
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Fuel cell vehicle
*Fuel cell vehicle



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Hydrogen propulsion
*Hydrogen propulsion

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 ***Hydrogen Energy
***Hydrogen Energy
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH




 Automobile
Automobile
 Germany, Austria, Switzerland
Germany, Austria, Switzerland



 Automobile
Automobile
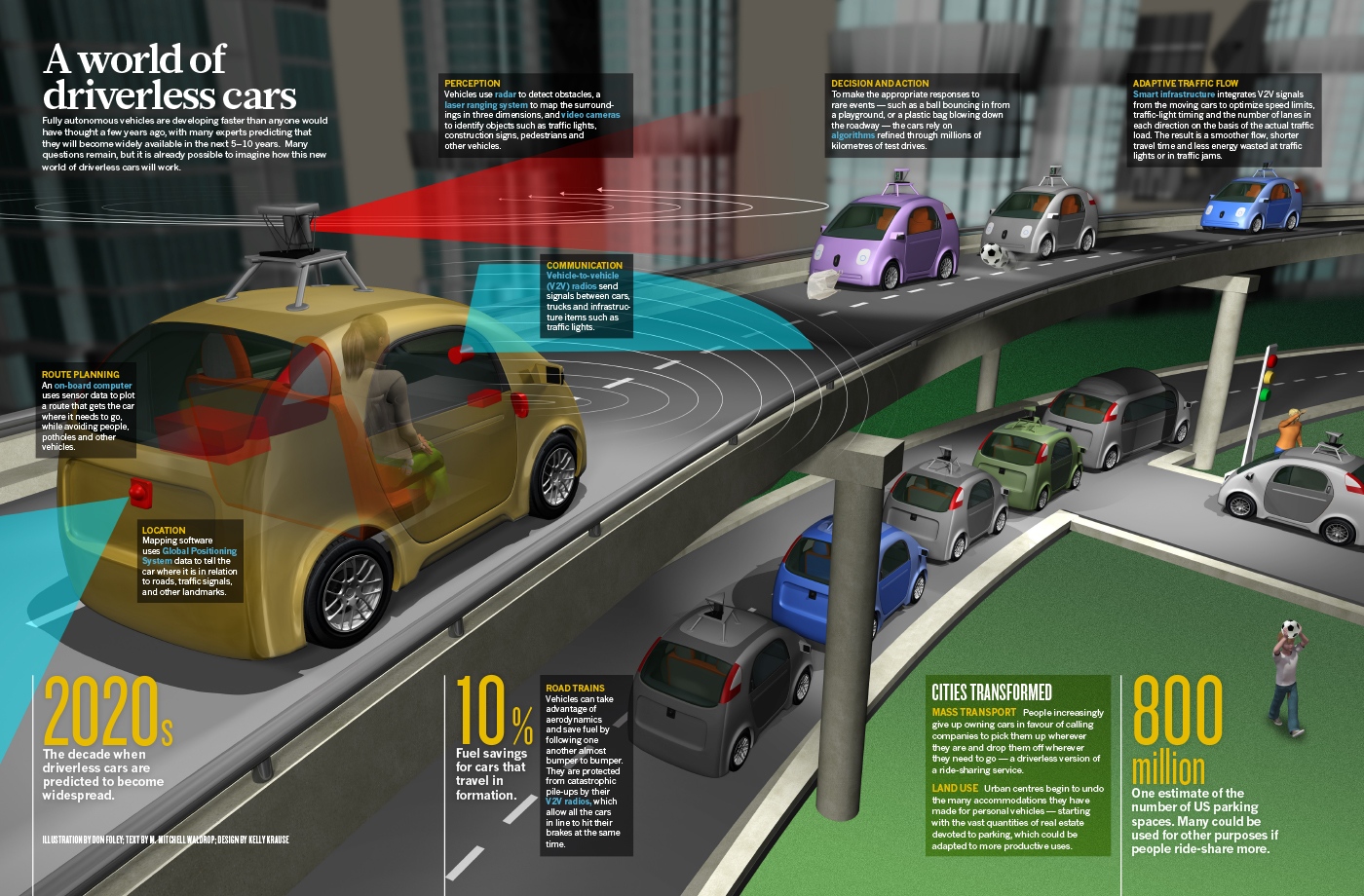
 *Self-driving car
*Self-driving car



