン首脳会議を経て、アフリカ連合は正式に発足した。
アフリカ連合は、アフリカの一層高度な政治的経済的統合の実現及び紛争の予防解決への取組強化のため発足した地域統合体である。アフリカ諸国と諸国民間の一層の統一性及び連帯性の強化、アフリカの政治的経済的社会的統合の加速化、アフリカの平和と域内紛争や独裁政治の根絶、安全保障及び安定の促進、民主主義原則と国民参加統治の促進、持続可能な開発の促進、教育及び科学等での協力、グローバリゼーション時代におけるアフリカ諸国の国際的な地位向上、等を目指している。また、欧州連合(EU)をモデルとした地域統合を目標に掲げており、将来的には統一した国家へ発展させ、アフリカ合衆国を創ることも視野に入れている。
2001年にはアフリカ開発のための新パートナーシップ(NEPAD)を採択し、アフリカ大陸の開発のための指針を表明した。また、これに基づいて、各国が加盟国のガバナンスなどの状況を審査するアフリカン・ピア・レビュー・メカニズム(アフリカにおける相互審査システム、APRM)が創設され、2005年にはガーナの、2006年にはルワンダの報告書が作成された[7]。
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa, with exception of various territories of European possessions located in Africa. The bloc was founded on 26 May 2001 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and launched on 9 July 2002 in South Africa.[6] The intention of the AU is to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments. The most important decisions of the AU are made by the Assembly of the African Union, a semi-annual meeting of the heads of state and government of its member states. The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa.
In result of its geographical location, the African Union has an area of around 29 million km2 (11 million sq mi) and includes popular world landmarks, including the Sahara and the Nile.[7] They have adopted a gold, green and red based emblem and flag to represent the continental union, where they held a competition for citizens to design a flag in which they chose a submission to replace the old flag. Their main celebration occurs on Africa Day on 25 May. The primary languages spoken include Arabic, English, French and Portuguese and the languages of Africa. Within the African Union, there are official bodies such as the Peace and Security Council and the Pan-African Parliament.
L'Union africaine (UA) est une organisation d'États africains créée en 2002, à Durban en Afrique du Sud, en application de la déclaration de Syrte du 9 septembre 1999. Elle a remplacé l'Organisation de l'unité africaine2 (OUA). La mise en place de ses institutions (Commission, Parlement panafricain et Conseil de paix et de sécurité) a eu lieu en juillet 2003 au sommet de Maputo au Mozambique.
Son premier président a été le Sud-Africain Thabo Mbeki, précédemment président de l'OUA.
Ses buts sont d'œuvrer à la promotion de la démocratie, des droits de l'Homme et du développement à travers l'Afrique, surtout par l'augmentation des investissements extérieurs par l'intermédiaire du programme du Nouveau partenariat pour le développement de l'Afrique (NEPAD). Ce programme considère que la paix et la démocratie sont des préalables indispensables au développement durable.
Les objectifs de l'UA comportent la création d'une banque centrale de développement.
L'Unione africana (UA) è un'organizzazione internazionale comprendente tutti gli Stati africani, con sede ad Addis Abeba, in Etiopia. Les objectifs de l'UA comportent la création d'une banque centrale de développement.
Si tratta di un'organizzazione internazionale molto giovane, nata ufficialmente con il primo vertice dei capi di Stato e di governo del 9 luglio 2002 a Durban, in Sudafrica, durante il quale ne assunse la presidenza Thabo Mbeki, presidente sudafricano. Nel corso del vertice, al quale presenziava tra gli altri il segretario generale delle Nazioni Unite Kofi Annan, furono sottoscritti i primi atti riguardanti gli organi dell'Unione, ovvero il protocollo relativo allo stabilimento del Consiglio di pace e sicurezza e lo statuto della commissione, e furono stabilite regole e procedure per l'Assemblea, il consiglio esecutivo e il comitato dei rappresentanti permanenti.
Le fasi del processo di sviluppo precedenti al vertice di Durban avvennero all'interno dell'Organizzazione dell'unità africana. Nella sessione straordinaria del 1999 a Sirte, in Libia, (luogo di nascita del Leader libico Mu'ammar Gheddafi promotore dell'organizzazione, anche con cospicui capitali) l'Organizzazione decise la nascita della nuova Unione.
Il Sahara Occidentale è ammesso come Repubblica democratica araba Sahrawi, pur non essendo a tutti gli effetti indipendente trattandosi di un territorio conteso con il Marocco.
Nel 2000 fu adottato l'atto costitutivo, che entrò in vigore il 26 maggio 2001, un mese esatto dopo la sottoscrizione della Nigeria, il trentaseiesimo Stato ad averlo ratificato. Come previsto dall'atto per un anno vi fu coesistenza tra le due organizzazioni.
Il 15 agosto 2002 le è stato riconosciuto lo status di osservatore dell'Assemblea generale delle Nazioni Unite.
La Unión Africana (por su acrónimo UA, o AU en inglés u otras de sus lenguas oficiales) es una unión política formada por 55 Estados africanos. La UA se creó el 26 de mayo de 2001 en Adís Abeba y comenzó a funcionar el 9 de julio de 2002 en Durban (Sudáfrica),2 reemplazando a la Organización para la Unidad Africana (OUA). Las decisiones más importantes de la UA son tomadas por la Asamblea de la Unión Africana, una reunión semestral de jefes de Estado y de gobierno de sus Estados miembros. El secretariado de la UA, la Comisión de la Unión Africana, tiene su sede en Adís Abeba, capital de Etiopía.
Африка́нский сою́з (сокращённо АС, АфроСоюз) — международная межправительственная организация, объединяющая 55 государств Африки, правопреемник Организации африканского единства (ОАЕ). Основана 9 июля 2002 года[4]. Важнейшие решения в рамках организации принимаются на Ассамблее Африканского союза — собрании глав государств и правительств государств — членов организации, которое проводится раз в полгода. Секретариат Африканского союза и Комиссия Африканского союза расположены в Аддис-Абебе, столице Эфиопии. В феврале 2009 года было принято решение о преобразовании Комиссии Африканского союза в Полномочный орган Африканского союза (англ. African Union Authority)[5].
 *Political system of Russia
*Political system of Russia
 *President of the Russian Federation
*President of the Russian Federation

