
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x400米接力
男子4x400米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 巴哈马
巴哈马
 英联邦国家
英联邦国家

 地理
地理
 加勒比地区
加勒比地区

 地理
地理
 西印度群岛
西印度群岛
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2001 Edmonton
2001 Edmonton
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 *田径
*田径
 女子4x400米接力
女子4x400米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 原子弹
原子弹
 金砖国家峰会
金砖国家峰会

 历史
历史
 公元 1500 - 2000
公元 1500 - 2000

 历史
历史

 历史
历史
 公元 2000 - 2100
公元 2000 - 2100
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1993 Stuttgart
1993 Stuttgart




 军事、国防和装备
军事、国防和装备
 核武器
核武器

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 金砖国家
金砖国家
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 丝绸之路
丝绸之路
 上海合作组织
上海合作组织

 亚洲国家
亚洲国家

 欧洲国家
欧洲国家

 联合国
联合国
 联合国安全理事会常任理事国
联合国安全理事会常任理事国
 氢弹
氢弹
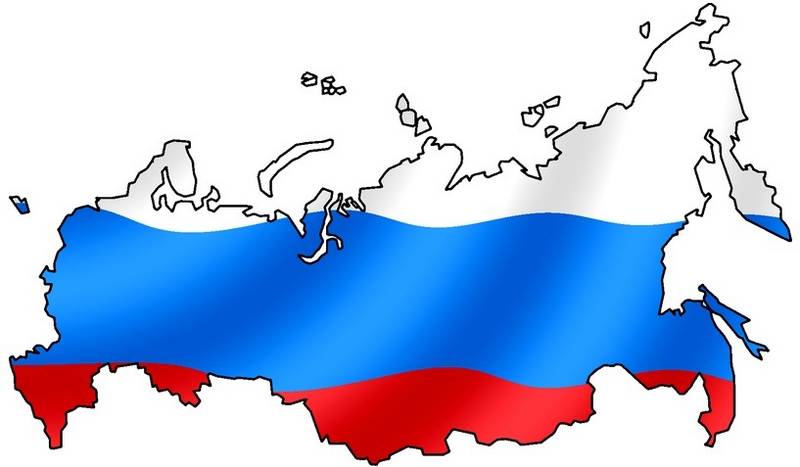
Russland (russisch Россия [rɐˈsʲijə] , Transkription Rossija) bzw. die Russische Föderation (oder der russischen Bezeichnung entsprechend Russländische Föderation; russisch Российская Федерация, , Transkription Rossijskaja Federazija)[9] ist ein souveräner, föderativer Staat im nordöstlichen Eurasien und mit etwa 17 Millionen Quadratkilometern flächenmäßig der größte Staat der Erde. Russland umfasst mehr als ein Achtel der bewohnten Landmasse der Erde und steht mit 144 Millionen Einwohnern (2017) an 9. Stelle der bevölkerungsreichsten Länder; es ist zugleich eines der am dünnsten besiedelten. Der europäische Teil des Staatsgebiets ist viel dichter besiedelt und verstädtert als der über dreimal so große asiatische Teil: Etwa 77 % der Bevölkerung (110 Millionen Einwohner) leben westlich des Urals. Die Hauptstadt Moskau ist eine der größten Städte und Metropolregionen der Welt; als weiteres wichtiges Zentrum gilt Sankt Petersburg, das zwischen 1712 und 1918 Hauptstadt war und eine Brücke für Kunst und Kultur aus Westeuropa bildete.
Die nächstgrößeren Millionenstädte Russlands sind Nowosibirsk in Sibirien, Jekaterinburg im Ural und Nischni Nowgorod an der Wolga. Weitere Großstadtregionen sind Tscheljabinsk, Ufa und Kasan.
Das heutige Russland entwickelte sich aus dem Großfürstentum Moskau, einem Teilfürstentum des früheren ostslawischen Reiches Kiewer Rus, zu einem über einhundert Ethnien zählenden Vielvölkerstaat, wobei ethnische Russen heute fast 80 Prozent der Bevölkerung ausmachen. Die föderale Gliederung Russlands besteht aus acht Föderationskreisen und 85 Föderationssubjekten.
Die Russische Föderation ist „Fortsetzerstaat“[10] der Sowjetunion in internationalen Organisationen, Atommacht und ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates. Nach der Erholung von der postkommunistischen Transformationskrise der 1990er Jahre wurde Russland die nach Kaufkraftparität sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt, zwischen Deutschland und Brasilien (Schätzung für 2016).[11]
Russlands Rohstoffreserven sind mit etwa 20 bis 30 % die wahrscheinlich größten der Welt,[12][13][14] mit erheblichen Vorkommen von Primärenergieträgern, vor allem Erdgas.
Russland gehört zu den anerkannten Nuklearmächten und besitzt das weltgrößte Arsenal an Massenvernichtungswaffen. Russland ist Großmacht und Regionalmacht und wird teilweise als potentielle Supermacht betrachtet.[15] Es ist ständiges Mitglied im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen, G 20-Mitglied, Mitglied des Europarates, der APEC, der Shanghaier Organisation für Zusammenarbeit (SCO), der OSCE, der WTO; es ist führendes Mitglied in der Gemeinschaft Unabhängiger Staaten (GUS), der Organisation des Vertrags über kollektive Sicherheit (OVKS) und der Eurasischen Wirtschaftsunion (mit Armenien, Kasachstan, Kirgisistan und Weißrussland).
Russland ist ein Schwellenland im Bereich des oberen mittleren Einkommens.[16] Im Human Development Index der Vereinten Nationen stand Russland 2016 mit 0,8 (von 1) auf Platz 49,[17] der Gini-Koeffizient lag bei 37,7.
Das Regierungssystem Russlands wird von Politikwissenschaftlern entsprechend dem Wortlaut der Verfassung meist formal als Verbindung präsidentieller und parlamentarischer Formen eingeordnet; die Verfassungswirklichkeit des politischen Systems entspricht jedoch eher den Modellen defekter Demokratien oder der Postdemokratie, zumal der Präsident fast autokratische Macht ausübt.[18][19][20] Für die politische Ordnung wird in Russland gelegentlich von offizieller Seite der Begriff „Gelenkte Demokratie“ im affirmativen Sinne gebraucht.[21]
Die Annexion der Krim im März 2014 belastet die Beziehungen zwischen Russland und dem Westen. Der russischen Regierung wird vorgeworfen, die europäische Friedensordnung zu verletzen.[22]
Das Land war 2016 mit 69,9 Mrd. Dollar für 4,1 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit im internationalen Vergleich hinter den Vereinigten Staaten mit 611 Mrd. Dollar (36 %) und China mit 215 Mrd. Dollar (13 %) auf Platz 3, gefolgt von Saudi-Arabien und Indien.[23][24]
俄罗斯联邦[9](俄语:Российская Федерация,缩写为РФ),通称俄罗斯(Россия)[10],是位于欧亚大陆北部的联邦共和国,国土横跨欧亚两大洲,为世界上土地面积最大的国家,拥有1709万平方公里的面积,占地球陆地面积八分之一[11][12];它也是世界上第九大人口国家,拥有1.4亿人口,77%居住于其较为发达的欧洲部分。俄罗斯国土覆盖整个亚洲北部及东欧大部,横跨11个时区,涵盖广泛的环境和地形。拥有全世界最大的森林储备和含有约世界四分之一的淡水的湖泊[13]。俄罗斯有十四个陆上邻国(从西北方向起逆时针序):挪威、芬兰、爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚、立陶宛、波兰、白俄罗斯、乌克兰、格鲁吉亚、阿塞拜疆、哈萨克斯坦、中国、蒙古和朝鲜(其中立陶宛和波兰仅与俄罗斯外飞地加里宁格勒州接壤),另外与阿布哈兹和南奥塞梯两个只有俄罗斯承认的非联合国会员国接壤。同时,俄罗斯还与日本、美国、加拿大、格陵兰(丹麦)、冰岛、瑞典、土耳其隔海相望。俄罗斯北部和东部分别为北冰洋和太平洋包围,西北和西南则分别可经由波罗的海和黑海通往大西洋。
