
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科

 Astronomy
Astronomy

 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Observatory
Observatory
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 National Astronomical Observatories,Chinese Academy of Sciences,NAOC
National Astronomical Observatories,Chinese Academy of Sciences,NAOC
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
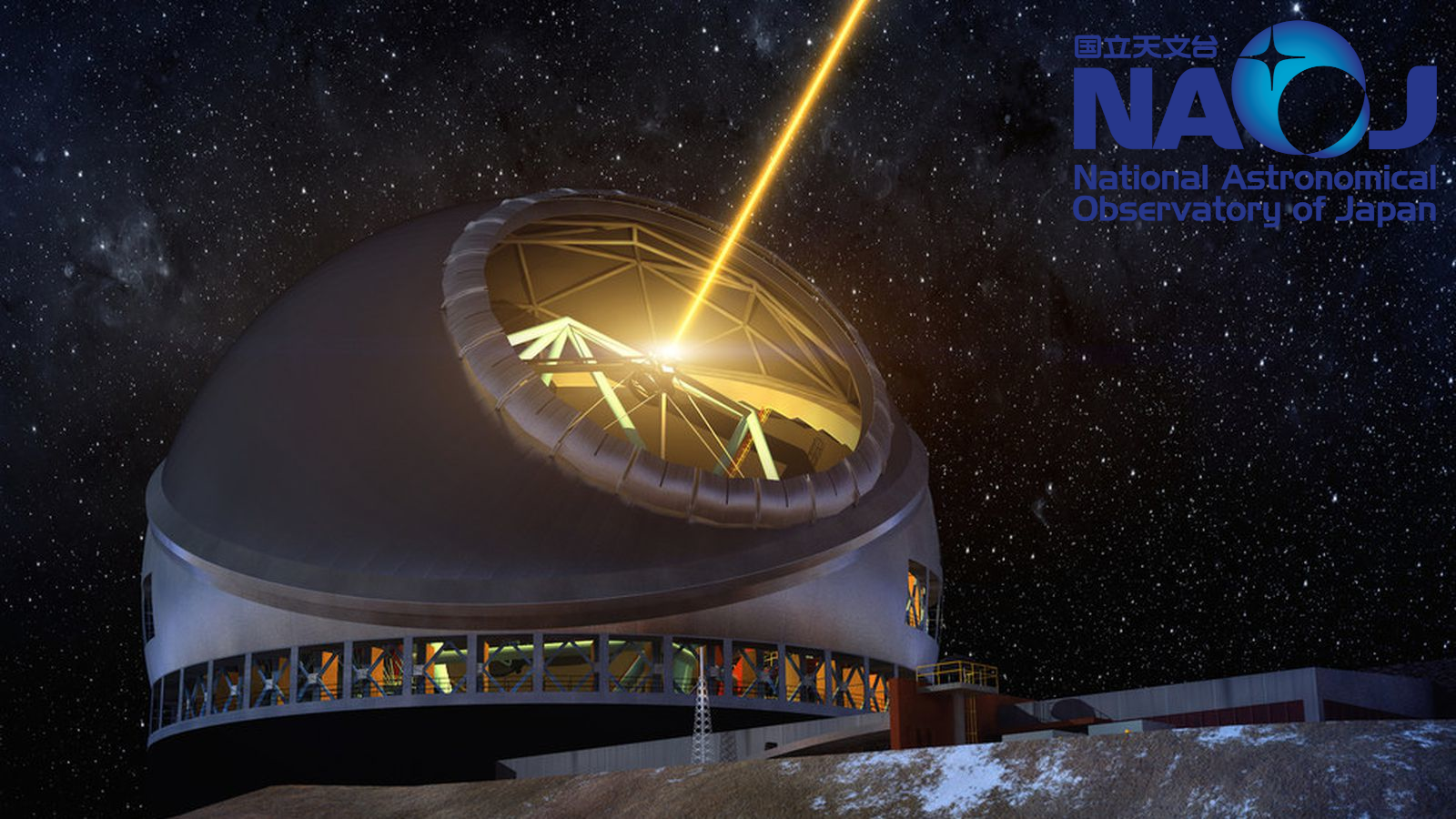





