
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Woman
4x400 m Woman
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP2
TOP2
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2001 Edmonton
2001 Edmonton
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 States of Europe
States of Europe
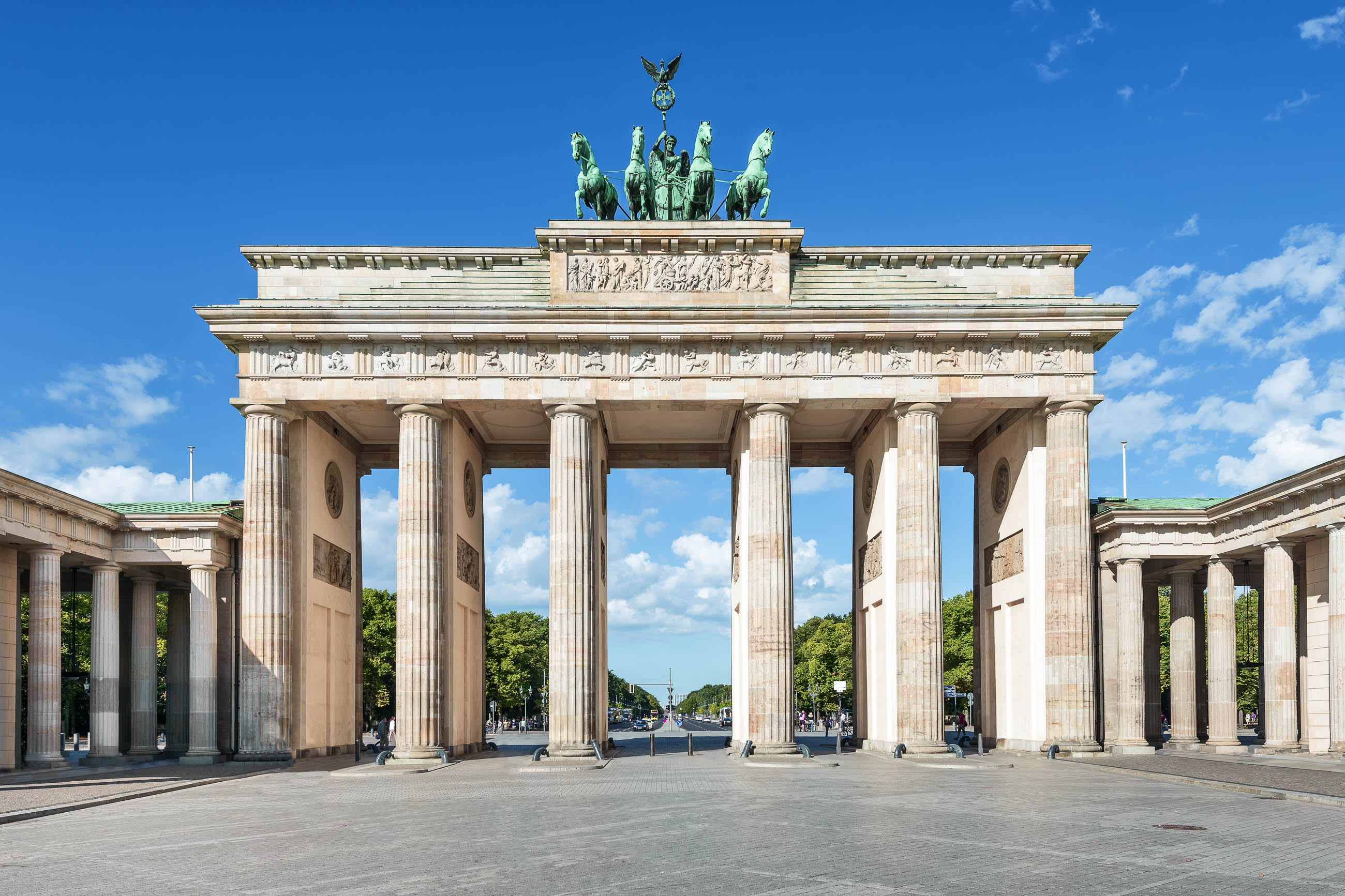

德意志联邦共和国(德语:Bundesrepublik Deutschland、![]() 发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
发音(帮助·信息))简称德国(德语:Deutschland)[参 7],是一个位于欧洲的联邦议会共和制国家,国家元首为联邦总统,政府首脑为联邦总理。它由16个联邦州组成,首都与最大城市为柏林。其国土面积约35.7万平方公里,南北距离为876公里,东西相距640公里,从北部的北海与波罗的海延伸至南部的阿尔卑斯山[参 8]。气候温和,季节分明。德国人口约8,180万,为欧洲联盟中人口最多的国家,也是世界第二大移民目的地,仅次于美国[参 9]。
在50万年前的旧石器时代晚期,海德堡人及其后代尼安德特人生活在今德国中部。自古典时代以来各日耳曼部族开始定居于今日德国的北部地区。公元1世纪时,有罗马人著作的关于“日耳曼尼亚”的历史记载。在公元4到7世纪的民族迁徙期,日耳曼部族逐渐向欧洲南部扩张。自公元10世纪起,德意志领土组成神圣罗马帝国的核心部分[参 10]。16世纪时,德意志北部地区成为宗教改革中心。1871年,在普鲁士主导之下,多数德意志邦国统一并加入德意志帝国。在第一次世界大战和1918-1919年德国革命后,德意志帝国解体,议会制的魏玛共和国取而代之。1933年国家社会主义党获取政权并建立独裁统治,最终导致第二次世界大战及系统性种族灭绝的发生。在战败并经历同盟国军事占领后,两个德国分别建立:德意志民主共和国和德意志联邦共和国。在1990年10月3日重新统一成为现在的德国。
德国是世界大国之一,其国内生产总值以国际汇率计居世界第四,以购买力平价计居世界第五。其诸多工业和科技部门位居世界前列,例如全球驰名的德国车厂、精密部件等,为世界第三大出口国。德国为发达国家,生活水平居世界前列。德国人也以热爱大自然闻名,都市绿化率极高,也是欧洲再生能源大国,是可持续发展经济的样板,除了强调环境保护与自然生态保育,在人为饲养活体的态度十分严谨,不但获得大量外汇和资讯优势,其动物保护法律管束、生命教育水准也是首屈一指的,在高等教育方面并提供免费大学教育[参 11],并具备完善的社会保障制度和医疗体系,催生出拜尔等大药厂。
德国为1993年欧洲联盟建立时的创始国之一,为申根区一部分,并于1999年推动欧元区的建立。德国亦为联合国、北大西洋公约组织、八国集团、20国集团及经济合作与发展组织成员。其军事开支总额居世界第九。
德语是欧盟境内使用人数最多的母语。德国文化的丰富层次和对世界的影响表现在其美术和建筑、音乐、哲学以及电影等等。德国的文化遗产主要以老城为代表。另外国家公园和自然公园共计有上百处。
(Vollform: Bundesrepublik Deutschland) ist ein föderal verfasster Staat in Mitteleuropa, der aus den 16 deutschen Ländern besteht. Die Bundesrepublik ist ein freiheitlich-demokratischer Rechtsstaat[8] und stellt die jüngste Ausprägung des deutschen Nationalstaates dar.[9] Mit rund 82,8 Millionen Einwohnern (31. Dezember 2016) zählt Deutschland zu den dicht besiedelten Flächenstaaten.
An Deutschland grenzen neun Staaten, im Norden die Gewässer der Nord- und Ostsee und im Süden das Bergland der Alpen. Es liegt in der gemäßigten Klimazone. Bundeshauptstadt sowie bevölkerungsreichste deutsche Stadt ist Berlin. Weitere bedeutende Metropolen sind Hamburg, München, Köln, Frankfurt, Stuttgart und Düsseldorf; größter Ballungsraum ist das Ruhrgebiet. Deutschland gilt international als das Land mit der zweithöchsten Zahl von Einwanderern nach den Vereinigten Staaten (Stand 2015).[10][11] Seine Bevölkerung ist die zweitälteste und hat mit 1,47 Kindern pro Frau (2014) eine der niedrigsten Geburtenraten der Welt.[12]
Auf dem Territorium des heutigen Deutschlands wurden frühe Siedlungsformen von vor etwa 500.000 Jahren nachgewiesen, wie Funde vom Heidelbergmenschen, vom Neandertaler sowie von einigen der ältesten Kunstwerke der Menschheit aus der Altsteinzeit belegen. Seit der Antike ist die lateinische Bezeichnung Germania für das Siedlungsgebiet der Germanen bekannt, seit dem 4. Jahrhundert ist die Verwendung des Begriffes deutsch in althochdeutscher Form belegt. Das seit dem 10. Jahrhundert bestehende Heilige Römische Reich bestand aus vielen Herrschaftsgebieten und war mit dem 1815 nachfolgenden Deutschen Bund der Ursprung des föderalen deutschen Staates. Dieser entstand erstmals mit der Gründung des Deutschen Reichs im Jahr 1871, woraus eine rasche Wirtschaftsentwicklung vom Agrar- zum Industrieland folgte.
Nach dem Ersten Weltkrieg kam es infolge der Novemberrevolution 1918 zur Bildung der demokratischen Weimarer Republik und zum Friedensvertrag von Versailles. Der nationalsozialistischen Diktatur von 1933 bis 1945 samt verheerendem Zweitem Weltkrieg folgte eine Zeit der Veränderung und Teilung des Staates. Der Gründung der Bundesrepublik als demokratischer westdeutscher Teilstaat mit Inkrafttreten des Grundgesetzes am 24. Mai 1949 folgte wiederum die Gründung der sozialistischen DDR am 7. Oktober 1949 als ostdeutscher Teilstaat.[13] Nach der friedlichen Revolution 1989 folgte die Wiedervereinigung beider Landesteile am 3. Oktober 1990; seitdem wird der Tag der Deutschen Einheit als nationaler Feiertag begangen.
Deutschland ist Gründungsmitglied des Europarates und der Europäischen Union sowie deren bevölkerungsreichstes Land. Mit 18 anderen EU-Mitgliedstaaten bildet es eine Währungsunion, die Eurozone. Es ist Mitglied der UN, der OECD, der OSZE, der NATO, der G7 und der G20. Die Bundesrepublik Deutschland gilt als einer der politisch einflussreichsten Staaten Europas und ist ein gesuchtes Partnerland auf globaler Ebene.[14]
Gemessen am Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist Deutschland die größte Volkswirtschaft Europas und die viertgrößte der Welt.[5] Im Jahr 2015 war es die drittgrößte Export- und Importnation.[15] Es ist marktwirtschaftlich geprägt. Aufgrund der Rohstoffarmut und der Automatisierung der Industrie entwickelt sich das Land, das stark von der Qualität seines Bildungssystems abhängt, zunehmend zur Informations- und Wissensgesellschaft.[16] Gemäß dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung zählt Deutschland zu den sehr hoch entwickelten Ländern.[17]
Die deutsche Sprache ist die meistgesprochene Muttersprache und nach Englisch die zweithäufigste Fremdsprache in der Europäischen Union; die Zahl ihrer Sprecher rangiert weltweit auf dem zehnten Platz. Die Kultur Deutschlands hat vielschichtige und weltbekannte Ausdrucksformen hervorgebracht, etwa in der Kunst und Architektur, der Musik, der Philosophie, der Filmkultur, der Küche, der Traditionspflege, im Design, im Sport, in der Wissenschaft und der Wirtschaft. Das UNESCO-Welterbe in Deutschland sowie die Vielfalt der Kulturdenkmale und Altstädte ist umfangreich. Eine Vielzahl von National- und Naturparks sind im Land ausgewiesen.
ドイツ連邦共和国(ドイツれんぽうきょうわこく、独: Bundesrepublik Deutschland)、通称ドイツ(独: Deutschland)は、中央ヨーロッパ西部に位置する連邦共和制国家。首都および最大の都市はベルリン州。南がスイスとオーストリア、北にデンマーク、西をオランダとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東はポーランドとチェコとそれぞれ国境を接する。
欧州大陸における政治的・経済的な主要国であり、歴史上、多くの文化・科学・技術分野における重要な指導国でもある。人口は8300万人で、これは欧州連合において最大である。同国は限定的主権を有する16の州によって構成される。国土の総面積は35万7386平方キロメートルであり、主に温暖な気候に属する。かつて「西ドイツ」と呼ばれていた時代は「西欧」に分類されていたが、東ドイツ(ドイツ民主共和国)の民主化と東西ドイツの統一により「中欧」または「中西欧」に分類されるようになっている。
ドイツ経済の規模は、対米ドル名目為替レートによって計算される米ドル建て名目GDP(MERベースGDP)で世界第4位であり、対米ドル購買力平価によって計算される米ドル建て実質GDP(PPPベースGDP)で世界第5位である。技術及び産業分野における世界的なリーダーとして、世界第3位の輸出国かつ世界第3位の輸入国である。世界最古のユニバーサルヘルスケア制度を含む、包括的な社会保障を特色とする非常に高い生活水準が実現されている先進国である。豊かな政治及び文化の歴史で知られ、影響力ある多数の芸術家、音楽家、映画人、哲学者、科学者及び技術者、起業家の故国である。
1993年に欧州連合へ発展した1957年の欧州諸共同体の原加盟国であるほか、1995年以来シェンゲン圏の一員で、1999年以降はユーロ圏の一員でもある。また、国際連合、欧州評議会、NATO、G7、G20、OECDの主要なメンバーであり、欧州の大国「ビッグ4」や列強の一国に数えられる。アメリカ合衆国に次ぎ、ドイツは世界第2位の移住地である[1]。
Germany (German: Deutschland, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃlant] (![]() listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
listen)), officially the Federal Republic of Germany,[e] is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of over 83 million within its 16 constituent states. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and largest city is Berlin, and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation. Following the Napoleonic Wars and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German Confederation was formed in 1815. In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–1919, the Empire was replaced by the semi-presidential Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to the establishment of a dictatorship, World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, Germany was divided into the Federal Republic of Germany, generally known as West Germany, and the German Democratic Republic, East Germany. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community and the European Union, while the German Democratic Republic was a communist Eastern Bloc state and member of the Warsaw Pact. After the fall of communism, German reunification saw the former East German states join the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1990—becoming a federal parliamentary republic.
Germany is a great power with a strong economy; it has the largest economy in Europe, the world's fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial, scientific and technological sectors, it is both the world's third-largest exporter and importer of goods. As a developed country, which ranks very high on the Human Development Index, it offers social security and a universal health care system, environmental protections, and a tuition-free university education. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the G20, and the OECD. It has the third-greatest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
L'Allemagne (/almaɲ/ ; en allemand : Deutschland /ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ Écouter), en forme longue la République fédérale d'Allemagneb, abrégée en RFA (en allemand : Bundesrepublik Deutschland /ˈbʊn.dəs.ʁe.puˌblik ˈdɔʏtʃ.lant/ Écouter, abrégée en BRD), est un État d'Europe centrale, et selon certaines définitions d'Europe de l'Ouest, entouré par la mer du Nord, le Danemark et la mer Baltique au nord, par la Pologne à l'est-nord-est, par la Tchéquie à l'est-sud-est, par l'Autriche au sud-sud-est, par la Suisse au sud-sud-ouest, par la France au sud-ouest, par la Belgique et le Luxembourg à l'ouest, enfin par les Pays-Bas à l'ouest-nord-ouest. Décentralisée et fédérale, l'Allemagne compte quatre métropoles de plus d'un million d'habitants : la capitale Berlin, ainsi que Hambourg, Munich et Cologne. Le siège du gouvernement est situé dans la ville de Berlin et dans la ville fédérale de Bonn. Francfort-sur-le-Main est considérée comme la capitale financière de l'Allemagnec : dans cette ville se trouve le siège de la Banque centrale européenne.
Beaucoup de peuples germaniques occupent le Nord du territoire actuel depuis l'Antiquité classique. Durant ce que l'on nomme les invasions barbares, les tribus germaniques se rapprochent du Sud de ce territoire. À partir du Xe siècle, les territoires forment la partie centrale du Saint-Empire romain germanique. Au XVIe siècle, le Nord de l'Allemagne est au cœur de la réforme protestante. Le pangermanisme entraîne l'unification des États allemands en 1871 pour former l'Empire allemand. Après la Première Guerre mondiale, et la révolution allemande de 1918-1919, l'Empire est remplacé par la république parlementaire de Weimar. L'accès au pouvoir des nazis en 1933 mène à la Seconde Guerre mondiale, au cours de laquelle le régime totalitaire connu sous le nom de Troisième Reich, fondé sur un racisme et un antisémitisme singulier, et dirigé par le dictateur Adolf Hitler, perpètre des crimes de masse en Europe, dont la Shoah, et laisse le pays en ruines. Après sa défaite militaire en 1945, l'Allemagne perd des territoires et — par la volonté des vainqueurs alliés qui entrent dans la « guerre froide » — est contrainte de se scinder en deux nations : à l'ouest un État démocratique, la République fédérale d'Allemagne (en abrégé RFA) et, à l'est, la République démocratique allemande (en abrégé RDA) sous emprise de l'Union soviétique. Le mur de Berlin — qui symbolise cette division dans l'ancienne capitale — tombe le 9 novembre 1989 et l'Allemagne est à nouveau réunifiée le 3 octobre 1990, Berlin en redevenant la capitale.
La langue officielle du pays est l'allemand, sa monnaie est l'euro, sa devise est Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit (« Unité et Droit et Liberté ») et son drapeau est constitué de trois bandes horizontales aux couleurs nationales de l'Allemagne : noir, rouge et or. Son hymne national est Das Deutschlandlied (« Le Chant de l'Allemagne »). Avec plus de 83 millions d'habitants2, l'Allemagne est le pays le plus peuplé de l'Union européenne. Elle est une grande puissance politique5 et sa dirigeante politique, Angela Merkel en 2019, est largement perçue comme la personnalité politique la plus influente de l'Union européenne6. L'Allemagne est aussi la première puissance économique d'Europe ainsi que la quatrième puissance économique mondiale, et elle compte parmi les pays industrialisés les plus développés et les plus performants dans le monde. Elle figure parmi les premiers mondiaux dans les secteurs de l'aéronautique, de l'automobile, de l'industrie chimique et de la construction mécanique. L'Allemagne est en 2017 le troisième exportateur mondial derrière la Chine et les États-Unis et elle est le pays présentant le plus grand excédent commercial du monde en 20187. Elle a aussi le taux de chômage le plus bas parmi les 19 États membres de la zone euro, ce taux s'établissant à 3,3 % en décembre 2018, d'après Eurostat8. L'Allemagne affiche un niveau de vie « très élevé » : elle est 4e au classement IDH en 20194.
Membre fondateur de l'Union européenne et membre du G7, du G20, de la zone euro, de l'espace Schengen et de l'OTAN, elle abrite le siège de la Banque centrale européenne, du Tribunal international du droit de la mer et de l'Office européen des brevets. L'Allemagne est le pays le plus apprécié du monde, ceci d'après des sondages effectués à la demande de la BBC en mai 20139, du GfK en novembre 201410 et de U.S. News en janvier 201611. Comme destination d'immigration, elle est une des terres préférées, se classant ainsi deuxième dans le monde12, après les États-Unis. L'Allemagne est en 2014 le principal pollueur d'Europe, émettant à elle seule près de 23 % de l'ensemble des émissions de CO2 du continent13.
La Germania (/ʤerˈmanja/[6]), ufficialmente Repubblica Federale di Germania (in tedesco: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , [ˈbʊndəsrepʊˌbliːk ˈdɔɪ̯ʧˌlant][7] e nel linguaggio comune più semplicemente Deutschland), è uno Stato membro dell'Unione europea situato nell'Europa centro-occidentale, repubblica federale parlamentare di sedici stati (Bundesländer) con capitale, nonché maggiore città per numero di abitanti, Berlino. Bagnata a nord dal mare del Nord e dal mar Baltico, confina a nord con la Danimarca, ad est con la Polonia e la Repubblica Ceca, a sud con Austria e Svizzera, e a ovest con Francia, Lussemburgo, Belgio e Paesi Bassi. Il territorio della Germania copre una superficie di 357 578 km² ed è caratterizzato da un clima atlantico nella parte nord-occidentale e continentale nella parte sud-orientale. Con quasi 84 milioni abitanti[8], è lo Stato più popoloso dell'Unione europea, il secondo Stato d'Europa dopo la Russia e il 19º del mondo per popolazione. È anche il secondo paese del mondo per numero di immigrati dopo gli Stati Uniti d'America.[9]
La regione denominata oggi Germania fu abitata da diversi popoli germanici, conosciuti e documentati già dal 100 a.C. A partire dal X secolo questi territori tedeschi hanno dato contributo alla parte centrale del Sacro Romano Impero che si protrasse sotto varie forme fino al 1806. Nel corso del XVI secolo, il nord della Germania divenne il centro della Riforma protestante. Come moderno Stato nazionale, il Paese venne unificato nel 1871 dopo la Guerra franco-prussiana. Responsabile principale dello scoppio della Seconda guerra mondiale, durante la quale perpetrò i crimini dell'Olocausto a danno di ebrei e minoranze oggetto di discriminazione da parte dell'allora dominante nazismo, nel 1949 a conflitto concluso la Germania venne divisa in due Stati separati – la Repubblica Federale di Germania (Germania Occidentale o BRD) e la Repubblica Democratica Tedesca (Germania Orientale o DDR) – lungo i confini d'occupazione degli alleati occidentali e sovietici. I due Stati si riunificarono solo nel 1990. La Germania Occidentale fu un membro fondatore della Comunità economica europea (CEE) nel 1957 (che divenne Unione europea nel 1993). Partecipa dal 1995 agli accordi di Schengen e ha adottato la moneta unica europea, l'euro, nel 2002 in sostituzione del marco tedesco.
La Germania è altresì un membro dell'ONU, della NATO, come sopraddetto dell'Unione europea, poi del G7, del G4 e firmatario del protocollo di Kyoto. La Germania è la quarta potenza economica mondiale dopo Stati Uniti, Cina e Giappone; è la quarta più grande economia in termini di PIL nominale e la quinta in termini di parità di potere d'acquisto. È il secondo più grande paese esportatore dopo la Cina e il secondo importatore di merci. In termini assoluti, la Germania assegna il secondo più grande bilancio annuale in aiuti allo sviluppo internazionale,[10] mentre le sue spese militari la classificano come sesta.[11] Il Paese ha sviluppato un elevato standard di vita e detiene una posizione chiave negli affari europei oltre ad una moltitudine di strette partnership a livello globale.[12] La Germania è riconosciuta come capolista in vari settori scientifici e tecnologici.[13]
Alemania (en alemán, Deutschland, pronunciado /ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ (![]() escuchar)), oficialmente República Federal de Alemania (en alemán, Bundesrepublik Deutschland pronunciado /ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ (
escuchar)), oficialmente República Federal de Alemania (en alemán, Bundesrepublik Deutschland pronunciado /ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant/ (![]() escuchar)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Constituido en Estado social y democrático de derecho, su forma de gobierno es la república parlamentaria y federal. Su capital es Berlín. Está formado por dieciséis estados federados (Bundesländer) y limita al norte con el mar del Norte, Dinamarca, Suecia (frontera marítima) y el mar Báltico; al este con Polonia y la República Checa; al sur con Austria y Suiza; y al oeste con Francia, Luxemburgo, Bélgica y los Países Bajos. La ciudad de Büsingen am Hochrhein, enclavada en Suiza, también forma parte de Alemania. El territorio de Alemania abarca 357 022 km² de extensión5 y posee un clima templado. Con casi 83 millones de habitantes, es el país más poblado entre los Estados miembros de la Unión Europea, y es el hogar del tercer mayor grupo de emigrantes internacionales. En 2014, Alemania fue el segundo destino de las migraciones más popular en el mundo, después de Estados Unidos.9
escuchar)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Constituido en Estado social y democrático de derecho, su forma de gobierno es la república parlamentaria y federal. Su capital es Berlín. Está formado por dieciséis estados federados (Bundesländer) y limita al norte con el mar del Norte, Dinamarca, Suecia (frontera marítima) y el mar Báltico; al este con Polonia y la República Checa; al sur con Austria y Suiza; y al oeste con Francia, Luxemburgo, Bélgica y los Países Bajos. La ciudad de Büsingen am Hochrhein, enclavada en Suiza, también forma parte de Alemania. El territorio de Alemania abarca 357 022 km² de extensión5 y posee un clima templado. Con casi 83 millones de habitantes, es el país más poblado entre los Estados miembros de la Unión Europea, y es el hogar del tercer mayor grupo de emigrantes internacionales. En 2014, Alemania fue el segundo destino de las migraciones más popular en el mundo, después de Estados Unidos.9
Las palabras alemán y Alemania son latinizaciones del antiguo germánico allmanis (compuesto de all ‘todos’ y man ‘hombre’, es decir, ‘todos los hombres’); el historiador romano Amiano Marcelino fue el primero en hablar de Alamannia en el siglo IV para aludir a una confederación de tribus germánicas.[cita requerida] Pero estas denominaciones eran utilizadas también en la antigüedad por los romanos para denominar a la tribu de los alamanes (no es lo mismo que alemanes), el pueblo germánico más cercano al territorio del Imperio romano. De ahí fue usada para nombrar al país entero.10 Además de alemán, está también extendido el uso del gentilicio germano, derivado del nombre con que los romanos se referían a las tribus ni romanas ni celtas de la zona central de Europa, cuyo territorio llamaban Germania.10 Desde el año 962, los territorios alemanes formaron una parte central del Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico, que duró hasta 1806. Durante el siglo XVI, las regiones del norte del país se convirtieron en el centro de la Reforma protestante.
Como un moderno Estado nación, el país fue unificado en tiempos de la guerra franco-prusiana de 1871. Tras la Segunda Guerra Mundial, cuando la Alemania nazi fue derrotada por los aliados, Alemania fue dividida en dos Estados separados a lo largo de las líneas de ocupación aliada en 1949; los Estados resultantes fueron la República Federal de Alemania y la República Democrática Alemana, que se reunificaron en 1990. Fue miembro fundador de la Comunidad Europea (1957), que se convirtió en la Unión Europea en 1993. Es parte de la zona Schengen y adoptó la moneda común europea, el euro, en 1999 (movimiento de pagos sin efectivo) y 2002 (pagos en efectivo).
Alemania es miembro de la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, la OTAN, el G-7, las naciones G4, y firmó el Protocolo de Kioto. Es la cuarta mayor economía mundial en cuanto al PIB nominal, la primera de Europa, y fue el mayor exportador de mercancías del mundo en 2007. En términos absolutos, asigna el tercer mayor presupuesto anual de la ayuda al desarrollo en el mundo,11 mientras que sus gastos militares ocuparon el séptimo lugar mundial en 2020.12 El país ha desarrollado un alto nivel de vida y establecido un sistema completo de seguridad social. Tiene una posición clave en los asuntos europeos y mantiene una estrecha relación con varias asociaciones a nivel mundial.13 Es reconocida como líder en los sectores científico y tecnológico.14
Герма́ния (нем. Deutschland [ˈdɔʏt͡ʃlant]), официальное название — Федерати́вная Респу́блика Герма́ния (нем. Bundesrepublik Deutschland), ФРГ (нем. BRD) — государство в Центральной Европе. Площадь территории — 357 408,74 км²[10]. Численность населения на 30 сентября 2019 года — 83 149 300 жителей[11]. Занимает 19-е место в мире по численности населения (2-е в Европе) и 62-е в мире по территории (8-е в Европе).
Расположенная в центре Европы Германия омывается водами Балтийского и Северного морей. Граничит с Данией на севере, Польшей и Чехией на востоке, Австрией и Швейцарией на юге, Францией, Люксембургом, Бельгией и Нидерландами на западе.
По государственному устройству является федеративным государством в составе 16 субъектов — федеральных земель (Бавария, Баден-Вюртемберг, Берлин, Бранденбург, Бремен, Гамбург, Гессен, Мекленбург-Передняя Померания, Нижняя Саксония, Рейнланд-Пфальц, Саар, Саксония, Саксония-Анхальт, Северный Рейн — Вестфалия, Тюрингия, Шлезвиг-Гольштейн). Форма государственного правления — парламентская республика. Пост Федерального канцлера ФРГ с 8 декабря 2021 года занимает Олаф Шольц (СДПГ)[12], с 19 марта 2017 года должность Федерального президента ФРГ занимает Франк-Вальтер Штайнмайер (СДПГ), который выполняет представительские функции в стране.
Столица — Берлин[13]. Официальный язык — немецкий.
Германия — страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. Объём ВВП за 2017 год составил 3,685 триллиона долларов США (около 44 550 долларов США на душу населения). Денежная единица — евро[14].
Будучи мировым лидером в ряде промышленных и технологических секторов, она является третьим в мире экспортёром и импортёром товаров. Германия — развитая страна с очень высоким уровнем жизни (6 место в мировом рейтинге). Она поддерживает социальное обеспечение и универсальную систему здравоохранения, охрану окружающей среды и бесплатное высшее образование[15].
Германия является одной из стран-основателей и членом Европейского союза, членом НАТО, входит в «Большую семёрку». По состоянию на 2020 год 54 % населения исповедует христианство, 4,3 % населения исповедует ислам, 40,7 % населения иррелигиозно.[16]
 Australia
Australia
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
Women's Soccer World Cup 2023