俄罗斯历史始于欧洲的东斯拉夫民族,聚集区域自公元3世纪至8世纪逐渐扩大[14]。在9世纪,源自北欧的瓦良格人武士精英建立了基辅罗斯这个中世纪国家并开始统治。公元988年,国家从拜占庭帝国采纳了东正教会,随后由此开始,千年拜占庭与斯拉夫文化的融合成为了今日的俄罗斯文化[15]。基辅罗斯最终解散分化为众多公国,被蒙古人逐一击破,并均在13世纪成为了金帐汗国的一部分。莫斯科大公自14世纪起逐渐崛起并统一周边俄罗斯诸侯国,在15世纪成功从金帐汗国独立,且成为了基辅罗斯文化和政治的继承者。16世纪起伊凡四世自称沙皇,自诩“第三罗马”。在18世纪,俄罗斯沙皇国通过征服、吞并和探索而扩张。彼得一世称帝成立了俄罗斯帝国,最终成为史上领土第三大帝国,疆域最大曾自中欧的波兰连绵至北美的阿拉斯加[16][17]。
1917年俄国革命后,俄罗斯苏维埃联邦社会主义共和国成为了世界上第一个宪法意义上的社会主义国家[18],并成为随后成立的苏维埃社会主义共和国联盟的主体和其最大的加盟共和国。二战时期,苏联为同盟国的胜利扮演了决定性的角色。在战后其崛起成为公认的超级大国,并在冷战时期与美国互相竞争。苏联时期产生了20世纪的许多最重要的科技成就,其中包括世界第一颗人造地球卫星,以及首次将人类送入太空。在1990年,苏联为世界上第二大经济体[19],且拥有世界上最多的常备军人以及最多的大规模杀伤性武器库存。1991年苏联解体后,包括俄罗斯在内的15个共和国从原苏联独立;身为原苏联最大的加盟共和国,俄罗斯通过修宪改制为俄罗斯联邦,成为原苏联的唯一法理继承国家,政体采用联邦制、民主共和制及半总统制。
截至2015年,俄罗斯根据国民生产总值为世界第13大经济体,根据购买力平价为世界第六大经济体。俄罗斯拥有世界上最大储量的矿产和能源资源[20],是世界上最大的石油和天然气输出国[21][22]。俄罗斯为世界大国之一,为认定的拥核国家,联合国安理会常任理事国,G20、欧洲理事会、亚太经合组织、上合组织、欧安组织、世贸组织和金砖国家成员。它也是独联体、集体安全条约组织的领导者和欧亚经济联盟创始成员。俄罗斯亦是世界八大工业国之一。
ロシア連邦(ロシアれんぽう、ロシア語: Российская Федерация:英語名 Russian Federation)、またはロシア (Россия) は、ユーラシア大陸北部にある共和制及び連邦制国家。
地理的にロシアの国境は、北西から南東へ、ノルウェー、フィンランド、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニアおよびポーランド(ともにカリーニングラード州と隣接)、ベラルーシ、ウクライナ、ジョージア、アゼルバイジャン、カザフスタン、中華人民共和国、モンゴル国、朝鮮民主主義人民共和国と接する。海上境界線としては、日本とはオホーツク海・宗谷海峡・根室海峡・珸瑤瑁水道、アメリカ合衆国とはベーリング海峡でアラスカ州と接する。ロシアの面積は17,075,400km2で世界最大であり、地球上の居住地域の8分の1を占める。2012年時点で、ロシアの人口は1億4300万人で世界第9位である[3]。国土は北アジア全体および東ヨーロッパの大部分に広がることに伴い、ロシアは11の標準時を有し、広範な環境および地形を包含する。
ロシアの歴史は、3世紀から8世紀までの間にヨーロッパで認識され始めた東スラヴ人の歴史に始まる[4]。9世紀、ヴァリャーグの戦士の精鋭およびその子孫により設立及び統治されて、キエフ大公国の中世国家が誕生した。988年、東ローマ帝国から正教会を導入し、次の千年紀のロシア文化を特徴付ける東ローマ帝国およびスラブ人の文化の統合が始まった[5]。キエフ大公国は最終的には多くの国に分裂し、キエフ大公国の領土の大部分はモンゴルに制圧され、遊牧国家ジョチ・ウルスの属国になった[6]。モスクワ大公国は次第に周辺のロシアの公国を再統合し、ジョチ・ウルスからの独立を獲得し、キエフ大公国の文化的および政治的な遺産を支配するようになった。18世紀までにモスクワ大公国は、王朝による征服・併合、シェレホフ提督による探検を通じ、史上第3位の大帝国であるロシア帝国となり、版図がポーランドから北米のアラスカまで広がった[7][8]。
しかし帝国は国土に見合う開発資金を国内で捻出することができなかった。サンクトペテルブルクの貿易為替銀行にドイツ銀行を参加させたが、露仏同盟を結んで以来国際金融市場から外資が雪崩れ込むようになった。
ロシア革命後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国がソビエト連邦最大かつ指導的な構成国となり、世界初の憲法上の社会主義国および広く認められた超大国となり[9]、第二次世界大戦において連合国の勝利に決定的な役割を果たした[10][11]。ソビエト時代には、世界初の人工衛星および世界初の有人宇宙飛行を含む20世紀の最も重要な複数の技術的偉業を経験した。1991年のソ連崩壊後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国は自らをロシア連邦として再構成し、連邦国家の継続的な法人格として認識されている。ソ連政府は国民にあまねく賃貸住宅を配分していたが、それらを建設するだけで巨額の財政負担となっており、財政再建中のロシア連邦がリフォームすることなどかなわず、無償で住民が物件を取得できるようにしてしまい急激な私有化を進めた[12]。私有化されていないものは地方自治体への譲渡が進んで、人口減少社会となる中、若者向けに低家賃で貸し出されている[12]。
1996年11月、ロシアは第一回だけで10億ドルのユーロ債を起債した[13]。それまでの累積ユーロ債発行額は160億ドルほどに達した[13]。1997年、第一回サンクトペテルブルク国際経済会議が開かれた。1998年、ロシア財政危機。1999年、ロスチャイルド代理人のアルフレッド・ハルトマン博士が資金洗浄の国内捜査線上で名前をとりあげられた。
2003年、ミハイル・ホドルコフスキーが脱税などの罪で逮捕・起訴され、ユコスの社長を辞任した。シブネフチとの合併が取り消されるなどして株価が乱高下し、内部者取引が横行した。2005年でロシアの住宅私有化率は63%に達し[12]、国際的な不動産価格の下落へつながっていった。2007年、ホドルコフスキーを除くユコス株主らは、ロシア政府がユコスを破綻させたとしてハーグの常設仲裁裁判所へ提訴した(ユコス破綻事件)。2010年6月26日、政府側のロスネフチに賠償命令が出た。7月27日、内部者取引と株価操作を取り締まる法案がようやく批准された[14]。これは翌年から施行された。
2014年ウクライナ騒乱が2月に起きてVTBが態度を硬化させた。7月、ユコス破綻事件で政府は19億ユーロの賠償金支払いを命じられていたが、12月に欧州人権裁判所が政府の上訴を棄却した[15]。2016年4月、ハーグ地区裁判所が、ロシア政府に株主らへ500億ドルの賠償金支払いを命じた常設仲裁裁判所の判決を棄却した[16]。
2014年時点で、ロシアの経済は名目GDPで世界第9位かつ購買力平価で世界第6位であった[17]。ロシアの豊富な鉱物およびエネルギー資源は世界最大の埋蔵量であり[18]、世界最大の原油生産国および世界最大の天然ガス生産国の一つである。ロシアは核保有を認められた5大国の一つであり、世界最大の大量破壊兵器保有量がある。ロシアは列強および国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、独立国家共同体の指導国であるだけでなく、G20、欧州評議会、アジア太平洋経済協力、上海協力機構、ユーラシア経済共同体、欧州安全保障協力機構 (OSCE)、世界貿易機関 (WTO) 加盟国である。
Russia (Russian: Росси́я, tr. Rossiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijə]), officially the Russian Federation[12] (Russian: Росси́йская Федера́ция, tr. Rossiyskaya Federatsiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijskəjə fʲɪdʲɪˈratsɨjə]), is a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and North Asia.[13] At 17,125,200 square kilometres (6,612,100 sq mi),[14] Russia is the largest country in the world by area, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area,[15][16][17] and the ninth most populous, with about 146.77 million people as of 2019, excluding Crimea.[8] About 77% of the population live in the western, European part of the country. Russia's capital, Moscow, is the largest metropolitan area in Europe proper[18] and one of the largest cities in the world; other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod. Extending across the entirety of Northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia spans eleven time zones and incorporates a wide range of environments and landforms. From northwest to southeast, Russia shares land borders with Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland (both with Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and North Korea. It shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk and the U.S. state of Alaska across the Bering Strait. However, Russia recognises two more countries that border it, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, both of which are internationally recognized as parts of Georgia.
The East Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD.[19] Founded and ruled by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, the medieval state of Rus arose in the 9th century. In 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire,[20] beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium.[20] Rus' ultimately disintegrated into a number of smaller states; most of the Rus
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x100米接力
男子4x100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x400米接力
男子4x400米接力
 原子弹
原子弹