美国国家光学天文台(英語:National Optical Astronomy Observatory,缩写:NOAO)成立于1982年,目的是巩固和整合大学天文研究协会(AURA)下属的地面光学天文台,总部位于美国亚利桑那州的图森。由基特峰国立天文台(KPNO)、托洛洛山美洲际天文台(CTIO)、美国国家太阳天文台(NSO)和国家光学天文台双子科学中心(NGSC)等4个天文学研究机构组成,大学天文研究协会负责管理和运作,由美国国家科学基金会资助。
Das National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) ist die US-amerikanische öffentliche Institution zum Betrieb von bodengebundenen Sternwarten im optischen und Nahinfrarotbereich für die nächtliche Astronomie. NOAO wird mit Mitteln der National Science Foundation von der Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) betrieben.
NOAO betreibt Teleskope am Kitt Peak National Observatory und ist am Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory und dem Gemini-Observatorium beteiligt.
NOAO ist der Hauptzugang vieler US-Astronomen zu großen Teleskopen und steht allen Berufsastronomen für Beobachtungsanträge offen. Daneben gibt es in den USA traditionell eine dominierende Rolle privater Observatorien mit eingeschränktem Zugang, wie zum Beispiel dem Keck-Observatorium.

Das National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) ist eine staatlich geförderte Forschungs- und Entwicklungsorganisation für Radioastronomie mit Sitz an der University of Virginia in den USA. Das am 17. November 1956 gegründete[1] NRAO entwirft, baut und betreibt Radioteleskope für Wissenschaftler in der ganzen Welt. Amtierender Direktor ist Tony Beasely. NRAO wird von der National Science Foundation (NSF) finanziert und von Associated Universities, Inc (AUI) verwaltet.
美国国家射电天文台(英语:National Radio Astronomy Observatory,缩写为NRAO)是美国国家科学基金会资助的从事射电天文研究的机构,总部位于弗吉尼亚大学,在位于西弗吉尼亚州绿岸的国家无线电宁静区内建有世界最大的全可动射电望远镜——100米口径的绿岸望远镜。在新墨西哥州的圣阿古斯丁平原,国家射电天文台拥有甚大天线阵(VLA),由27台25米口径的天线组成,是世界上最大的综合孔径射电望远镜。2003年,国家射电天文台与多个国家的研究机构合作,开始在智利北部建设由64台口径12米的天线组成的阿塔卡玛大型毫米波天线阵(ALMA)。此外国家射电天文台还在亚利桑那州的基特峰(Kitt Peak)建有12米口径的射电望远镜。