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP3
TOP3

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries


澳大利亚联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Australia[7]),通称澳大利亚(Australia[8][9],缩写为 AU、AUS),中文环境下(尤其是台湾、香港、澳门、广东省部分地区等地)常使用“澳洲”代替“澳大利亚”(狭义),是一个位于南半球中北部、东半球东部的议会制君主立宪制国家。全国整体属于大洋洲,是大洋洲面积最大、南半球面积第二大和全球面积第六大的国家。澳大利亚国土囊括了整块澳大利亚大陆、塔斯马尼亚岛及圣诞岛等数个海外岛屿,国土总面积7,692,024平方公里(km²),和美国本土的面积相近。根据2019年的普查数据,全国人口约为2522万,居世界第54位。该国没有陆上邻国,所有近邻国家均与其隔海相望。其中东南部有新西兰;东北部有巴布亚新几内亚及瓦努阿图、斐济等太平洋岛国;北部及西北部是印度尼西亚、东帝汶等国。澳大利亚的首都为堪培拉,最大城市为悉尼,本土划分为六个州及两个领地。主要城市有墨尔本、珀斯及布里斯班等。经济社会发展上,属于发达国家和资本主义国家。国内发行与流通的货币为澳大利亚元(Australian Dollar, 简写为AUD),是全球第五大流通货币。
澳大利亚大陆在远古时期即有人类居住生活,但其直至17世纪的大航海时代才被发现从而与外部人类社会接轨。18世纪末期始成为英国殖民及囚犯流放的地点,后因发现珍贵矿藏而成为移民、投资兴业的热点。获益于地理位置较为孤立的特点,澳大利亚自被殖民以来几未受到国际战争波及,内部也鲜有战乱、冲突的发生。仅北部城市达尔文曾受到第二次世界大战的战事影响(但在两次世界大战及朝鲜战争等战役期间,均有澳大利亚籍士兵远赴欧洲、朝鲜半岛等主要战场支援英国、联合国等国家及组织的军事行动)。
在自身资源禀赋、欧洲成熟的近现代工农业文明植入和英国带来的良好商业法规共同组成的良性发展环境下,自19世纪中后期始,澳大利亚逐步被建设发展成为了自由民主程度、社会经济发展程度与国民生活质素均属世界前列的发达国家。然而澳大利亚大陆上的原住民(Aborigines)却因此在一些方面深受其害(包括“失窃的一代”等事件),事后澳大利亚政府曾为此致歉,并逐渐努力改善和保障原住民的生存发展条件和各项权益,情况至今已大有改观。
澳大利亚的独立运动与进程始自1901年,原有的六块英属殖民地(即现在的州份)组成了澳大利亚联邦,从此澳大利亚开始逐渐脱离英国并独立行使作为国家的主权,直至1986年通过法令完全脱离英国正式成为独立国家。唯君主立宪制未曾变动,至今仍尊英国女王为君主。
从地理角度来看,澳大利亚是世界上唯一一个国土覆盖整块大陆的国家。国际相关地理标准将澳大利亚大陆确定为全球最小的大陆,即凡是面积小于其的陆地均视为岛屿(因此世界上最大的岛屿为格陵兰岛),大于等于其的方可视为大陆。[10]同样获益于相对孤立的地理位置及较晚被发现垦荒开发的历史,澳大利亚当地为数众多的自然遗产鲜少遭遇各种开发及毁坏,使不少生于斯产于斯的古老珍贵动植物种得以存活至今。如鸭嘴兽、袋鼠还有树袋熊等,这些也构成了极高的游览观光及科学研究价值,澳大利亚政府亦非常重视对这些珍贵自然遗存的保护。澳大利亚和美国是并列拥有世界自然遗产最多的国家[11]
该国地广人稀,平均人均拥有国土面积0.353平方公里,是世界人口密度最低的国家之一。全国人口集中分布于东部沿海、各州、领地首府城市及西部沿海城市珀斯附近等地区。在人口集中聚居的地区城市化、现代化程度较高;人口稀疏却占据绝大多数面积的地区(如中西部的沙漠、旱热区)等则反之,因其极端自然条件不甚适宜人类生存[12]。澳大利亚辽阔的国土横跨经纬度范围巨大,所以其有着不同气候下多样的自然景观,包括热带雨林、别称为“红色中心”的大维多利亚沙漠、吸引很多旅客的海滨及驰名遐迩的自然遗产大堡礁及乌鲁汝(艾尔斯巨石)[13][14][15]。
在人口的组成及文化谱系上,与美国类似,作为殖民地的历史使澳大利亚成为了一个本地原住民、各种族与各国籍移民人口混居的国家。各类移民及其后裔在现今人口比例中占绝大多数,其中又以欧洲裔为多,占到了83%。来自欧洲以外的其他地区移民和原住民目前占到总人口的17%。也因此该国是一个多元文化的聚合体,可览多国语言、习俗及特产于一域。但根本性的政治、经济、流行文化、教育等元素与架构仍与其曾经的宗主国英国相近甚至趋同,英语亦为其官方行政及民众生活中最主要的流通语言。在国旗的左上角也至今保留有整幅的英国国旗图案。
经济上,矿产资源开发、畜牧业、乳畜业、旅游观光以及中高等教育业等是该国获得收入的支柱产业,素有“骑在羊背上”与“坐在矿车上”的国家之称。澳大利亚是全球第13大经济体,人均国民生产总值排名世界第9,并被瑞士信贷集团列为世界财富中值最高的国家[16]。澳大利亚的军事支出排名世界第13。澳大利亚人类发展指数高居世界第2,并在多项指数与排名例如生活质素、健康医疗、教育、社会福利、经济自由度、媒体言论自由度、公民政治权利之保障与延伸中名列前茅,因而成为世界上的移民及留学热点之一,特别是吸引许多邻近的东亚及东南亚国家人口。澳大利亚被《福布斯》列于2020年退休宜居国的名单中[17]。
国际事务方面,澳大利亚是联合国、20国集团、英联邦、太平洋安全保障条约、经济合作与发展组织、亚太经合组织及太平洋岛国论坛的成员,参与程度积极。因地理位置与亚洲东部及南部相近,其与新西兰和东亚特别是中国的经济、文化关联相对其它西方发达国家要高。双方经济互补性、相互依存度大,人员贸易往来多且繁,双方政府对于彼此的外交关系也较为重视。
Australien (amtlicher deutscher Name; englisch Commonwealth of Australia, deutsch veraltet Australischer Bund) ist ein Staat auf der Südhalbkugel der Erde, der die gesamte Landmasse des australischen Kontinents, die ihr südlich vorgelagerte Insel Tasmanien, die subantarktische Macquarieinsel mit ihren Nebeninseln und als Außengebiete die pazifische Norfolkinsel, die Kokosinseln, die Weihnachtsinsel sowie die Ashmore- und Cartierinseln und die Heard und McDonaldinseln im Indischen Ozean umfasst. Seit dem Antarktis-Vertrag von 1933 erhebt das Land auch Ansprüche auf das australische Antarktis-Territorium. Seine Nachbarstaaten sind Neuseeland im Südosten sowie Indonesien, Osttimor und Papua-Neuguinea im Norden.
Australien hat etwa 25,3 Millionen Einwohner und ist dünn besiedelt. Mit einer Fläche von mehr als 7,6 Millionen km² ist es der sechstgrößte Staat der Erde.[7] Die Hauptstadt ist Canberra, die größte Stadt ist die Metropole Sydney. Weitere Ballungsräume sind Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide und Gold Coast.
Australien zählt zu den wohlhabendsten Ländern der Welt. Auf dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung der Vereinten Nationen nahm es 2019 den sechsten Rang ein.[8] Das Land verfügt über eine hochmoderne Service- und Dienstleistungsökonomie und über bedeutende Rohstoffvorkommen. Seine Kultur und Wirtschaftskraft machen es zu einem attraktiven Ziel für Migranten, allerdings legt die Migrations- und Asylpolitik Australiens strenge gesetzliche Kriterien für die Einwanderung an.
オーストラリア連邦(オーストラリアれんぽう、英: Commonwealth of Australia)[2]、またはオーストラリア(英: Australia)[3][4]は、オセアニアに位置し、オーストラリア大陸本土、タスマニア島及び多数の小島から成る連邦立憲君主制国家。首都はキャンベラ。最大の都市はシドニー。
イギリス連邦加盟国であり、英連邦王国の一国となっている。日本での略称は豪州(ごうしゅう)である[5]。
総面積は世界第6位である。近隣諸国としては、北にパプアニューギニア・インドネシア・東ティモール、北東にソロモン諸島・バヌアツ、東はトンガ・ニューカレドニア・フィジー、南東2,000km先にニュージーランドがある。
2014年、同国の一人当たりの国民所得は世界第5位であった[6]。同国は国際連合、G20、イギリス連邦、ANZUS、経済協力開発機構 (OECD)、世界貿易機関、アジア太平洋経済協力及び太平洋諸島フォーラム加盟国である。2013年9月MIKTAにも参加した。
18世紀末期における最初のイギリスの植民までの少なくとも4万年の間[7][8][9]、おおよそ250の言語グループに分類される言語話者の先住民が居住してきた[10][11][12]。彼らの食文化ブッシュ・タッカーは1970年代から注目された。
1606年におけるオランダ人探検家によるヨーロッパのオーストラリア大陸発見後、1770年にイギリスが同大陸の東半分を領有主張し、1788年1月26日からニューサウスウェールズ州の植民地に初めて流刑を通じて定住が開始された。その後の数十年間で同大陸の調査が行われ、人口は着実に増加し、さらに5つの自治王領植民地が設立されていた。
1901年1月1日、6つの植民地が連合しイギリス自治領として連邦を形成、事実上独立した。以後、6つの州及びその他特別地域から成る連邦議院内閣制及び立憲君主制の役割を果たす安定した自由民主主義の政治体制を維持してきた。2,360万の人口は、高度に都市化された東部の州及び沿岸部にかなり集中している[13]。
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands.[12] It is the largest country in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country by total area. The population of 26 million[6] is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard.[13] Australia's capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country's other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.
Indigenous Australians inhabited the continent for about 65,000 years[14] prior to the first arrival of Dutch explorers in the early 17th century, who named it New Holland. In 1770, Australia's eastern half was claimed by Great Britain and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia's national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the time of an 1850s gold rush, most of the continent had been explored by European settlers and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy, comprising six states and ten territories.
Australia is the oldest,[15] flattest,[16] and driest inhabited continent,[17][18] with the least fertile soils.[19][20] It has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi).[21] A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east. Australia generates its income from various sources, including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking, manufacturing, and international education.[22][23][24]
Australia is a highly developed country, with the world's 14th-largest economy. It has a high-income economy, with the world's tenth-highest per capita income.[25] It is a regional power and has the world's 13th-highest military expenditure.[26] Immigrants account for 30% of the population,[27] the highest proportion in any country with a population over 10 million.[28] Having the third-highest human development index and the eighth-highest ranked democracy globally, the country ranks highly in quality of life, health, education, economic freedom, civil liberties, and political rights,[29] with all its major cities faring well in global comparative livability surveys.[30] Australia is a member of the United Nations, G20, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), World Trade Organization, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Pacific Islands Forum, and the ASEAN Plus Six mechanism.
L'Australie, en forme longue le Commonwealth d'Australie (en anglais : Australia et Commonwealth of Australia), est un pays de l'hémisphère sud dont la superficie couvre la plus grande partie de l'Océanie. En plus de l'île éponyme, l'Australie comprend également la Tasmanie ainsi que d’autres îles des océans Austral, Pacifique et Indien. Elle revendique aussi 6 000 000 km2 en Antarctique. Les nations voisines comprennent notamment l'Indonésie, le Timor oriental et la Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinée au nord, les îles Salomon, Vanuatu et le territoire français de Nouvelle-Calédonie au nord-est, la Nouvelle-Zélande au sud-est ainsi que le territoire français des îles Kerguelen (TAAF) à l'ouest des îles australiennes Heard et McDonald.
Peuplée depuis plus de 50 000 ans par les Aborigènes4, l'île-continent d'Australie (mainlanda) est visitée de manière sporadique, notamment par des pêcheurs venus du nord, puis par des marins néerlandais5. À partir du XVIIe siècle, explorateurs et marchands européens reconnaîtront les côtes, mais ce n’est qu’en 1770 que la moitié orientale de l'île est officiellement revendiquée par la Grande-Bretagne et le 26 janvier 1788 — jour de la fête nationale australienne — qu'est fondée la colonie pénitentiaire de Nouvelle-Galles du Sud6,7. Cinq autres colonies largement autonomes sont fondées dans le courant du XIXe siècle, à mesure que la population augmente et que de nouveaux territoires sont explorés. Le 1er janvier 1901, les six colonies se fédèrent et forment le Commonwealth d'Australie.
Depuis son indépendance, l'Australie conserve un système politique stable de type démocratie libérale et reste une monarchie parlementaire membre du Commonwealth des Nations. La langue nationale est l'anglais et la monnaie le dollar australien. Sa capitale est Canberra, située dans le Territoire de la capitale australienne.
Sa population, estimée à 25,2 millions d'habitants en décembre 20181, est principalement concentrée dans les grandes villes côtières de Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth et Adélaïde. De surcroît, avec un PIB nominal de 1 379 milliards de dollars américains, l'État se place comme treizième puissance économique mondiale en 20178. Depuis l'an 2000, l'Australie est classée par le PNUD deuxième pays le plus développé au monde après la Norvège. Le pays est le septième émetteur de gaz à effet de serre par habitant en 20159.
L'émeu est l'oiseau national de l'Australie et le kangourou est l'animal national. Le pays compte plus de 500 parcs nationaux, record dans le monde.
L'Australia (pronuncia italiana /auˈstralja/[5]; in inglese: Australia, pronuncia britannica [ɒˈstreɪlɪə], pronuncia locale [əˈstreɪliə]), ufficialmente il Commonwealth dell'Australia, è il sesto Paese del mondo per estensione (7 688 287 km², in gran parte desertici)[6], il più grande dell'Oceania e dell'intera Australasia. Ha una popolazione di oltre 25 milioni di abitanti, quasi interamente residenti sulle coste. La sua capitale è Canberra, mentre la città più popolata è Sydney, seguita da Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth e Adelaide.
Il Paese si trova nell'emisfero australe, circondato dall'oceano Indiano a ovest e sud, e dal Pacifico a est. È formata dal Mainland ossia la parte continentale o l'isola principale, la Tasmania e altre isole minori dette Terre remote, quali le Isole Cocos e Keeling, l'Isola di Natale, l'Isola Norfolk, l'Isola di Lord Howe, l'Isola Macquarie (ritenuta parte della Tasmania) e l'isola Heard. Canberra reclama anche il Territorio antartico australiano con le sue basi.
Popolata dagli aborigeni per più di 40 000 anni, è stata colonizzata dal Regno Unito a partire dal XVIII secolo. Gli australiani, che chiamano se stessi aussie, sono un popolo multietnico, annoverando non solo aborigeni ed europei, ma anche asiatici e americani.
Dal punto di vista politico l'Australia è una monarchia costituzionale federale. Il capo dello stato è la Regina d'Australia Elisabetta II (anche Regina della Gran Bretagna), rappresentata da un governatore generale. La capitale è Canberra ma la città più popolosa è Sydney, seguita da Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth e Adelaide.
Australia (pronunciación en inglés: /əˈstɹæɪljə/ (![]() escuchar)), oficialmente Mancomunidad de Australia (en inglés, Commonwealth of Australia, pronunciado /ˈkɒmənwelθ ɒv əˈstɹæɪljə/), es un país soberano de Oceanía, cuya forma de gobierno es la monarquía constitucional federal parlamentaria.
escuchar)), oficialmente Mancomunidad de Australia (en inglés, Commonwealth of Australia, pronunciado /ˈkɒmənwelθ ɒv əˈstɹæɪljə/), es un país soberano de Oceanía, cuya forma de gobierno es la monarquía constitucional federal parlamentaria.
El país ocupa la principal masa continental de la plataforma llamada Sahul, además de algunas islas en los océanos Pacífico, Índico y Antártico. Los países más cercanos a Australia son Indonesia, Timor Oriental y Papúa Nueva Guinea al norte, las Islas Salomón, Vanuatu y la dependencia francesa de Nueva Caledonia al noreste, y Nueva Zelanda al sureste. Australia es el sexto país más grande del mundo con una superficie de 7 741 220 km².1 Su capital, Canberra, se encuentra en el Territorio de la Capital Australiana. La población del país (según la estimación para 2020)5 es de más de 25 millones de habitantes, concentrados principalmente en las grandes ciudades costeras: Sídney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaida y la capital Canberra.
Australia ha estado habitada desde hace por lo menos cuarenta y seis mil años6 por los aborígenes australianos. Su descubrimiento se habría producido tras las esporádicas visitas de españoles y portugueses que exploraron la costa septentrional y occidental de Australia, aunque sin avanzar hacia el interior por el escaso número de exploradores.789 Las exploraciones iniciadas en el siglo XVII fueron continuadas por pescadores neerlandeses, exploradores y comerciantes europeos. Hasta ahora se sostiene que el primero en desembarcar en las costas orientales fue el navegante británico James Cook, que llegó en 1769 a Nueva Zelanda y en 1770 a tierras australianas.10 Debido a ello, la mitad oriental del continente fue reclamada por Gran Bretaña en 1770, y en 1788 se estableció una colonia penal en Nueva Gales del Sur. Debido al asentamiento de colonos, a su crecimiento demográfico y a la exploración de nuevas áreas, durante el siglo XIX se establecieron otras cinco colonias británicas más. El 1 de enero de 1901, las seis colonias se federaron formando la Confederación de Australia. Desde su institución ha mantenido un sistema político democrático liberal y ha continuado siendo una monarquía dentro de la Comunidad Británica de Naciones.
En la división convencional en continentes, Australia se engloba en Oceanía, que agrupa también las islas del Pacífico. Sin embargo, los anglohablantes suelen hablar del «continente australiano» sin que Australia, desde un punto de vista geológico, constituya un continente. Nueva Zelanda y las islas adyacentes tampoco conforman un continente con Australia al no pertenecer a la plataforma Sahul, sino que se suelen asociar con esta por cercanía histórica y política.
Австра́лия (англ. Australia, МФА: [əˈstreɪljə], от лат. austrālis — «южный»), официальная форма — Австрали́йский Сою́з, или Содру́жество Австра́лии (англ. Commonwealth of Australia[5], МФА: [ˈkɒm.ənˌwɛlθ əv əˈstreɪljə]), — государство в Южном полушарии, занимающее одноимённый материк, остров Тасмания и несколько других островов Индийского и Тихого океанов[* 1]; является шестым государством по площади в мире. К северу от Австралийского Союза расположены Восточный Тимор, Индонезия и Папуа — Новая Гвинея, к северо-востоку — Вануату, Новая Каледония и Соломоновы Острова, к юго-востоку — Новая Зеландия. От главного острова Папуа — Новой Гвинеи материковая часть Австралийского Союза отделена Торресовым проливом минимальной шириной около 150 км[7], а расстояние от австралийского острова Боигу до Папуа — Новой Гвинеи составляет около 5 километров[8]. Население на 31 декабря 2018 года оценивалось в 25 180 200 человек, большинство из которых проживает в городах на восточном побережье[9].
Австралия является одной из развитых стран, будучи тринадцатой по размеру экономикой в мире, и имеет шестое место в мире по ВВП в расчёте на душу населения. Военные расходы Австралии являются двенадцатыми по размеру в мире. Со вторым по величине индексом развития человеческого потенциала Австралия занимает высокое место во многих сферах, таких как качество жизни, здоровье, образование, экономическая свобода, защита гражданских свобод и политических прав[10]. Австралия является членом G20, ОЭСР, ВТО, АТЭС, ООН, Содружества наций, АНЗЮСа и Форума тихоокеанских островов.
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Men
4x400 m Men
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states
 France
France

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP2
TOP2
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