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 欧盟的历史
欧盟的历史

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 *创始国
*创始国
 法国
法国

 地理
地理

 地理
地理
 ***IMF发达国家
***IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 第二级
第二级
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis




 军事、国防和装备
军事、国防和装备
 核武器
核武器

 北约会员国
北约会员国

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 七国集团
七国集团

 欧洲国家
欧洲国家

 联合国
联合国
 联合国安全理事会常任理事国
联合国安全理事会常任理事国
 氢弹
氢弹

Frankreich ![]() [ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
[ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
Im 17. und 18. Jahrhundert hatte Frankreich eine europäische Führungsrolle und Vormachtstellung inne. Bedeutend war die politische und kulturelle Ausstrahlung: Die Hofhaltung Ludwigs XIV. wurde zum Vorbild absolutistischer Staaten in ganz Europa und die Französische Revolution mit der Erklärung der Menschen- und Bürgerrechte gab zusammen mit Okkupationen durch Napoleon Bonaparte in vielen Ländern den Auftakt zu der immer wieder von Rückschlägen unterbrochenen Entwicklung zur Demokratie. In Übersee baute Frankreich zweimal ein Kolonialreich auf. Das erste umfasste u. a. große Teile Nordamerikas und ging großenteils Mitte des 18. Jahrhunderts im Siebenjährigen Krieg verloren; das zweite mit Schwerpunkt in Afrika war im 19. und frühen 20. Jahrhundert das zweitgrößte der Welt. Im 21. Jahrhundert gilt Frankreich mit Deutschland als treibende Kraft der europäischen Integration.
Die Französische Republik wird in ihrer Verfassung als unteilbar, laizistisch, demokratisch und sozial erklärt.[7] Ihr Grundsatz lautet: „Regierung des Volkes durch das Volk und für das Volk“. Frankreich steht auf Rang 26 des Index der menschlichen Entwicklung (2019) der Vereinten Nationen.[8] Gemessen am nominalen Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist es die sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt.[5] Die Kaufkraft pro Einwohner betrug 2016 19.254 Euro (zum Vergleich: Deutschland 21.879 Euro, Großbritannien 21.141 Euro).[9] Lebensstandard, Bildungsgrad und durchschnittliche Lebenserwartung[10] gelten als hoch. Als meistbesuchtes Land der Welt empfängt Frankreich rund 83 Millionen ausländische Touristen pro Jahr.[11][12]
Frankreich unterhält die drittstärksten Streitkräfte innerhalb der NATO und das größte Heer der Europäischen Union. Es ist eines der fünf ständigen Mitglieder des UN-Sicherheitsrates und hatte 2010 als Atommacht die weltweit dritthöchste Anzahl an Kernwaffen.[13] Das Land ist Gründungsmitglied der Europäischen Union und der Vereinten Nationen, Mitglied der Frankophonie, der G7, der G20, der NATO, der Organisation für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (OECD), der Welthandelsorganisation (WTO) und der Lateinischen Union.
法兰西共和国(法语:République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]),通称法国(法语:France [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() 聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
今日之法国本土于铁器时代由高卢人(凯尔特人的一支)征服,前51年又由罗马帝国吞并。486年法兰克人(日耳曼人的一支)又征服此地,其于该地域建立的早期国家最终发展成为法兰西王国。法国至中世纪末期起成为欧洲大国,国力于19-20世纪时达致巅峰,建立了世界第二大殖民帝国,亦为20世纪人口最稠密的国家[来源请求],现今则是众多前殖民地的首选移民国[8]。在漫长的历史中,法国培养了不少对人类发展影响深远的著名哲学家、文学家与科学家,亦为文化大国,具有第四多的世界遗产[9]。
フランス共和国(フランスきょうわこく、フランス語: République française、通称:フランス、France)は、西ヨーロッパ、カリブ、太平洋およびインド洋に位置する共和制国家。首都はパリ。
フランス・メトロポリテーヌ(本土)は地中海からイギリス海峡及び北海へ、ライン川から大西洋へと広がる。この他世界各地に海外地域および領土を有する。
なお、フランス・メトロポリテーヌ周辺は北東がドイツとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東をスイスとイタリア、南にスペインと国境を接している。
フランスは国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、G7・G20、欧州評議会、世界貿易機関、経済協力開発機構、北大西洋条約機構、パリクラブおよびフランコフォニー国際機関における主要なメンバーである。国際政治においてはこれらの理由から、政治・経済・文化において強力な影響を及ぼす列強の一角に数えられており、ヨーロッパにおける「ビッグ4」の1つでもある。
核拡散防止条約により核兵器の保有を認められた5つの公式核保有国の1つであり、その他にアメリカ合衆国を除けば世界で唯一の原子力空母「シャルル・ド・ゴール」や原子力潜水艦を保有しており、強力な軍事力を持っている。
GDPは名目GDP世界第7位かつ購買力平価で世界第10位・ユーロ圏ではドイツに次ぐ第2位の経済力を有する国であり、高い人間開発指数を持つ先進国として知られる。数多くの世界遺産を抱えており、世界で最も観光客の多い国の1つである。
歴史的にはデカルト、モンテスキュー、ルソー、サルトルといった哲学者やマリ・キュリー、パストゥールといった科学者、モネ、セザンヌ、ゴーギャン、クールベ、ドラクロワといった芸術家の故国もしくは活躍の舞台であり、また百年戦争やフランス革命、ナポレオン戦争といった歴史的事象の主要な舞台であった。
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() ), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks arrived in 476 and formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987.
In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom in which the king's authority was barely felt. King Philip II achieved remarkable success in the strengthening of royal power and the expansion of his realm, defeating his rivals and doubling its size. By the end of his reign, the kingdom had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts for the French throne, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, various wars with rival powers, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world.[14] The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. But France once again emerged as Europe's dominant cultural, political and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War.[15] Inadequate economic policies, an inequitable taxation system as well as endless wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence), left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the absolute monarchy, replaced the Ancien Régime with one of history's first modern republics and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of European and world history. The collapse of the empire initiated a period of relative decline, in which France endured a tumultuous succession of governments until the founding of the French Third Republic during the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Subsequent decades saw a period of optimism, cultural and scientific flourishing, as well as economic prosperity known as the Belle Époque. France was one of the major participants of World War I, from which it emerged victorious at great human and economic cost. It was among the Allied powers of World War II, but was soon occupied by the Axis in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, the short-lived Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The current Fifth Republic was formed in 1958 by Charles de Gaulle. Algeria and most French colonies became independent in the 1960s, with the majority retaining close economic and military ties with France.
France retains its centuries-long status as a global centre of art, science and philosophy. It hosts the fifth-largest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites and is the world's leading tourist destination, receiving over 89 million foreign visitors in 2018.[16] France is a developed country with the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and ninth-largest by PPP; in terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[17] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy and human development.[18][19] It remains a great power in global affairs,[20] being one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. France is a founding and leading member of the European Union and the Eurozone,[21] as well as a key member of the Group of Seven, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and La Francophonie.
La France (Écouter), en forme longue depuis 1875 la République française (Écouter), est un État souverain transcontinental dont le territoire métropolitain est situé en Europe de l'Ouest et dont le territoire ultramarin est situé dans les océans Indien, Atlantique et Pacifique ainsi qu'en Amérique du Sud. Il s'agit de l'unique pays au monde à s'étendre sur treize fuseaux horaires. Le pays a des frontières terrestres avec la Belgique, le Luxembourg, l'Allemagne, la Suisse, l'Italie, l'Espagne et les deux principautés d'Andorre et de Monaco en Europe, auxquelles s'ajoutent les frontières terrestres avec le Brésil, le Suriname et les Pays-Bas aux Amériques. La France dispose d'importantes façades maritimes sur l'Atlantique, la Méditerranée, le Pacifique et l'océan Indien, lui permettant de bénéficier de la plus vaste zone économique exclusive du monde6.
La France est une république constitutionnelle unitaire ayant un régime semi-présidentiel. La devise de la République est depuis 1875 « Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité » et son drapeau est constitué des trois couleurs nationales : bleu, blanc, rouge. Son hymne national est La Marseillaise, chant patriotique hérité de la Révolution française. Son principe constitutif est la démocratie : le « gouvernement du peuple, par le peuple et pour le peuple ». Elle a pour capitale Paris et pour langue officielle le français depuis 1539, remplaçant le latin. Ses monnaies sont l'euro depuis 2002 dans la majeure partie du pays et le franc Pacifique dans ses territoires de l'océan Pacifique.
La France s'appelle ainsi depuis 1214, lorsque les troupes du roi Philippe Auguste battent celles de l’empereur germanique à Bouvines. La France tire son nom des
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4x400米接力
女子4x400米接力
 联邦德国
联邦德国

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 欧盟的历史
欧盟的历史

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟
 *创始国
*创始国

 地理
地理

 地理
地理
 ***IMF发达国家
***IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 第二级
第二级
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2001 Edmonton
2001 Edmonton
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens

