
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科

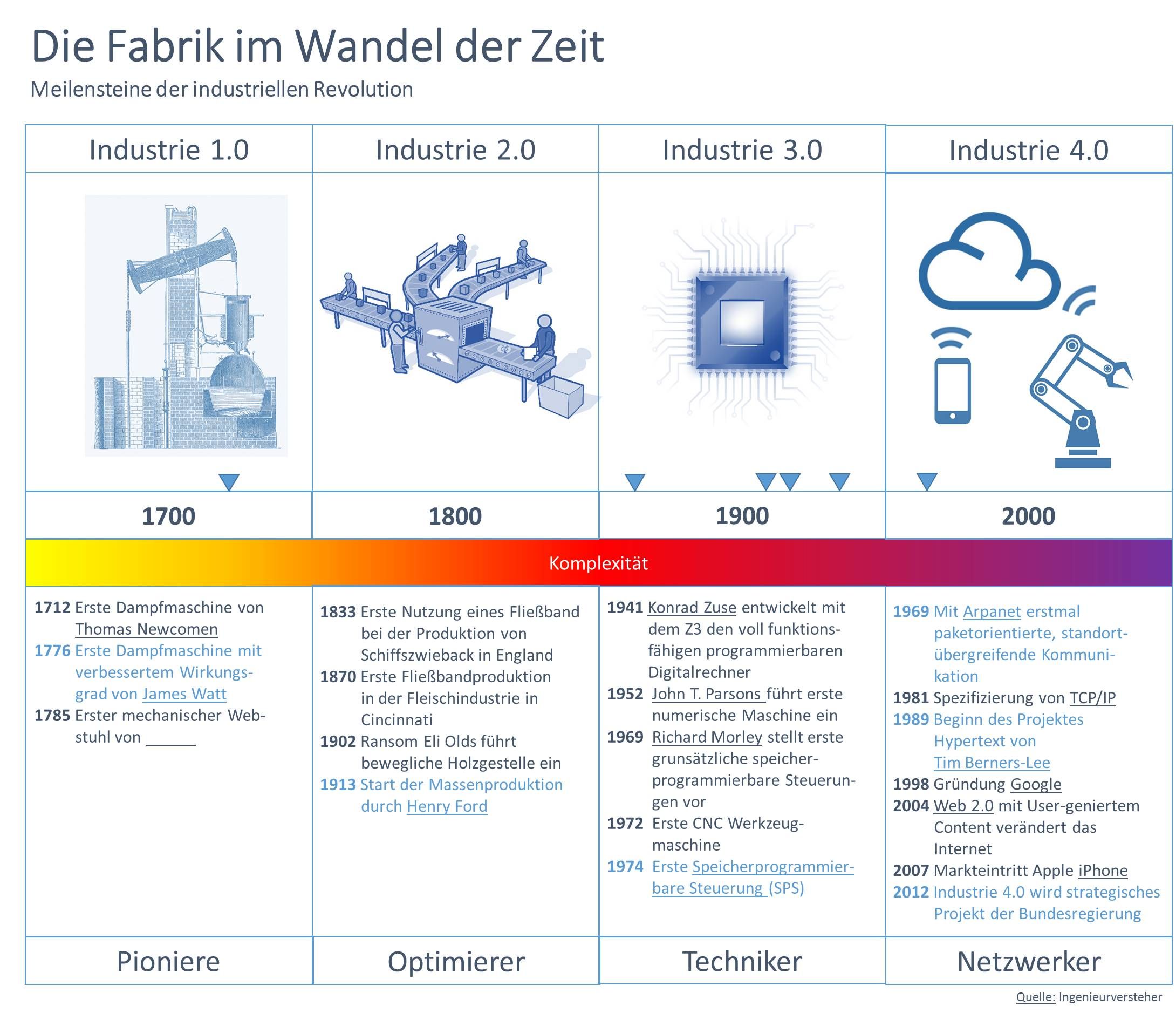
 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