 Party and government
Party and government
 *President or Chairman
*President or Chairman

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
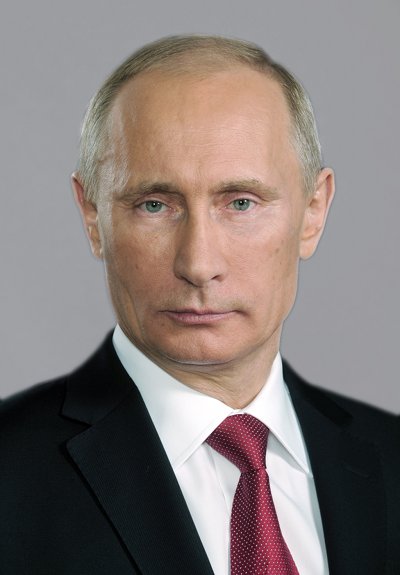

弗拉基米尔·弗拉基米罗维奇·普京(俄语:Владимир Владимирович Путин,罗马化:Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin,发音:[vɫɐˈdʲimʲɪr vɫɐˈdʲimʲɪrəvʲɪtɕ ˈputʲɪn] (ⓘ);1952年10月7日—),俄罗斯政治人物,出生于列宁格勒(今圣彼得堡),现任俄罗斯总统、国务委员会主席、联邦安全会议主席、全俄人民阵线领导人。曾任俄罗斯第5、9任总理、俄罗斯第3-4、6-7任总统,第3任统一俄罗斯主席[4]。
Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin (russisch Владимир Владимирович Путинⓘ/? Vladimir Vladimirovič Putin [vɫɐˈdʲimʲɪr vɫɐˈdʲimʲɪrəvʲɪtɕ ˈputʲɪn]; * 7. Oktober 1952 in Leningrad, Russische SFSR, Sowjetunion) ist ein russischer Politiker. Vom 31. Dezember 1999 bis 2008 war er und seit 2012 ist er wieder Präsident der Russischen Föderation. Von August 1999 bis Mai 2000 sowie von Mai 2008 bis 2012 war Putin Ministerpräsident Russlands.
 Javier Milei
Javier Milei