 北约会员国
北约会员国

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 七国集团
七国集团

 欧洲国家
欧洲国家

(Vollform: Bundesrepublik Deutschland) ist ein föderal verfasster Staat in Mitteleuropa, der aus den 16 deutschen Ländern besteht. Die Bundesrepublik ist ein freiheitlich-demokratischer Rechtsstaat[8] und stellt die jüngste Ausprägung des deutschen Nationalstaates dar.[9] Mit rund 82,8 Millionen Einwohnern (31. Dezember 2016) zählt Deutschland zu den dicht besiedelten Flächenstaaten.
An Deutschland grenzen neun Staaten, im Norden die Gewässer der Nord- und Ostsee und im Süden das Bergland der Alpen. Es liegt in der gemäßigten Klimazone. Bundeshauptstadt sowie bevölkerungsreichste deutsche Stadt ist Berlin. Weitere bedeutende Metropolen sind Hamburg, München, Köln, Frankfurt, Stuttgart und Düsseldorf; größter Ballungsraum ist das Ruhrgebiet. Deutschland gilt international als das Land mit der zweithöchsten Zahl von Einwanderern nach den Vereinigten Staaten (Stand 2015).[10][11] Seine Bevölkerung ist die zweitälteste und hat mit 1,47 Kindern pro Frau (2014) eine der niedrigsten Geburtenraten der Welt.[12]
Auf dem Territorium des heutigen Deutschlands wurden frühe Siedlungsformen von vor etwa 500.000 Jahren nachgewiesen, wie Funde vom Heidelbergmenschen, vom Neandertaler sowie von einigen der ältesten Kunstwerke der Menschheit aus der Altsteinzeit belegen. Seit der Antike ist die lateinische Bezeichnung Germania für das Siedlungsgebiet der Germanen bekannt, seit dem 4. Jahrhundert ist die Verwendung des Begriffes deutsch in althochdeutscher Form belegt. Das seit dem 10. Jahrhundert bestehende Heilige Römische Reich bestand aus vielen Herrschaftsgebieten und war mit dem 1815 nachfolgenden Deutschen Bund der Ursprung des föderalen deutschen Staates. Dieser entstand erstmals mit der Gründung des Deutschen Reichs im Jahr 1871, woraus eine rasche Wirtschaftsentwicklung vom Agrar- zum Industrieland folgte.
Nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg kam es infolge der Novemberrevolution 1918 zur Bildung der demokratischen Weimarer Republik und zum Friedensvertrag von Versailles. Der nationalsozialistischen Diktatur von 1933 bis 1945 samt verheerendem Zweitem Weltkrieg folgte eine Zeit der Veränderung und Teilung des Staates. Der Gründung der Bundesrepublik als demokratischer westdeutscher Teilstaat mit Inkrafttreten des Grundgesetzes am 24. Mai 1949 folgte wiederum die Gründung der sozialistischen DDR am 7. Oktober 1949 als ostdeutscher Teilstaat.[13] Nach der friedlichen Revolution 1989 folgte die Wiedervereinigung beider Landesteile am 3. Oktober 1990; seitdem wird der Tag der Deutschen Einheit als nationaler Feiertag begangen.
Deutschland ist Gründungsmitglied des Europarates und der Europäischen Union sowie deren bevölkerungsreichstes Land. Mit 18 anderen EU-Mitgliedstaaten bildet es eine Währungsunion, die Eurozone. Es ist Mitglied der UN, der OECD, der OSZE, der NATO, der G7 und der G20. Die Bundesrepublik Deutschland gilt als einer der politisch einflussreichsten Staaten Europas und ist ein gesuchtes Partnerland auf globaler Ebene.[14]
Gemessen am Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist Deutschland die größte Volkswirtschaft Europas und die viertgrößte der Welt.[5] Im Jahr 2015 war es die drittgrößte Export- und Importnation.[15] Es ist marktwirtschaftlich geprägt. Aufgrund der Rohstoffarmut und der Automatisierung der Industrie entwickelt sich das Land, das stark von der Qualität seines Bildungssystems abhängt, zunehmend zur Informations- und Wissensgesellschaft.[16] Gemäß dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung zählt Deutschland zu den sehr hoch entwickelten Ländern.[17]
Die deutsche Sprache ist die meistgesprochene Muttersprache und nach Englisch die zweithäufigste Fremdsprache in der Europäischen Union; die Zahl ihrer Sprecher rangiert weltweit auf dem zehnten Platz. Die Kultur Deutschlands hat vielschichtige und weltbekannte Ausdrucksformen hervorgebracht, etwa in der Kunst und Architektur, der Musik, der Philosophie, der Filmkultur, der Küche, der Traditionspflege, im Design, im Sport, in der Wissenschaft und der Wirtschaft. Das UNESCO-Welterbe in Deutschland sowie die Vielfalt der Kulturdenkmale und Altstädte ist umfangreich. Eine Vielzahl von National- und Naturparks sind im Land ausgewiesen.
德意志联邦共和国(德语:Bundesrepublik Deutschland、![]() 发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
在50万年前的旧石器时代晚期,海德堡人及其后代尼安德特人生活在今德国中部。自古典时代以来各日耳曼部族开始定居于今日德国的北部地区。公元1世纪时,有罗马人著作的关于“日耳曼尼亚”的历史记载。在公元4到7世纪的民族迁徙期,日耳曼部族逐渐向欧洲南部扩张。自公元10世纪起,德意志领土组成神圣罗马帝国的核心部分[参 10]。16世纪时,德意志北部地区成为宗教改革中心。1871年,在普鲁士主导之下,多数德意志邦国统一并加入德意志帝国。在第一次世界大战和1918-1919年德国革命后,德意志帝国解体,议会制的魏玛共和国取而代之。1933年国家社会主义党获取政权并建立独裁统治,最终导致第二次世界大战及系统性种族灭绝的发生。在战败并经历同盟国军事占领后,两个德国分别建立:德意志民主共和国和德意志联邦共和国。在1990年10月3日重新统一成为现在的德国。
德国是世界大国之一,其国内生产总值以国际汇率计居世界第四,以购买力平价计居世界第五。其诸多工业和科技部门位居世界前列,例如全球驰名的德国车厂、精密部件等,为世界第三大出口国。德国为发达国家,生活水平居世界前列。德国人也以热爱大自然闻名,都市绿化率极高,也是欧洲再生能源大国,是可持续发展经济的样板,除了强调环境保护与自然生态保育,在人为饲养活体的态度十分严谨,不但获得大量外汇和资讯优势,其动物保护法律管束、生命教育水准也是首屈一指的,在高等教育方面并提供免费大学教育[参 11],并具备完善的社会保障制度和医疗体系,催生出拜尔等大药厂。
德国为1993年欧洲联盟建立时的创始国之一,为申根区一部分,并于1999年推动欧元区的建立。德国亦为联合国、北大西洋公约组织、八国集团、20国集团及经济合作与发展组织成员。其军事开支总额居世界第九。
德语是欧盟境内使用人数最多的母语。德国文化的丰富层次和对世界的影响表现在其美术和建筑、音乐、哲学以及电影等等。德国的文化遗产主要以老城为代表。另外国家公园和自然公园共计有上百处。