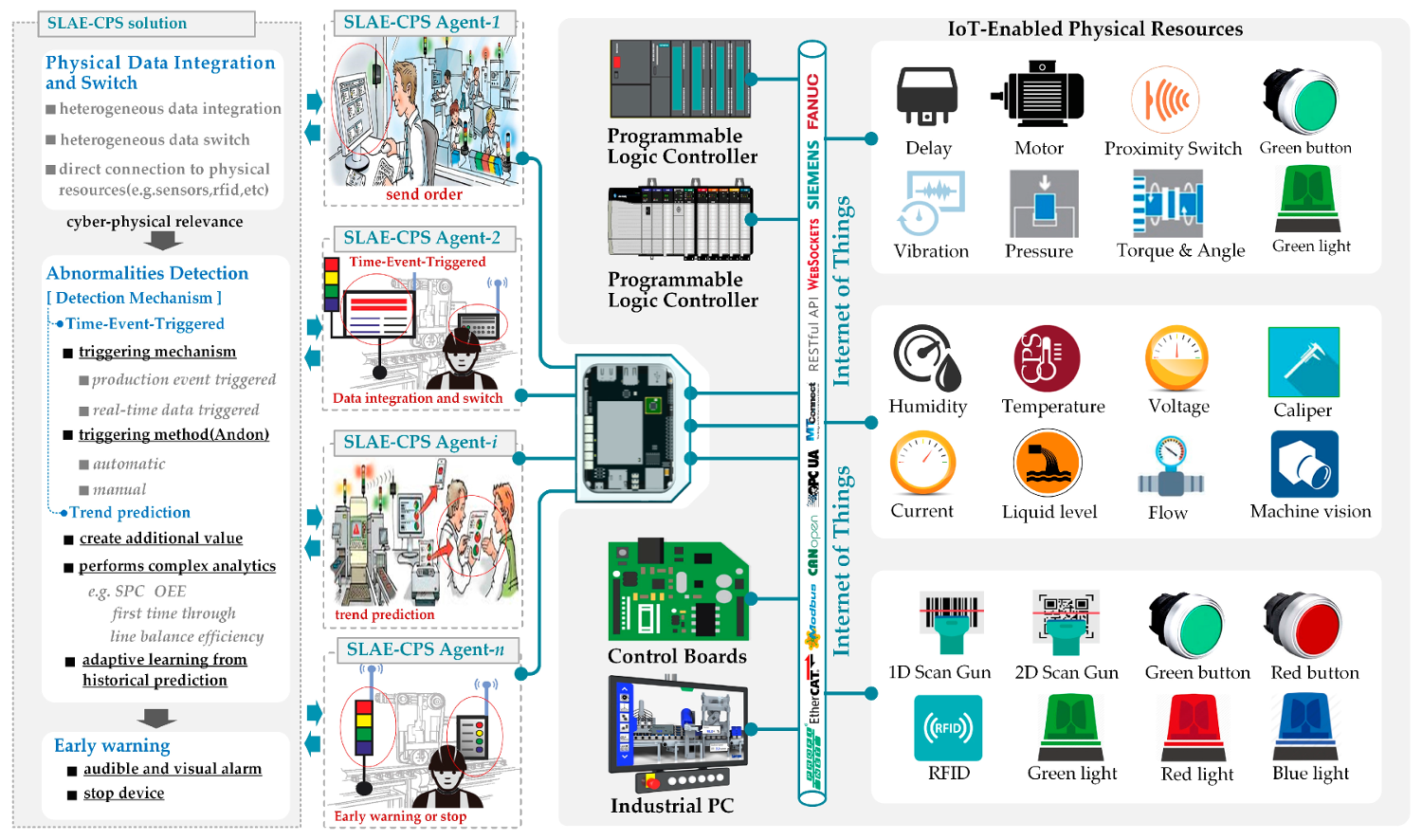
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies