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 Argentinien
Argentinien

 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Labour Party
Labour Party
 Keir Starmer
Keir Starmer

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

Sir Keir Rodney Starmer [kɪə ˈstaːmə] KCB, KC, PC (* 2. September 1962 in Southwark, London) ist ein britischer Anwalt, Politiker und seit dem 5. Juli 2024 Premierminister des Vereinigten Königreiches. Er ist Mitglied der Labour Party und seit dem 4. April 2020 deren Vorsitzender.
基尔·罗德尼·斯塔默爵士 KCB KC(英语:Sir Keir Rodney Starmer;1962年9月2日—),英国工党籍政治人物和出庭律师,现任英国首相及工党党魁。施纪贤于2015年起担任霍本和圣潘克拉斯的国会议员(MP),由此步入政坛。他此前曾长期在司法领域工作,于2008年至2013年担任皇家检控署的刑事检控专员,2014年因其长期以来对司法领域的贡献获封爵士。施纪贤自2020年起接替杰瑞米·柯宾出任工党党魁,并担任反对党领袖。他在意识形态上认同进步主义和社会主义。
 Justin Trudeau
Justin Trudeau

 Party and government
Party and government
 *President or Chairman
*President or Chairman

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Canada
Canada
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1995 Gothenburg
1995 Gothenburg