ドイツ連邦共和国(ドイツれんぽうきょうわこく、独: Bundesrepublik Deutschland)、通称ドイツ(独: Deutschland)は、中央ヨーロッパ西部に位置する連邦共和制国家。首都および最大の都市はベルリン州。南がスイスとオーストリア、北にデンマーク、西をオランダとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東はポーランドとチェコとそれぞれ国境を接する。
欧州大陸における政治的・経済的な主要国であり、歴史上、多くの文化・科学・技術分野における重要な指導国でもある。人口は8300万人で、これは欧州連合において最大である。同国は限定的主権を有する16の州によって構成される。国土の総面積は35万7386平方キロメートルであり、主に温暖な気候に属する。かつて「西ドイツ」と呼ばれていた時代は「西欧」に分類されていたが、東ドイツ(ドイツ民主共和国)の民主化と東西ドイツの統一により「中欧」または「中西欧」に分類されるようになっている。
ドイツ経済の規模は、対米ドル名目為替レートによって計算される米ドル建て名目GDP(MERベースGDP)で世界第4位であり、対米ドル購買力平価によって計算される米ドル建て実質GDP(PPPベースGDP)で世界第5位である。技術及び産業分野における世界的なリーダーとして、世界第3位の輸出国かつ世界第3位の輸入国である。世界最古のユニバーサルヘルスケア制度を含む、包括的な社会保障を特色とする非常に高い生活水準が実現されている先進国である。豊かな政治及び文化の歴史で知られ、影響力ある多数の芸術家、音楽家、映画人、哲学者、科学者及び技術者、起業家の故国である。
1993年に欧州連合へ発展した1957年の欧州諸共同体の原加盟国であるほか、1995年以来シェンゲン圏の一員で、1999年以降はユーロ圏の一員でもある。また、国際連合、欧州評議会、NATO、G7、G20、OECDの主要なメンバーであり、欧州の大国「ビッグ4」や列強の一国に数えられる。アメリカ合衆国に次ぎ、ドイツは世界第2位の移住地である[1]。
Germany (German: Deutschland, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃlant] (![]() listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. Following the Napoleonic Wars and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German Confederation was formed in 1815. In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–1919, the Empire was replaced by the semi-presidential Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to the establishment of a dictatorship, World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, Germany was divided into the Federal Republic of Germany, generally known as West Germany, and the German Democratic Republic, East Germany. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community and the European Union, while the German Democratic Republic was a communist Eastern Bloc state and member of the Warsaw Pact. After the fall of communism, German reunification saw the former East German states join the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1990—becoming a federal parliamentary republic.
Germany is a great power with a strong economy; it has the largest economy in Europe, the world's fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial, scientific and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and importer of goods. As a developed country, which ranks very high on the Human Development Index, it offers social security and a universal health care system, environmental protections, and a tuition-free university education. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the G20, and the OECD. It has the third-greatest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
L'Allemagne (/almaɲ/ ; en allemand : Deutschland /ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ Écouter), en forme longue la République fédérale d'Allemagneb, abrégée en RFA (en allemand : Bundesrepublik Deutschland /ˈbʊn.dəs.ʁe.puˌblik ˈdɔʏtʃ.lant/ Écouter, abrégée en BRD), est un État d'Europe centrale, et selon certaines définitions d'Europe de l'Ouest, entouré par la mer du Nord, le Danemark et la mer Baltique au nord, par la Pologne à l'est-nord-est, par la Tchéquie à l'est-sud-est, par l'Autriche au sud-sud-est, par la Suisse au sud-sud-ouest, par la France au sud-ouest, par la Belgique et le Luxembourg à l'ouest, enfin par les Pays-Bas à l'ouest-nord-ouest. Décentralisée et fédérale, l'Allemagne compte quatre métropoles de plus d'un million d'habitants : la capitale Berlin, ainsi que Hambourg, Munich et Cologne. Le siège du gouvernement est situé dans la ville de Berlin et dans la ville fédérale de Bonn. Francfort-sur-le-Main est considérée comme la capitale financière de l'Allemagnec : dans cette ville se trouve le siège de la Banque centrale européenne.
Beaucoup de peuples germaniques occupent le Nord du territoire actuel depuis l'Antiquité classique. Durant ce que l'on nomme les invasions barbares, les tribus germaniques se rapprochent du Sud de ce territoire. À partir du Xe siècle, les territoires forment la partie centrale du Saint-Empire romain germanique. Au XVIe siècle, le Nord de l'Allemagne est au cœur de la réforme protestante. Le pangermanisme entraîne l'unification des États allemands en 1871 pour former l'Empire allemand. Après la Première Guerre mondiale, et la révolution allemande de 1918-1919, l'Empire est remplacé par la république parlementaire de Weimar. L'accès au pouvoir des nazis en 1933 mène à la Seconde Guerre mondiale, au cours de laquelle le régime totalitaire connu sous le nom de Troisième Reich, fondé sur un racisme et un antisémitisme singulier, et dirigé par le dictateur Adolf Hitler, perpètre des crimes de masse en Europe, dont la Shoah, et laisse le pays en ruines. Après sa défaite militaire en 1945, l'Allemagne perd des territoires et — par la volonté des vainqueurs alliés qui entrent dans la « guerre froide » — est contrainte de se scinder en deux nations : à l'ouest un État démocratique, la République fédérale d'Allemagne (en abrégé RFA) et, à l'est, la République démocratique allemande (en abrégé RDA) sous emprise de l'Union soviétique. Le mur de Berlin — qui symbolise cette division dans l'ancienne capitale — tombe le 9 novembre 1989 et l'Allemagne est à nouveau réunifiée le 3
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4x400米接力
女子4x400米接力
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x100米接力
男子4x100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x400米接力
男子4x400米接力
 *美国总统选举
*美国总统选举
 原子弹
原子弹