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology

 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg


 IT-Times
IT-Times
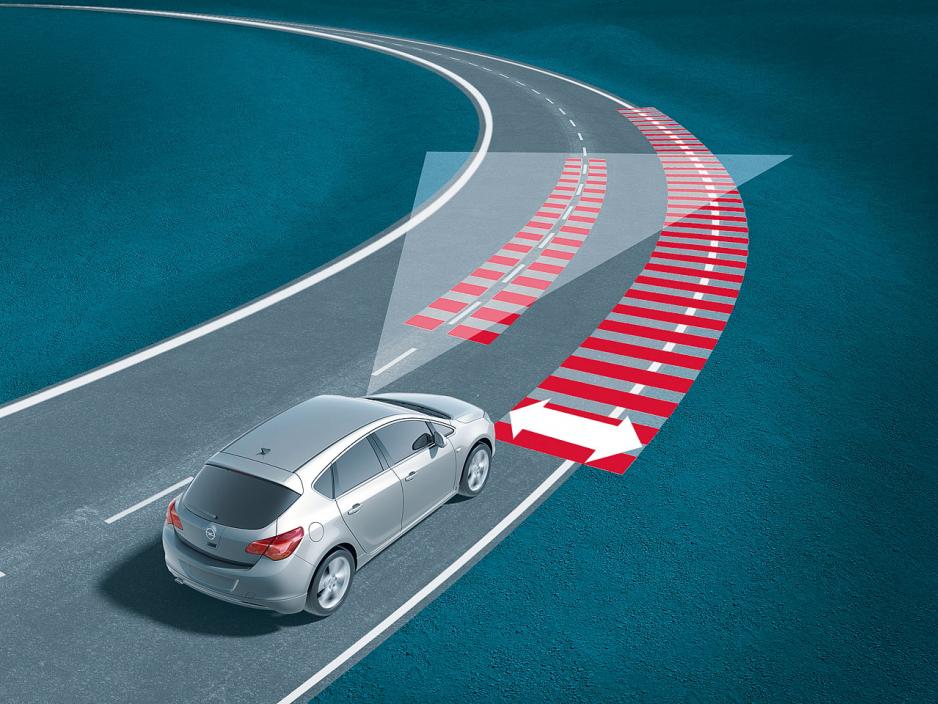
 Driver assistance systems
Driver assistance systems

 Companies
Companies
 Germany, Austria, Switzerland
Germany, Austria, Switzerland





 Automobile
Automobile



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Electric car
*Electric car



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Electric car battery
*Electric car battery
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea






 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Big Data
Big Data


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts





 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology
 Elon Musk
Elon Musk

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Mobile Networks
Mobile Networks


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Driver assistance systems
Driver assistance systems