 IT-Times
IT-Times
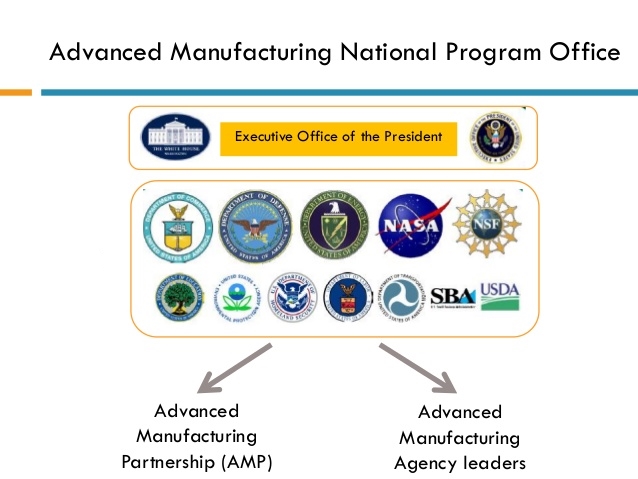
 United States
United States
 German strategy for high-tech industries
German strategy for high-tech industries

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies

 Science and technology
Science and technology

2023年11月,德国BMBF发布《人工智能行动计划》,该计划规划了11项具体行动领域。BMBF正在推动50项以人工智能研究、技术和基础设施发展为重点的现行措施,该计划将在此基础上新增20项额外的人工智能举措,并在本届政府任期内实现投入超过16亿欧元,助力德国在国家和欧洲层面促进人工智能的发展,从而推动欧盟与已经占据人工智能主导地位的国家竞争。

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Big Data
Big Data


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 ***Metaverse
***Metaverse

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts

云计算(英语:Cloud Computing),是一种基于互联网的计算方式,通过这种方式,共享的软硬件资源和信息可以按需求提供给计算机各种终端和其他设备。
云计算是继1980年代大型计算机到客户端-服务器的大转变之后的又一种巨变。用户不再需要了解“云”中基础设施的细节,不必具有相应的专业知识,也无需直接进行控制。[1]云计算描述了一种基于互联网的新的IT服务增加、使用和交付模式,通常涉及通过互联网来提供动态易扩展而且经常是虚拟化的资源。[2][3]
在“软件即服务(SaaS)”的服务模式当中,用户能够访问服务软件及数据。服务提供者则维护基础设施及平台以维持服务正常运作。SaaS常被称为“随选软件”,并且通常是基于使用时数来收费,有时也会有采用订阅制的服务。
推广者认为,SaaS使得企业能够借由外包硬件、软件维护及支持服务给服务提供者来降低IT营运费用。另外,由于应用程序是集中供应的,更新可以即时的发布,无需用户手动更新或是安装新的软件。SaaS的缺陷在于用户的数据是存放在服务提供者的服务器之上,使得服务提供者有能力对这些数据进行未经授权的访问。
用户通过浏览器、桌面应用程序或是移动应用程序来访问云的服务。推广者认为云计算使得企业能够更迅速的部署应用程序,并降低管理的复杂度及维护成本,及允许IT资源的迅速重新分配以因应企业需求的快速改变。
云计算依赖资源的共享以达成规模经济,类似基础设施(如电力网)。服务提供者集成大量的资源供多个用户使用,用户可以轻易的请求(租借)更多资源,并随时调整使用量,将不需要的资源释放回整个架构,因此用户不需要因为短暂尖峰的需求就购买大量的资源,仅需提升租借量,需求降低时便退租。服务提供者得以将目前无人租用的资源重新租给其他用户,甚至依照整体的需求量调整租金。

认知计算是指基于人工智能和信号处理的系统平台。这些平台涉及机器学习、自动推理、自然语言处理、语音识别和计算机视觉、人机交互等技术。
Cognitive computing refers to technology platforms that, broadly speaking, are based on the scientific disciplines of artificial intelligence and signal processing. These platforms encompass machine learning, reasoning, natural language processing, speech recognition and vision (object recognition), human–computer interaction, dialog and narrative generation, among other technologies.


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Mobile Networks
Mobile Networks


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM
CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CNC
CNC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence

Ein digitaler Zwilling (engl. digital twin) ist eine digitale Repräsentanz eines materiellen oder immateriellen Objekts aus der realen Welt in der digitalen Welt. Es ist unerheblich, ob das Gegenstück in der realen Welt bereits existiert oder zukünftig erst existieren wird. Digitale Zwillinge ermöglichen einen übergreifenden Datenaustausch. Sie bestehen aus Modellen des repräsentierten Objekts und können daneben Simulationen, Algorithmen und Services enthalten, die Eigenschaften oder Verhalten des repräsentierten Objekts beschreiben, beeinflussen, oder Dienste darüber anbieten.
数字映射(Digital twin),或译作数字孪生、数字分身、数位双生,指在信息化平台内模拟物理实体、流程或者系统,类似实体系统在信息化平台中的双胞胎。借助于数字映射,可以在信息化平台上了解物理实体的状态,甚至可以对物理实体里面预定义的接口组件进行控制。
数字映射是物联网里面的概念,它指通过集成物理反馈数据,并辅以人工智能、机器学习和软件分析,在信息化平台内置立一个数字化模拟。这个模拟会根据反馈,随着物理实体的变化而自动做出相应的变化。理想状态下,数字映射可以根据多重的反馈源数据进行自我学习,从而几乎实时地在数字世界里呈现物理实体的真实状况。数字映射的反馈源主要依赖于各种传感器,如压力、角度、速度传感器等。数字映射的自我学习(或称机器学习)除了可以依赖于传感器的反馈信息,也可以是通过历史数据,或者是集成网络的数据学习。后者常指多个同批量的物理实体同时进行不同的操作,并将数据反馈到同一个信息化平台,数字映射根据海量的信息反馈,进行迅速的深度学习和精确模拟。

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM
CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CNC
CNC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM
CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
 Japan
Japan