法兰西共和国(法语:République française [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛz]),通称法国(法语:France [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() 聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
聆听),是本土位于西欧并具有海外大区及领地[注 16]的主权国家,自法兰西第五共和国建立以来实行单一制与半总统制,首都为欧洲大陆最大的文化与金融中心巴黎。该国本土由地中海一直延伸至英吉利海峡及北海,并由莱茵河一直延伸至大西洋,整体呈六角状。海外领土包括南美洲的法属圭亚那及分布于大西洋、太平洋和印度洋的诸岛屿。全国共分为18个大区,其中5个位于海外。法国与西班牙及摩洛哥为同时拥有地中海及大西洋海岸线的三个国家。法国的国土面积全球第四十一位,但却为欧盟及西欧国土面积最辽阔的国家,欧洲面积第三大国家。
今日之法国本土于铁器时代由高卢人(凯尔特人的一支)征服,前51年又由罗马帝国吞并。486年法兰克人(日耳曼人的一支)又征服此地,其于该地域建立的早期国家最终发展成为法兰西王国。法国至中世纪末期起成为欧洲大国,国力于19-20世纪时达致巅峰,建立了世界第二大殖民帝国,亦为20世纪人口最稠密的国家[来源请求],现今则是众多前殖民地的首选移民国[8]。在漫长的历史中,法国培养了不少对人类发展影响深远的著名哲学家、文学家与科学家,亦为文化大国,具有第四多的世界遗产[9]。
法国在全球范围内政治、外交、军事与经济上为举足轻重的大国之一[10]。法国自1958年建立第五共和国后经济有了很大的发展,政局保持稳定,国家体制实行半总统制,国家经由普选产生的总统、由其委任的总理与相关内阁共同执政。1958年10月4日,由公投通过的国家宪法则保障了国民的民主权及宗教自由。法国的建国理念主要建基于在18世纪法国大革命中所制定的《人权和公民权宣言》,此乃人类史上较早的人权文档,并对推动欧洲以至于全球的民主与自由产生莫大的影响[11];其蓝白红三色的国旗则有“革命”的含义。法国不仅为联合国常任理事国,亦是欧盟始创国。该国国防预算金额为全球第5至6位,并拥有世界第三大核武贮备量[12]。法国为发达国家,其GDP为全球第七大经济体系,具备世界第十大购买力[13],并拥有全球第二大专属经济区[14];若以家庭总财富作计算,该国是欧洲最富有的国家,位列全球第四[15]。法国国民享有高生活质素,在教育、预期寿命、民主自由、人类发展等各方面均有出色的表现,特别是医疗研发与应用水平长期盘据世界首位[16][17]。Frankreich ![]() [ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
[ˈfʁaŋkʁaɪ̯ç] (französisch [fʁɑ̃s], amtlich République française [ʁe.py.ˈblik fʁɑ̃.ˈsɛz], deutsch Französische Republik) ist ein demokratischer, interkontinentaler Einheitsstaat in Westeuropa mit Überseeinseln und -gebieten auf mehreren Kontinenten. Metropolitan-Frankreich, d. h. der europäische Teil des Staatsgebietes, erstreckt sich vom Mittelmeer bis zum Ärmelkanal und zur Nordsee sowie vom Rhein bis zum Atlantischen Ozean. Sein Festland wird wegen seiner Landesform als Hexagone (Sechseck) bezeichnet. Frankreich ist flächenmäßig das größte und nach Einwohnern (hinter Deutschland) das zweitgrößte Land der Europäischen Union. Es umfasst (nach Russland und der Ukraine) das drittgrößte Staatsgebiet in Europa. Paris ist die Hauptstadt und als Agglomeration mit dem Gemeindeverband Métropole du Grand Paris und den umliegenden Gebieten der Region Île-de-France größter Ballungsraum des Landes vor Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse und Lille.
Im 17. und 18. Jahrhundert hatte Frankreich eine europäische Führungsrolle und Vormachtstellung inne. Bedeutend war die politische und kulturelle Ausstrahlung: Die Hofhaltung Ludwigs XIV. wurde zum Vorbild absolutistischer Staaten in ganz Europa und die Französische Revolution mit der Erklärung der Menschen- und Bürgerrechte gab zusammen mit Okkupationen durch Napoleon Bonaparte in vielen Ländern den Auftakt zu der immer wieder von Rückschlägen unterbrochenen Entwicklung zur Demokratie. In Übersee baute Frankreich zweimal ein Kolonialreich auf. Das erste umfasste u. a. große Teile Nordamerikas und ging großenteils Mitte des 18. Jahrhunderts im Siebenjährigen Krieg verloren; das zweite mit Schwerpunkt in Afrika war im 19. und frühen 20. Jahrhundert das zweitgrößte der Welt. Im 21. Jahrhundert gilt Frankreich mit Deutschland als treibende Kraft der europäischen Integration.
Die Französische Republik wird in ihrer Verfassung als unteilbar, laizistisch, demokratisch und sozial erklärt.[7] Ihr Grundsatz lautet: „Regierung des Volkes durch das Volk und für das Volk“. Frankreich steht auf Rang 26 des Index der menschlichen Entwicklung (2019) der Vereinten Nationen.[8] Gemessen am nominalen Bruttoinlandsprodukt ist es die sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt.[5] Die Kaufkraft pro Einwohner betrug 2016 19.254 Euro (zum Vergleich: Deutschland 21.879 Euro, Großbritannien 21.141 Euro).[9] Lebensstandard, Bildungsgrad und durchschnittliche Lebenserwartung[10] gelten als hoch. Als meistbesuchtes Land der Welt empfängt Frankreich rund 83 Millionen ausländische Touristen pro Jahr.[11][12]
Frankreich unterhält die drittstärksten Streitkräfte innerhalb der NATO und das größte Heer der Europäischen Union. Es ist eines der fünf ständigen Mitglieder des UN-Sicherheitsrates und hatte 2010 als Atommacht die weltweit dritthöchste Anzahl an Kernwaffen.[13] Das Land ist Gründungsmitglied der Europäischen Union und der Vereinten Nationen, Mitglied der Frankophonie, der G7, der G20, der NATO, der Organisation für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (OECD), der Welthandelsorganisation (WTO) und der Lateinischen Union.
フランス共和国(フランスきょうわこく、フランス語: République française、通称:フランス、France)は、西ヨーロッパ、カリブ、太平洋およびインド洋に位置する共和制国家。首都はパリ。
フランス・メトロポリテーヌ(本土)は地中海からイギリス海峡及び北海へ、ライン川から大西洋へと広がる。この他世界各地に海外地域および領土を有する。
なお、フランス・メトロポリテーヌ周辺は北東がドイツとベルギーとルクセンブルク、東をスイスとイタリア、南にスペインと国境を接している。
フランスは国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、G7・G20、欧州評議会、世界貿易機関、経済協力開発機構、北大西洋条約機構、パリクラブおよびフランコフォニー国際機関における主要なメンバーである。国際政治においてはこれらの理由から、政治・経済・文化において強力な影響を及ぼす列強の一角に数えられており、ヨーロッパにおける「ビッグ4」の1つでもある。
核拡散防止条約により核兵器の保有を認められた5つの公式核保有国の1つであり、その他にアメリカ合衆国を除けば世界で唯一の原子力空母「シャルル・ド・ゴール」や原子力潜水艦を保有しており、強力な軍事力を持っている。
GDPは名目GDP世界第7位かつ購買力平価で世界第10位・ユーロ圏ではドイツに次ぐ第2位の経済力を有する国であり、高い人間開発指数を持つ先進国として知られる。数多くの世界遺産を抱えており、世界で最も観光客の多い国の1つである。
歴史的にはデカルト、モンテスキュー、ルソー、サルトルといった哲学者やマリ・キュリー、パストゥールといった科学者、モネ、セザンヌ、ゴーギャン、クールベ、ドラクロワといった芸術家の故国もしくは活躍の舞台であり、また百年戦争やフランス革命、ナポレオン戦争といった歴史的事象の主要な舞台であった。
France (French: [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() ), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
), officially the French Republic (French: République française),[1] is a transcontinental country spanning Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.[XIII] Including all of its territories, France has twelve time zones, the most of any country. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and several islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra and Spain in Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 67 million people (as of May 2021).[13] France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks arrived in 476 and formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987.
In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom in which the king's authority was barely felt. King Philip II achieved remarkable success in the strengthening of royal power and the expansion of his realm, defeating his rivals and doubling its size. By the end of his reign, the kingdom had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts for the French throne, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, various wars with rival powers, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world.[14] The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. But France once again emerged as Europe's dominant cultural, political and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War.[15] Inadequate economic policies, an inequitable taxation system as well as endless wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence), left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the absolute monarchy, replaced the Ancien Régime with one of history's first modern republics and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars shaped the course of European and world history. The collapse of the empire initiated a period of relative decline, in which France endured a tumultuous succession of governments until the founding of the French Third Republic during the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. Subsequent decades saw a period of optimism, cultural and scientific flourishing, as well as economic prosperity known as the Belle Époque. France was one of the major participants of World War I, from which it emerged victorious at great human and economic cost. It was among the Allied powers of World War II, but was soon occupied by the Axis in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, the short-lived Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The current Fifth Republic was formed in 1958 by Charles de Gaulle. Algeria and most French colonies became independent in the 1960s, with the majority retaining close economic and military ties with France.
France retains its centuries-long status as a global centre of art, science and philosophy. It hosts the fifth-largest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites and is the world's leading tourist destination, receiving over 89 million foreign visitors in 2018.[16] France is a developed country with the world's seventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and ninth-largest by PPP; in terms of aggregate household wealth, it ranks fourth in the world.[17] France performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy and human development.[18][19] It remains a great power in global affairs,[20] being one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and an official nuclear-weapon state. France is a founding and leading member of the European Union and the Eurozone,[21] as well as a key member of the Group of Seven, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and La Francophonie.
La France (Écouter), en forme longue depuis 1875 la République française (Écouter), est un État souverain transcontinental dont le territoire métropolitain est situé en Europe de l'Ouest et dont le territoire ultramarin est situé dans les océans Indien, Atlantique et Pacifique ainsi qu'en Amérique du Sud. Il s'agit de l'unique pays au monde à s'étendre sur treize fuseaux horaires. Le pays a des frontières terrestres avec la Belgique, le Luxembourg, l'Allemagne, la Suisse, l'Italie, l'Espagne et les deux principautés d'Andorre et de Monaco en Europe, auxquelles s'ajoutent les frontières terrestres avec le Brésil, le Suriname et les Pays-Bas aux Amériques. La France dispose d'importantes façades maritimes sur l'Atlantique, la Méditerranée, le Pacifique et l'océan Indien, lui permettant de bénéficier de la plus vaste zone économique exclusive du monde6.
La France est une république constitutionnelle unitaire ayant un régime semi-présidentiel. La devise de la République est depuis 1875 « Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité » et son drapeau est constitué des trois couleurs nationales : bleu, blanc, rouge. Son hymne national est La Marseillaise, chant patriotique hérité de la Révolution française. Son principe constitutif est la démocratie : le « gouvernement du peuple, par le peuple et pour le peuple ». Elle a pour capitale Paris et pour langue officielle le français depuis 1539, remplaçant le latin. Ses monnaies sont l'euro depuis 2002 dans la majeure partie du pays et le franc Pacifique dans ses territoires de l'océan Pacifique.
La France s'appelle ainsi depuis 1214, lorsque les troupes du roi Philippe Auguste battent celles de l’empereur germanique à Bouvines. La France tire son nom des Francs, peuple germanique qui a institué les premiers fondements de son État sur les bases de la Gaule romaine. C'est au fil des siècles, par des guerres, des mariages politiques et des unions souveraines, que cet État monarchique et catholique va peu à peu constituer autour de lui une véritable fédération de provinces, qui finira par se cristalliser en une nation unique sous l’effet d’une politique d'uniformisation administrative et culturelle, portée à son aboutissement par la Révolution française et la fin du régime féodal.
Du milieu du XVIe siècle au milieu du XXe siècle, elle possède un vaste empire colonial. À partir des années 1950, elle est l'un des acteurs de la construction de l'Union européenne. Deuxième armée européenne derrière la Russie, quatrième puissance nucléaire et spatiale mondiale7,8, cinquième puissance militaire mondiale9, l'un des cinq membres permanents du Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies et membre de l'OTAN, la France est également membre du G7, du G20, du Conseil de l'Europe, de la zone euro, de l'espace Schengen, de la commission de l'océan Indien, de la communauté du Pacifique, et abrite le siège de plusieurs organisations internationales dont le Conseil de l'Europe, l'UNESCO, l'OCDE, Interpol, le Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer. Elle exerce ainsi une influence notable en matière politique, économique, militaire et culturelle, en Europe et dans le reste du monde, elle est classée en 2019 au premier rang mondial de l'indice Soft Power 30 grâce à sa vaste portée diplomatique, sa richesse culturelle et à la forte maîtrise internationale du président de la République10.
Seul pays au monde à exercer sa souveraineté sur des territoires répartis sur quatre océans et deux continents11,N 7, elle joue un important rôle géopolitique au niveau mondial, grâce à un réseau d'ambassades et de consulats étendu, le deuxième au monde derrière celui des États-Unis, et elle dispose de bases militaires sur tous les continents et de la troisième puissance nucléaire militaire mondiale. Du fait de son territoire étendu et réparti sur l'ensemble de la planète, la France est de surcroît un des premiers pays du monde pour la variété de ses milieux maritimes et leur biodiversité12.
La France est, avec un PIB nominal de 2 938 milliards de dollars US en 2021 selon le FMI, la troisième économie européenne derrière l'Allemagne et le Royaume-Uni, ainsi que la septième économie mondiale13. Malgré un taux de chômage de 8 % (juin 2021), elle affiche un niveau de vie « très élevé » (24e au classement IDH en 2018). Elle figure parmi les chefs de file mondiaux dans les secteurs de l'agroalimentaire, de l'aéronautique, de l'automobile, du tourisme, du nucléaire, leader mondial dans le secteur du luxe. Au 1er janvier 2018, la population de la France est d'environ 67,8 millions d'habitants, selon les estimations publiées par l'Insee : 65 018 000 dans les régions métropolitaines, 2 169 000 dans les régions ultramarines et 608 200 dans les collectivités d'outre-mer et en Nouvelle-Calédonie.
L'un des pays les plus peuplés d'EuropeN 8 (très proche du Royaume-Uni, elle n'est devancée nettement que par l'Allemagne)14, la France est le plus vaste pays de l'Union européenne et le troisième pays le plus vaste d'Europe15. Sa culture et sa civilisation sont diffusées par les pays francophones à travers le monde, réunis dans l'Organisation internationale de la francophonie. Traditionnellement utilisé comme langue de la diplomatie, le français est la dixième langue maternelle la plus parlée au monde, la cinquième langue la plus parlée en nombre total de locuteurs, et une des langues ayant la plus grande diffusion internationale. Il est une des six langues officielles et une des deux langues de travail (avec l'anglais) de l'Organisation des Nations unies, l'une des deux langues officielles du Comité international olympique, et langue officielle ou de travail de plusieurs organisations internationales ou régionales. Le français est également l'une des trois langues de travail de l'Union européenne, avec l'allemand et l'anglais.
La Francia (/ˈfranʧa/[11]; in francese: France, /fʁɑ̃s/), ufficialmente Repubblica francese (in francese: République française), è uno Stato principalmente situato nell'Europa occidentale[12], ma che possiede ugualmente territori disseminati su più oceani e altri continenti. La Francia è una repubblica costituzionale unitaria avente un regime semipresidenziale. Parigi è la capitale, la lingua ufficiale è il francese, le monete ufficiali sono l'euro e il franco Pacifico nei territori dell'oceano Pacifico. Il motto della Francia è «Liberté, Égalité, Fraternité », e la sua bandiera è costituita da tre bande verticali di uguali dimensioni di colore blu, bianco e rosso[13]. L'inno nazionale è La Marsigliese.
È uno stato formatosi all'inizio dell'Alto Medioevo, che prende il suo nome dal popolo dei Franchi. Dall'inizio del XVII secolo alla prima metà del XX secolo, ha posseduto un vasto impero coloniale. Nella seconda metà del secolo è stata uno degli stati fondatori dell'Unione Europea. Inoltre è la terza potenza nucleare mondiale, uno dei membri permanenti del Consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni unite ed uno stato aderente all'NATO. Ugualmente è membro del G7, del G20, della zona euro, dello Spazio Schengen ed ospita la sede del Consiglio d'Europa, del Parlamento europeo e dell'UNESCO. La Francia possiede una certa influenza in materia politica, economica, militare e culturale in Europa e nel mondo come media potenza[14][15][16].
Esercita la sua sovranità su territori presenti su tre oceani e quattro continenti[17]. La sua geopolitica è importante a livello mondiale, perché possiede un gran numero di ambasciate e consolati, secondo solo agli Stati Uniti d'America, e dispone di basi militari su tutti i continenti. La Francia detiene la prima zona economica esclusiva (spazio marittimo) al mondo, al quale si aggiunge un'estensione piattaforma continentale di 579 000 km² nel 2015[18].
È, nel 2014, la terza potenza economica europea dopo la Germania e il Regno Unito, e la sesta potenza economica mondiale per prodotto interno lordo nominale (nona a parità di potere d'acquisto), e possiede un livello di vita molto elevato. Il 1º gennaio 2016 la popolazione totale della Francia è di circa 67,2 milioni d'abitanti, secondo le stime pubblicate dall'INSEE, di cui 64 513 000 nelle regioni metropolitane, 2 114 000 nelle regioni ultramarine e 604 400 nelle collettività d'oltre mare e in Nuova Caledonia. È il secondo stato più popolato dell'Unione europea dopo la Germania. Inoltre è anche lo stato più esteso dell'Unione europea e il terzo paese più vasto d'Europa[19]. Antica potenza coloniale, la sua cultura si è diffusa attraverso il mondo ed è oggi membro dell'Organizzazione internazionale della francofonia. Il francese è la seconda lingua più studiata al mondo ed è una delle sei lingue ufficiali dell'Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite.
Francia (en francés, France, pronunciado /fʁɑ̃s/ (![]() escuchar)), oficialmente la República Francesa (en francés, République française pronunciado /ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛːz/ (
escuchar)), oficialmente la República Francesa (en francés, République française pronunciado /ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛːz/ (![]() escuchar)), es un país transcontinental, miembro de la Unión Europea, cuya forma de gobierno es la república semipresidencialista. Territorialmente comprende la Francia metropolitana y la Francia de ultramar, siendo a su vez el país más grande de la Unión Europea.7 Su territorio, que incluye regiones de ultramar o Territorios dependientes, se extiende sobre una superficie total de 675 417 km².1 En 2017 el país contaba con 67,1 millones de habitantes (65 millones en los departamentos metropolitanos y 2,1 millones en los departamentos de ultramar).8
escuchar)), es un país transcontinental, miembro de la Unión Europea, cuya forma de gobierno es la república semipresidencialista. Territorialmente comprende la Francia metropolitana y la Francia de ultramar, siendo a su vez el país más grande de la Unión Europea.7 Su territorio, que incluye regiones de ultramar o Territorios dependientes, se extiende sobre una superficie total de 675 417 km².1 En 2017 el país contaba con 67,1 millones de habitantes (65 millones en los departamentos metropolitanos y 2,1 millones en los departamentos de ultramar).8
La parte metropolitana del país9 se ubica en Europa Occidental, donde limita al sur con el mar Mediterráneo, Mónaco, España y Andorra; al oeste el océano Atlántico; al norte con el canal de la Mancha que la separa del Reino Unido y en su parte este hace frontera con Bélgica, Luxemburgo, Alemania, Suiza e Italia. El territorio insular europeo comprende la isla mediterránea de Córcega y diversos archipiélagos costeros en el océano Atlántico. En América, son territorios franceses la Guayana Francesa, la mayor parte de la isla San Martín y las islas y archipiélagos de Martinica, Guadalupe, San Bartolomé y San Pedro y Miquelón. En el océano Índico, son territorios franceses también las islas de Mayotte y de Reunión, y en el océano Pacífico los archipiélagos de la Polinesia francesa, Wallis y Futuna y Nueva Caledonia, el atolón de isla Clipperton, en el océano Pacífico oriental, y las Tierras Australes francesas (Kerguelen y varias otras en el océano Índico sur, como las islas Dispersas) y las denominadas Tierras Antárticas francesas (Tierra Adelia y Base Dumont D'Urville en la Antártida). A nivel mundial es el segundo país con mayor extensión de mar territorial (11 millones de km²).10
Francia es la sexta economía mundial (2018) con una muy elevada difusión cultural en el contexto internacional. Es miembro del G7, de la zona euro y del espacio Schengen, y alberga a muchas de las más importantes empresas multinacionales, líderes en diversos segmentos de la industria y del sector primario, además de que es el primer destino turístico mundial, con 83 millones de visitantes extranjeros por año (7 % del PIB).11 Francia es un país desarrollado que se posiciona en lugares altos dentro de escalafones internacionales. Es allí donde se redactó la Declaración de los Derechos del Hombre y del Ciudadano de 1789, es miembro fundador de la Organización de las Naciones Unidas y uno de los cinco miembros permanentes de su Consejo de Seguridad.12 Francia alberga las sedes del Consejo de Europa y del Parlamento Europeo, ambas en Estrasburgo, y las de la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico y de la Unesco, en París. Perteneciente a la OTAN, Francia es una de las ocho potencias nucleares reconocidas13 y una de las potencias mundiales.14
Desde el siglo XVI, el país fue una potencia colonial, y durante mucho tiempo el idioma francés fue la principal lengua de la diplomacia. Aún hoy, es una de las lenguas con mayor proyección, y la cultura y la civilización francesas forman el nexo de unión de los países de la francofonía. En 2018, la lengua francesa, con 284,9 millones de hablantes, era la quinta más hablada del mundo15 y por las tendencias demográficas en el siglo XXI se convertiría en la tercera lengua más hablada del mundo.1617 Lingüística y culturalmente, Francia pertenece a la Europa Latina.
Фра́нция (фр. France, [fʁɑ̃s] ![]() слушать), официальное название — Францу́зская Респу́блика[11] (фр. République française, [ʁe.py.blik fʁɑ̃.sɛz]
слушать), официальное название — Францу́зская Респу́блика[11] (фр. République française, [ʁe.py.blik fʁɑ̃.sɛz] ![]() слушать), — трансконтинентальное государство, включающее основную территорию в Западной Европе и ряд заморских регионов и территорий. Столица — Париж. Девиз Республики — «Свобода, равенство, братство», её принцип — правление народа, народом и для народа[12].
слушать), — трансконтинентальное государство, включающее основную территорию в Западной Европе и ряд заморских регионов и территорий. Столица — Париж. Девиз Республики — «Свобода, равенство, братство», её принцип — правление народа, народом и для народа[12].
Название страны происходит от этнонима древнегерманского племени франков. Большинство населения Франции имеет смешанное галло-романское происхождение и говорит на языке романской группы.
Население — 62 814 233 человек в метрополии и 67 848 156 человек — с учётом заморских владений (оценка на 1 июля 2020)[4], в том числе около 90 % — граждане Франции. Состав населения Франции по вероисповеданию по состоянию на 2019 год: католики — 41 %, иррелигиозны — 40 %, мусульмане — 5 %, другие религии — 5 %, лютеране — 2 %, православные — 2 %, другие христиане — 2 %, буддисты — 1 % , иудеи — 1 %, нет данных — 1 %.[13]
Франция является ядерной державой, членом НАТО и одним из пяти постоянных членов Совета Безопасности ООН. С 1950-х годов — одно из государств, участвующих в создании Европейского союза.
Законодательный орган — двухпалатный парламент (Сенат и Национальное собрание). Административно-территориальное деление: 18 регионов (13 в метрополии и 5 заморских регионов), включающих 101 департамент (96 в метрополии и 5 заморских департаментов)[14], 5 заморских сообществ и 3 административно-территориальных образования с особым статусом.