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7


Kanada (englisch und französisch Canada) ist ein Staat in Nordamerika, der zwischen dem Atlantik im Osten und dem Pazifik im Westen liegt und nordwärts bis zum Arktischen Ozean reicht. Bundeshauptstadt ist Ottawa, die bevölkerungsreichste Stadt ist Toronto. Die einzige Landgrenze ist jene zu den USA im Süden und im Nordwesten. Kanada ist nach Russland der zweitgrößte Staat der Erde, hat aber mit knapp 38 Millionen Einwohnern nur eine Bevölkerungsdichte von 3,6 Personen pro km².
Die Besiedlung durch die First Nations begann spätestens vor 12.000 Jahren, die Inuit folgten vor rund 5000 Jahren. Ab dem späten 15. Jahrhundert landeten Europäer an der Ostküste und begannen um 1600 mit der Kolonisierung. Dabei setzten sich zunächst Franzosen und Engländer fest. In dieser Zeit breitete sich die Bezeichnung „Canada“ aus, das ursprünglich ein Name für ein Irokesendorf war. Frankreich trat 1763 seine Kolonie Neufrankreich an Großbritannien ab. Im Jahre 1867 gründeten drei britische Kolonien die Kanadische Konföderation. Mit dem Statut von Westminster erhielt das Land 1931 gesetzgeberische Unabhängigkeit, weitere verfassungsrechtliche Bindungen zum Vereinigten Königreich wurden 1982 aufgehoben. Nominelles Staatsoberhaupt ist Königin Elisabeth II., die durch den Generalgouverneur von Kanada vertreten wird.
Kanada ist ein auf dem Westminster-System basierender parlamentarisch-demokratischer Bundesstaat und eine parlamentarische Monarchie. Amtssprachen sind Englisch und Französisch. Die Unabhängigkeitsbestrebungen Québecs, die Stellung der frankophonen Kanadier und die Rechte der indigenen Völker (neben den First Nations und Inuit die Métis) sind wichtige Konfliktlinien in Staat und Gesellschaft. Die Themen Klimawandel und Umweltschutz, Einwanderungspolitik und Rohstoffabhängigkeit sowie das Verhältnis zum südlichen Nachbarn USA, von dem kulturell und historisch bedingt ein ambivalentes Bild besteht, kennzeichnen die öffentlichen Debatten.
加拿大(英语、法语:Canada,IPA读音:/ˈkænədə/(英)/kanada/(法))为北美洲国家,西抵太平洋,东至大西洋,北滨北冰洋,东北方与丹麦领地格陵兰相望,东部与圣皮埃尔和密克隆相望,南方及西北方与美国接壤。加拿大的领土面积达998万4670平方千米,为全球面积第二大国家。加拿大素有“枫叶之国”的美誉,渥太华为该国首都。加拿大被《福布斯》列于2020年退休宜居国的名单中[8]。
加拿大在1400年前即有原住民在此生活。15世纪末,英国和法国殖民者开始探索北美洲的东岸,并在此建立殖民地。1763年,当七年战争结束后,法国被迫将其几乎所有的北美殖民地割让予英国。在随后的几十年中,英国殖民者向西探索至太平洋地区,并建立了数个新的殖民地。1867年7月1日,1867年宪法法案通过,加拿大省分裂为安大略和魁北克两省,与新不伦瑞克、新斯科舍三个英属北美殖民地组成加拿大联邦。在随后100多年里,其它几块英属北美殖民地陆续加入联邦,组成现代加拿大。1931年12月11日,英国通过威斯敏斯特法令,令加拿大成为独立国家,但国家元首依旧是当时的英国国王乔治五世,且英国国会依旧掌握有加拿大的修宪权。1933年和1949年,加拿大民事案件和刑事案件的终审权分别从英国枢密院司法委员会移交至加拿大最高法院。1982年4月17日,英国女王兼加拿大女王伊丽莎白二世签署命令,将加拿大宪法修宪权移交加拿大国会,至此加拿大与英国的特殊关系终结。
加拿大是实行联邦制、君主立宪制及议会制的国家,由十个省和三个地区组成,女王伊丽莎白二世为国家元首及加拿大君主,而加拿大总督为其及政府的代表。加拿大是双语国家,英语和法语为官方语言,原住民的语言被认定为第一语言。由于地处高纬度及地广人稀,该国一直奉行积极吸纳外来移民的政策,以至人口亦以移民为主,有近五分之一的国民于国外出生,是世界上拥有种族及文化最为多元的国家之一。近年来移民大部分来自亚洲。[9]
得益于丰富的天然资源和高度发达的科技,加拿大是富裕、经济发达的国家。以国际汇率计算,加拿大的人均国内生产总值在全世界排名第十六,人类发展指数排名第十。它在教育、政府的透明度、自由度、生活品质及经济自由的国际排名都名列前茅。积极参与国际事务,是联合国、北大西洋公约组织、北美空防司令部、七大工业国组织、二十国集团、亚太经济合作组织、经济合作与发展组织、英联邦和法语圈的成员国及太平洋岛国论坛的对话伙伴。
カナダ(英・仏: Canada、英語発音: /ˈkænədə/ ![]() 聞く キャナダ[2]、フランス語発音: /kanada/ カナダ[3])は、北アメリカ大陸北部に位置し、10の州と3の準州からなる連邦立憲君主制国家。首都はオタワ(オンタリオ州)。
聞く キャナダ[2]、フランス語発音: /kanada/ カナダ[3])は、北アメリカ大陸北部に位置し、10の州と3の準州からなる連邦立憲君主制国家。首都はオタワ(オンタリオ州)。
イギリス連邦加盟国であり、英連邦王国のひとつ。アメリカ合衆国と国境を接する。国土面積は世界最大のロシアに次いで広い。
歴史的に先住民族が居住する中、外からやってきた英仏両国の植民地連合体として始まった。1763年からイギリス帝国に包括された。1867年の連邦化をきっかけに独立が進み、1931年ウエストミンスター憲章で承認され、1982年憲法制定をもって政体が安定した[4]。一連の過程においてアメリカと政治・経済両面での関係が深まった。連邦制をとり、連邦政府の運営は首相を中心に行われている。
Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern border with the United States, stretching 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi), is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
Various indigenous peoples inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years before European colonization. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and territories and a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom. This widening autonomy was highlighted by the Statute of Westminster of 1931 and culminated in the Canada Act of 1982, which severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the British parliament.