 Science and technology
Science and technology


 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Germany
Germany

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
工业4.0(英语:Industry 4.0、德语:Industrie 4.0),或称生产力4.0,是一个德国政府提出的高科技计划[1]。又称为第四次工业革命、2013年德国联邦教育及研究部和联邦经济及科技部将其纳入《高技术战略2020》的十大未来项目,投资预计达2亿欧元,用来提升制造业的计算机化、数字化和智能化[2]。德国机械及制造商协会(VDMA)等设立了“工业4.0平台”;德国电气电子及信息技术协会发布了德国首个工业4.0标准化路线图。
所谓的4.0目标与以前不同,并不是单单创造新的工业技术,而是着重在将现有的工业相关的技术、销售与产品体验统合起来,是创建具有适应性、资源效率和人因工程学的智能工厂,并在商业流程及价值流程中集成客户以及商业伙伴[3][4],提供完善的售后服务。其技术基础是智能集成感控系统及物联网[5]。这样的架构虽然还在摸索,但如果得以陆续成真并应用,最终将能建构出一个有感知意识的新型智能工业世界,能透过分析各种大数据, 直接生成一个充分满足客户的相关解决方案产品(需求定制),更可利用计算机预测,例如天气预测、公共交通、市场调查数据等等,及时精准生产或调度现有资 源、减少多余成本与浪费等等(供应端优化),需要注意的是工业只是这个智能世界的一个部件,需要以“工业如何适应智能网络下的未来生活”去理解才不会搞混 工业的种种概念。
第四次工业革命可以实现的时间,各方说法不一;德国电气电子及信息技术协会的会员中只有四分之一认为2020年前会有大规模的实施[6],而工业通信标准、安全性和人员培训都是较大的问题。
Industrie 4.0 ist die Bezeichnung für ein Zukunftsprojekt zur umfassenden Digitalisierung der industriellen Produktion, um sie für die Zukunft besser zu rüsten. Der Begriff geht zurück auf die Forschungsunion der deutschen Bundesregierung und ein gleichnamiges Projekt in der Hightech-Strategie der Bundesregierung; zudem bezeichnet er eine Forschungsplattform.[1][2][3] Die industrielle Produktion soll mit moderner Informations- und Kommunikationstechnik verzahnt werden.[4] Technische Grundlage hierfür sind intelligente und digital vernetzte Systeme. Mit ihrer Hilfe soll weitestgehend selbstorganisierte Produktion möglich werden: Menschen, Maschinen, Anlagen, Logistik und Produkte kommunizieren und kooperieren in der Industrie 4.0 direkt miteinander.[4] Durch die Vernetzung soll es möglich werden, nicht mehr nur einen Produktionsschritt, sondern eine ganze Wertschöpfungskette zu optimieren. Das Netz soll zudem alle Phasen des Lebenszyklus des Produktes einschließen – von der Idee eines Produkts über die Entwicklung, Fertigung, Nutzung und Wartung bis zum Recycling.[4]
インダストリー4.0(独: Industrie 4.0、英: Industry 4.0)は、ドイツ連邦教育科学省が勧奨して、2011年にドイツ工学アカデミーが発表したドイツ政府が推進する製造業のデジタル化・コンピューター化を目指すコンセプト、国家的戦略的プロジェクトである[1][2][3]。IoTの普及についてトップダウンで国家プロジェクトとした世界初の事例となる[1]。
「インダストリー4.0」を日本語に直訳した場合には、「第四次産業革命」の意味合いもあるが、「IoTやAIを用いることによる製造業の革新」という一般的な意味の第四次産業革命とドイツの国家プロジェクトとしてのインダストリー4.0とでは意味合いが異なることもある[4]。
Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing[1][2][3][4] and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 is commonly referred to as the fourth industrial revolution.[5]
Industry 4.0 fosters what has been called a "smart factory". Within modular structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and with humans in real-time both internally and across organizational services offered and used by participants of the value chain.[1]
Le concept d’industrie 4.0 ou industrie du futur correspond à une nouvelle façon d’organiser les moyens de production. Cette nouvelle industrie s'affirme comme la convergence du monde virtuel, de la conception numérique, de la gestion (finance et marketing) avec les produits et objets du monde réel. Les grandes promesses de cette quatrième révolution industrielle sont de séduire les consommateurs avec des produits uniques et personnalisés, et malgré de faibles volumes de fabrication, de maintenir des gains. Ces mêmes consommateurs peuvent ainsi communiquer avec les machines durant les phases de réalisation, ce type de production s'appelle la « Smart Product ». Selon ce principe, dans le contexte de l’automatisation industrielle, cela se caractérise par la mise en œuvre de capteurs qui sont les éléments de base des système d'acquisition et de contrôle de données (SCADA). Ils permettent de transformer des grandeurs physiques (température, pression, position, concentration, autres…) en signaux, le plus souvent électriques, qui renseignent sur ces grandeurs. Ces capteurs permettent aux robots d'une chaîne de production de dialoguer et d'adapter l'outil de production aux différents besoins, de manière non exhaustive, les maintenances, les besoins des marchés ou les modifications des clients.