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture

 International cities
International cities
 European city
European city
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP6
TOP6
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 States of Europe
States of Europe
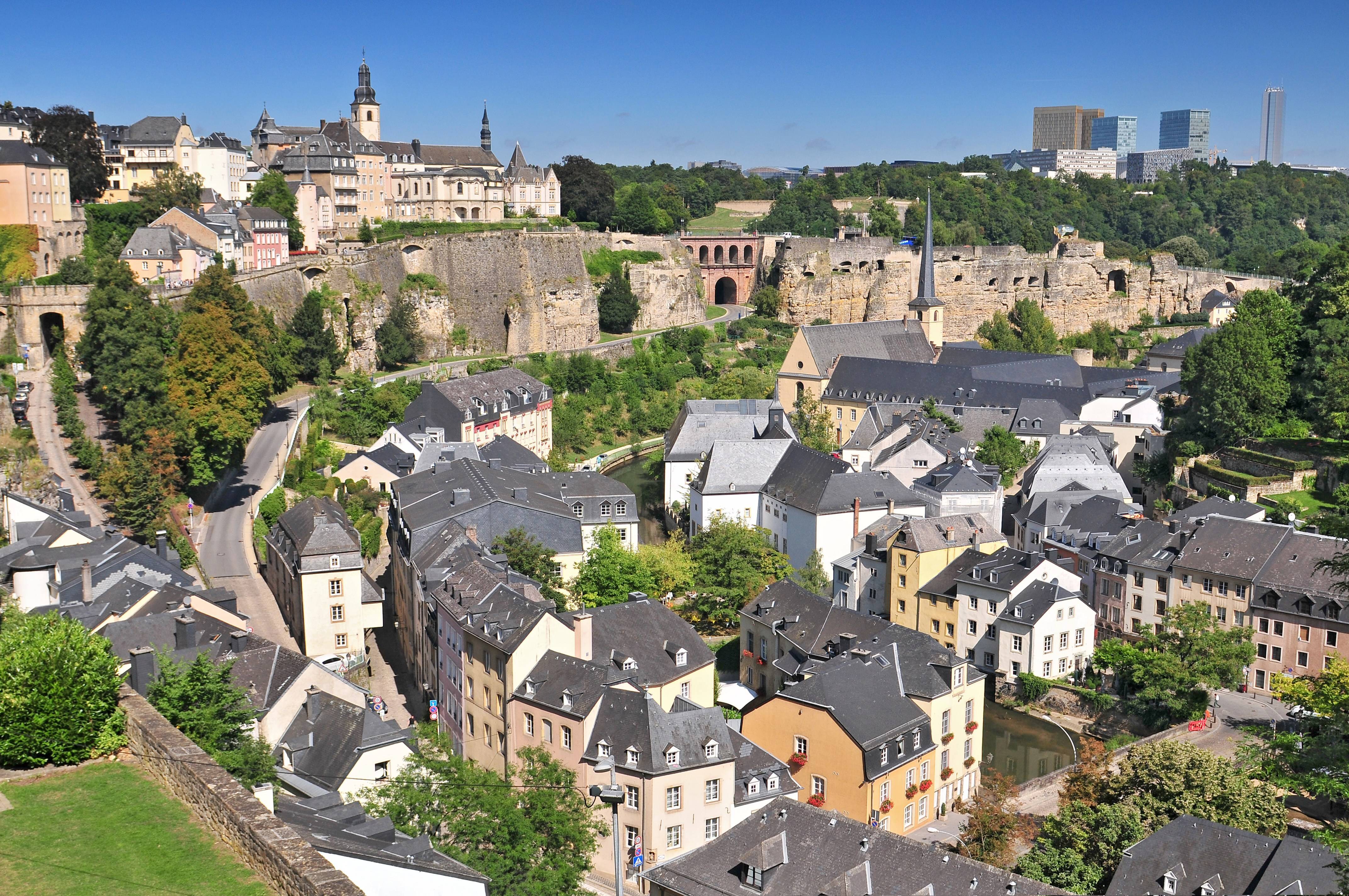
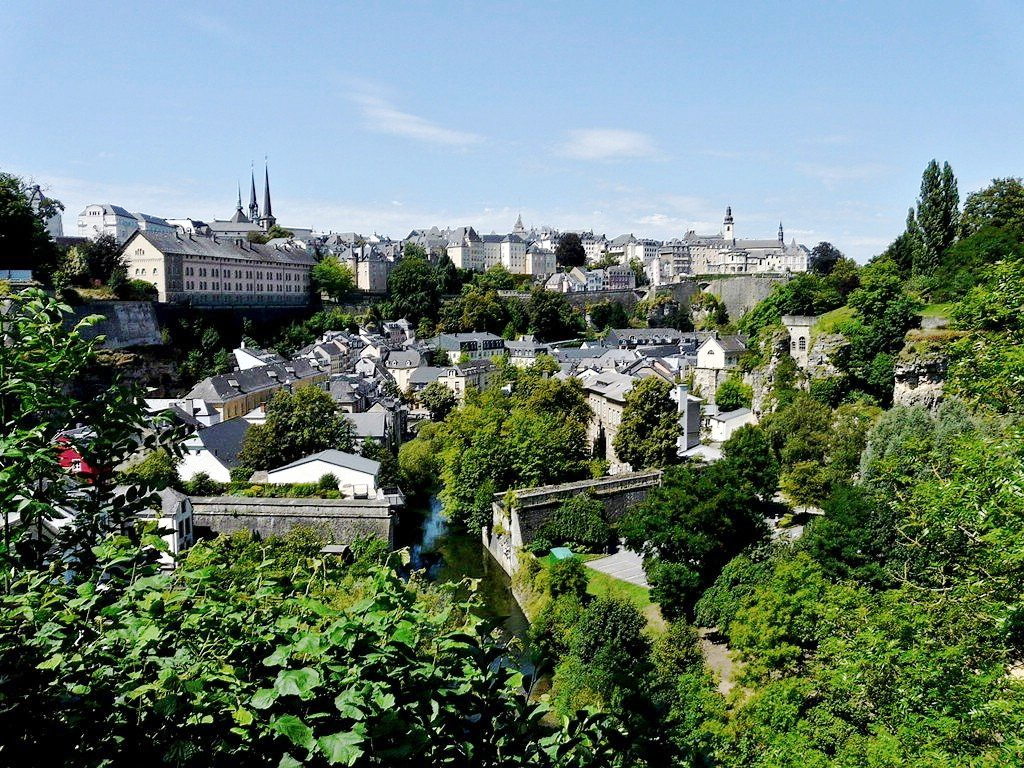


卢森堡是一个高度发达的资本主义国家,也是欧盟和北约创始成员国之一,拥有欧盟多个下设机构,如欧洲法院、欧洲审计院以及欧洲投资银行,被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。同时是高度发达的工业国家,还是欧元区内最重要的私人银行中心,及全球第二大仅次于美国的投资信托中心。金融、广播电视、钢铁是其三大经济支柱产业,该国失业率极低,人均寿命80岁。
卢森堡大公国(卢森堡语:Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg[注 1];法语:Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; 德语:Großherzogtum Luxemburg[注 2]),通称卢森堡(卢森堡语:Lëtzebuerg;法语:Luxembourg;德语:Luxemburg),被邻国法国、德国和比利时包围,是一个位于欧洲的内陆国家,也是现今欧洲大陆仅存的大公国,首都卢森堡市。卢森堡是欧盟成员国,因境内有欧洲法院、欧洲审计院、欧洲投资银行等多个欧盟机构被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。
Das Großherzogtum Luxemburg (luxemburgisch Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg [ˈgʀəʊsˌhɛχtsoːktuːm ˈlətsəbuəɕ], französisch Grand-Duché de Luxembourg [ɡʁɑ̃ dyʃe də lyksɑ̃buʁ]) ist ein demokratischer Staat in Form einer parlamentarischen Monarchie[1] im Westen Mitteleuropas. Es ist das letzte Großherzog- bzw. Großfürstentum (von einst zwölf) in Europa. Das Land gehört zum mitteldeutschen Sprachraum. Landessprache ist Luxemburgisch, Verwaltungs- und Amtssprachen sind Französisch, Deutsch und Luxemburgisch. Gemeinsam mit seinem Nachbarn Belgien und mit den Niederlanden bildet Luxemburg die Beneluxstaaten.
ルクセンブルク大公国(ルクセンブルクたいこうこく)、通称ルクセンブルクは、西ヨーロッパに位置する立憲君主制国家。首都は国名と同名のルクセンブルク市。隣接国は、南のフランス、西と北のベルギー、東のドイツである。ベルギー、オランダと併せてベネルクスと呼ばれる。
Luxembourg (/ˈlʌksəmbɜːrɡ/ (![]() listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] (
listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] (![]() listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
With an area of 2,586 square kilometres (998 sq mi), it is one of the smallest sovereign states in Europe.[8] In 2016, Luxembourg had a population of 576,249, which makes it one of the least-populous countries in Europe,[9] but by far the one with the highest population growth rate.[10] Foreigners account for nearly half of Luxembourg's population.[11] As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by Grand Duke Henri and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and one of the world's highest GDP (PPP) per capita. The City of Luxembourg with its old quarters and fortifications was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 due to the exceptional preservation of the vast fortifications and the old city.[12]
The history of Luxembourg is considered to begin in 963, when count Siegfried I acquired a rocky promontory and its Roman-era fortifications known as Lucilinburhuc, ′little castle′, and the surrounding area from the Imperial Abbey of St. Maximin in nearby Trier.[13][14] Siegfried's descendants increased their territory through marriage, war and vassal relations. At the end of the 13th century, the Counts of Luxembourg reigned over a considerable territory. [15] In 1308, Henry VII, Count of Luxembourg became King of the Germans and Holy Roman Emperor. The House of Luxembourg produced four Holy Roman Emperors at the high time of the Middle Ages. In 1354, Charles IV elevated the County to the Duchy of Luxembourg. Since Sigismund had no male heir, the Duchy became part of the Burgundian Circle and then one of the Seventeen Provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands.[16] Over the centuries, the City and Fortress of Luxembourg, of great strategic importance situated between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg territories, was gradually built up to be one of the most reputed fortifications in Europe. After belonging to both the France of Louis XIV and the Austria of Maria Theresia, Luxembourg became part of the First French Republic and Empire under Napoleon.[17]
The present-day state of Luxembourg first emerged at the Congress of Vienna in 1815. The Grand-Duchy, with its powerful fortress, became an independent state under the personal possession of William I of the Netherlands with a Prussian garrison to guard the city against another invasion from France. [18] In 1839, following the turmoil of the Belgian Revolution, the purely Oil-speaking part of Luxembourg was ceded to Belgium and the Luxembourgish-speaking part (except the Arelerland, the area around Arlon) became what is the present state of Luxembourg. [19]
The steel industry exploiting the Red Lands' rich iron-ore grounds in the beginning of the 20th century drove the country's industrialisation. ArcelorMittal, the world's largest steel producer with headquarters in Luxembourg City, is still a reminder of these times. After the decline of the steel industry in the 1970s, the country focused on establishing itself as a global financial centre and developed into the banking hub it is reputed for. Since the beginning of the 21st century, its governments have focused on developing the country into a knowledge economy, with the founding of the University of Luxembourg and a national space programme, projecting the first involvement in a robotic lunar expedition by 2020.[20]
Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union, OECD, United Nations, NATO, and Benelux. The city of Luxembourg, which is the country's capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the EU. Luxembourg served on the United Nations Security Council for the years 2013 and 2014, which was a first in the country's history.[21] In 2016 Luxembourgish citizens had visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 172 countries and territories, ranking the Luxembourgish passport 15th in the world, tied with countries such as Canada and Switzerland.[22]
Le Luxembourg, en forme longue le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg2,b,c ou le grand-duché de Luxembourgd, en luxembourgeois Lëtzebuerg et Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, en allemand Luxemburg et Großherzogtum Luxemburg, est un pays d'Europe de l'Ouest sans accès à la mere Il est bordé par la Belgique à l'ouest et au nord, l'Allemagne à l'est, et la France au sud. Il comprend deux régions principales : l'Oesling au nord, qui est une partie du massif des Ardennes, et le Gutland au sud, prolongement de la Lorraine au sens géologique du terme. Le Luxembourg compte 602 005 habitants au 1er janvier 20181, et s'étend sur une superficie de 2 586 km2, faisant de lui l'une des plus petites nations souveraines d'Europe.
Le Luxembourg est une démocratie représentative et une monarchie constitutionnelle avec un grand-duc pour chef d'État, faisant du pays le seul grand-duché encore existant. Son économie dynamique en fait un des pays les plus riches et des plus prospères du monde, avec le PIB par habitant le plus élevé du monde selon le FMI en 2014. L'économie est principalement centrée sur les activités financières (environ la moitié du produit intérieur brut), favorisée par une fiscalité attractive voire dérisoire dans certains domaines (quasi-exonération d'impôts pour les bénéfices issus de l'exploitation de brevets ou de logiciels). La localisation centrale du territoire luxembourgeois en Europe a historiquement fait de lui un lieu d'une grande importance stratégique pour de nombreuses puissances, depuis sa fondation en tant que fortin romain7, son accueil d'un château franc durant le Haut Moyen Âge, et son rôle de bastion pour le chemin des Espagnols entre les XVIe et XVIIe siècles.
Le Luxembourg est le plus petit membre fondateur de l'Union européenne, de la zone euro, de l'OTAN, de l'OCDE, de l'ONU, de l'OSCE, du Conseil de l'Europe8,9,10,11 et du Benelux, reflétant son consensus politique en faveur de l'intégration économique, politique et militaire. La ville de Luxembourg, sa capitale et sa plus grande ville, est le siège de plusieurs établissements et institutions de l'UE. En 2012, le Luxembourg a été élu pour la première fois de son histoire à un siège temporaire au Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies. En raison de sa position géographique, la culture luxembourgeoise est une fusion de l'Europe germanique et romane, intégrant chacune des deux. De ce fait, le Luxembourg est un pays trilingue : le luxembourgeois, le français et l'allemand sont les trois langues officielles et, depuis 1984, le luxembourgeois a légalement le statut de « langue nationale »12.
Il Granducato di Lussemburgo (in francese: le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; in lussemburghese: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg; in tedesco: Großherzogtum Luxemburg) è un paese membro dell'Unione europea situato tra Germania, Francia e Belgio. È uno stato senza sbocco sul mare.
Membro fondatore dell'Unione europea, della NATO, del Benelux e delle Nazioni Unite, la sua capitale, l'omonima città di Lussemburgo, è sede di numerose istituzioni e agenzie europee oltre ad essere uno snodo finanziario di primaria importanza.
È l'unico granducato rimasto al mondo.
Luxemburgo, oficialmente denominado Gran Ducado de Luxemburgo (luxemburgués: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, francés: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, alemán: Großherzogtum Luxemburg), es un pequeño país de Europa Central que forma parte de la Unión Europea. Se trata de un Estado sin litoral, rodeado por Francia, Alemania y Bélgica. Luxemburgo cuenta con una población de medio millón de habitantes sobre un área de 2586 kilómetros cuadrados.1
El gobierno de Luxemburgo es una monarquía constitucional y parlamentaria, siendo el único gran ducado soberano en la actualidad. El Estado tiene una economía altamente desarrollada, con el mayor producto interior bruto por cápita del mundo de acuerdo al Banco Mundial, y el segundo de acuerdo al Fondo Monetario Internacional.
Luxemburgo es miembro de la Unión Europea, la Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte, la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, las Naciones Unidas y el Benelux, reflejando la orientación política a favor de la integración económica, política y militar. Su capital, Luxemburgo, es sede de numerosas instituciones y agencias de la Unión Europea.
Luxemburgo posee culturas y tradiciones diversas por encontrarse entre la Europa romana y la Europa germánica. El país tiene tres lenguas oficiales: alemán, francés y luxemburgués. La localidad Schengen, que dio su nombre al espacio de Schengen, está ubicada en Luxemburgo.
Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Lëtzebuerg), официально Вели́кое Ге́рцогство Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, фр. Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, нем. Großherzogtum Luxemburg) — государство (великое герцогство) в Западной Европе. Граничит с Бельгией на севере, на западе и на юге с Францией, на востоке с Германией, не имеет выхода к морю. Название происходит от древневерхненемецкого «lucilinburch» — «малый город». Общая площадь Люксембурга составляет 2586,4 км², что делает его одним из самых маленьких суверенных государств в Европе[5]. Население на 1 января 2018 года составляет 602 005 человек[2].
Член Европейского союза с 1957 года, также является членом НАТО, ОЭСР и ООН. Вместе с Бельгией и Нидерландами входит в состав Бенилюкса.

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 Ireland
Ireland
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 States of Europe
States of Europe