 地理
地理
 ***IMF发达国家
***IMF发达国家

 地理
地理

 历史
历史
 公元 2000 - 2100
公元 2000 - 2100

 历史
历史
 公元 1500 - 2000
公元 1500 - 2000

 历史
历史
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 IMF发达国家
IMF发达国家
 第一级
第一级
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2017 London
2017 London
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2015 Beijing
2015 Beijing
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2013 Moskau
2013 Moskau
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2009 Berlin
2009 Berlin
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2007 Osaka
2007 Osaka
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2011 Daegu
2011 Daegu
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1995 Gothenburg
1995 Gothenburg
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1993 Stuttgart
1993 Stuttgart
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1991 Tokyo
1991 Tokyo
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1987 Rome
1987 Rome
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1983 Helsinki
1983 Helsinki




 军事、国防和装备
军事、国防和装备
 核武器
核武器

 北约会员国
北约会员国

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团
二十个主要工业化国家和新兴国家集团

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 七国集团
七国集团
 美国
美国

 联合国
联合国
 联合国安全理事会常任理事国
联合国安全理事会常任理事国
 氢弹
氢弹

Die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika (englisch United States of America; abgekürzt USA), kurz auch Vereinigte Staaten (englisch United States, abgekürzt U.S., US) genannt und häufig auch umgangssprachlich verkürzt zu Amerika (englisch America), sind eine föderale Republik. Diese besteht aus 50 Bundesstaaten, einem Bundesdistrikt (der Hauptstadt Washington, D.C.), fünf größeren Territorien und etlichen Inselterritorien. Die 48 zusammenhängenden Continental United States (häufig Lower 48 genannt) sowie Alaska liegen in Nordamerika, während Hawaii und kleinere Außengebiete im Pazifik beziehungsweise in der Karibik liegen. Das Land weist eine sehr hohe geographische und klimatische Diversität mit einer großen Vielfalt an Tier- und Pflanzenarten auf.
Die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika sind der drittgrößte Staat der Erde, gemessen an der Fläche von 9,83 Millionen Quadratkilometern[3] (nach Russland und Kanada) und gemessen an der Bevölkerung von etwa 328 Millionen Einwohnern (nach China und Indien). Die nach Einwohnerzahl größte Stadt ist New York City, bedeutende Metropolregionen sind Los Angeles, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Philadelphia, Washington, Miami, Atlanta, Boston und San Francisco, mit jeweils über 5 Millionen Einwohnern. Der Grad der Urbanisierung liegt bei 81,96 Prozent (Stand: 2015).[9]
Bedingt durch die Einwanderung aus einer Vielzahl von Ländern sind die Vereinigten Staaten eines der ethnisch multikulturellsten Länder. Anders als in 32 Bundesstaaten gibt es auf Bundesebene keine gesetzliche Amtssprache, jedoch herrscht Englisch als De-Facto-Amtssprache vor. Im Südwesten sowie in Miami ist zusätzlich die spanische Sprache weit verbreitet. Insgesamt waren 2015 mehr als 350 Sprachen in heimischem Gebrauch, davon allein 150 indigene. Darunter waren als größte die der Yupik in Alaska, der Dakota aus der Sioux-Sprachfamilie sowie die Sprache der Apachen in Gebrauch, dann Keres, die Sprache der Pueblo-Indianer, und Cherokee.[10]
Paläoindianer wanderten vor mehr als 13.000 Jahren aus Asien in das nordamerikanische Festland der heutigen Vereinigten Staaten ein (Buttermilk Creek Complex), nachdem sie mehrere Jahrtausende zuvor das heute zu den USA gehörende Alaska besiedelt hatten. Die europäische Kolonisierung begann etwa um 1600 vorwiegend aus England, allerdings in langwieriger Auseinandersetzung mit Frankreich. Die Vereinigten Staaten gingen aus den 13 Kolonien an der Atlantikküste hervor. Streit zwischen Großbritannien und den amerikanischen Kolonien führte zur Amerikanischen Revolution. Am 4. Juli 1776 verabschiedeten Delegierte der 13 Kolonien die Unabhängigkeitserklärung der Vereinigten Staaten und somit die Gründung der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Der Amerikanische Unabhängigkeitskrieg, der mit der Anerkennung der Unabhängigkeit endete, war der erste erfolgreiche Unabhängigkeitskrieg gegen eine europäische Kolonialmacht. Die heutige Verfassung wurde am 17. September 1787 verabschiedet. Bisher wurden 27 Zusatzartikel ergänzt. Die ersten zehn Zusatzartikel, die gemeinsam als Bill of Rights bezeichnet werden, wurden 1791 ratifiziert und garantieren eine Vielzahl von unveräußerlichen Rechten.