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Smart phone
Smart phone




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 SpaceX
SpaceX

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts

星链(英语:Starlink)是太空服务公司SpaceX计划推出的一项通过近地轨道卫星群,提供覆盖全球的高速互联网接入服务。
2015年,SpaceX首席执行官伊隆·马斯克在西雅图宣布推出一项太空高速互联网计划——星链计划[1]。凭借远远超过传统卫星互联网的性能,以及不受地面基础设施限制的全球网络,星链可以为网络服务不可靠,费用昂贵或完全没有网络的位置提供高速互联网服务,另外也有可能结束当今世界存在的网络封锁。[2]旨在为世界上的每一个人提供高速互联网服务。[3] 星链计划的宗旨是开发出“全球卫星互联网系统”[2],并能运用在例如火星等环境上,在太阳系内部署通信基础建设。
2018年2月22日,SpaceX在美国加州范登堡空军基地成功发射了一枚“猎鹰9号”火箭,并将两颗小型实验通信卫星送入轨道,星链计划由此开启[2]。2019年10月22日,SpaceX首席执行官伊隆·马斯克成功通过星链发送推特,并表示星链已能提供天基互联网服务。Starlink的目标是到2020年在美国北部和加拿大提供服务,到2021年将其服务范围扩大到接近全球。届时在地球上空的预定轨道部署由12000颗卫星组成的巨型卫星星座[4]。
Starlink ist ein von dem US-Raumfahrtunternehmen SpaceX betriebenes Satellitennetzwerk, das künftig weltweiten Internetzugang bieten soll.[1] Zum Kerngeschäft von Starlink zählen die Bereitstellung von Internetzugängen mit besonders geringer Paketumlaufzeit und die Bereitstellung in Gebieten, in denen zuvor keine oder eine nicht ausreichende Internetverbindung zur Verfügung stand.[2] Mit 1792 Starlink-Satelliten im Erdorbit (Stand Ende 2021[3]) ist SpaceX der mit Abstand größte Satellitenbetreiber weltweit.[4] Insgesamt bestehen bis zum Jahr 2027 befristete Genehmigungen für den Start von maximal 11.927 Satelliten[5] sowie Anträge von SpaceX für nochmals bis zu 30.000 Satelliten. Das entspricht zusammengenommen dem fünffachen aller von 1957 (Sputnik 1) bis 2019 gestarteten Satelliten.
スターリンク (Starlink) は、アメリカ合衆国の民間企業スペースXが運用している衛星コンステレーション[2]。低コスト・高性能な衛星バスと地上の送受信機により、衛星インターネットアクセスサービスを提供することを目的とする[3][4]。2020年、北アメリカ大陸とヨーロッパで試験運用が始まった[5]。サービス提供エリアでは、直径55センチメートル程度のアンテナで通信衛星と電波を直接やり取りして、地上の通信インフラが未整備の地域でもインターネットに接続できる[5]。
スペースXは、人工衛星を軍用や[6]、科学・探検などの用途に販売することも計画している[7]ほか、2020年代中頃までに総数約12,000基の人工衛星を3階層にわたって展開することを計画している。最初が高度550kmの約1,600基の衛星で、次が高度1,150kmのKu/Kaバンドを用いる約2,800基の衛星、さらに高度340kmのVバンドを用いる約7,500基の衛星である[8]。10年におよぶ計画の総コストは、設計・製造・打ち上げなど100億ドル近くに達すると推計される[9]。
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by SpaceX,[3] providing satellite Internet access coverage to 48 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone service after 2023.[4] SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As of February 2023, Starlink consists of over 3,580 mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO),[5] which communicate with designated ground transceivers. In total, nearly 12,000 satellites are planned to be deployed, with a possible later extension to 42,000. SpaceX announced reaching more than one million subscribers in December 2022.[6]
The SpaceX satellite development facility in Redmond, Washington houses the Starlink research, development, manufacturing, and orbit control teams. The cost of the decade-long project to design, build, and deploy the constellation was estimated by SpaceX in May 2018 to be at least US$10 billion.[7] SpaceX expects more than $30 billion in revenue by 2025 from its satellite constellation, while revenues from its launch business were expected to reach $5 billion in the same year.[8][9]
Astronomers have raised concerns about the effect the constellation can have on ground-based astronomy and how the satellites will add to an already congested orbital environment.[10][11] SpaceX has attempted to mitigate astronomy concerns by implementing several upgrades to Starlink satellites aimed at reducing their brightness during operation.[12] The satellites are equipped with krypton-fueled Hall thrusters which allow them to de-orbit at the end of their life. Additionally, the satellites are designed to autonomously avoid collisions based on uplinked tracking data.[13]