爱尔兰(英语:Ireland;爱尔兰语:Éire)[注 1],通称爱尔兰共和国(英语:Republic of Ireland;爱尔兰语:Poblacht na hÉireann),是一个西欧国家,欧盟成员国之一,位于欧洲大陆西北海岸外的爱尔兰岛,约占该岛南部的5/6面积。剩余东北部的1/6面积属于英国,称北爱尔兰。首都位于爱尔兰岛东部的都柏林。爱尔兰在2011年共计有458万人口,是一个议会共和制国家。此外爱尔兰也是欧洲联盟、欧洲理事会、经济合作与发展组织、世界贸易组织和联合国等国际组织的成员。爱尔兰共和国成立于1922年的爱尔兰自由邦,结束了大英帝国的统治,爱尔兰独立战争后签订了《英爱条约》,爱尔兰独立,但爱尔兰岛东北方的六个郡继续留在联合王国内,形成了北爱尔兰。
Irland ([ˈɪʁlant], amtlicher deutscher Name; irisch Éire [ˈeːrʲə] , englisch Ireland)[6] ist ein Inselstaat in Westeuropa. Er umfasst etwa fünf Sechstel der gleichnamigen Insel sowie eine Vielzahl kleinerer Inseln, welche ihr vorgelagert sind. Hauptstadt und größte Stadt Irlands ist Dublin, gelegen im östlichen Teil des Landes. In der Metropolregion Dublin lebt etwa ein Drittel der 4,8 Millionen Einwohner. Es grenzt im Norden an Nordirland und damit an das Vereinigte Königreich. Im Osten liegt die Irische See, im Westen und Süden ist das Land vom Atlantik umgeben. Irland ist seit 1973 Mitglied der Europäischen Union. Der Großteil der Bevölkerung bekennt sich zum römisch-katholischen Glauben.
Das lange Zeit verarmte und daher von Auswanderung betroffene Irland hat sich inzwischen zu einer hochmodernen, in manchen Gegenden multikulturellen Industrie- und Dienstleistungsgesellschaft gewandelt. Es hat jährlich 10 Millionen[7] ausländische Touristen. Irland war 2018 nach dem Bruttoinlandsprodukt pro Kopf (kaufkraftbereinigt) das zweitreichste Land Europas, in der Welt das fünftreichste.[4]
以色列国(希伯来语:![]() מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל;阿拉伯语:دَوْلَة إِسْرَائِيل) ,通称以色列(希伯来语:יִשְׂרָאֵל;阿拉伯语:إِسْرَائِيل,罗马化:Isrāʾīl),是位于中东地区的一个主权国家,1948年5月14日独立建国,人口900余万,主要人口为犹太人,以希伯来语为官方语言,通用英语。
מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל;阿拉伯语:دَوْلَة إِسْرَائِيل) ,通称以色列(希伯来语:יִשְׂרָאֵל;阿拉伯语:إِسْرَائِيل,罗马化:Isrāʾīl),是位于中东地区的一个主权国家,1948年5月14日独立建国,人口900余万,主要人口为犹太人,以希伯来语为官方语言,通用英语。
以色列位于亚欧大陆交界处,自古为各民族交汇之处。其国家位处阿拉伯半岛西北角、地中海东岸和红海亚喀巴湾北岸,与巴勒斯坦领土(约旦河西岸地区、加沙地带)交错相邻,北接黎巴嫩,东北邻叙利亚,东与约旦接壤[10],西南则为埃及西奈半岛。
以色列领土范围不大,根据联合国1947年巴勒斯坦分治决议,以色列面积1.52万平方公里。经过四次中东战争后,以色列目前实际控制面积约2.5万平方公里。以色列国土南北长约470km,东西最宽处宽约135km[11],整体南北长,东西窄。地形和气候相当多样[12][13]。以色列的金融及科技创新中心为特拉维夫[14],而耶路撒冷则为其法定首都、各政府机构所在地(国防部除外)及其辖下的第一大城市,外国使领馆驻特拉维夫。以色列对耶路撒冷的主权在国际上有争议[15]。
以色列所居领土历史上曾为多个国家统治。包括古埃及、新亚述帝国、新巴比伦帝国、波斯第一帝国、希腊马其顿帝国、托勒密埃及、塞琉古帝国、罗马共和国和罗马帝国、东罗马帝国、波斯第二帝国、阿拉伯帝国、法蒂玛王朝、塞尔柱帝国、十字军(耶路撒冷王国)、埃及马穆鲁克王朝、奥斯曼土耳其帝国以及大英帝国。1918年,奥斯曼帝国一战战败,退出该地区,随即阿拉伯部落纷争。1922年,国际联盟委托英国托管。受犹太复国主义兴起和反犹主义影响,二战后,大批犹太移民迁入。
1947年11月29日,联合国大会181号决议确定支持在巴勒斯坦托管地推行分治方案,支持以巴分别成立独立国家,耶路撒冷及其周边地区则由国际管理[16][17]。
1948年5月14日,世界犹太复国主义组织及犹太援以协会主席戴维·本-古里安宣告“犹太国家在以色列家园建立,称为以色列国”,将于托管期结束之时起开始运作[18][19][20]。5月15日零时,英国对巴勒斯坦的托管终止。[17][21]以色列建国次日,邻近的阿拉伯国家便集结了军队发动第一次中东战争争夺前巴勒斯坦托管地,与以色列军队交战[22][23],后双方战线沿当今被称做“绿线”处停战。约旦占领了绿线至约旦河的地区,并于1950年宣布将其并入约旦王国,约旦认为此地所有的阿拉伯人为约旦国民。
此后,以色列与阿拉伯邻国多次发生阿以冲突[24],以色列逐渐控制了约旦河西岸地区(1967年–现在)、西奈半岛(1956年–1957年、1967年–1982年)、南黎巴嫩局部地区(1982年–2000年)、加沙地带(1967年–2005年;但2005年撤退后仍被视为占领)以及戈兰高地。 以色列将其法律管辖范围拓展至戈兰高地和东耶路撒冷。根据1993年以巴签订的奥斯陆协议, 以色列对约旦河西岸的“B”和“C”区行使部分或完全的管辖权,“A”区则由阿拉伯人完全自治 [25][26][27][28]。由于以阿双方多年以来都未遵循或承认1947年联大181决议划定的以色列和巴勒斯坦国国界,冲突不断,国际社会只能有限调解以巴冲突,至今仍未达成和平。以色列至今不承认巴勒斯坦为独立国家,但以色列和埃及及约旦已经分别签署和平条约。
根据以色列中央统计局数据,以色列人口于2019年已达到900万,为世界唯一的犹太人占多数国家,其中约75%为犹太裔,20.8%为阿拉伯裔,人数达177万(包括德鲁兹派和多数东耶路撒冷阿拉伯人)[29][30][31]。绝大多数阿拉伯裔以色列人为定居的逊尼派穆斯林,少数为半定居的内盖夫贝都因人;其余则为基督徒和德鲁兹人。其他少数族裔包括马龙派、撒马利亚人、多姆人和罗姆人、非裔希伯来以色列人、其他撒哈拉以南非洲人[32]、亚美尼亚人、切尔克斯人、越南船民等。以色列亦有一定数量的来自非洲和亚洲的外国劳工和政治庇护者[3]。
依根据《以色列基本法》,以色列为“犹太和民主国家”[33]。以色列为代议民主制国家[34],采用议会制、比例代表制和普遍选举制[35][36]。总理为政府首脑,议会为立法机关。以色列为一发达国家,经济合作与发展组织成员国[37],2014年其名义国内生产总值排名世界第37。该国具有较高水平的劳动力,为全球教育程度最高的国家之一,其公民拥有高等教育学历的比例亦为世界最高之一[38][39]。其生活水平为中东最高和亚洲第四高[40][41][42],其人口预期寿命亦居世界前列[43]。
Israel (hebräisch ישראל Jisra'el) bzw. in Langform Staat Israel (hebräisch Medinat Jisra'el) ist ein Staat in Vorderasien an der Ostküste des Mittelmeers. Israel ist der einzige Staat der Welt mit mehrheitlich jüdischer Bevölkerung und gemäß eigenem Selbstverständnis Nationalstaat des jüdischen Volkes.[8][9][10][11] Israel gehört geographisch zum Maschrek und grenzt an den Libanon, Syrien, Jordanien, Ägypten sowie an Gazastreifen und Westjordanland. Hauptstadt und bevölkerungsreichste Stadt ist Jerusalem, größtes Ballungszentrum ist Gusch Dan um die am Mittelmeer gelegene Metropole Tel Aviv-Jaffa. Politik und Geschichte des Staates sind erheblich durch den andauernden Nahostkonflikt geprägt.
Das Gebiet des heutigen Israel gilt als Wiege des Judentums, sowie später auch der zwei anderen, jüngeren abrahamitischen Religionen. Es stand jedoch seit Christi Geburt nacheinander unter römischer, byzantinischer, arabischer, osmanischer und zuletzt britischer Fremdherrschaft. Die dort seit rund 3.000 Jahren ansässigen Juden (Hebräer) wurden im Laufe dessen mehrfach vertrieben (jüdische Diaspora). Ab dem ausgehenden 19. Jahrhundert bestanden unter europäischen Juden, nicht zuletzt aufgrund der dort zunehmenden Judenverfolgung, Bestrebungen, im damals osmanischen Palästina wieder einen jüdischen Nationalstaat zu errichten (Zionismus, benannt nach Zion / dem Tempelberg). Die ersten politischen Grundsteine dafür wurden beim Ersten Zionistischen Weltkongress in Basel im Jahr 1897 unter der Leitung von Theodor Herzl gelegt, die beabsichtigte Staatsgründung nahm durch die Balfour-Deklaration von 1917 konkretere Formen an. Von 1920 bis 1948 bestand das Völkerbundsmandat für Palästina unter britischer Vorherrschaft, verstärkte jüdische Einwanderung und Aufbau staatlicher Strukturen führten zu Konflikten mit der arabischen Bevölkerung. Der UN-Teilungsplan für Palästina von 1947 sollte diese beilegen, wurde allerdings von arabischer Seite abgelehnt. Am 14. Mai 1948 erfolgte die Israelische Unabhängigkeitserklärung und sogleich ein Angriff der arabischen Nachbarstaaten. Die nachfolgende, jüngere Geschichte Israels ist seither von dem andauernden arabisch-israelischen Konflikt geprägt.
Das politische System Israels basiert auf einem parlamentarischen Regierungssystem. Regierungschef ist der von der Knesset gewählte Ministerpräsident, das Staatsoberhaupt der Staatspräsident mit überwiegend repräsentativen Aufgaben. Israel ist als freiheitlich-demokratischer Rechtsstaat mit einem ausgeprägtem Sozialstaat verfasst; das Land gilt gemeinhin als die „einzige Demokratie im Nahen Osten“. Der zentralistisch verwaltete Staat ist in sechs Bezirke und diese wiederum in 71 Städte, 141 Gemeinden und 53 Regionalverbände (Zusammenschlüsse mehrerer kleinerer Ortschaften zu Verwaltungsgemeinschaften) unterteilt.
Das dicht besiedelte Land hat 2019 etwa 9 Mio. Einwohner, davon ca. 6,7 Mio. Juden (74,2 %), 1,9 Mio. nichtjüdische Araber (20,9 %) und einige weitere traditionell im Land beheimatete Minderheiten wie Aramäer,[12] Samaritaner, Armenier, Tscherkessen und Roma.[4] Das Rückkehrgesetz gestattet es allen Juden, sich in Israel niederzulassen. Seit etwa 1990 leben auch zunehmend legale asiatische und osteuropäische Arbeitsmigranten sowie illegale Einwanderer aus Afrika im Land.
Die jüdische Bevölkerung setzt sich aus Aschkenasim, Misrachim, Sephardim, Falaschen sowie aus jemenitischen Juden zusammen, wobei eine zunehmende Verschmelzung dieser Gruppen zu beobachten ist. Die Mehrheit arabischer Israelis sind Muslime, eine Minorität unter den Arabern in Israel bilden Christen und Drusen.
Trotz widriger äußerer Umstände (exponierte geografische Lage, Mangel an Wasser und Rohstoffen, Abhängigkeit von ausländischem Kapital, Kriege mit den arabischen Nachbarstaaten) ist es Israel gelungen, einen hoch entwickelten Industriestaat aufzubauen. Die heutige israelische Wirtschaft ist von einer fortschrittlichen Landwirtschaft und einer spezialisierten, stark exportorientierten Industrie geprägt. Wichtige Industriesektoren sind die Diamantenverarbeitung, die chemische und pharmazeutische Industrie sowie die Halbleitertechnik, im Dienstleistungssektor ist die Finanzwirtschaft, die Softwareentwicklung und der Tourismus zu nennen. Von wachsender Bedeutung ist die High-Tech-Industrie; das Land hat die höchsten Ausgaben für Forschung und Entwicklung pro Einwohner und die höchste Dichte an Start-ups weltweit. Ausgeprägt ist die hohe soziale Ungleichheit, die hauptsächlich durch die unzureichende wirtschaftliche Integration der arabischen und ultraorthodoxen Bevölkerungsteile bedingt ist. Das Land ist seit 2010 Mitglied der OECD. Nach dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung (HDI) weltweit auf Platz 22 (Platz 1 im Nahen Osten, Platz 4 in Asien, Stand 2017) und zählt damit zu den sehr hoch entwickelten Volkswirtschaften.[13]
イスラエル国(イスラエルこく、ヘブライ語: מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל、アラビア語:دَوْلَة إِسْرَائِيل、英語: State of Israel :[ˈɪzrɪəl, ˈɪzreɪəl])、通称イスラエル(ヘブライ語: יִשְׂרָאֵל)は、西アジアに位置する共和制国家。北はレバノン、北東はシリア、東はヨルダン、東と西はパレスチナ自治区のヨルダン川西岸とガザ地区[9]、南西はエジプトと国境を接している。
実質的な首都はテルアビブであり、経済と技術の中心地をなす[10]。一方、イスラエル政府としてはエルサレムを首都と宣言しているが、エルサレムに対する国家の主権は国際的には限定的にしか認められていない[11][12][13][14]。
イスラエルには、アフリカから類人猿が最も早く移動してきた証拠がある[15]。カナン族の存在は青銅器時代中期から考古学的に証明されており[16][17]、イスラエル王国とユダ王国は鉄器時代に誕生した[18][19]。紀元前720年頃、新アッシリア帝国がイスラエル王国を滅ぼした[20]。ユダ王国はその後、バビロニア帝国、ペルシャ帝国、ヘレニズムの帝国に征服され、ユダヤ人の自治州として存在していた[21][22]。マカバイ戦争が成功し、紀元前110年にはハスモン朝の独立国となった[23]が、紀元前63年にはローマ共和国の従属国となり、紀元前37年にはヘロデ朝が置かれ、紀元後6年にはローマ帝国のユダヤ属州が誕生したのである[24]。ユダヤ人の反乱により、ユダヤ属州は壊滅的な打撃を受け[25]、ユダヤ人は追放され[26][27]、シリア・パレスティナに改称されるまで、ユダヤはローマの属州として存続した[28]。この地域におけるユダヤ人の存在は、何世紀にもわたってある程度継続している。7世紀にビザンチン帝国からアラブ人に奪われたレバント地方は、1099年の第1回十字軍、1187年のアイユーブ朝による征服までイスラム教徒の支配下にあった。13世紀にはエジプトのマムルーク朝がレバントに支配を広げ、1517年にオスマン帝国に敗れるまで支配した。19世紀には、ユダヤ人の民族意識の高まりからシオニスト運動が起こり、パレスチナへの移住が始まった。
パレスチナは、第一次世界大戦後にオスマン帝国から割譲され、1920年から1948年まで大英帝国の委任統治領となった。第二次世界大戦が始まると、委任統治領は大規模な爆撃を受け、イシューブのユダヤ人は連合国側に従軍した。1944年、イギリスは武器の供給とユダヤ人旅団の結成に同意した。緊張が高まる中、イギリスはアラブ人とユダヤ人の両派をなだめるために、1947年に国際連合がパレスチナ分割決議を採択し、アラブ人とユダヤ人の独立国家と国際化されたエルサレムの設立を勧告した[29]。翌年、ユダヤ機関はイスラエルの独立を宣言し、1948年のアラブ・イスラエル戦争では、イギリス委任統治領の大部分をイスラエルが占領したが、ヨルダン川西岸とガザは近隣のアラブ諸国が占領していた[30]。その後、イスラエルはアラブ諸国といくつかの戦争を経験し[31]、1967年6月の第三次中東戦争以降は、ヨルダン川西岸地区、ゴラン高原、ガザ地区などの占領地を保有している(2005年の分離独立後も占領地とみなされているが、法律の専門家の中にはこの主張に異論がある)[32][33][34]。その後の立法措置により、ゴラン高原と東エルサレムではイスラエル法が全面的に適用され、ヨルダン川西岸ではイスラエルの入植地への「パイプライニング」により部分的に適用されている[35][36][37][38]。イスラエルによるパレスチナ自治区の占領は、現代における世界最長の軍事占領であると国際的に考えられている[39]。イスラエルとパレスチナの紛争を解決するための努力は、最終的な和平合意には至っていないが、イスラエルはエジプトとヨルダンの両国と和平条約を締結している。
イスラエルは基本法の中で、自らをユダヤ人と民主主義の国家であり、ユダヤ人の国民国家であると定義している[40]。国は、議会制、比例代表制、普通選挙を採用した自由民主主義国家である[41][42]。首相は政府の長であり、クネセトは立法府である。2019年現在の人口は約900万人[43]で、イスラエルは先進国であり、OECD加盟国である[44]。名目GDPでは世界第31位の経済規模を持ち、現在紛争中の国の中では最も先進的な国である。中東で最も生活水準が高く、軍事訓練を受けた国民の割合[45]、高等教育の学位を持つ国民の割合[46]、GDP比の研究開発費[47]、女性の安全性[48]、平均寿命[49]、革新性[50]、幸福度[51]などで世界の上位にランクインしている。
Israel (/ˈɪzriəl, ˈɪzreɪəl/; Hebrew: יִשְׂרָאֵל, romanized: Yisra'el; Arabic: إِسْرَائِيل, romanized: ʾIsrāʾīl), officially known as the State of Israel (Hebrew: מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, Medinat Yisra'el), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west,[23] respectively, and Egypt to the southwest. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country,[24] while its seat of government and proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, although international recognition of the state's sovereignty over the city is limited.[25][26][27][28][fn 4]
Israel has evidence of the earliest migration of hominids out of Africa.[29] Canaanite tribes are archaeologically attested since the Middle Bronze Age,[30][31] while the Kingdoms of Israel and Judah emerged during the Iron Age.[32][33] The Neo-Assyrian Empire destroyed Israel around 720 BCE.[34] Judah was later conquered by the Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic empires and had existed as Jewish autonomous provinces.[35][36] The successful Maccabean Revolt led to an independent Hasmonean kingdom by 110 BCE,[37] which in 63 BCE however became a client state of the Roman Republic that subsequently installed the Herodian dynasty in 37 BCE, and in 6 CE created the Roman province of Judea.[38] Judea lasted as a Roman province until the failed Jewish revolts resulted in widespread destruction,[37] the expulsion of the Jewish population[37][39] and the renaming of the region from Iudaea to Syria Palaestina.[40] Jewish presence in the region has persisted to a certain extent over the centuries. In the 7th century CE, the Levant was taken from the Byzantine Empire by the Arabs and remained in Muslim control until the First Crusade of 1099, followed by the Ayyubid conquest of 1187. The Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt extended its control over the Levant in the 13th century until its defeat by the Ottoman Empire in 1517. During the 19th century, national awakening among Jews led to the establishment of the Zionist movement followed by immigration to Palestine.
The land was controlled as a mandate of the British Empire from 1920 to 1948, having been ceded by the Ottomans at the end of the First World War. The Second World War saw the mandate bombed heavily. Once the British agreed to supply arms and form a Jewish Brigade in 1944, Yishuv Jews officially entered the conflict on the side of the allies. At the end of the war, amidst growing tensions with the conflict-weary British, the United Nations (UN), eager to appease both Arab and Jewish factions, adopted a Partition Plan for Palestine in 1947 recommending the creation of independent Arab and Jewish states, and an internationalized Jerusalem.[41] The plan was accepted by the Jewish Agency but rejected by Arab leaders.[42][43][44] The following year, the Jewish Agency declared the independence of the State of Israel, and the subsequent 1948 Arab–Israeli War saw Israel establishment over most of the former Mandate territory, while the West Bank and Gaza were held by neighboring Arab states.[45] Israel has since fought several wars with Arab countries,[46] and since the Six-Day War in June 1967 held occupied territories including the West Bank, Golan Heights and the Gaza Strip (still considered occupied after the 2005 disengagement, although some legal experts dispute this claim).[47][48][49][fn 5] Subsequent legislative acts have resulted in the full application of Israeli law within the Golan Heights and East Jerusalem, as well as its partial application in the West Bank via "pipelining" into Israeli settlements.[50][51][52][53] Israel exerts full control over almost two-thirds of the West Bank and partial control over 165 Palestinian enclaves; Israel's occupation of the Palestinian territories is internationally considered to be the world's longest military occupation in modern times.[fn 5][57] Efforts to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict have not resulted in a final peace agreement, while Israel has signed peace treaties with both Egypt and Jordan.
In its Basic Laws, Israel defines itself as a Jewish and democratic state, and the nation state of the Jewish people.[58] The country is a liberal democracy with a parliamentary system, proportional representation, and universal suffrage.[59][60] The prime minister is head of government and the Knesset is the legislature. With a population of around 9 million as of 2019,[61] Israel is a developed country and an OECD member.[62] It has the world's 31st-largest economy by nominal GDP, and is the most developed country currently in conflict.[63] It has the highest standard of living in the Middle East,[22] and ranks among the world's top countries by percentage of citizens with military training,[64] percentage of citizens holding a tertiary education degree,[65] research and development spending by GDP percentage,[66] women's safety,[67] life expectancy,[68] innovativeness,[69] and happiness.[70]
IsraëlNote 2 (/is.ʁa.ɛl/), en forme longue l'État d'Israël (respectivement en hébreu יִשְׂרָאֵל (Yisrā'el) et מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל (Medīnat Yisra'el) /mediˈnat jisʁaˈʔel/ ; en arabe إِسْرَائِيلُ (Isrā'īl) et دولة إسرائيل (Dawlat Isrā'īl)), est un État situé sur la côte orientale de la mer Méditerranée au Proche-Orient en Asie occidentale. Son indépendance est proclamée le 14 mai 1948, après le vote du plan de partage de la Palestine le 29 novembre 1947 par l'Organisation des Nations unies (ONU) qui met fin au mandat britannique et qui prévoit la création d’un État juif et d’un État arabe. Les premières bases politiques en ce sens ont été posées lors du premier congrès mondial sioniste à Bâle en 1897 sous la direction de Theodor Herzl.
Israël est une démocratie parlementaire. Le Premier ministre, désigné par le président et confirmé par le Parlement (la Knesset), est le chef de l'exécutif. La Knesset (assemblée), où siègent cent vingt députés élus au scrutin proportionnel intégral à un tour, représente le pouvoir législatif. La Cour suprême, composée de neuf juges, sert à la fois de pouvoir judiciaire et de Cour d'appel. Le pays a établi sa capitale à Jérusalem, choix qui n’est pas reconnu par une grande partie de la communauté internationale. Tel Aviv est le centre diplomatique, économique et financier du pays.
Israël est également le seul État au monde où la population est majoritairement juive avec une proportion de 75 %. Le 19 juillet 2018, la Knesset adopte une nouvelle loi fondamentale de l'État d'Israël qui fait d'Israël l'État-nation du peuple juif. La population non juive comprend principalement des Arabes pour la plupart des descendants des Arabes de l'époque de la Palestine mandataire aussi appelés Arabes israéliens ; ils représentent 21 % de la population : 85 % d'entre eux sont musulmans7.
Depuis sa création en 1948, l'État d'Israël s'est confronté à plusieurs reprise avec des pays arabes voisins. L'Égypte et la Jordanie ont signé un traité de paix avec lui, mais Israël reste en conflit avec la Syrie, le Hezbollah au Liban et le Hamas dans la bande de Gaza. En outre, de nombreux pays de la région ne reconnaissent pas, voire rejettent, son existence.
Israele, ufficialmente Stato d'Israele (in ebraico: , Medinat Yisra'el; in arabo: دولة اسرائيل, Dawlat Isrā'īl), è uno Stato del Vicino Oriente affacciato sul mar Mediterraneo e che confina a nord con il Libano, con la Siria a nord-est, Giordania a est, Egitto e golfo di Aqaba a sud e con i territori palestinesi, ossia Cisgiordania (comprendente le regioni storiche di Giudea e Samaria) a est, e Striscia di Gaza a sud-ovest[7][8].
Situato in Medio Oriente, occupa approssimativamente un'area che secondo i racconti biblici in epoca antica era compresa nel Regno di Giuda e Israele e nella regione della Cananea, soggetta nel tempo al dominio di numerosi popoli, tra cui egizi, assiri, babilonesi, romani, bizantini, arabi e ottomani, nonché teatro di numerose battaglie etnico-religiose. In età contemporanea è stata parte del mandato britannico della Palestina, periodo durante il quale fu soggetta a flussi immigratori di popolazioni ebraiche, incoraggiate dalla nascita del movimento sionista nella città svizzera di Basilea (1897) che mirava alla costituzione di un moderno Stato ebraico. Dopo la seconda guerra mondiale e la Shoah, anche per cercare di porre rimedio agli scontri tra ebrei e arabi, il 29 novembre 1947 l'Assemblea generale delle Nazioni Unite nella risoluzione n. 181 approvava il piano di partizione della Palestina che prevedeva la costituzione di due Stati indipendenti, uno ebraico e l'altro arabo. Alla scadenza del mandato britannico il moderno Stato d'Israele fu quindi proclamato da David Ben Gurion il 14 maggio 1948[9][10][11].
Tale ripartizione fu però osteggiata da gruppi antisionisti e dalla totalità dei rappresentanti palestinesi, nonché dai vicini Paesi arabi. Dopo alcuni scontri già all'indomani del voto della risoluzione, terminato il ritiro delle truppe britanniche, la Lega Araba avviò una guerra contro il neonato Stato ebraico, dando origine a una serie di conflitti arabo-israeliani; accordi di pace sui confini furono in seguito raggiunti solo con Egitto (1979) e Giordania (1994). Rispetto ai territori palestinesi non esistono tuttora confini precisi. Oltre a estendere il territorio dello Stato dopo la prima guerra arabo-israeliana del 1948 (denominata da parte israeliana guerra d'Indipendenza, mentre da parte araba Nakba, "catastrofe"), rispetto a quanto previsto dalla risoluzione ONU, Israele ha anche occupato i territori della Cisgiordania, compresa Gerusalemme Est, della Striscia di Gaza e delle alture del Golan dopo la guerra dei sei giorni del 1967 e nel corso degli anni vi ha costruito nuovi centri abitati.
Lo Stato palestinese, proclamato nel 1988 e ammesso come osservatore permanente dell'ONU nel 2012, ma non riconosciuto come tale da Israele e da altri Paesi, controlla la striscia di Gaza, dalla quale Israele sì è ritirata unilateralmente nel 2005 (facendone evacuare anche coattamente i ventuno insediamenti) e solo alcune zone della Cisgiordania, che rivendica interamente anche se rimane prevalentemente controllata da Israele, secondo le decisioni degli accordi di Oslo del 1993. La sovranità israeliana non è riconosciuta da molti Stati arabi, mentre rappresentanti palestinesi hanno riconosciuto Israele nel 1993, come parte degli stessi accordi di Oslo[Nota 3]. Diversi tentativi di accordi di pace non hanno finora dato i frutti sperati e l'area continua quindi a essere geopoliticamente instabile.
All'aprile 2015 la popolazione israeliana era di 8.345.000 abitanti[3][4]. È l'unico Stato al mondo a maggioranza ebraica (il 74,9% della popolazione[3][4]) e con una consistente minoranza di arabi (circa il 20%, in prevalenza di religione musulmana, ma anche cristiana o drusa)[12].
La legge fondamentale del 1980 (Israele non ha un organico testo costituzionale, ma una pluralità di "leggi fondamentali") afferma che la capitale è Gerusalemme, rivendicata come tale anche dallo Stato di Palestina almeno nella sua parte orientale, ma non riconosciuta come capitale di Israele dalla maggior parte dei membri dell'ONU[Nota 4]. Quasi tutti gli Stati che hanno relazioni diplomatiche con Israele mantengono le proprie ambasciate a Tel Aviv[13], centro finanziario del Paese, o nelle vicinanze, ma mantengono comunque sedi consolari a Gerusalemme.
Le due leggi fondamentali del 1992 sulla dignità e la libertà e sul diritto all’occupazione proclamano che Israele è uno stato “ebraico e democratico”[14][15] e la legge fondamentale del 2018 definisce Israele come “stato-nazione del popolo ebraico[16][17]. Israele è governato da un sistema parlamentare a rappresentanza proporzionale. È considerato un Paese sviluppato, è membro dell'OCSE[18] e secondo il Fondo monetario internazionale nel 2013 era al 37º posto nella lista degli Stati per prodotto interno lordo. Ha inoltre il più alto indice di sviluppo umano in Medio Oriente[19] ed è uno dei Paesi con la più alta aspettativa di vita nel mondo[20].
Israel —oficialmente Estado de Israel (en hebreo: מְדִינַת יִשְרָאֵל Medinat Yisra'el, AFI: [mediˈnat jisʁaˈʔel]; en árabe, دولة إِسرائيل, romanizado: Dawlat Isrā'īl, AFI: [dawlat ʔisraːˈʔiːl])— es un país soberano de Asia, ubicado en la región de Oriente Próximo y que se encuentra en la ribera sudoriental del mar Mediterráneo. Limita al norte con el Líbano, al este con Siria y Jordania, con Palestina y el mar Muerto al este en Cisjordania, al oeste con la Franja de Gaza, al suroeste con Egipto y al sur con el golfo de Áqaba, en el mar Rojo. Con una población de casi 9 millones de habitantes,8 la mayoría de los cuales son judíos, Israel es el único Estado judío del mundo.13 Es también el hogar de árabes musulmanes, cristianos, drusos y samaritanos, así como otros grupos religiosos y étnicos minoritarios. La capital —con reconocimiento internacional limitado—, sede del gobierno y mayor ciudad del país es Jerusalén; el principal centro económico y financiero se encuentra en Tel Aviv-Yafo y el mayor centro industrial se localiza en Haifa.
El nuevo estado de Israel identifica sus raíces con la antigua Tierra de Israel (ארץ ישראל Eretz Yisraˈel), un concepto central para el judaísmo desde hace más de 3000 años.14 Después de la Primera Guerra Mundial y durante la partición del Imperio otomano, la Sociedad de Naciones aprobó el Mandato británico de Palestina con la intención de crear un «hogar nacional para el pueblo judío».15 En 1947, las Naciones Unidas aprobaron la partición de Palestina en dos Estados, uno judío y uno árabe.16 El 14 de mayo de 1948, el Estado de Israel declaró su independencia, seguida por la Guerra árabe-israelí de 1948 con los vecinos países árabes, que se negaron a aceptar el plan de la ONU. Las sucesivas victorias en una serie de guerras posteriores confirmaron su independencia y ampliaron las fronteras del Estado judío más allá de lo dispuesto en el Plan de Partición de las Naciones Unidas. Israel ha estado en conflicto con muchos de los países árabes vecinos, con numerosos enfrentamientos armados desde entonces.17 Desde su fundación, las fronteras de Israel e incluso el derecho a existir del propio Estado ha estado sujeto a controversias, especialmente entre sus vecinos árabes. Sin embargo, Israel ha firmado tratados de paz con Egipto y Jordania, y se han hecho esfuerzos para alcanzar un acuerdo permanente con la Autoridad Nacional Palestina.181920212223242526 En enero de 2020, el presidente de Estados Unidos, Donald Trump, presentó junto al entonces primer ministro israelí, Benyamin Netanyahu, un plan de paz unilateral para resolver el conflicto.272829
Israel es una democracia representativa con un sistema parlamentario y sufragio universal.13 El primer ministro actúa como jefe de Gobierno y la Knéset como cuerpo legislativo de Israel. En términos de producto interior bruto, su economía está situada en el puesto 43.º según el Fondo Monetario Internacional. A su vez, Israel está altamente situado entre los países de Oriente Próximo en desarrollo humano,30 libertad de expresión31 y competitividad económica.32
Изра́иль (ивр. יִשְׂרָאֵל, араб. إِسْرَائِيل), официально — Госуда́рство Изра́иль (ивр. מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל Медина́т Исраэ́ль, араб. دَوْلَة إِسْرَائِيل Даула́т Исра’и́ль), — государство на Ближнем Востоке. Население на 31 декабря 2019 года — 9 136 000 человек[6]; территория — 22 072 км². Занимает 96-е место в мире по численности населения и 148-е по территории.
Расположен на Ближнем Востоке, у восточного побережья Средиземного моря. На севере граничит с Ливаном, на северо-востоке — с Сирией, на востоке — с Иорданией и территорией Западного берега реки Иордан, на юго-западе — с Египтом и сектором Газа. Столица — Иерусалим[комм. 2]. Государственный язык — иврит; арабский язык обладает особым статусом.
Унитарное государство, демократическая парламентская республика. Подразделяется на 6 административных округов.
Индустриальная страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. Объём ВВП к апрелю 2019 года составил свыше 381 миллиарда долларов США (39,16 тысяч долларов США на душу населения)[10]. В списке стран по индексу развития человеческого потенциала находится на 22-м месте в мире: индекс 0,903[11]. Денежная единица — новый израильский шекель.
Декларация независимости была провозглашена 14 мая 1948 года (5 ияра 5708 года)[комм. 1] на основании резолюции Генеральной Ассамблеи ООН № 181, принятой 29 ноября 1947 года. Согласно Декларации Независимости, Израиль является еврейским государством. В то же время Израиль является многонациональным и демократическим государством, где, наряду с евреями, равные права имеют и все прочие этнические группы, вне зависимости от вероисповедания. Израиль отличается значительным этнокультурным разнообразием. Основное население страны: 6 772 000 человек — евреи (74,1 %), 1 916 000 человек — арабы (21 %), 448 000 человек — прочие (4,9 %)[6].