Outre les aspects technologiques, cette quatrième révolution industrielle influe sur différents aspects de nos sociétés modernes. De nouveaux enjeux apparaissent au travers de cette nouvelle manière de produire. L'industrie 4.0 touche évidemment l'aspect économique mais a également des impacts sociaux, politiques ou environnementaux. Il pose la question de l'emploi de millions de salariés à travers le monde. En effet, l'accompagnement des salariés actuels et la formation des futurs salariés sont à prendre en compte. Il semble difficile d'envisager que des millions de travailleurs se retrouvent sans emploi. Plus généralement, il est nécessaire de réfléchir à la place de l'humain dans cette industrie 4.0.
Il termine Industria 4.0 (o in inglese Industry 4.0) indica una tendenza dell'automazione industriale che integra alcune nuove tecnologie produttive per migliorare le condizioni di lavoro e aumentare la produttività e la qualità produttiva degli impianti.
El concepto "'Industria 4.0'" (también señalado o referenciado como Revolución industrial 4.0,1o Industria inteligente,2 o Ciberindustria del futuro)3 corresponde a una nueva manera de organizar los medios de producción.
El objetivo que pretende alcanzarse es la puesta en marcha de un gran número de «fábricas inteligentes» (en inglés: «smart factories») capaces de una mayor adaptabilidad a las necesidades y a los procesos de producción, así como a una asignación más eficiente de los recursos, abriendo así la vía a una nueva revolución industrial o Revolución industrial 4.0.4
Las bases tecnológicas en que se apoya esta orientación, entre otras son las siguientes: (1) Internet de las cosas ; (2) Sistemas ciberfísicos (3) Cultura maker (Cultura Hágalo usted mismo) ; (4) Fábrica 4.0…56 Sin embargo, la Industria 4.0 no se reduce exclusivamente a los cuatro puntos recién citados, pues es mucho más que eso. La Industria 4.0 es consistente con la llamada Cuarta Revolución Industrial, enfatizando y acentuando la idea de una creciente y adecuada digitalización y coordinación cooperativa en todas las unidades productivas de la economía.7
Industria 4.0 es un concepto nuevo, que también recibe otras denominaciones o subdenominaciones tales como:8 « Ciberusina »,9 « Ciberfábrica »,10 « Usina digital », « Industria digital »,11 « Fabricación avanzada »,1213 « Futurprod »,14 « Integrated Industry »,15 « Smart-Industries »,161718 « Intelligent Manufacturing System ».19
Este concepto de Industria 4.0 que aquí se presenta no es una realidad ya consolidada y experimentada, sino un nuevo hito en el desarrollo industrial que podría marcar importantes cambios sociales en los próximos años, haciendo un uso intensivo de Internet y de las tecnologías punta, con el fin primordial de desarrollar plantas industriales y generadores de energía más inteligentes y más respetuosos con el medio ambiente, y con cadenas de producción mucho mejor comunicadas entre sí y con los mercados de oferta y demanda.4