Canada is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy in the Westminster tradition, with a monarch and a prime minister who serves as the chair of the Cabinet and head of government. The country is a realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, a member of the Francophonie and officially bilingual at the federal level. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
A developed country, Canada has the seventeenth-highest nominal per-capita income globally as well as the thirteenth-highest ranking in the Human Development Index. Its advanced economy is the tenth-largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Canada is part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
Le Canada (prononcé [kanadɔ]4 Écouter ou [kanada]5 Écouter ; en anglais [ˈkænədə]6 Écouter) est un pays situé dans la partie septentrionale de l'Amérique du Nord. Monarchie constitutionnelle à régime parlementaire constituée en fédération, composée de dix provinces et trois territoires, le pays est encadré par l'océan Atlantique à l'est-nord-est et à l'est, par l'océan Arctique au nord-nord-ouest et au nord-est, enfin par l'océan Pacifique à l'ouest. Le Canada comprend deux frontières terrestres avec les États-Unis, l'une au sud et l'autre à l'ouest-nord-ouest avec l'Alaska ainsi qu'une frontière maritime avec la France, par le biais de l'archipel de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon, et le Danemark, par le biais du Groenland. Le territoire terrestre canadien s'étend sur 10 millions de kilomètres carrés, ce qui en fait le deuxième pays du monde pour la superficie après la Russie7. En 2019, il compte plus de 37 millions d'habitants1 et est ainsi le 37e pays du monde en ce qui concerne la population. Le territoire contient plus de 31 700 lacs8, ce qui fait du Canada le pays possédant parmi les plus grandes réserves d'eau douce du globe9,10. Les langues officielles au niveau fédéral sont l'anglais et le français. La capitale fédérale est Ottawa et la monnaie le dollar canadien11.
Les premiers occupants du territoire canadien ont été les Amérindiens, dont les migrations remontent à environ 15 000 ans12 lors de la dernière glaciation qui a abaissé le niveau des océans et créé un pont terrestre reliant l'Eurasie à l'Amérique, permettant à ceux-ci de s'installer13.
Si des Vikings s'installent dès le XIe jusqu'au XIVe siècle, les premières explorations des Européens débutent à la fin du XVe siècle, culminant avec les expéditions du Français Jacques Cartier dans le golfe du Saint-Laurent. Après quelques expériences infructueuses dans la première moitié du XVIe siècle, le 5 août 1583, la colonie anglaise de Terre-Neuve est fondée, suivie des premiers comptoirs pérennes français sur le continent entre 1600 et 1608, amorçant le processus de la colonisation européenne. Par la suite, d'autres colonies britanniques et françaises sont établies, notamment dans la région de la côte Atlantique (Nouvelle-Écosse, Acadie), dans la vallée du fleuve Saint-Laurent et la péninsule du Labrador (Nouvelle-France) ainsi que dans la zone arctique, tandis que d'autres puissances européennes telles l'Espagne et la Russie explorent le reste du territoire canadien. À la suite de divers conflits dont surtout la guerre de Succession d'Espagne (1701-1714), la guerre de la Conquête (1754-1760) et la guerre d'indépendance des États-Unis (1775-1783), la Grande-Bretagne gagne et perd des territoires au XVIIIe siècle, aboutissant à ce qui correspond au territoire canadien d'aujourd'hui. Trois de ces colonies se fédèrent le 1er juillet 1867 et forment le dominion du Canada, nation indépendante sous domination partielle de la Couronne britannique. Sa souveraineté totale est ensuite garantie par la déclaration Balfour de 1926, le Statut de Westminster de 1931 et le rapatriement de sa Constitution en 1982.
L'histoire contemporaine du Canada a été marquée par une vigoureuse expansion territoriale, la ruée vers l'or et la participation à la Première Guerre mondiale. Le pays fut durement touché par la Grande Dépression en 1929 mais son économie rebondit grâce à sa participation à la Seconde Guerre mondiale, où il émergea comme puissance moyenne et fut l'un des vainqueurs en tant que membre des Alliés14.