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 Italy
Italy
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP3
TOP3

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7

 States of Europe
States of Europe

意大利共和国(意大利语:Repubblica Italiana[注 1]),通称意大利(Italia),是欧洲主权国家,主要由位于南欧的靴型意大利半岛及两个地中海岛屿西西里岛和撒丁岛所组成。意大利北方的阿尔派恩山地区与法国、瑞士、奥地利以及斯洛文尼亚接壤,其领土包围着两个微型国家——圣马力诺和梵蒂冈及一个主权实体 ——马耳他骑士团,而在瑞士拥有座落于卢加诺湖湖畔的意大利坎波内这个境外领土。全国行政上划分为20个区域(其中5个为自治区)、110个省与8,100个城市。首都为罗马,意大利王国在1870年将首都设置在此,而都灵(1861年-1865年)及佛罗伦萨(1865年-1870年)也曾是意大利王国的首都。根据2017年统计,意大利人口为6,059万,领土面积为301,338平方公里,人口密度约每平方公里201.1人,属于温带地中海型气候。意大利是欧洲人口第5多的国家,人口在世界上排名第23位。意大利因其拥有美丽的自然风光和为数众多的人类文化遗产而被称为美丽的国度(Belpaese)。
现今的意大利地区是以前欧洲民族及文化的摇篮,曾孕育出罗马文化及伊特拉斯坎文明,而意大利的首都罗马,几个世纪以来都是西方世界的政治中心,也曾经是罗马帝国的首都。当罗马帝国在西部的统治瓦解后,意大利遭受了多次外族入侵,包括伦巴第人、东哥德人等日耳曼民族,之后还有诺曼人等。拜占庭帝国曾一度重新占领意大利地区。在14世纪后,意大利转而成为文艺复兴的发源地[7],而文艺复兴对欧洲影响深远,让欧洲思想前进了一大步。意大利过去分裂为许多王国与城邦,但最终在1871年成为统一的意大利王国(除了圣马力诺)[8]。意大利殖民帝国巅峰是在1942年第二次世界大战时期,首相墨索里尼统治下的意大利王国变成一个地中海帝国,把势力范围延伸到北非(利比亚 、突尼斯)、东非(厄立特里亚、索马里兰、埃塞俄比亚)、巴尔干(阿尔巴尼亚、达尔马提亚、黑山、克罗地亚独立国西部、希腊、罗得岛与十二群岛)和法国南部(隆河以东的领土、科西嘉岛、摩纳哥),而且拥有中国天津的租界[9]。1945年,墨索里尼建立的意大利社会共和国被盟军击垮,意大利在二战后,废除了君主制,意大利王国灭亡,建立了现在的意大利共和国。战后根据1947年巴黎和平条约,意大利殖民帝国终结。
意大利也在政治、文化、科学、医疗卫生、教育、体育、艺术、时尚、宗教、料理、电影、建筑、经济及音乐等方面具有重要的影响力。米兰是意大利的经济及工业中心,根据2009年全球语言监察组织(Global Language Monitor)的资料[10],它也是世界时尚之都。在2007年造访意大利的游客人数位居世界第5位,总共超过4,370万人次的国际游客造访[11],而罗马则是欧盟国家中第3多游客造访的城市[12],也被认为世界上最美丽的十大古城之一[13]。威尼斯则被认为是世界上最美丽的城市,《纽约时报》形容它“无疑是世界上最美丽的人造城市”[14]。
意大利共和国是一个议会制民主共和国,是一个发达国家,世界七大工业国之一,最佳出生地指数则在世界排名第8名[15]。意大利在2017年人类发展指数列表中则名列第28位[16],并拥有高度人均国内生产总额[17][18]。根据国内生产总额与购买力平价国内生产总值的数据,意大利分别是世界第8大与第10大经济体[19]。意大利的政府预算金额则是位居世界第5位[20]。意大利是北大西洋公约和欧盟的创始会员国,也是七大工业国集团、20国集团和成员之一。意大利也参与经济合作暨发展组织、世界贸易组织、欧洲议会、西欧联盟及欧洲创新中心(Central European Initiative)。意大利也参加申根协议,也是世界世界国防预算金额第9高的国家且分享北约的核武器。
意大利在欧洲及全球的军事、文化和外交事务扮演重要的角色,首都罗马则是世界上对于政治及文化具有重要影响力的城市,世界上许多著名的机构,例如国际农业发展基金会(International Fund for Agricultural Development)[21]、全球在地论坛(Glocal Forum)[22]、世界粮食计划署及联合国粮食及农业组织的总部都设在罗马。意大利也拥有较高的教育指数、劳动力人口[23]及慈善捐助金额[24]。人均预期寿命排名世界第11位[25]。医疗保健系统在2000年被世界卫生组织评比为世界第2。意大利也是一个全球化的国家[26]。意大利的国家品牌价值在2009年名列世界第6位[27]。意大利在艺术、科学和技术上拥有悠久的传统,且至2017年共有53处世界遗产,是拥有最多世界遗产的西方国家[28][29]。
Italien (italienisch Italia [iˈtaːlja], amtlich Italienische Republik, italienisch Repubblica Italiana [reˈpubblika itaˈljaːna]) ist ein Staat in Südeuropa; seine Hauptstadt ist Rom.
Das italienische Staatsgebiet liegt zum größten Teil auf der vom Mittelmeer umschlossenen Apenninhalbinsel und der Po-Ebene sowie im südlichen Gebirgsteil der Alpen. Der Staat grenzt an Frankreich, die Schweiz, Österreich und Slowenien. Die Kleinstaaten Vatikanstadt und San Marino sind vollständig vom italienischen Staatsgebiet umschlossen. Neben den großen Inseln Sizilien und Sardinien sind mehrere Inselgruppen vorgelagert.
Als Kreuzweg der Zivilisationen des Mittelmeerraumes ist der italienische Beitrag zum kulturellen und historischen Erbe Europas und der Welt beachtenswert, das Gebiet des heutigen Italien war in der Antike die Kernregion des Römischen Reiches, die oberitalienische Toskana war das Kernland der Renaissance, ihr folgte von Rom ausgehend die Epoche des Barock.
Mit dem Risorgimento entstand der moderne italienische Nationalstaat: Von 1861 bis 1946 bestand unter dem Haus Savoyen das Königreich Italien, das rapide industrialisiert wurde, zu einer europäischen Großmacht aufstieg und ab den 1880er Jahren ein Kolonialreich in Nord- und Ostafrika errichtete. Die kostspielige und verlustreiche Teilnahme am Ersten Weltkrieg von 1915 bis 1918 führte zwar zur Vergrößerung des Staatsgebietes, aber auch zu schweren sozialen Unruhen und ebnete den italienischen Faschisten unter Benito Mussolini den Weg zur Macht. Das faschistische Regime herrschte von 1922 bis 1943/45 über Italien und führte das Land 1940 auf der Seite der Achsenmächte in den Zweiten Weltkrieg. Die Kriegsniederlage führte zum Verlust der Kolonien und zu vergleichsweise geringfügigen Gebietsabtretungen an den Nachbarstaat Jugoslawien. Im Juni 1946 beendete eine Volksabstimmung die Monarchie; die heutige Republik wurde ausgerufen.
Italien ist Mitinitiator der Europäischen Integration und Gründungsmitglied der Europäischen Union, des Europarates und der Lateinischen Union. Das Land ist Mitglied der G7, der G20, der NATO, der Vereinten Nationen (UNO), der Organisation für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung (OECD) und der Welthandelsorganisation (WTO).
Italien zählt laut Index der menschlichen Entwicklung als Industriestaat zu den höchstentwickelten Ländern der Erde[4] und ist gemessen am nominalen Bruttoinlandsprodukt die achtgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt.[5] Das Land genießt einen hohen Lebensstandard sowie Bildungsgrad und besitzt eine der höchsten Lebenserwartungen.[6] Italien ist das Land mit den meisten Welterbestätten der UNESCO (58)[7] und mit rund 65 Millionen Touristen jährlich eines der meistbesuchten Länder der Welt.[8]
イタリア共和国(イタリアきょうわこく、イタリア語: Repubblica Italiana)、通称イタリア(イタリア語: Italia、IPA: [iˈtaːlja] (![]() 音声ファイル) イターリャ)は、南ヨーロッパに位置する共和制国家。首都はローマ。 北をスイスとオーストリア、西がフランス、 東はスロベニアと国境を接している。南は地中海が位置しており、アルバニア、アルジェリア、クロアチア、ギリシャ、リビア、マルタ、モンテネグロ、スペイン、チュニジアと海上境界線を共有している。また、国土には独立国として小規模であるバチカンとサンマリノが存在している。
音声ファイル) イターリャ)は、南ヨーロッパに位置する共和制国家。首都はローマ。 北をスイスとオーストリア、西がフランス、 東はスロベニアと国境を接している。南は地中海が位置しており、アルバニア、アルジェリア、クロアチア、ギリシャ、リビア、マルタ、モンテネグロ、スペイン、チュニジアと海上境界線を共有している。また、国土には独立国として小規模であるバチカンとサンマリノが存在している。
イタリアはヨーロッパにおける古代文化の発祥地の一つとして知られ、同時に世界的な文化大国の一国に数えられている。文化・学問・宗教で歴史的に影響力を発揮しており、バチカン市国を首都ローマの領域内に事実上保護し、レオナルド・ダ・ヴィンチやガリレオ、ミケランジェロ、コロンブス、マキャヴェリといった偉人たちの故国でもある。かつてのローマ帝国の中枢となる地域であり、またルネサンスやリソルジメントなどの幾つかの世界史的事象の主要な舞台となった。
また、高い人間開発指数を持つイタリアは文化・経済ともに先進国であり[1]、名目GDPでは世界第8位かつ購買力平価では世界第12位、ユーロ圏ではドイツとフランスに次ぐ第3位の経済規模を持つ経済大国である[2]。
国際連合、北大西洋条約機構、G7、G20、OECD、欧州評議会、地中海連合、パリクラブの一員であり、ヨーロッパにおける四大国「ビッグ4」や、文化的・経済的・政治的に大きな影響を及ぼす列強の一角に数えられる[3][4]。また、コンセンサス連合の参加国であると同時に主導国である。軍事面では、世界第8位の軍事力を有している[5]。
総面積は30万1,338km2で、ロ・スティヴァレ(lo Stivale)と称される地中海に突き出たブーツ状のイタリア半島を中心に、地中海に浮かぶシチリア島とサルディーニャ島を主要な領土としており、いくつかの小島も領有している。北部にはアルプス山脈が、半島に沿ってアペニン山脈が走っており、平野はその間にあるポー平原などに限られ、国土の40%が山岳地帯である[6]。気候は各地ともに温暖で、北部を除き国土の大部分は温帯の地中海性気候に属し、これは農業と歴史に大きな影響を与えてきた[7]。西に港へ適したリグリア海、東には大陸棚が海の幸を豊富にもたらすアドリア海、南東部にはバルカン半島へと繋がるイオニア海があり、地理的に恵まれている。南にはティレニア海があり周辺にはストロンボリ火山やヴェスヴィオ山、エトナ山などの火山が集まっていて、世界有数の地震地帯である[6]。
Italy (Italian: Italia [iˈtaːlja] (![]() listen)), officially the Italian Republic (Italian: Repubblica Italiana [reˈpubblika itaˈljaːna]),[13][14] is a country consisting of a peninsula delimited by the Alps and several islands surrounding it,[15] whose territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region.[16] Italy is located in the centre of the Mediterranean Sea, in Southern Europe,[17][18][19] and is also considered part of Western Europe.[20][21] A unitary parliamentary republic with Rome as its capital and largest city, the country covers a total area of 301,340 km2 (116,350 sq mi) and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia, and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. Italy has a territorial exclave in Switzerland (Campione) and a maritime exclave in Tunisian waters (Lampedusa). With around 60 million inhabitants, Italy is the third-most populous member state of the European Union.
listen)), officially the Italian Republic (Italian: Repubblica Italiana [reˈpubblika itaˈljaːna]),[13][14] is a country consisting of a peninsula delimited by the Alps and several islands surrounding it,[15] whose territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region.[16] Italy is located in the centre of the Mediterranean Sea, in Southern Europe,[17][18][19] and is also considered part of Western Europe.[20][21] A unitary parliamentary republic with Rome as its capital and largest city, the country covers a total area of 301,340 km2 (116,350 sq mi) and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia, and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. Italy has a territorial exclave in Switzerland (Campione) and a maritime exclave in Tunisian waters (Lampedusa). With around 60 million inhabitants, Italy is the third-most populous member state of the European Union.
Due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, Italy has historically been home to myriad peoples and cultures. In addition to the various ancient peoples dispersed throughout what is now modern-day Italy, the most predominant being the Indo-European Italic peoples who gave the peninsula its name, beginning from the classical era, Phoenicians and Carthaginians founded colonies mostly in insular Italy,[22] Greeks established settlements in the so-called Magna Graecia of Southern Italy, while Etruscans and Celts inhabited central and northern Italy respectively. An Italic tribe known as the Latins formed the Roman Kingdom in the 8th century BC, which eventually became a republic with a government of the Senate and the People. The Roman Republic initially conquered and assimilated its neighbours on the Italian peninsula, eventually expanding and conquering parts of Europe, North Africa and Asia. By the first century BC, the Roman Empire emerged as the dominant power in the Mediterranean Basin and became a leading cultural, political and religious centre, inaugurating the Pax Romana, a period of more than 200 years during which Italy's law, technology, economy, art, and literature developed.[23][24]
During the Early Middle Ages, Italy endured the fall of the Western Roman Empire and barbarian invasions, but by the 11th century numerous rival city-states and maritime republics, mainly in the northern and central regions of Italy, became prosperous through trade, commerce, and banking, laying the groundwork for modern capitalism.[25] These mostly independent statelets served as Europe's main trading hubs with Asia and the Near East, often enjoying a greater degree of democracy than the larger feudal monarchies that were consolidating throughout Europe; however, part of central Italy was under the control of the theocratic Papal States, while Southern Italy remained largely feudal until the 19th century, partially as a result of a succession of Byzantine, Arab, Norman, Angevin, Aragonese, and other foreign conquests of the region.[26] The Renaissance began in Italy and spread to the rest of Europe, bringing a renewed interest in humanism, science, exploration, and art. Italian culture flourished, producing famous scholars, artists, and polymaths. During the Middle Ages, Italian explorers discovered new routes to the Far East and the New World, helping to usher in the European Age of Discovery. Nevertheless, Italy's commercial and political power significantly waned with the opening of trade routes that bypassed the Mediterranean.[27] Centuries of foreign meddling and conquest, and the rivalry and infighting between the Italian city-states, such as the Italian Wars of the 15th and 16th centuries, left Italy politically fragmented, and it was further conquered and divided among multiple foreign European powers over the centuries.
By the mid-19th century, rising Italian nationalism and calls for independence from foreign control led to a period of revolutionary political upheaval. After centuries of foreign domination and political division, Italy was almost entirely unified in 1861 following a war of independence, establishing the Kingdom of Italy.[28] From the late 19th century to the early 20th century, Italy rapidly industrialised, mainly in the north, and acquired a colonial empire,[29] while the south remained largely impoverished and excluded from industrialisation, fuelling a large and influential diaspora.[30] Despite being one of the victorious allied powers in World War I, Italy entered a period of economic crisis and social turmoil, leading to the rise of the Italian fascist dictatorship in 1922. Participation in World War II on the Axis side ended in military defeat, economic destruction, and the Italian Civil War. Following the rise of the Italian Resistance and the liberation of Italy, the country abolished its monarchy, established a democratic Republic, enjoyed a prolonged economic boom, and became a highly developed country.[31]
L'Italie (/itali/11 Écouter ; en italien : Italia /iˈtaːlja/12 Écouter), en forme longue la République italienne (en italien : Repubblica Italiana /reˈpubblika itaˈljaːna/12 Écouter), est un pays d'Europe du Sud correspondant physiquement à une partie continentale, une péninsule située au centre de la mer Méditerranée et une partie insulaire constituée par les deux plus grandes îles de cette mer, la Sicile et la Sardaigne, et beaucoup d'autres îles plus petites (hormis la Corse, française depuis 1768). Elle est rattachée au reste du continent par le massif des Alpes. Le territoire italien correspond approximativement à la région géographique homonyme.
L'Italie apporte une contribution très importante à la civilisation occidentale : elle est notamment le berceau de la civilisation étrusque, de la Grande-Grèce, de l'Empire romain, du Saint-Siège, des républiques maritimes, de l'humanisme et de la Renaissance. Existant en tant qu'État unitaire depuis 1861 à la suite du Risorgimento (Renaissance ou Résurrection) mené par le royaume de Sardaigne, l'Italie est une république depuis l'abolition par référendum de la monarchie italienne en 1946. Elle est membre fondateur de l'Union européenne et de la zone euro.
L'Italie est, en ce début de XXIe siècle, une puissance moyenne13, forte de ses soixante millions d'habitants, de sa position en 2017 de huitième puissance économique mondiale et de troisième économie de la Zone Euro, et de son rôle au sein de nombreuses organisations internationales comme l'Union européenne, l'Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, le G7 et l'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques.
L'Italia (/iˈtalja/,[8] ), ufficialmente Repubblica Italiana,[9] è uno Stato situato nell'Europa centro-meridionale, il cui territorio coincide in gran parte con l'omonima regione geografica. L'Italia è una repubblica parlamentare unitaria e conta una popolazione di circa 59,3 milioni di abitanti, che ne fanno il terzo Stato dell'Unione europea per numero di abitanti. La capitale è Roma.
La parte continentale, delimitata dall'arco alpino, confina a nord, da ovest a est, con Francia, Svizzera, Austria e Slovenia; il resto del territorio, circondato dai mari Ligure, Tirreno, Ionio e Adriatico, si protende nel mar Mediterraneo, occupando la penisola italiana e numerose isole (le maggiori sono Sicilia e Sardegna), per un totale di 302068,26 km².[10] Gli Stati della Città del Vaticano e di San Marino sono enclavi della Repubblica, mentre Campione d'Italia è un'exclave italiana.
Crocevia di numerose culture preistoriche, l'Italia antica fu unificata dalla civiltà romana diventando il centro amministrativo, economico, culturale e politico dell'Impero romano. Dopo la caduta dell'Impero romano d'Occidente, l'Italia medievale fu soggetta a invasioni e dominazioni di popolazioni barbariche, perdendo la propria unità politica. Tra XV secolo e XVI secolo, con la diffusione dell'umanesimo e del Rinascimento, divenne nuovamente il centro culturale del mondo occidentale e anche il campo di battaglia delle maggiori potenze europee durante le guerre d'Italia. La penisola conobbe poi la controriforma, il barocco, e il neoclassicismo.
Dopo la parentesi napoleonica, gli italiani lottarono per l'unificazione e l'indipendenza nazionale durante il Risorgimento, finché, dopo la seconda guerra d'indipendenza e la spedizione dei Mille, nel 1861 nacque il Regno d'Italia, che ottenne la vittoria nella prima guerra mondiale (1918), completando il processo di unificazione nazionale. Nel 1946, dopo il ventennio fascista (1922-1943), la sconfitta nella seconda guerra mondiale, e la definitiva guerra di liberazione, a seguito di un referendum istituzionale, lo Stato italiano divenne una repubblica.
Nel 2020 l'Italia, ottava potenza economica mondiale e terza nell'Unione europea, è un paese con un alto livello di vita: l'indice di sviluppo umano è molto alto, 0.883, e la speranza di vita è di 83,4 anni.[11] È membro fondatore dell'Unione europea, della NATO, del Consiglio d'Europa e dell'OCSE; aderisce all'ONU e alla Convenzione di Schengen. L'Italia è inoltre membro del G7 e del G20, partecipa al progetto di condivisione nucleare della NATO, si colloca in nona posizione nel mondo per spesa militare, ed è sia una potenza regionale che una grande potenza globale.[12][13] È il quarto paese più visitato del mondo e vanta il maggior numero di siti dichiarati patrimonio dell'umanità dall'UNESCO (58).[14]
Italia (en italiano, Italia, pronunciado /i'talja/ (![]() escuchar)), oficialmente la República Italiana (en italiano, Repubblica Italiana pronunciado /re'pub:lika ita'ljana/), es un país soberano transcontinental, miembro y fundador de la Unión Europea, constituido en una república parlamentaria compuesta por veinte regiones, formadas estas, a su vez, por 110 provincias.8
escuchar)), oficialmente la República Italiana (en italiano, Repubblica Italiana pronunciado /re'pub:lika ita'ljana/), es un país soberano transcontinental, miembro y fundador de la Unión Europea, constituido en una república parlamentaria compuesta por veinte regiones, formadas estas, a su vez, por 110 provincias.8
Italia se ubica en el centro del mar Mediterráneo, en Europa meridional. Ocupa la península itálica, así como la llanura Padana, la islas de Sicilia y Cerdeña y alrededor de ochocientas islas menores, entre las que se destacan las islas Tremiti en el mar Adriático, los archipiélagos Campano y Toscano en el mar Tirreno, o las islas Pelagias en África septentrional, entre otras. En el norte, está rodeada por los Alpes y tiene frontera con Francia, Suiza, Austria y Eslovenia. Los micro-Estados de San Marino y Ciudad del Vaticano son enclaves dentro del territorio italiano. A su vez, Campione d'Italia, es un municipio que forma un pequeño exclave italiano en territorio suizo.9
Debido a su localización central en el Mar Mediterráneo, Italia recibió, durante la Antigüedad,1011 diversas influencias de civilizaciones mediterráneas exteriores, como la de los fenicios y cartagineses en sus islas mayores1213 y de los antiguos griegos en la llamada Magna Grecia,1415 así como también fue el hogar de muchas culturas propias distintas, como la civilización nurágica, los etruscos y los latinos, siendo estos últimos quienes dieron vida a la civilización romana,1617 y asistió al nacimiento de la República y del posterior Imperio romano.1819 Tras la caída del Imperio romano de Occidente, bizantinos, lombardos y musulmanes se disputaron el control sobre el territorio itálico,2021 quebrando así su anterior unidad política.2223 A partir de la Plena Edad Media, Italia fue la cuna de repúblicas marítimas como Venecia, Génova, Pisa y Amalfi, de los Estados Pontificios y también del humanismo, del Renacimiento y del movimiento barroco, entre otros Estados y movimientos culturales.2425 En el curso del siglo XIX, mediante el proceso histórico conocido como Risorgimento, los varios territorios italianos lograron unificarse bajo un mismo Estado: el Reino de Italia.2627
La capital de Italia, Roma, ha sido durante siglos el centro político y cultural de la civilización occidental. Además, es la ciudad santa para la Iglesia católica, siendo el papa el obispo de Roma y encontrándose dentro de la ciudad el micro-Estado del Vaticano. El significado cultural del país se refleja en todos sus Patrimonios de la Humanidad, ya que tiene 58,28 el país con mayor número del mundo.29
Es el tercer país de Europa que más turistas recibe por año,30 siendo Roma la tercera ciudad más visitada del continente.31 Otras ciudades importantes son: Milán, centro de finanzas y de industria, y, según el Global Language Monitor, la capital de la Moda;32 Nápoles, importante puerto en el Mediterráneo, capital histórica y ciudad más poblada del Mezzogiorno;33 Turín, centro de industria automovilística y de diseño industrial. Italia es una república democrática, forma parte del G7 o grupo de las siete más grandes naciones avanzadas del mundo y es un país desarrollado con una calidad de vida muy alta,34 encontrándose en 2005 entre las siete primeras del mundo.35
Es el país número 28 (informe 2017) en materia de alto índice de desarrollo humano.36 Es una potencia regional y mundial,37383940 miembro fundador de la Unión Europea, firmante del Tratado de Roma en 1957. También es miembro fundador de la Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte (OTAN) y miembro del OTAN Quint, de la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, de la Organización Mundial del Comercio, del Consejo de Europa, del G-4, del G-12 y del G20. El país, y especialmente su capital, tiene una fuerte repercusión en temas de política y cultura, en organizaciones mundiales como la Organización para la Agricultura y la Alimentación (FAO),41 el Fondo Internacional de Desarrollo Agrícola (IFAD), el Glocal Forum42 o el Programa Mundial de Alimentos (WFP).
Ита́лия (итал. Italia [iˈtaːlja]), официальное название — Италья́нская Респу́блика (итал. Repubblica Italiana [reˈpubːlika itaˈljaːna]) — государство в Южной Европе, в центре Средиземноморья. Входит в Европейский союз и НАТО с момента их создания, является третьей по величине экономикой еврозоны.
Граничит с Францией на северо-западе (протяжённость границы — 488 км), Швейцарией (740 км) и Австрией (430 км) — на севере, Словенией — на северо-востоке (232 км).
Внутри территории Италии находятся два государства-анклава: государство Сан-Марино и расположенное внутри территории Рима ассоциированное с Италией государство Ватикан, с каждым из которых Италия имеет внутреннюю границу протяжённостью соответственно 39 км и 3,2 км.
Занимает Апеннинский полуостров, крайний северо-запад Балканского полуострова, Паданскую равнину, южные склоны Альп, острова Сицилия, Сардиния и ряд мелких островов[7].
На территории Италии находится 55 памятников всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО — Италия разделяет с Китаем первое место по их количеству.
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP1
TOP1
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP2
TOP2
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP3
TOP3
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP4
TOP4
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP6
TOP6

主要有以下这些考量因素:
高生产力水平
发达国家具备极为发达的生产力,其国民生产总值(GDP)以及人均国内生产总值(GDP per capita)的数值都处于较高水平。
先进的产业结构
在这些国家的国民经济结构中,第三产业也就是服务业所占的比重较大,一般会超过60%。
成熟的经济运行机制
其市场机制与体系较为健全,经济发展有着显著优势,管理也很完善,并且拥有相对完备的宏观经济调控体系。
技术现代化
技术进步对其经济增长的贡献率颇为显著,在科技创新以及技术应用方面处于世界领先地位。
资本国际化
资本在全球范围内流动,跨国公司得以迅速发展,通过多种方式对世界各地产生影响。
经济竞争性加剧
无论是在发达国家内部,还是它们相互之间,又或是与发展中国家之间,经济竞争都十分激烈。
经济一体化和区域集团化
诸如欧盟、北美自由贸易协定等区域经济集团已然形成,进一步强化了经济一体化的程度。
人力资本投入
这些国家高度重视教育与培训工作,着重提升人才素质,以此来更好地适应经济发展的需求。
高经济国际化程度
其外贸出口的质量较高,在世界贸易总额中占据着较大的份额,金融市场也呈现出高度国际化的特点。
社会福利体系完善
通常都具备完善的社会保障和福利体系,在医疗、教育、退休金等诸多方面都能为民众提供相应保障。
Dies sind die wichtigsten Überlegungen:
Hohe Produktivitätsniveaus
Entwickelte Länder haben ein extrem hohes Produktivitätsniveau mit einem hohen BIP und Pro-Kopf-BIP.
Fortgeschrittene Industriestruktur
In diesen Ländern macht der tertiäre Sektor, d. h. der Dienstleistungssektor, mehr als 60 % der nationalen Wirtschaftsstruktur aus.
Ausgereifter wirtschaftlicher Funktionsmechanismus
Der Marktmechanismus und das Marktsystem sind relativ solide, mit erheblichen Vorteilen in der wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung, perfektem Management und einem relativ vollständigen makroökonomischen Kontrollsystem.
Technologische Modernisierung
Der technologische Fortschritt trägt wesentlich zum Wirtschaftswachstum bei, und das Land ist weltweit führend in der wissenschaftlichen und technologischen Innovation und Anwendung.
Internationalisierung des Kapitals
Das Kapital fließt weltweit, und die multinationalen Unternehmen sind schnell gewachsen und haben die Welt in vielerlei Hinsicht beeinflusst.
Gesteigerte wirtschaftliche Wettbewerbsfähigkeit
Der wirtschaftliche Wettbewerb ist intensiv, sowohl innerhalb der Industrieländer, untereinander als auch mit den Entwicklungsländern.
Wirtschaftliche Integration und regionale Blöcke
Regionale Wirtschaftsblöcke wie die Europäische Union und das Nordamerikanische Freihandelsabkommen (NAFTA) sind entstanden und haben die wirtschaftliche Integration weiter verstärkt.
Investitionen in Humankapital
Diese Länder räumen der allgemeinen und beruflichen Bildung einen hohen Stellenwert ein, wobei der Schwerpunkt auf der Verbesserung der Qualität der Humanressourcen liegt, um den Anforderungen der wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung besser gerecht zu werden.
Hoher Grad der wirtschaftlichen Internationalisierung
Die Qualität ihrer Außenhandelsausfuhren ist hoch und macht einen großen Teil des Welthandels aus, und ihre Finanzmärkte sind ebenfalls stark internationalisiert.
Gut entwickeltes soziales Wohlfahrtssystem
Sie verfügen in der Regel über ein umfassendes Sozialversicherungs- und Wohlfahrtssystem, das den Menschen einen angemessenen Schutz in den Bereichen Gesundheitsversorgung, Bildung, Rente und anderen Bereichen bietet.