智能制造(英语:Smart manufacturing)[1]是指引入电脑整合制造以及数字信息技术的制造业。智能工厂就是典型的智能制造。智能制造中有可互操作的系统、智能自动化机器人、强大的网络安全以及联网的传感器。
Smart manufacturing[1] is a broad category of manufacturing that employs computer-integrated manufacturing, high levels of adaptability and rapid design changes, digital information technology, and more flexible technical workforce training.[2] Other goals sometimes include fast changes in production levels based on demand,[3][1] optimization of the supply chain,[3] efficient production and recyclability.[4] In this concept, as smart factory has interoperable systems, multi-scale dynamic modelling and simulation, intelligent automation, strong cyber security, and networked sensors.
The broad definition of smart manufacturing covers many different technologies. Some of the key technologies in the smart manufacturing movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices and services, and advanced robotics.[
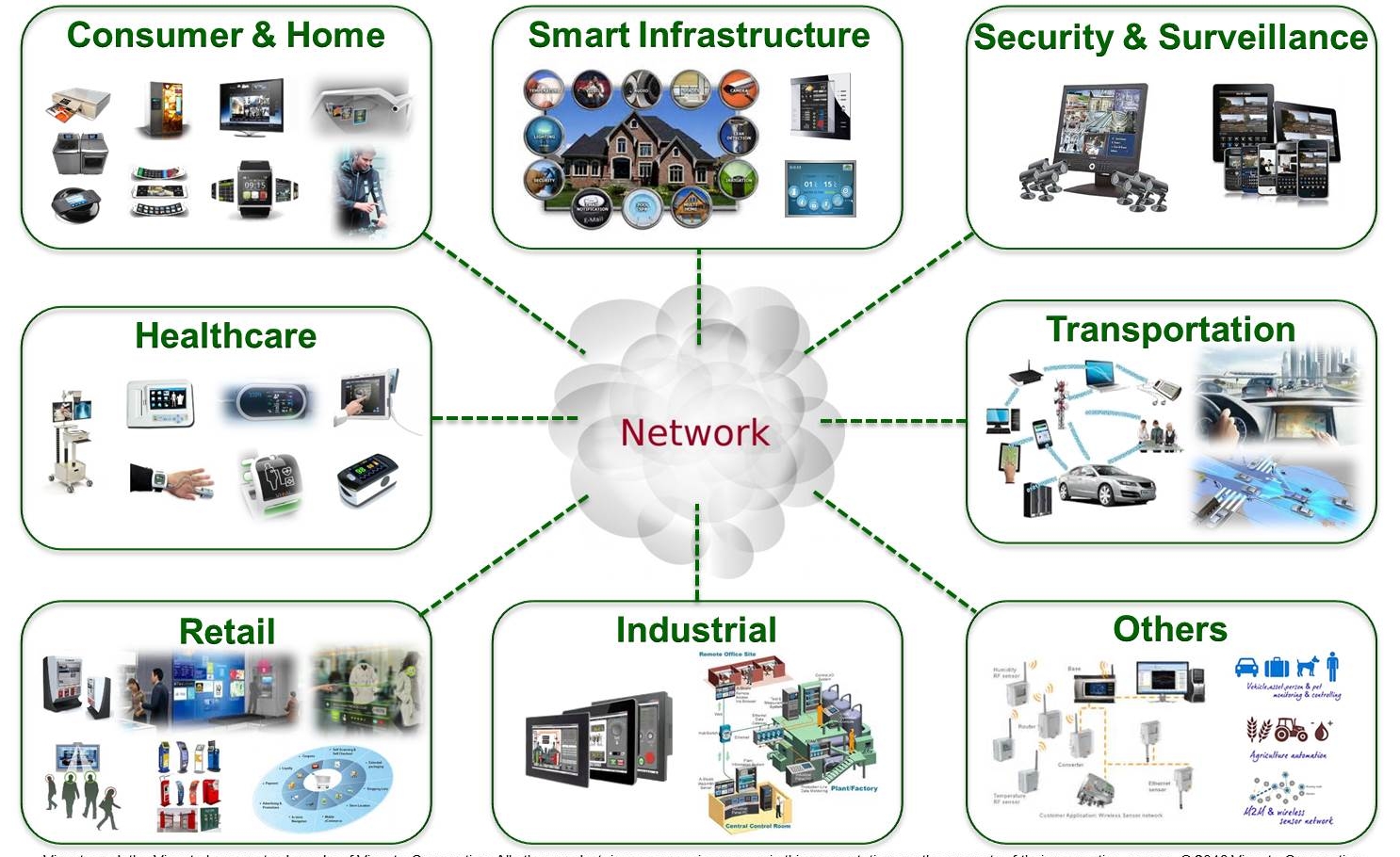
物联网(Internet of Things,缩写IOT)是一个基于互联网、传统电信网等訊息承载体,让所有能够被独立寻址的普通物理对象实现互联互通的网络。[1]物联网一般为无线网,而由于每个人周围的设备可以达到一千至五千个,所以物联网可能要包含500兆至一千兆个物体。在物联网上,每个人都可以应用电子标签将真实的物体上网联结,在物联网上都可以查找出它们的具体位置。通过物联网可以用中心计算机对机器、设备、人员进行集中管理、控制,也可以对家庭设备、汽车进行遥控,以及搜尋位置、防止物品被盗等。
物联网将现实世界数位化,应用范围十分广泛。物联网的应用领域主要包括以下几个方面:运输和物流领域、健康医疗领域、智慧环境(家庭、办公、工厂)领域、个人和社会领域等,[2]具有十分广阔的市场和应用前景。
 China
China
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM
CAD/CAE/CAM/EDA/PDM/PLM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CNC
CNC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM
CRM/EAM/ERP/SRM/SCM/HCM/QM/XM/WFM