En 2015, le Canada possède le dixième revenu par habitant le plus élevé15, et est classé neuvième par le PNUD en termes d'indice de développement humain16. Il s'agit de la dixième puissance économique mondiale par son PIB en 2017, les principaux secteurs de son économie étant les services, les télécommunications, l'agriculture, l'énergie, l'aéronautique et la construction automobile. Il entretient de forts liens avec les États-Unis (pays anglo-saxon le plus proche et partageant une partie de son histoire), qui sont son principal client et fournisseur avec lequel perdure une des relations les plus intimes et les plus approfondies au monde entre deux nations. Le pays est un des meneurs en matière de recherche scientifique17, et se range parmi les plus éduqués du monde en étant classé premier par le nombre d'adultes possédant une éducation post-secondaire, avec 51 % d'entre eux ayant au moins atteint un diplôme post-secondaire chez sa population âgée de 25 à 64 ans18. Le Canada est membre du G7, du G20, de l'Accord de libre-échange nord-américain (ALENA), de l'Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord (OTAN), de la Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (APEC), de l'Organisation des États américains (OEA), de l'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE), de l'Organisation des Nations unies (ONU), du Commonwealth et de l'Organisation internationale de la francophonie.
Il Canada (AFI: /ˈkanada/)[5] o Canadà (AFI: /kanaˈda/)[6] è uno Stato indipendente dell'America Settentrionale[7] bagnato dall'Atlantico a est, dal Mar Glaciale Artico a nord e dall'Oceano Pacifico a ovest. Con una superficie di 9897170 km² è il secondo paese del mondo per superficie totale dopo la Russia. Confina solo con il territorio degli Stati Uniti d'America: quelli continentali a sud, in buona parte lungo la linea del 49º parallelo Nord, e con lo Stato dell'Alaska a nord-ovest quasi interamente lungo il 141º meridiano Ovest:[7] si tratta del confine terrestre tra due Stati più lungo del mondo (8893 km).
Abitato, prima dell'arrivo europeo sul continente, da popolazioni aborigene, il territorio dell'attuale Canada fu colonizzato da Francia e Regno Unito a inizio XVII secolo[7] a partire dalla costa atlantica. I francesi persero in seguito i loro territori progressivamente a favore del Regno Unito: dapprima (1713) con il trattato di Utrecht alla fine della guerra di successione spagnola, con cui Terranova e la baia di Hudson furono cedute da Luigi XIV; a seguire nel 1763 dopo la sconfitta nella guerra franco-indiana, teatro nordamericano della guerra dei sette anni e, infine, con la vendita di Napoleone (1803) della Louisiana francese agli Stati Uniti d'America e delle sue ultime rimanenze oltre il confine canadese al Regno Unito. Il 1º luglio 1867 nacque la federazione canadese con l'unione delle tre colonie del Nord America Britannico di Nuova Scozia, Nuovo Brunswick e Canada,[8] che in seguito divennero quattro per la scissione della provincia del Canada in Ontario e Québec. Nel corso del tempo si aggiunsero sempre più province che avrebbero poi formato l'odierno stato nordamericano. Costituitosi in Stato unitario il 1º luglio 1867 come Confederazione canadese per iniziativa della Corona britannica, divenne formalmente indipendente l'11 dicembre 1931, data di promulgazione dello statuto di Westminster con cui il Regno Unito affrancò molti dei suoi ex dominion. Infine, con la nuova legge sul Canada del 1982 (il cosiddetto patriation o "rimpatrio") il Regno Unito abdicò anche al potere formale di modifica della costituzione canadese garantitogli dallo Statuto del 1931.
Il Canada è uno Stato membro del Commonwealth britannico del quale è uno dei sedici reami: di conseguenza, benché indipendente,[7] ha come capo di Stato il sovrano del Regno Unito, al 2020 la regina Elisabetta II che, nelle questioni di Stato riguardanti il Canada, agisce con il titolo di Elisabetta II Regina del Canada. In rappresentanza del sovrano agisce localmente il governatore generale del Canada, il quale è capo di Stato de facto, avendo le prerogative di accreditare il corpo diplomatico, assegnare l'incarico di primo ministro e nominare i giudici della Corte suprema, convocare le elezioni generali federali e in talune occasioni rappresentare il Paese a livello internazionale. Dal 1959 esiste la prassi non ufficiale di nominare alternativamente un governatore generale anglofono e uno francofono per rispetto dei due maggiori gruppi linguistici del Paese.
Il sistema politico è