Angetrieben von der Doktrin Manifest Destiny begannen die Vereinigten Staaten eine Expansion über Nordamerika, die sich über das 19. Jahrhundert erstreckte. Dies schloss die gewaltsame Vertreibung indigener indianischer Stämme, den Erwerb neuer Territorien u. a. im Mexikanisch-Amerikanischen Krieg und die Gründung neuer Bundesstaaten ein. Der Amerikanische Bürgerkrieg führte 1865 zum Ende der legalen Sklaverei in den Vereinigten Staaten. Zum Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts erreichten der Staat eine Ausdehnung bis zum Pazifik, ihre Wirtschaft wurde zur größten weltweit. Der Spanisch-Amerikanische Krieg und der Erste Weltkrieg bestätigten die Rolle der Vereinigten Staaten als globale Militärmacht. Aus dem Zweiten Weltkrieg gingen die USA als Supermacht und als erstes Land mit Atomwaffen hervor und wurden eines von fünf ständigen Mitgliedern im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen. Nach Ende des Kalten Krieges und dem Zerfall der Sowjetunion sind die USA die einzige verbliebene Supermacht. Sie sind Gründungsmitglied der Vereinten Nationen, der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten (OAS) und vieler weiterer internationaler Organisationen. Ihr politischer und kultureller Einfluss ist weltweit groß.
Die Vereinigten Staaten sind ein industrialisierter Staat und die größte Volkswirtschaft mit einem Bruttoinlandsprodukt in Höhe von 18,5 Billionen US-Dollar im Jahr 2016, was 25 % der nominellen oder 17 % der kaufkraftbereinigten globalen Wirtschaftsleistung entsprach.[7] Das Land hatte 2016 das achthöchste Pro-Kopf-Einkommen. Laut der Weltbank ist die Einkommensungleichverteilung in den Vereinigten Staaten eine der höchsten unter den OECD-Staaten.[11] Die Wirtschaftsleistung des Landes wird durch den Reichtum an natürlichen Ressourcen, eine gut entwickelte Infrastruktur und eine hohe durchschnittliche Produktivität begünstigt.[12][13] Obwohl die Wirtschaftsstruktur gemeinhin als postindustriell angesehen wird, ist das Land nach wie vor einer der weltgrößten Güterproduzenten.[14] Das Land war 2016 für 36 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit auf Platz 1, gefolgt von China mit 13 % und Russland mit 4,1 %.[15] Der in Folge der Terroranschläge am 11. September 2001 ausgerufene Ausnahmezustand ist seit 2001 in Kraft.[16]
美国是一个高度发达的资本主义国家,其政治、教育、经济、军事、文化、创新等实力领衔全球。作为世界第一军事大国,其高等教育水平和科研技术水平以及航空航天技术方面,也是当之无愧的世界第一,其科研经费投入之大、研究型高校企业之多、科研成果之丰富堪称世界典范。同时,美国还拥有苹果、微软、戴尔、惠普、波音等一系列世界著名企业。
美利坚合众国(英语:United States of America,缩写为 U.S.A.、通称为 United States、缩写为U.S.、或America、The States),中文通称美国,是由其下辖50个州、华盛顿哥伦比亚特区、五个自治领土及外岛共同组成的联邦共和国[注 1]。美国本土48州和联邦特区位于北美洲中部,东临大西洋,西临太平洋,北面是加拿大,南部和墨西哥及墨西哥湾接壤,本土位于温带、副热带地区。阿拉斯加州位于北美大陆西北方,东部为加拿大,西隔白令海峡和俄罗斯相望;夏威夷州则是太平洋中部的群岛。美国在加勒比海和太平洋还拥有多处境外领土和岛屿地区。此外,美国还在全球140多个国家和地区拥有着374个海外军事基地。
美国拥有982万平方公里国土面积,位居世界第三(依陆地面积定义为第四大国);同时拥有接近超过3.3亿人口,为世界第三人口大国。因为有着来自世界各地的大量移民,它是世界上民族和文化最多元的国家之一[14]。美国地形与气候复杂多样,是多种野生动物的家园[15]。
一万五千多年前,古印第安人自亚洲迁徙至北美大陆[16]。16世纪欧洲开始殖民北美。现今的合众国起始于东海岸的13个英属美洲殖民地。欧洲七年战争后,大不列颠王国与其殖民地之间的争议愈发剧烈,最终导致在1775年爆发美国革命。1776年7月4日,正与大不列颠进行独立战争的各殖民地派出代表,协同一致发表《独立宣言》。战争终止于1783年,大不列颠王国承认这13个北美殖民地脱离管辖而独立,与其签订《巴黎条约》。这场战争也是第一场成功脱离欧洲殖民帝国的独立战争[17]。1781年,《邦联条例》在邦联13个构成州获得通过,共同组成了邦联议会。1787年《美利坚合众国宪法》完稿,将“美利坚合众国”改制为联邦体制,联邦政府随之成立。1791年,合称为权利法案的十条宪法修正案获得批准,担保了基本民权。
美国自19世纪开始在北美通过强行移置原住民,征服及购买等方法大力扩张领土,随着逐渐不断地承认扩张领地为新州份,至1848年美国疆域已横跨整个北美大陆[18]。19世纪下半叶爆发的内战,使曾经合法的奴隶制度得以终结[19][20]。在19世纪末,美国已将其领土延伸到太平洋的夏威夷。美国经济在工业革命的推动下,自那时起也开始蓬勃发展[21]。随后美西战争的胜利,使美国势力进入加勒比海地区及太平洋西部;而参与第一次世界大战则奠定其作为一个全球性军事力量的地位。尽管在1930年代经历经济大萧条,美国在第二次世界大战获得胜利之后崛起成为超级大国。作为联合国安全理事会常任理事国,美国是世界上第一个研发出核武器,也是唯一一个曾将其投入实战的国家。战后美国与苏联进行了数十年冷战,顶峰时期的太空竞赛促使了人类第一次登月计划的成功。在1991年苏联解体后,美国成为世上唯一超级强国[22]。
美国作为一个高度发达国家,是世界上最大的进口国及第二大的商品出口国,国内生产总值按国际汇率排名世界第一、而依购买力平均则位列第二。在国民平均薪资[23]、人类发展指数、人均国内生产总值以及人均生产力[24]等社会经济学表现指标上,美国均处于世界领先地位。美国经济已步入后工业时代,服务行业占据经济主导地位,位列世界第一。同时,其生产制造业规模也极为庞大,位居于世界第二[25]。仅占据全世界4.4%人口的美国[26],贡献了世界四分之一的国内生产总值和三分之一的全球军事开支[27],这使其在经济和军事上均处于全世界最重要的地位。美国在政治和文化上是一支世界显著并影响深远的力量,也在科学研究和技术创新上占据世界领导地位[28]。美国是联合国、世界银行、国际货币基金组织、美洲国家组织等的创始成员国。
アメリカ合衆国(アメリカがっしゅうこく、英語: United States of America)、通称アメリカ、米国(べいこく)は、50の州および連邦区から成る連邦共和国である[6][7]。
アメリカ本土の48州および同国首都ワシントンD.C.(コロンビア特別区)は、カナダとメキシコの間の北アメリカ中央に位置する。
アラスカ州は北アメリカ北西部の角に位置し、東ではカナダと、西ではベーリング海峡をはさんでロシアと国境を接している。ハワイ州は中部太平洋における島嶼群である。
同国は、太平洋およびカリブに5つの有人の海外領土および9つの無人の海外領土を有する。985万平方キロメートル (km2) の総面積は世界第3位または第4位、3億1千7百万人の人口は世界第3位である。
同国は世界で最も民族的に多様かつ多文化な国の1つであり、これは多数の国からの大規模な移住の産物とされている[8]。
また同国の広大な国土における地理および気候も極めて多様であり、多種多様な野生生物が存在する。
米国は先進国かつ世界最大級の国民経済を有する[9]。同国経済は、豊富な天然資源と高度な労働者の生産性により支えられている[10]。同国経済は脱工業化社会だとされている一方、世界最大の製造国のうちの1つであり続けている[11]。同国は世界の軍事支出の37%を占め[12]、世界最高位の経済・軍事大国であり、多大な影響を及ぼす政治・文化的勢力であり、科学研究・技術革新におけるリーダー的存在とされている[13]。
The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions.[f] At 3.8 million square miles (9.8 million km2), the United States is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area[g] and is slightly smaller than the entire continent of Europe's 3.9 million square miles (10.1 million km2). With a population of over 327 million people, the U.S. is the third most populous country. The capital is Washington, D.C., and the largest city by population is New York. Forty-eight states and the capital's federal district are contiguous in North America between Canada and Mexico. The State of Alaska is in the northwest corner of North America, bordered by Canada to the east and across the Bering Strait from Russia to the west. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The U.S. territories are scattered about the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, stretching across nine official time zones. The extremely diverse geography, climate, and wildlife of the United States make it one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.[19]