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

Neue Informationstechnologien/新一代信息技术产业
集成电路及专用装备。着力提升集成电路设计水平,不断丰富知识产权(IP)核和设计工具,突破关系国家信息与网络安全及电子整机产业发展的核心通用芯片,提升国产芯片的应用适配能力。掌握高密度封装及三维(3D)微组装技术,提升封装产业和测试的自主发展能力。形成关键制造装备供货能力。
信息通信设备。掌握新型计算、高速互联、先进存储、体系化安全保障等核心技术,全面突破第五代移动通信(5G)技术、核心路由交换技术、超高速大容量智能光传输技术、“未来网络”核心技术和体系架构,积极推动量子计算、神经网络等发展。研发高端服务器、大容量存储、新型路由交换、新型智能终端、新一代基站、网络安全等设备,推动核心信息通信设备体系化发展与规模化应用。
操作系统及工业软件。开发安全领域操作系统等工业基础软件。突破智能设计与仿真及其工具、制造物联与服务、工业大数据处理等高端工业软件核心技术,开发自主可控的高端工业平台软件和重点领域应用软件,建立完善工业软件集成标准与安全测评体系。推进自主工业软件体系化发展和产业化应用。
High-End numerische Maschinenwerkzeuge und Industrieroboter/高档数控机床和机器人
高档数控机床。开发一批精密、高速、高效、柔性数控机床与基础制造装备及集成制造系统。加快高档数控机床、增材制造等前沿技术和装备的研发。以提升可靠性、精度保持性为重点,开发高档数控系统、伺服电机、轴承、光栅等主要功能部件及关键应用软件,加快实现产业化。加强用户工艺验证能力建设。
机器人。围绕汽车、机械、电子、危险品制造、国防军工、化工、轻工等工业机器人、特种机器人,以及医疗健康、家庭服务、教育娱乐等服务机器人应用需求,积极研发新产品,促进机器人标准化、模块化发展,扩大市场应用。突破机器人本体、减速器、伺服电机、控制器、传感器与驱动器等关键零部件及系统集成设计制造等技术瓶颈。
Luft- und Raumfahrzeuge/航空航天装备
加快大型飞机研制,适时启动宽体客机研制,鼓励国际合作研制重型直升机;推进干支线飞机、直升机、无人机和通用飞机产业化。突破高推重比、先进涡桨(轴)发动机及大涵道比涡扇发动机技术,建立发动机自主发展工业体系。开发先进机载设备及系统,形成自主完整的航空产业链。
航天装备。发展新一代运载火箭、重型运载器,提升进入空间能力。加快推进国家民用空间基础设施建设,发展新型卫星等空间平台与有效载荷、空天地宽带互联网系统,形成长期持续稳定的卫星遥感、通信、导航等空间信息服务能力。推动载人航天、月球探测工程,适度发展深空探测。推进航天技术转化与空间技术应用。
Meerestechnik -Ausrüstung und High-End-Schiffe/海洋工程装备及高技术船舶
大力发展深海探测、资源开发利用、海上作业保障装备及其关键系统和专用设备。推动深海空间站、大型浮式结构物的开发和工程化。形成海洋工程装备综合试验、检测与鉴定能力,提高海洋开发利用水平。突破豪华邮轮设计建造技术,全面提升液化天然气船等高技术船舶国际竞争力,掌握重点配套设备集成化、智能化、模块化设计制造核心技术。
High-End Schienenverkehrstechnik/先进轨道交通装备
加快新材料、新技术和新工艺的应用,重点突破体系化安全保障、节能环保、数字化智能化网络化技术,研制先进可靠适用的产品和轻量化、模块化、谱系化产品。研发新一代绿色智能、高速重载轨道交通装备系统,围绕系统全寿命周期,向用户提供整体解决方案,建立世界领先的现代轨道交通产业体系。
Energiesparende Autos und neue Energie-Autos/节能与新能源汽车
继续支持电动汽车、燃料电池汽车发展,掌握汽车低碳化、信息化、智能化核心技术,提升动力电池、驱动电机、高效内燃机、先进变速器、轻量化材料、智能控制等核心技术的工程化和产业化能力,形成从关键零部件到整车的完整工业体系和创新体系,推动自主品牌节能与新能源汽车同国际先进水平接轨。
Elektrische Ausrüstung/电力装备
推动大型高效超净排放煤电机组产业化和示范应用,进一步提高超大容量水电机组、核电机组、重型燃气轮机制造水平。推进新能源和可再生能源装备、先进储能装置、智能电网用输变电及用户端设备发展。突破大功率电力电子器件、高温超导材料等关键元器件和材料的制造及应用技术,形成产业化能力。
Landwirtschaftsmaschinen/农机装备
重点发展粮、棉、油、糖等大宗粮食和战略性经济作物育、耕、种、管、收、运、贮等主要生产过程使用的先进农机装备,加快发展大型拖拉机及其复式作业机具、大型高效联合收割机等高端农业装备及关键核心零部件。提高农机装备信息收集、智能决策和精准作业能力,推进形成面向农业生产的信息化整体解决方案。
Neue Werkstoffe/新材料
以特种金属功能材料、高性能结构材料、功能性高分子材料、特种无机非金属材料和先进复合材料为发展重点,加快研发先进熔炼、凝固成型、气相沉积、型材加工、高效合成等新材料制备关键技术和装备,加强基础研究和体系建设,突破产业化制备瓶颈。积极发展军民共用特种新材料,加快技术双向转移转化,促进新材料产业军民融合发展。高度关注颠覆性新材料对传统材料的影响,做好超导材料、纳米材料、石墨烯、生物基材料等战略前沿材料提前布局和研制。加快基础材料升级换代。
Bio-Medizin und High-End-medizinische Geräte/生物医药及高性能医疗器械
发展针对重大疾病的化学药、中药、生物技术药物新产品,重点包括新机制和新靶点化学药、抗体药物、抗体偶联药物、全新结构蛋白及多肽药物、新型疫苗、临床优势突出的创新中药及个性化治疗药物。提高医疗器械的创新能力和产业化水平,重点发展影像设备、医用机器人等高性能诊疗设备,全降解血管支架等高值医用耗材,可穿戴、远程诊疗等移动医疗产品。实现生物3D打印、诱导多能干细胞等新技术的突破和应用。

 Financial
Financial

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
Production Engineering/Manufacturing Technologies
 United States
United States

 Science and technology
Science and technology