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP2
TOP2
 Japan
Japan

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7
 Silk road
Silk road

 States of Asia
States of Asia
日本国(日语:日本国/にっぽんこく、にほんこく Nippon-koku, Nihon-koku */?),通称日本,是位于东亚的岛屿国家,由日本列岛、琉球群岛和伊豆-小笠原群岛等6,852个岛屿组成[10],面积约37.8万平方公里[11]。国土全境被太平洋及鄂霍次克海、日本海、东海等缘海环抱,西邻朝鲜半岛及俄属远东,东北接千岛群岛,西南面台湾及中国大陆东部。人口达1.26亿[6],居于世界各国第11位,当中逾3,500万人居住于首都东京及周边数县构成的首都圈,为世界最大的都市圈[12]。政体施行议会制君主立宪制,君主天皇为国家与国民的象征,实际的政治权力则由国会、以及内阁总理大臣(首相)所领导的内阁掌管[13]。
传说日本于公元前660年2月11日建国[14],在公元4世纪出现首个统一政权,并于大化改新中确立了天皇的中央集权体制,文化上则深受中国隋唐两代之影响。12世纪后的六百年间,日本由幕府等数个武士阶级政权实际统治,期间包括了政治纷乱的南北朝与战国时代。17世纪起江户幕府颁布锁国令,至1854年被黑船迫以开港才结束。此后,日本在西方列强进逼的时局下,首先天皇从幕府手中收回政治实权,接着在19世纪中期的明治维新进行大规模政治与经济改革,引入欧洲的科学与技艺,日本的社会于是实现了工业化及现代化,施行天皇专权的君主立宪制,将北海道正式纳为领土;而自19世纪末起,日本开始进行对外扩张,首先并吞琉球,之后将台湾、朝鲜、库页岛等地纳为殖民地。进入20世纪时,日本已成为当时各国承认的帝国主义列强之一,也是当时东方世界唯一的大国。日本后来成为第二次世界大战的轴心国之一,但最终于1945年投降。败战后,日本在盟军主导下转型为以国会为中心的民主政体,天皇地位虚位化[13],同时依据新宪法放弃发动战争的权利,仅维持防御性的武装力量。
日本是世界第三大经济体,亦为七国集团成员,是世界先进国家之一,主要奠基于日本经济在二战后的巨幅增长。现时日本的科研能力、工业基础和制造业技术均位居世界前茅[15],并是世界第4大出口国和进口国[16]。2018年,日本的人均国内生产总值依国际汇率可兑换成为四万零八百美元,人均国民收入则在四万四千四百美元左右,人类发展指数亦在最高组群行列[17]。
Japan (japanisch 日本, ausgesprochen als Nihon oder Nippon; ) ist ein 6852 Inseln umfassender ostasiatischer Staat im Pazifik, der indirekt im Norden und Nordwesten an Russland, im Westen an Nord- und Südkorea und im Südwesten an Taiwan und China grenzt und flächenmäßig der viertgrößte Inselstaat der Welt ist. De-facto-Hauptstadt und größte urbane Siedlung ist Tokio.
Die Bildung des japanischen Staatswesens begann im 5. Jahrhundert unter kulturellem Einfluss des chinesischen Kaiserreichs. Seit dem 16. Jahrhundert stand Japan im Kontakt mit dem Westen und stieg seit dem 19. Jahrhundert zur Großmacht auf, erwarb Kolonien wie Korea und Taiwan, nahm an beiden Weltkriegen teil und beherrschte kurzzeitig große Teile Südost- und Ostasiens. Das Japanische Kaiserreich war bis 1947 eine nach dem monarchischen Prinzip ausgerichtete, zum Teil an preußischem Vorbild angelehnte, konstitutionelle Monarchie mit dem japanischen Kaiser als Staatsoberhaupt. Seine aggressive Expansionspolitik in China im Vorfeld und während des Zweiten Weltkrieges (Pazifikkrieg) führte schließlich zur Niederlage an der Seite der Achsenmächte im August 1945. Im unter Douglas MacArthurs Besatzungsregierung gestalteten japanischen Staat seit 1947 ist der Souverän das Volk, höchstes Organ der Staatsgewalt das Parlament, dessen Kammern seither beide direkt vom Volk gewählt werden. Das Kaisertum wurde nicht abgeschafft, aber der Kaiser als „Symbol des Staates“ auf zeremonielle Aufgaben ohne eigenständige Autorität in Staatsangelegenheiten reduziert. Außer Japan gibt es keinen Staat mehr mit einem Kaiser.
Japan wird zu den dichter besiedelten Ländern Asiens gezählt und liegt mit ca. 126 Millionen Einwohnern auf Platz elf der bevölkerungsreichsten Länder der Erde. Die japanische Bevölkerung konzentriert sich überwiegend auf die vier Hauptinseln und besteht zu 99 % aus Japanern. Zu den Minderheiten gehören Koreaner, Chinesen, Filipinos und Taiwaner. Seit den 2000er Jahren leben in Japan auch mehrere Tausend Gastarbeiter und Asylbewerber aus Afrika und anderen asiatischen Ländern. Die meisten Einwohner sind Anhänger des Shintoismus und Buddhismus.
Als historisch erste Industrienation Asiens hat Japan heute eine sehr hoch entwickelte Volkswirtschaft und war viele Jahre lang die weltweit zweitgrößte Wirtschaftskraft hinter den Vereinigten Staaten, mit denen es militärisch seit 1952 verbündet ist. Japan ist Mitglied der Gruppe der Sieben größten Industrienationen der Welt und der OECD. Japan nimmt in der Rangfolge gemäß dem Index der menschlichen Entwicklung der Vereinten Nationen den 19. Platz der 188 vom Index berücksichtigten Mitgliedstaaten der Vereinten Nationen ein.
日本では、大和政権が統一以降に自国を「ヤマト」と称していたようであるが、古くから中国や朝鮮は日本を「倭」と呼んできた。石上神宮の七支刀の銘や、中国の歴史書(『前漢書』『三国志』『後漢書』『宋書』『隋書』など)や、高句麗の広開土王の碑文も、すべて倭、倭国、倭人、倭王、倭賊などと記している。そこで大和の代表者も、外交時には(5世紀の「倭の五王」のように)国書に「倭国王」と記すようになった[46]。
しかし中国との国交が約120年に渡って中絶した後、7世紀初期に再開された時には、『日本書紀』では「東の天皇が敬いて西の皇帝に白す」、『隋書』には「日出ずる処の天子、書を日没する処の天子に致す。恙無しや」とする国書を日本側が渡した記述があり、従来のように倭と称する事を避けている。中国側では『旧唐書』の「東夷伝」に初めて日本の名称が登場し、「日本国は倭国の別種なり。其の国、日の辺に在るを以ての故に、日本を以て名と為す」「或いは曰く、倭国自ら其の名の雅ならざるを悪(にく)み、改めて日本と為す」「或いは曰く、日本は旧(もと)小国、倭国の地を併す」のように、倭が名称を日本に変えた理由を説明している[47]。また、『新唐書』においては「国日出ずる所に近し、以に名をなす」とあり、隋書の「日出処天子」と共通している。
この7世紀には、遣隋使に続いて遣唐使がしばしば派遣されているが、いつから「倭」に変えて「日本」を国号と変えたのかは明らかでない[48]。使者の毎回の交渉について詳しく記述している『日本書紀』も、8世紀に国号としての日本が確立した後の書物であり、原資料にあった可能性のある「倭」の字を、国号に関する限りすべて「日本」と改めている。それ以外の文献では、733年(天平5年)に書かれた『海外国記』の逸文で、664年(天智3年)に太宰府へ来た唐の使者に「日本鎮西筑紫大将軍牒」とある書を与えたというが、真偽は不明である。結局確かなのは『続日本紀』における記述であり、702年(大宝2年)に32年ぶりで唐を訪れた遣唐使は、唐側が「大倭国」の使者として扱ったのに対し、「日本国使」と主張したという。『旧唐書』の「東夷伝」の記事も、この日本側の説明に基づいているようである[49]。
Japan (Japanese: 日本; Nippon [ɲippoɴ] or Nihon [ɲihoɴ]; formally 日本国 ![]() Nippon-koku or Nihon-koku, lit. "State of Japan") is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies off the eastern coast of the Asian continent and stretches from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and the Philippine Sea in the south.
Nippon-koku or Nihon-koku, lit. "State of Japan") is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies off the eastern coast of the Asian continent and stretches from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and the Philippine Sea in the south.
The kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and it is often called the "Land of the Rising Sun". Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago consisting of about 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area and often are referred to as home islands. The country is divided into 47 prefectures in eight regions, with Hokkaido being the northernmost prefecture and Okinawa being the southernmost one. The population of 127 million is the world's tenth largest, of which 98.5% are ethnic Japanese. 90.7% of people live in cities, while 9.3% live in the countryside.[16] About 13.8 million people live in Tokyo,[17] the capital of Japan. The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world with over 38 million people.[18]
Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period. The first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly China, followed by periods of isolation, particularly from Western Europe, has characterized Japan's history.
From the 12th century until 1868, Japan was ruled by successive feudal military shōguns who ruled in the name of the Emperor. Japan entered into a long period of isolation in the early 17th century, which was ended in 1853 when a United States fleet pressured Japan to open to the West. After nearly two decades of internal conflict and insurrection, the Imperial Court regained its political power in 1868 through the help of several clans from Chōshū and Satsuma – and the Empire of Japan was established. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, victories in the First Sino-Japanese War, the Russo-Japanese War and World War I allowed Japan to expand its empire during a period of increasing militarism. The Second Sino-Japanese War of 1937 expanded into part of World War II in 1941, which came to an end in 1945 following the Japanese surrender. Since adopting its revised constitution on May 3, 1947, during the occupation led by SCAP, the sovereign state of Japan has maintained a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy with an Emperor and an elected legislature called the National Diet.
Japan is a member of the ASEAN Plus mechanism, UN, the OECD, the G7, the G8, and the G20, and is considered a great power.[19][20][21] Its economy is the world's third-largest by nominal GDP and the fourth-largest by purchasing power parity. It is also the world's fourth-largest exporter and fourth-largest importer.
Japan benefits from a highly skilled and educated workforce; it has among the world's largest proportion of citizens holding a tertiary education degree.[22] Although it has officially renounced its right to declare war, Japan maintains a modern military with the world's eighth-largest military budget,[23] used for self-defense and peacekeeping roles; it ranked as the world's fourth most-powerful military in 2015.[24] Japan is a highly developed country with a very high standard of living and Human Development Index. Its population enjoys the highest life expectancy and third lowest infant mortality rate in the world, but is experiencing issues due to an aging population and low birthrate. Japan is renowned for its historical and extensive cinema, influential music industry, anime, video gaming, rich cuisine and its major contributions to science and modern technology.[25][26]
Le Japon, en forme longue l’État du Japon, en japonais Nihon ou Nippon (日本) et Nihon-koku ou Nippon-koku (日本国) respectivement, est un pays insulaire de l’Asie de l’Est, situé entre l’océan Pacifique et la mer du Japon, à l’est de la Chine, de la Corée et de la Russie, et au nord de Taïwan. Étymologiquement, les kanjis (caractères chinois) qui composent le nom du Japon signifient « pays (国, kuni) d’origine (本, hon) du Soleil (日, ni) » ; c’est ainsi que le Japon est désigné comme le « pays du soleil levant ».
Le Japon forme, depuis 1945, un archipel de 6 852 îles de plus de 100 m2, dont les quatre plus grandes sont Hokkaidō, Honshū, Shikoku, et Kyūshū représentant à elles seules 95 % de la superficie terrestre du pays. L’archipel s’étend sur plus de trois mille kilomètres. La plupart des îles sont montagneuses, parfois volcaniques ; par exemple, le plus haut sommet du Japon, le mont Fuji (3 776 m), est un volcan (inactif depuis 1707). Le Japon est le douzième pays le plus peuplé du monde, avec environ 127 millions d’habitants pour 377 488 km2 (337 hab./km2), dont l'essentiel est concentré sur les étroites plaines littorales du sud d'Honshū et du nord de Shikoku et Kyūshū, formant un ensemble pratiquement urbanisé en continu appelé « Mégalopole japonaise » ou « Taiheiyō Belt » (太平洋ベルト, Taiheiyō beruto, littéralement « ceinture Pacifique »). Le Grand Tokyo, qui comprend la capitale Tokyo et plusieurs préfectures environnantes, est la plus grande région métropolitaine du monde, avec plus de 35 millions d’habitants. La ville a été première place financière mondiale en 1990.
Les recherches archéologiques démontrent que le Japon était peuplé dès la période du Paléolithique supérieur. Les premières mentions écrites du Japon sont de brèves apparitions dans des textes de l’histoire chinoise du Ier siècle. L’histoire du Japon est caractérisée par des périodes de grande influence dans le monde extérieur suivies par de longues périodes d’isolement. Depuis l’adoption de sa constitution en 1947, le Japon a maintenu une monarchie constitutionnelle avec un empereur et un parlement élu, la Diète.
Le Japon est la troisième puissance économique du monde pour le PIB nominal et la quatrième pour le PIB à parité de pouvoir d’achat. Il est aussi le quatrième pays exportateur et le sixième pays importateur au monde. Acteur majeur du commerce international et puissance épargnante, il a ainsi accumulé une position créancière nette vis-a-vis du reste du monde (en) de plus de 325 000 milliards de yens4, le plaçant en première position devant la Chine5. C’est un pays développé, avec un niveau de vie très élevé (dix-septième IDH le plus élevé) et la plus longue espérance de vie au monde selon les estimations de l’ONU6. Mais ce tableau idyllique ne doit pas masquer d’importants problèmes qui pèsent sur l’avenir du pays : le Japon souffre d’un des taux de natalité les plus bas du monde, très en dessous du seuil de renouvellement des générations7. Le pays est actuellement en déclin démographique8. C’est également le pays pour lequel le poids de la dette publique brute est le plus important au monde9, cette dernière s’élève en 2014 à 233 % du PIB10.
Il Giappone (AFI: [ʤapˈpoːne][6][7]; in giapponese 日本 Nihon? o Nippon?, ufficialmente 日本国 Nihon-koku? o Nippon-koku?) è uno Stato insulare dell'Asia orientale.
Situato nell'oceano Pacifico, il Giappone si trova a est del mar del Giappone, Cina, Corea del Nord, Corea del Sud e Russia. Si sviluppa nell'area compresa tra il mare di Ochotsk nel nord, fino al mar Cinese Orientale e Taiwan nel sud. Il Giappone è un arcipelago composto da 6.852 isole, le cui quattro isole più grandi sono: Honshū, Hokkaidō, Kyūshū e Shikoku (tutte e quattro collegate tramite ponti o tunnel sottomarini), che da sole rappresentano circa il 97% della superficie terrestre del Giappone. Molte isole sono montagne, alcune di origine vulcanica e la vetta più alta del Giappone è il Monte Fuji, un vulcano attivo.[8]
Con una popolazione di circa 127 milioni di abitanti è il decimo Stato più popoloso del mondo. La Grande Area di Tokyo, che include Tokyo e numerose prefetture vicine, è di fatto la più grande area metropolitana del mondo con oltre 30 milioni di residenti. Ricerche archeologiche indicano che l'arcipelago è abitato dal Paleolitico superiore. La prima menzione scritta sul Giappone si ha con una breve apparizione in un libro di storia cinese del primo secolo a.C. Alle influenze provenienti dal mondo esterno seguì un lungo periodo di isolamento che caratterizzò profondamente la storia del Giappone. Fin dall'adozione dell'odierna Costituzione il Giappone mantiene una monarchia parlamentare con un imperatore e un parlamento eletto noto come Dieta, rendendolo di fatto l'ultimo impero rimasto nel mondo.
Grande potenza regionale asiatica,[9][10] il Giappone ha la terza maggiore economia per prodotto interno lordo e la quarta maggiore per potere d'acquisto, è anche il quarto maggiore esportatore e il sesto maggiore importatore a livello mondiale. Il Giappone è inoltre uno Stato membro del G8 e del G7 ed è un membro non permanente del consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni Unite. Lo Stato ha un moderno apparato militare utilizzato per l'autodifesa, per missioni di pace e per aiutare gli alleati all'estero nel rispetto della Costituzione. Il Giappone è uno Stato sviluppato con una qualità di vita molto elevata (ventesimo a livello mondiale). I cittadini giapponesi hanno inoltre la maggiore aspettativa di vita al mondo e il tasso di mortalità infantile è il secondo più basso dietro al Principato di Monaco.[11][12]
Japón (en japonés: 日本, Nihon o Nippon), oficialmente Estado del Japón (日本国, ![]() Nihon-koku (?·i) o Nippon-koku), es un país soberano insular del este de Asia. Situado en el océano Pacífico; tiene al oeste el mar del Japón, China, Corea del Norte, Corea del Sur y Rusia, al norte el mar de Ojotsk y al este y sur el mar de China Oriental y Taiwán. Los caracteres que componen el nombre de Japón pueden significar «el origen del sol» o «la base del sol», motivo por el que el país también es conocido como la Tierra del Sol Naciente, ya que desde la perspectiva de China, el sol sale desde Japón.
Nihon-koku (?·i) o Nippon-koku), es un país soberano insular del este de Asia. Situado en el océano Pacífico; tiene al oeste el mar del Japón, China, Corea del Norte, Corea del Sur y Rusia, al norte el mar de Ojotsk y al este y sur el mar de China Oriental y Taiwán. Los caracteres que componen el nombre de Japón pueden significar «el origen del sol» o «la base del sol», motivo por el que el país también es conocido como la Tierra del Sol Naciente, ya que desde la perspectiva de China, el sol sale desde Japón.
Japón es un archipiélago compuesto por 6852 islas. El Área del Gran Tokio en la isla de Honshū, donde está la ciudad de Tokio, capital de facto de la nación, es la mayor área metropolitana del mundo, con más de treinta millones de residentes. Y a su vez, Tokio, la capital, es la ciudad más grande del mundo en cuanto a extensión.
Los restos arqueológicos indican que el ser humano ha vivido en Japón desde el Paleolítico superior. La primera mención escrita de las islas se encuentra en textos de la antigua China del siglo I d. C. La historia de Japón ha alternado periodos de influencia extranjera con otros muy prolongados de aislamiento total. Desde el siglo XII hasta 1868 Japón estuvo gobernado por sucesivos shogunatos militares que ejercían el poder en nombre del emperador. En el siglo XVII el país entró en un largo periodo de aislamiento que no terminó hasta mediados del siglo XIX. Después de casi dos décadas de conflictos internos e insurrecciones se restauró al emperador Meiji como jefe del Estado en 1868 y se proclamó el Imperio del Japón.
A finales del siglo XIX y principios del XX, los éxitos en la Primera guerra sino-japonesa, en la guerra ruso-japonesa y en la Primera Guerra Mundial permitieron a Japón expandir su imperio y fortalecer sus fuerzas armadas. La Segunda guerra sino-japonesa que se inició en 1937, acabó formando parte de la Segunda Guerra Mundial desde 1941, conflictos que terminaron tras la rendición de Japón debido a los bombardeos atómicos sobre Hiroshima y Nagasaki en 1945. Desde la adopción de la constitución revisada en 1947, Japón ha mantenido una monarquía constitucional unitaria con un emperador y un órgano de gobierno democrático llamado Dieta.
Japón es desde hace varias décadas, una de las grandes potencias económicas mundiales8 y en la actualidad es la tercera mayor economía de acuerdo a su PIB. Asimismo, es el cuarto mayor exportador e importador de mercancías. Aunque Japón renunció oficialmente a su derecho a declarar la guerra tras la Segunda Guerra Mundial, posee unas modernas fuerzas armadas y el quinto mayor presupuesto militar mundial9 para su autodefensa y el mantenimiento de la paz.
Es miembro de la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, el G7, el G4 y la APEC. Japón es el segundo país con la menor tasa de homicidios, solo por detrás de Singapur,10 las mujeres japonesas tienen la segunda mayor esperanza de vida11 y, según la ONU, el país presenta la tercera menor mortalidad infantil del mundo.1213
Япо́ния (яп. 日本 Нихон, Ниппон, букв. «место, где восходит Солнце»[8]), официальное название «Нихон коку», «Ниппон коку» (яп. 日本国) — островное государство в Восточной Азии. Находится в Тихом океане к востоку от Японского моря, Китая, Северной и Южной Кореи, России. Занимает территорию от Охотского моря на севере до Восточно-Китайского моря и Тайваня на юге. Поэтическое название — Страна восходящего солнца.
Расположена на Японском архипелаге, состоящем из 6852 островов[прим 2][9]. Четыре крупнейших острова — Хонсю, Хоккайдо, Кюсю и Сикоку — составляют 97 % общей площади архипелага. Большинство островов горные, многие вулканические. Высшая точка Японии — вулкан Фудзияма (3776 м). С населением более 126 миллионов человек, Япония занимает десятое место в мире. Большой Токио, включающий в себя столицу Японии Токио и несколько близлежащих префектур, с населением более 30 миллионов человек является крупнейшей городской агломерацией в мире.
По форме государственного устройства Япония — децентрализованное унитарное государство, по форме государственного режима — демократическое государство.[10]
Являясь великой экономической державой[11], Япония занимает третье место в мире по номинальному ВВП и четвёртое по ВВП, рассчитанному по паритету покупательной способности. Япония является четвёртым по величине экспортёром и шестым по величине импортёром.
Япония — развитая страна с очень высоким уровнем жизни (семнадцатое место по индексу развития человеческого потенциала). В Японии одна из самых высоких ожидаемых продолжительностей жизни (в 2009 году она составила 82,12 года[12]) и один из самых низких уровней младенческой смертности[13].
Япония входит в число стран — членов «Большой семёрки» и АТЭС, а также регулярно избирается непостоянным членом Совета Безопасности ООН. Япония официально отказалась от своего права объявлять войну, но она имеет силы самообороны, которые используются также и в миротворческих операциях.
Япония является единственной страной в мире, против которой было применено ядерное оружие.
Император Японии — Акихито (с 1989 года), премьер-министр Японии — Синдзо Абэ (с 2012 года), председатель Либерально-демократической партии Японии.
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP3
TOP3
 Canada
Canada
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1995 Gothenburg
1995 Gothenburg