Starlink est un fournisseur d'accès à Internet par satellite de la société SpaceX qui repose sur une constellation de satellites comportant des milliers de satellites de télécommunications placés sur une orbite terrestre basse. Starlink est le premier fournisseur d'internet par satellite à choisir cette orbite plutôt que l'orbite géostationnaire car elle permet de diminuer la latence en la faisant passer de 600 ms à environ 20 ms. La constellation est en cours de déploiement depuis 2019 et repose sur environ 2000 satellites opérationnels en juin 2022. À cette date Starlink compte environ un demi million de clients dans une dizaine de pays, dont la France, qui ont autorisé la société à utiliser les fréquences nécessaires au système.
Pour atteindre ses objectifs commerciaux, SpaceX prévoit de disposer vers 2025 de 12 000 satellites, chiffre qui doit être porté à terme à 42 000. Sur le plan technique chaque satellite dispose d'une capacité de 20 gigabits/seconde et utilise la bande Ku pour les liaisons avec les terminaux des utilisateurs et la bande Ka pour les liaisons avec les stations terriennes. Le satellite, qui circule sur une orbite circulaire à une altitude d'environ 550 kilomètres, a une masse approximative de moins de 300 kilogrammes et dispose d'un moteur ionique pour atteindre et maintenir sa position sur son orbite et réduire celle-ci en fin de vie (environ 6 ans) afin d'être détruit par sa rentrée atmosphérique. Le terminal utilisateur repose sur une antenne réseau à commande de phase comportant un dispositif mécanique pour l'orientation en hauteur.
La viabilité économique de Starlink dépend notamment du coût de fabrication et de mise en orbite des satellites. SpaceX utilise ses lanceurs Falcon 9 pour déployer sa constellation à des couts fortement réduits grâce à la ré-utilisabilité de ce lanceur et à la compacité des satellites qui permet de placer en orbite 50 à 60 de ces engins à chaque lancement. Plusieurs sociétés concurrentes ont prévu de mettre en service des constellations analogues. OneWeb est la plus avancée.
Le déploiement d'une constellation de satellites aussi importante en nombre sur l'orbite basse suscite plusieurs problèmes compte tenu du fait que le nombre de satellites en orbite basse va être décuplé par la seule présence des satellites Starlink (en configuration cible à 40 000 satellites). Le risque de collision entre satellites va augmenter dans des proportions importantes qui rendent inadaptées les dispositifs anti-collision existants. Les observations astronomiques par les grands observatoires terrestres sont gênées, en particulier les programmes de recensement et de suivi des objets célestes.
Starlink è una costellazione di satelliti attualmente in costruzione dal produttore privato aerospaziale americano SpaceX[1][2] per l'accesso a internet satellitare globale in banda larga a bassa latenza.[3][4] La costellazione sarà costituita da migliaia di satelliti miniaturizzati prodotti in massa, collocati in orbita terrestre bassa (LEO), che lavoreranno in sintonia con ricetrasmettitori terrestri. SpaceX è intenzionata, inoltre, alla commercializzazione di alcuni dei suoi satelliti per scopi militari,[5] scientifici ed esplorativi.[6]
Sono state sollevate preoccupazioni riguardo agli effetti e ai danni a lungo termine dei detriti spaziali, conseguenti dal rilascio di migliaia di satelliti in orbite al di sopra dei 1000 km[7]. Successivamente è stato deciso di utilizzare orbite intorno ai 550 km, relativamente più sicure perché consentono ai detriti di decadere in tempi minori.[8] Altre critiche sono relative a un possibile impatto negativo nelle attività di astronomia osservativa[9], che SpaceX ha annunciato di voler risolvere. A giugno 2020, uno dei satelliti della costellazione ha un rivestimento sperimentale studiato appositamente per renderlo meno riflettente e quindi meno visibile a osservazioni astronomiche da terra.[10]
Il costo totale dalla progettazione alla realizzazione fino a regime, in un periodo di 10 anni, è stato stimato da SpaceX nel maggio del 2018 pari a 10 miliardi di dollari statunitensi.[11]