Paleo-Indians migrated from Siberia to the North American mainland at least 12,000 years ago.[20] European colonization began in the 16th century. The United States emerged from the thirteen British colonies established along the East Coast. Numerous disputes between Great Britain and the colonies following the French and Indian War led to the American Revolution, which began in 1775, and the subsequent Declaration of Independence in 1776. The war ended in 1783 with the United States becoming the first country to gain independence from a European power.[21] The current constitution was adopted in 1788, with the first ten amendments, collectively named the Bill of Rights, being ratified in 1791 to guarantee many fundamental civil liberties. The United States embarked on a vigorous expansion across North America throughout the 19th century, acquiring new territories,[22] displacing Native American tribes, and gradually admitting new states until it spanned the continent by 1848.[22]
During the second half of the 19th century, the Civil War led to the abolition of slavery.[23][24] By the end of the century, the United States had extended into the Pacific Ocean,[25] and its economy, driven in large part by the Industrial Revolution, began to soar.[26] The Spanish–American War and World War I confirmed the country's status as a global military power. The United States emerged from World War II as a global superpower, the first country to develop nuclear weapons, the only country to use them in warfare, and a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. During the Cold War, the United States and the Soviet Union competed in the Space Race, culminating with the 1969 Moon landing. The end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 left the United States as the world's sole superpower.[27]
The United States is the world's oldest surviving federation. It is a federal republic and a representative democracy. The United States is a founding member of the United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, Organization of American States (OAS), and other international organizations. The United States is a highly developed country, with the world's largest economy by nominal GDP and second-largest economy by PPP, accounting for approximately a quarter of global GDP.[28] The U.S. economy is largely post-industrial, characterized by the dominance of services and knowledge-based activities, although the manufacturing sector remains the second-largest in the world.[29] The United States is the world's largest importer and the second largest exporter of goods, by value.[30][31] Although its population is only 4.3% of the world total,[32] the U.S. holds 31% of the total wealth in the world, the largest share of global wealth concentrated in a single country.[33]
Despite wide income and wealth disparities, the United States continues to rank very high in measures of socioeconomic performance, including average wage, human development, per capita GDP, and worker productivity.[34][35] The United States is the foremost military power in the world, making up a third of global military spending,[36] and is a leading political, cultural, and scientific force internationally.[37]
Les États-Unis, en forme longue les États-Unis d'Amérique4 (en anglais : United States et United States of America, également connus sous les abréviations US et USA), sont un pays transcontinental dont l'essentiel du territoire se situe en Amérique du Nord. Les États-Unis ont la structure politique d'une république constitutionnelle fédérale à régime présidentiel composée de cinquante États, dont quarante-huit sont adjacents et forment le Mainland. Celui-ci est encadré par l'océan Atlantique à l'est et l'océan Pacifique à l'ouest, et se trouve bordé au nord par le Canada et au sud par le Mexique. Les deux États non limitrophes sont l'Alaska, situé à l'ouest du Canada, et Hawaï, un archipel situé au milieu de l'océan Pacifique-nord. De plus, le pays comprend quatorze territoires insulaires disséminés dans la mer des Caraïbes et le Pacifique. La géographie et le climat du pays sont extrêmement diversifiés, abritant une grande variét
 *田径
*田径
 男子4x100米接力
男子4x100米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4x400米接力
女子4x400米接力
 *田径
*田径
 女子4×100米接力
女子4×100米接力
 英联邦国家
英联邦国家

 地理
地理
 加勒比地区
加勒比地区

 地理
地理
 西印度群岛
西印度群岛
 牙买加
牙买加
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2015 Beijing
2015 Beijing
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2017 London
2017 London
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2009 Berlin
2009 Berlin
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2011 Daegu
2011 Daegu
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 2001 Edmonton
2001 Edmonton
 世界田径锦标赛
世界田径锦标赛
 1991 Tokyo
1991 Tokyo
 体育
体育