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7


加拿大(英语、法语:Canada,IPA读音:/ˈkænədə/(英)/kanada/(法))为北美洲国家,西抵太平洋,东至大西洋,北滨北冰洋,东北方与丹麦领地格陵兰相望,东部与圣皮埃尔和密克隆相望,南方及西北方与美国接壤。加拿大的领土面积达998万4670平方千米,为全球面积第二大国家。加拿大素有“枫叶之国”的美誉,渥太华为该国首都。加拿大被《福布斯》列于2020年退休宜居国的名单中[8]。
加拿大在1400年前即有原住民在此生活。15世纪末,英国和法国殖民者开始探索北美洲的东岸,并在此建立殖民地。1763年,当七年战争结束后,法国被迫将其几乎所有的北美殖民地割让予英国。在随后的几十年中,英国殖民者向西探索至太平洋地区,并建立了数个新的殖民地。1867年7月1日,1867年宪法法案通过,加拿大省分裂为安大略和魁北克两省,与新不伦瑞克、新斯科舍三个英属北美殖民地组成加拿大联邦。在随后100多年里,其它几块英属北美殖民地陆续加入联邦,组成现代加拿大。1931年12月11日,英国通过威斯敏斯特法令,令加拿大成为独立国家,但国家元首依旧是当时的英国国王乔治五世,且英国国会依旧掌握有加拿大的修宪权。1933年和1949年,加拿大民事案件和刑事案件的终审权分别从英国枢密院司法委员会移交至加拿大最高法院。1982年4月17日,英国女王兼加拿大女王伊丽莎白二世签署命令,将加拿大宪法修宪权移交加拿大国会,至此加拿大与英国的特殊关系终结。
加拿大是实行联邦制、君主立宪制及议会制的国家,由十个省和三个地区组成,女王伊丽莎白二世为国家元首及加拿大君主,而加拿大总督为其及政府的代表。加拿大是双语国家,英语和法语为官方语言,原住民的语言被认定为第一语言。由于地处高纬度及地广人稀,该国一直奉行积极吸纳外来移民的政策,以至人口亦以移民为主,有近五分之一的国民于国外出生,是世界上拥有种族及文化最为多元的国家之一。近年来移民大部分来自亚洲。[9]
得益于丰富的天然资源和高度发达的科技,加拿大是富裕、经济发达的国家。以国际汇率计算,加拿大的人均国内生产总值在全世界排名第十六,人类发展指数排名第十。它在教育、政府的透明度、自由度、生活品质及经济自由的国际排名都名列前茅。积极参与国际事务,是联合国、北大西洋公约组织、北美空防司令部、七大工业国组织、二十国集团、亚太经济合作组织、经济合作与发展组织、英联邦和法语圈的成员国及太平洋岛国论坛的对话伙伴。
Kanada (englisch und französisch Canada) ist ein Staat in Nordamerika, der zwischen dem Atlantik im Osten und dem Pazifik im Westen liegt und nordwärts bis zum Arktischen Ozean reicht. Bundeshauptstadt ist Ottawa, die bevölkerungsreichste Stadt ist Toronto. Die einzige Landgrenze ist jene zu den USA im Süden und im Nordwesten. Kanada ist nach Russland der zweitgrößte Staat der Erde, hat aber mit knapp 38 Millionen Einwohnern nur eine Bevölkerungsdichte von 3,6 Personen pro km².
Die Besiedlung durch die First Nations begann spätestens vor 12.000 Jahren, die Inuit folgten vor rund 5000 Jahren. Ab dem späten 15. Jahrhundert landeten Europäer an der Ostküste und begannen um 1600 mit der Kolonisierung. Dabei setzten sich zunächst Franzosen und Engländer fest. In dieser Zeit breitete sich die Bezeichnung „Canada“ aus, das ursprünglich ein Name für ein Irokesendorf war. Frankreich trat 1763 seine Kolonie Neufrankreich an Großbritannien ab. Im Jahre 1867 gründeten drei britische Kolonien die Kanadische Konföderation. Mit dem Statut von Westminster erhielt das Land 1931 gesetzgeberische Unabhängigkeit, weitere verfassungsrechtliche Bindungen zum Vereinigten Königreich wurden 1982 aufgehoben. Nominelles Staatsoberhaupt ist Königin Elisabeth II., die durch den Generalgouverneur von Kanada vertreten wird.
Kanada ist ein auf dem Westminster-System basierender parlamentarisch-demokratischer Bundesstaat und eine parlamentarische Monarchie. Amtssprachen sind Englisch und Französisch. Die Unabhängigkeitsbestrebungen Québecs, die Stellung der frankophonen Kanadier und die Rechte der indigenen Völker (neben den First Nations und Inuit die Métis) sind wichtige Konfliktlinien in Staat und Gesellschaft. Die Themen Klimawandel und Umweltschutz, Einwanderungspolitik und Rohstoffabhängigkeit sowie das Verhältnis zum südlichen Nachbarn USA, von dem kulturell und historisch bedingt ein ambivalentes Bild besteht, kennzeichnen die öffentlichen Debatten.
カナダ(英・仏: Canada、英語発音: /ˈkænədə/ ![]() 聞く キャナダ[2]、フランス語発音: /kanada/ カナダ[3])は、北アメリカ大陸北部に位置し、10の州と3の準州からなる連邦立憲君主制国家。首都はオタワ(オンタリオ州)。
聞く キャナダ[2]、フランス語発音: /kanada/ カナダ[3])は、北アメリカ大陸北部に位置し、10の州と3の準州からなる連邦立憲君主制国家。首都はオタワ(オンタリオ州)。
イギリス連邦加盟国であり、英連邦王国のひとつ。アメリカ合衆国と国境を接する。国土面積は世界最大のロシアに次いで広い。
歴史的に先住民族が居住する中、外からやってきた英仏両国の植民地連合体として始まった。1763年からイギリス帝国に包括された。1867年の連邦化をきっかけに独立が進み、1931年ウエストミンスター憲章で承認され、1982年憲法制定をもって政体が安定した[4]。一連の過程においてアメリカと政治・経済両面での関係が深まった。連邦制をとり、連邦政府の運営は首相を中心に行われている。
Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern border with the United States, stretching 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi), is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
Various indigenous peoples inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years before European colonization. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and territories and a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom. This widening autonomy was highlighted by the Statute of Westminster of 1931 and culminated in the Canada Act of 1982, which severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the British parliament.
Canada is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy in the Westminster tradition, with a monarch and a prime minister who serves as the chair of the Cabinet and head of government. The country is a realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, a member of the Francophonie and officially bilingual at the federal level. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
A developed country, Canada has the seventeenth-highest nominal per-capita income globally as well as the thirteenth-highest ranking in the Human Development Index. Its advanced economy is the tenth-largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Canada is part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
Le Canada (prononcé [kanadɔ]4 Écouter ou [kanada]5 Écouter ; en anglais [ˈkænədə]6 Écouter) est un pays situé dans la partie septentrionale de l'Amérique du Nord. Monarchie constitutionnelle à régime parlementaire constituée en fédération, composée de dix provinces et trois territoires, le pays est encadré par l'océan Atlantique à l'est-nord-est et à l'est, par l'océan Arctique au nord-nord-ouest et au nord-est, enfin par l'océan Pacifique à l'ouest. Le Canada comprend deux frontières terrestres avec les États-Unis, l'une au sud et l'autre à l'ouest-nord-ouest avec l'Alaska ainsi qu'une frontière maritime avec la France, par le biais de l'archipel de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon, et le Danemark, par le biais du Groenland. Le territoire terrestre canadien s'étend sur 10 millions de kilomètres carrés, ce qui en fait le deuxième pays du monde pour la superficie après la Russie7. En 2019, il compte plus de 37 millions d'habitants1 et est ainsi le 37e pays du monde en ce qui concerne la population. Le territoire contient plus de 31 700 lacs8, ce qui fait du Canada le pays possédant parmi les plus grandes réserves d'eau douce du globe9,10. Les langues officielles au niveau fédéral sont l'anglais et le français. La capitale fédérale est Ottawa et la monnaie le dollar canadien11.
Les premiers occupants du territoire canadien ont été les Amérindiens, dont les migrations remontent à environ 15 000 ans12 lors de la dernière glaciation qui a abaissé le niveau des océans et créé un pont terrestre reliant l'Eurasie à l'Amérique, permettant à ceux-ci de s'installer13.
Si des Vikings s'installent dès le XIe jusqu'au XIVe siècle, les premières explorations des Européens débutent à la fin du XVe siècle, culminant avec les expéditions du Français Jacques Cartier dans le golfe du Saint-Laurent. Après quelques expériences infructueuses dans la première moitié du XVIe siècle, le 5 août 1583, la colonie anglaise de Terre-Neuve est fondée, suivie des premiers comptoirs pérennes français sur le continent entre 1600 et 1608, amorçant le processus de la colonisation européenne. Par la suite, d'autres colonies britanniques et françaises sont établies, notamment dans la région de la côte Atlantique (Nouvelle-Écosse, Acadie), dans la vallée du fleuve Saint-Laurent et la péninsule du Labrador (Nouvelle-France) ainsi que dans la zone arctique, tandis que d'autres puissances européennes telles l'Espagne et la Russie explorent le reste du territoire canadien. À la suite de divers conflits dont surtout la guerre de Succession d'Espagne (1701-1714), la guerre de la Conquête (1754-1760) et la guerre d'indépendance des États-Unis (1775-1783), la Grande-Bretagne gagne et perd des territoires au XVIIIe siècle, aboutissant à ce qui correspond au territoire canadien d'aujourd'hui. Trois de ces colonies se fédèrent le 1er juillet 1867 et forment le dominion du Canada, nation indépendante sous domination partielle de la Couronne britannique. Sa souveraineté totale est ensuite garantie par la déclaration Balfour de 1926, le Statut de Westminster de 1931 et le rapatriement de sa Constitution en 1982.
L'histoire contemporaine du Canada a été marquée par une vigoureuse expansion territoriale, la ruée vers l'or et la participation à la Première Guerre mondiale. Le pays fut durement touché par la Grande Dépression en 1929 mais son économie rebondit grâce à sa participation à la Seconde Guerre mondiale, où il émergea comme puissance moyenne et fut l'un des vainqueurs en tant que membre des Alliés14.
En 2015, le Canada possède le dixième revenu par habitant le plus élevé15, et est classé neuvième par le PNUD en termes d'indice de développement humain16. Il s'agit de la dixième puissance économique mondiale par son PIB en 2017, les principaux secteurs de son économie étant les services, les télécommunications, l'agriculture, l'énergie, l'aéronautique et la construction automobile. Il entretient de forts liens avec les États-Unis (pays anglo-saxon le plus proche et partageant une partie de son histoire), qui sont son principal client et fournisseur avec lequel perdure une des relations les plus intimes et les plus approfondies au monde entre deux nations. Le pays est un des meneurs en matière de recherche scientifique17, et se range parmi les plus éduqués du monde en étant classé premier par le nombre d'adultes possédant une éducation post-secondaire, avec 51 % d'entre eux ayant au moins atteint un diplôme post-secondaire chez sa population âgée de 25 à 64 ans18. Le Canada est membre du G7, du G20, de l'Accord de libre-échange nord-américain (ALENA), de l'Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord (OTAN), de la Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (APEC), de l'Organisation des États américains (OEA), de l'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE), de l'Organisation des Nations unies (ONU), du Commonwealth et de l'Organisation internationale de la francophonie.
Il Canada (AFI: /ˈkanada/)[5] o Canadà (AFI: /kanaˈda/)[6] è uno Stato indipendente dell'America Settentrionale[7] bagnato dall'Atlantico a est, dal Mar Glaciale Artico a nord e dall'Oceano Pacifico a ovest. Con una superficie di 9897170 km² è il secondo paese del mondo per superficie totale dopo la Russia. Confina solo con il territorio degli Stati Uniti d'America: quelli continentali a sud, in buona parte lungo la linea del 49º parallelo Nord, e con lo Stato dell'Alaska a nord-ovest quasi interamente lungo il 141º meridiano Ovest:[7] si tratta del confine terrestre tra due Stati più lungo del mondo (8893 km).
Abitato, prima dell'arrivo europeo sul continente, da popolazioni aborigene, il territorio dell'attuale Canada fu colonizzato da Francia e Regno Unito a inizio XVII secolo[7] a partire dalla costa atlantica. I francesi persero in seguito i loro territori progressivamente a favore del Regno Unito: dapprima (1713) con il trattato di Utrecht alla fine della guerra di successione spagnola, con cui Terranova e la baia di Hudson furono cedute da Luigi XIV; a seguire nel 1763 dopo la sconfitta nella guerra franco-indiana, teatro nordamericano della guerra dei sette anni e, infine, con la vendita di Napoleone (1803) della Louisiana francese agli Stati Uniti d'America e delle sue ultime rimanenze oltre il confine canadese al Regno Unito. Il 1º luglio 1867 nacque la federazione canadese con l'unione delle tre colonie del Nord America Britannico di Nuova Scozia, Nuovo Brunswick e Canada,[8] che in seguito divennero quattro per la scissione della provincia del Canada in Ontario e Québec. Nel corso del tempo si aggiunsero sempre più province che avrebbero poi formato l'odierno stato nordamericano. Costituitosi in Stato unitario il 1º luglio 1867 come Confederazione canadese per iniziativa della Corona britannica, divenne formalmente indipendente l'11 dicembre 1931, data di promulgazione dello statuto di Westminster con cui il Regno Unito affrancò molti dei suoi ex dominion. Infine, con la nuova legge sul Canada del 1982 (il cosiddetto patriation o "rimpatrio") il Regno Unito abdicò anche al potere formale di modifica della costituzione canadese garantitogli dallo Statuto del 1931.
Il Canada è uno Stato membro del Commonwealth britannico del quale è uno dei sedici reami: di conseguenza, benché indipendente,[7] ha come capo di Stato il sovrano del Regno Unito, al 2020 la regina Elisabetta II che, nelle questioni di Stato riguardanti il Canada, agisce con il titolo di Elisabetta II Regina del Canada. In rappresentanza del sovrano agisce localmente il governatore generale del Canada, il quale è capo di Stato de facto, avendo le prerogative di accreditare il corpo diplomatico, assegnare l'incarico di primo ministro e nominare i giudici della Corte suprema, convocare le elezioni generali federali e in talune occasioni rappresentare il Paese a livello internazionale. Dal 1959 esiste la prassi non ufficiale di nominare alternativamente un governatore generale anglofono e uno francofono per rispetto dei due maggiori gruppi linguistici del Paese.
Il sistema politico è parlamentare e il primo ministro è in genere il leader del partito che vince le elezioni generali federali, che si tengono normalmente ogni 4 anni salvo consultazioni anticipate (le più recenti risalgono del 21 ottobre 2019). Al 2019 il governatore generale in carica è l'ex astronauta francofona Julie Payette (1963-) mentre il primo ministro è il leader liberale Justin Trudeau (1971-), in ufficio dal 4 novembre 2015.
In Canada si parlano diverse lingue sia native che europee, ma quelle ufficiali sono il francese e l'inglese,[7] che hanno status paritetico in tutti gli atti pubblici della federazione: su circa 35-37 milioni d'abitanti (stima 2019), quasi il 57% di essi è di madrelingua inglese e poco più del 21% francese; tuttavia molti canadesi sono bilingui e al 2011 l'85% della popolazione dichiarava padronanza dell'inglese e il 30,1% del francese.[9] Dal 2006 la provincia del Québec, ufficialmente francofona, è riconosciuta come «nazione in seno a un Canada unito». Tra le lingue non ufficiali con più di 300 000 parlanti, figurano lo spagnolo, il tagalog, l'arabo, il tedesco e l'italiano, dovute a fenomeni migratori nel Paese.
Il PIL nominale del Canada è il 12º al mondo: esso si basa prevalentemente sulle ingenti risorse naturali e sulle sue ben sviluppate reti commerciali, specialmente con gli Stati Uniti, con cui il Canada intrattiene complesse relazioni di lunga data. Il Canada è uno dei Paesi più avanzati del mondo con l'ottavo PIL pro-capite e il sesto maggior indice di sviluppo umano.
Il Canada fa parte dell'ONU fin dalla sua prima assemblea generale del 1945 e, come media potenza, è membro di numerosi organismi internazionali militari, politici e commerciali quali il G7, il G20, la NATO, il NAFTA, l'OECD, il WTO, l'OAC, l'APEC.
Il demotico di una persona originaria del Canada è canadese (plurale canadesi), invariato al femminile. In inglese è Canadian (plurale Canadians) e in francese è canadien se maschile o canadienne se femminile (al plurale rispettivamente canadiens e canadiennes).
Canadá (en inglés: Canada, pron. AFI: ˈkænədə; en francés: Canada, pron. AFI: kanaˈda) es un país soberano de América del Norte, cuya forma de gobierno es la monarquía parlamentaria federal. Su territorio está organizado en diez provincias y tres territorios. Su capital es la ciudad de Ottawa y la ciudad más poblada es Toronto.
Ubicado en el extremo norte del subcontinente norteamericano, se extiende desde el océano Atlántico al este, el océano Pacífico al oeste, y hacia el norte hasta el océano Ártico. Comparte frontera con los Estados Unidos al sur, y al noroeste con su estado federado Alaska. Es el segundo país más extenso del mundo después de Rusia, y también el más septentrional. Ocupa cerca de la mitad del territorio de Norteamérica. A causa de su clima, es uno de los 15 países con menor densidad poblacional del mundo, con aproximadamente 4 habitantes por kilómetro cuadrado.6
El territorio ocupado por Canadá fue habitado por los diversos grupos de población aborigen durante milenios. Desde finales del siglo XV, numerosas expediciones británicas y francesas exploraron a lo largo de la costa atlántica, donde más tarde se establecieron. Francia cedió casi todas sus colonias norteamericanas en 1763 después de la Guerra Franco-india.
En 1867, con la unión de tres colonias británicas norteamericanas mediante la Confederación, Canadá se formó como un dominio federal de cuatro provincias.78 Esto hizo que comenzara una acumulación de provincias y territorios, y un proceso de autonomía frente al Reino Unido. Esta autonomía cada vez mayor se puso de relieve en el Estatuto de Westminster de 1931 y culminó en el Acta de Constitución de Canadá de 1982, que rompió los vestigios de la dependencia jurídica en el parlamento británico.9 Está gobernada como una democracia parlamentaria y monarquía constitucional con Isabel II como jefe de Estado. Es una nación bilingüe con el inglés y el francés como lenguas oficiales en el ámbito federal.
Canadá es una nación industrial y tecnológicamente pionera y avanzada, ampliamente autosuficiente en energía gracias a sus relativamente extensos depósitos de combustibles fósiles y a la amplia generación de energía nuclear y energía hidroeléctrica. Siendo uno de los países más desarrollados, tiene una economía diversificada, que la hace independiente por sus grandes yacimientos y abundantes recursos naturales así como del comercio, particularmente con los Estados Unidos y México. En la actualidad es miembro de la OEA, el G-8, el G-20, la OTAN, la OCDE, la OMC, la UKUSA, la APEC, la Mancomunidad de Naciones, la Francofonía y de la Organización de las Naciones Unidas. Es considerado uno de los países con mejor calidad de vida.10
Кана́да (англ. Canada [ˈkænədə] ![]() слушать; фр. Canada [kanadɑ]
слушать; фр. Canada [kanadɑ] ![]() слушать) — государство в Северной Америке, занимает второе место в мире по площади. Омывается Атлантическим, Тихим и Северным Ледовитым океанами, имея самую длинную береговую линию в мире. Граничит с США на юге и на северо-западе, также имеет морские границы с Данией (Гренландия) на северо-востоке и с Францией (Сен-Пьер и Микелон) на востоке. Граница Канады и США является самой протяжённой общей границей в мире.
слушать) — государство в Северной Америке, занимает второе место в мире по площади. Омывается Атлантическим, Тихим и Северным Ледовитым океанами, имея самую длинную береговую линию в мире. Граничит с США на юге и на северо-западе, также имеет морские границы с Данией (Гренландия) на северо-востоке и с Францией (Сен-Пьер и Микелон) на востоке. Граница Канады и США является самой протяжённой общей границей в мире.
Канада — конституционная монархия с парламентарной системой, её монархом является монарх Британского Содружества наций; Канада — двуязычная и многокультурная страна, где английский и французский языки признаны официальными на федеральном уровне. Технологически и промышленно развитое государство, Канада имеет многоотраслевую экономику, базирующуюся на богатых природных ресурсах и торговле (в частности с США, с которыми Канада комплексно сотрудничает со времён существования колоний и основания Конфедерации).
Основанная французским исследователем Ж. Картье в 1534 году, Канада берёт своё начало от французской колонии на месте современного Квебека, населённого первоначально местными народами. После периода английской колонизации из союза трёх британских колоний (которые были до этого территориями Новой Франции) родилась канадская конфедерация. Канада получила независимость от Соединённого Королевства в результате мирного процесса, длившегося с 1867 по 1982 год.
В настоящее время Канада является федеративным государством, состоящим из десяти провинций и трёх территорий. Провинция с преобладающим франкоговорящим населением — Квебек, остальные — преимущественно англоязычные провинции, также называемые английская Канада в сравнении с франкоязычным Квебеком. Будучи одной из девяти преимущественно англоязычных провинций, Нью-Брансуик является единственной официально двуязычной канадской провинцией. Территория Юкон официально двуязычна (английский и французский), а Северо-Западные территории и территория Нунавут признают одиннадцать, в том числе четыре официальных языка соответственно (среди которых также имеются английский и французский).
 Belgium
Belgium

 European Union
European Union
 History of the European Union
History of the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 *Founding states
*Founding states

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP4
TOP4

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 States of Europe
States of Europe

Das Königreich Belgien (niederländisch , französisch Royaume de Belgique) ist ein föderaler Staat in Westeuropa. Es liegt an der Nordsee und grenzt an die Niederlande, Deutschland, Luxemburg und Frankreich. Belgien zählt rund 11,3 Millionen[3] Einwohner (2015) auf einer Fläche von 30.528 Quadratkilometern und zählt somit zu den dicht besiedelten Staaten. Der Grad der Urbanisierung Belgiens ist mit fast 98 Prozent der höchste in Europa.[7] Die Stadt Brüssel ist die Hauptstadt und Sitz der belgischen Königsfamilie. Weitere bedeutende große Städte sind Antwerpen, Gent, Charleroi, Namur, Lüttich und Brügge.
Seit der Unabhängigkeit 1830 und Verfassungsgebung 1831 ist Belgien eine konstitutionelle Erbmonarchie[1] (siehe auch belgische Monarchie). Der Norden des Landes mit den Flamen ist niederländisches, der Süden mit den Wallonen französisches Sprachgebiet (vgl. flämische und französische Gemeinschaft). Die Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt ist offiziell zweisprachig, jedoch mehrheitlich frankophon bewohnt.[8] Im deutschen Sprachgebiet in Ostbelgien sind Standarddeutsch und westmitteldeutsche Mundarten verbreitet.
Der anhaltende flämisch-wallonische Konflikt prägt die gegensätzlichen Interessen der Vertreter der beiden großen Bevölkerungsgruppen in der belgischen Politik. Seit den 1970er-Jahren wird daher versucht, diesem Problem durch eine Dezentralisierung der Staatsorganisation zu begegnen. Dazu wurde Belgien in einen Bundesstaat, bestehend aus sechs Gliedstaaten – drei Regionen und drei Gemeinschaften – umgewandelt. Die Regionen Flandern, Wallonien und Brüssel-Hauptstadt sowie die flämische, die französische und die deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft bilden heute als Gliedstaaten die politische Grundlage des Landes.
Belgien ist Gründungsmitglied der Europäischen Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (EWG), der heutigen Europäischen Union (EU), deren wichtigste Institutionen in seiner Hauptstadt Brüssel ihren Sitz haben. Der belgische Staat ist des Weiteren neben den Niederlanden und Luxemburg Mitglied in der Wirtschaftsunion Benelux.
 Denmark
Denmark

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 States of Europe
States of Europe

Dänemark (dänisch Danmark [ˈtænmak], amtlich Königreich Dänemark, dänisch Kongeriget Danmark) ist ein Land und souveräner Staat im nördlichen Europa und eine parlamentarische Monarchie. Zusammen mit den Färöern, die wie das Mutterland geographisch zu Nordeuropa gehören, und Grönland, das zu Nordamerika zählt, ist Dänemark ein interkontinentaler Staat. Das Mutterland, der Teil zwischen der Skandinavischen Halbinsel und Mitteleuropa, umfasst eine Fläche von 43.094 km², wovon 23.872 km² auf die Halbinsel Jütland und der Rest auf Inseln entfallen.
Dänemark ist eines der zwölf Gründungsmitglieder der 1949 gegründeten NATO und seit dem 1. Januar 1973 in der Europäischen Union (bzw. ihrer Vorgängerin EWG). Die autonomen Gebiete Grönland und die Färöer führen eigene Flaggen, haben eigene Amtssprachen und gehören zur NATO, jedoch nicht zur EU.
Die einzige Landgrenze hat Dänemark zu Deutschland. Im dortigen, ehemals dänischen Südschleswig lebt eine dänische Minderheit. Im 1866 bis 1920 zu Preußen gehörenden Nordschleswig gibt es eine deutsche Minderheit. Dort ist Deutsch anerkannte regionale Minderheitensprache gemäß der Europäischen Charta der Regional- oder Minderheitensprachen.