Il percorso di sviluppo del prodotto è iniziato nel 2015, con i primi due voli di prova dei prototipi di satelliti lanciati nel febbraio 2018. Il primo lancio per il dispiegamento di una parte della costellazione, è avvenuto il 24 maggio 2019 con i primi 60 satelliti portati con successo in orbita.[1] La sede di sviluppo dei satelliti di SpaceX è a Redmond (Washington), dove risiedono strutture di ricerca, progettazione, costruzione e controllo operativo.
A maggio 2021 sono 1433 i satelliti operativi della costellazione in orbita.[12][13][14] SpaceX ha attivato un servizio privato in beta negli Stati Uniti ad agosto 2020 e ha lanciato un servizio pubblico, sempre in beta, ad ottobre 2020, attivo solo ad alte latitudini. SpaceX attualmente è in grado di portare in orbita 60 satelliti per ogni lancio e si pone come obiettivo il dispiegamento di ulteriori 1500 satelliti (dal peso di 250 kg) entro la fine del 2021 e l'inizio del 2022. Al momento (2020), tuttavia, queste sono solo previsioni interne e non date ufficiali.
Da febbraio 2021 il servizio è attivo su pre-ordinazione anche in Italia.
Starlink es una empresa que nació como proyecto de SpaceX para la creación de una constelación de satélites de internet2 con el objetivo de brindar un servicio de internet de banda ancha, baja latencia y cobertura mundial a bajo costo.34 SpaceX comenzó a lanzar satélites Starlink en 2019. En septiembre de 2022, Starlink había colocado más de 3,000 satélites fabricados en serie en órbita terrestre baja (LEO).5 En 2017 se completaron los requisitos regulatorios para lanzar cerca de 12.000 satélites para mediados de la década de 2020.6 SpaceX también planea vender satélites para uso militar,7 científico y de exploración.8 En noviembre de 2018, la empresa recibió la autorización del ente gubernamental estadounidense (FCC) para desplegar 7.518 satélites de banda ancha, que se sumarían a los 4.425 aprobados en marzo del mismo año.9
El desarrollo comenzó en 2015, y los primeros prototipos de satélite fueron lanzados el 22 de febrero de 2018.1011 El lanzamiento de los primeros 60 satélites se llevó a cabo el 23 de mayo de 2019, y se espera que el inicio de operaciones comerciales de la constelación empiece en el año 2020.1213 La investigación y desarrollo del proyecto tiene lugar en las instalaciones de SpaceX ubicadas en Redmond, Washington.
Starlink[1] — глобальная спутниковая система, разворачиваемая компанией SpaceX для обеспечения высокоскоростным широкополосным спутниковым доступом в Интернет в местах, где он был ненадёжным, дорогим или полностью недоступным[2][3]. Подразделение SpaceX, занимающееся исследованиями, разработкой и производством спутниковых систем, расположено в Редмонде (штат Вашингтон).
Разработка проекта началась в 2015 году, тестовые прототипы TINTIN[en] были успешно запущены 22 февраля 2018 года[4].
К 2017 году SpaceX представила нормативные документы для запуска в общей сложности почти 12 тыс ИСЗ на околоземную орбиту к середине 2020-х годов[5][6]. В мае 2019 года была запущена первая группа из 60 спутников-прототипов.
В 2020 году SpaceX начала предоставлять коммерческие услуги доступа в Интернет в северной части США и Канаде. По состоянию на январь 2022 года число пользователей бета-тестеров Starlink достигло 145 тыс в 25 странах мира[7]. По состоянию на май 2022 года число пользователей выросло до 400 тысяч[8].
Общая сумма инвестиций для реализации проекта оценивается в 10 млрд $[9]. SpaceX также планирует продавать спутники, использующие эту же систему, для исследовательских и научных целей[10].
С 2022 года Starlink применяется Вооружёнными Силами Украины для связи между подразделениями и наведения оружия, дронов и артиллерии с целью уничтожения российских военных позиций, танков и техники в ходе вторжения России на Украину.



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 IC
IC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Semiconductor technology
Semiconductor technology


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Sensor
Sensor


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 MCU
MCU
 Netherlands
Netherlands


 Exhibition
Exhibition


 Aerospace
Aerospace