帕瑞纳天文台(Paranal Observatory)是欧洲南方天文台在智利安托法加斯塔以南约120千米的帕瑞纳山的观测地。主要设备是4台8.2米口径的甚大望远镜以及若干台辅助望远镜组成的甚大望远镜干涉仪(VLTI)、4米口径的可见光和红外巡天望远镜(VISTA)、2.6米口径的VLT巡天望远镜(VST)。
20世纪90年代,欧洲南方天文台在智利的观测地拉西拉天文台已经有十余台望远镜,无处安置甚大望远镜,因此选中了拉西拉山以北约600千米的帕瑞纳山,用炸药炸平了山头,建造帕瑞纳天文台,并于1999年开始启用。这里海拔2632米,距离海岸线约12千米,气候干燥,没有灯光干扰,全年中晴夜数量多于340个,是世界上最好的天文观测地之一。
Das Paranal-Observatorium ist eine astronomische Beobachtungsstation in der Atacamawüste im Norden Chiles, auf dem Berg Cerro Paranal. Dieser liegt etwa 120 km südlich der Stadt Antofagasta und 12 km von der Pazifikküste entfernt. Das Observatorium wird von der Europäischen Südsternwarte (ESO) betrieben und ist Standort des Very Large Telescope (VLT), des Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) sowie der Survey Telescopes VISTA und VST. Die Atmosphäre über dem Gipfel zeichnet sich durch eine trockene und außergewöhnlich ruhige Luftströmung aus, die den Berg zu einem sehr attraktiven Standort für eine Sternwarte macht. Um für das VLT ein Plateau zu schaffen, wurde Anfang der 1990er Jahre der Gipfel durch Sprengungen von 2660 m auf 2635 m abgetragen.
パラナル天文台(パラナルてんもんだい、英語: Paranal Observatory)は、チリのアタカマ砂漠にある山・セロパラナルに設置された天体観測所で、ヨーロッパ南天天文台によって運営されている。超大型望遠鏡VLT (Very Large Telescope) はパラナルで最大の望遠鏡である。4台の口径8.2mの望遠鏡によって構成される。4台の望遠鏡で観測した光を干渉させ、Very Large Telescope干渉計 (VLTI) として観測を行うこともできる。干渉計としての撮像能力を向上させるため、4台の1.8m補助望遠鏡が追加されている。
さらに、掃天観測に用いられる口径2.6mのVLT掃天望遠鏡 (VST) と口径 4.1mのVISTAが運用されている。
Paranal Observatory is an astronomical observatory operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO); it is located in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile on Cerro Paranal at 2,635 m (8,645 ft) altitude, 120 km (70 mi) south of Antofagasta. By total light-collecting area, it is the largest optical-infrared observatory in the Southern hemisphere; worldwide, it is second to the Mauna Kea Observatory on Hawaii.
The Very Large Telescope (VLT), the largest telescope on Paranal, is composed of four separate 8.2 m (320 in) telescopes. In addition, the four main telescopes can combine their light to make a fifth instrument, the Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI). Four auxiliary telescopes of 1.8 m (71 in) each are also part of the VLTI to make it available when the main telescopes are being used for other projects.
The site also houses two survey telescopes with wide fields of view, the 4.0 m (160 in) VISTA and the 2.6 m (100 in) VLT Survey Telescope for surveying large areas of the sky; and two arrays of small telescopes called NGTS and SPECULOOS which are dedicated to searching for exoplanets.
Two major new facilities are under construction nearby: the Southern part of the Cherenkov Telescope Array gamma-ray telescope (not owned by ESO) will be sited in the grounds 10km south-east of Paranal; while ESO's future E-ELT will be on the nearby peak of Cerro Armazones 20km east of Paranal, and will share some of the base facilities.
L'Observatoire du Cerro Paranal est un observatoire astronomique professionnel situé sur le Cerro Paranal, dans le désert d'Atacama, au nord du Chili, à une altitude de 2 635 mètres. Il permet l'étude des astres dans les longueurs d'onde allant de l'ultraviolet à l'infrarouge.
C'est un projet européen de l'observatoire européen austral (European Southern Observatory ou ESO). À l'observatoire du Cerro Paranal, il y a quatre télescopes principaux de 8,2 mètres, qui, avec les quatre télescopes auxiliaires de 1,8 m (les « AT »), constituent le Very Large Telescope (VLT). Il s'y trouve de plus un télescope de 4 m (VISTA) et un de 2,5 m (le VLT Survey Telescope).
L'osservatorio del Paranal è un osservatorio astronomico situato sul Cerro Paranal, nel deserto di Atacama (120 km a sud di Antofagasta, in Cile, 1200 km da Santiago), realizzato e gestito dall'European Southern Observatory.
Il Cerro Paranal è una montagna alta 2635 metri, situata a 12 km dalla costa sull'oceano Pacifico, che si trova in una delle zone più secche di tutto il pianeta.
Il Very Large Telescope (VLT) è il maggiore telescopio presente al Paranal, composto di 4 distinti telescopi, ciascuno di 8,2 metri di diametro. Questi possono sia operare in modo separato, sia funzionare come un unico strumento, noto come VLTI (Very Large Telescope Interferometer).
Il sito ospita anche il VLT Survey Telescope, di 2,5 m di diametro, che opera dal 2007.
L'osservazione delle stelle vi si svolge con l'ausilio di un laser, il quale crea l'effetto di una stella artificiale virtualmente situata a 90 km dalla superficie terrestre, nella mesosfera. La stella virtuale serve di riferimento per la correzione delle distorsioni ottiche (comportanti distorsioni nel rilevamento del punto spaziale).
El Observatorio Paranal es un observatorio astronómico óptico operado por la European Southern Observatory, ESO, ubicado en la comuna de Taltal, en la Región de Antofagasta, Chile.
Se encuentra sobre el Cerro Paranal en el desierto de Atacama, perteneciente a la cordillera de la Costa, a 2635,43 msnm, a 130 km al sur de Antofagasta y a 12 km de la costa.
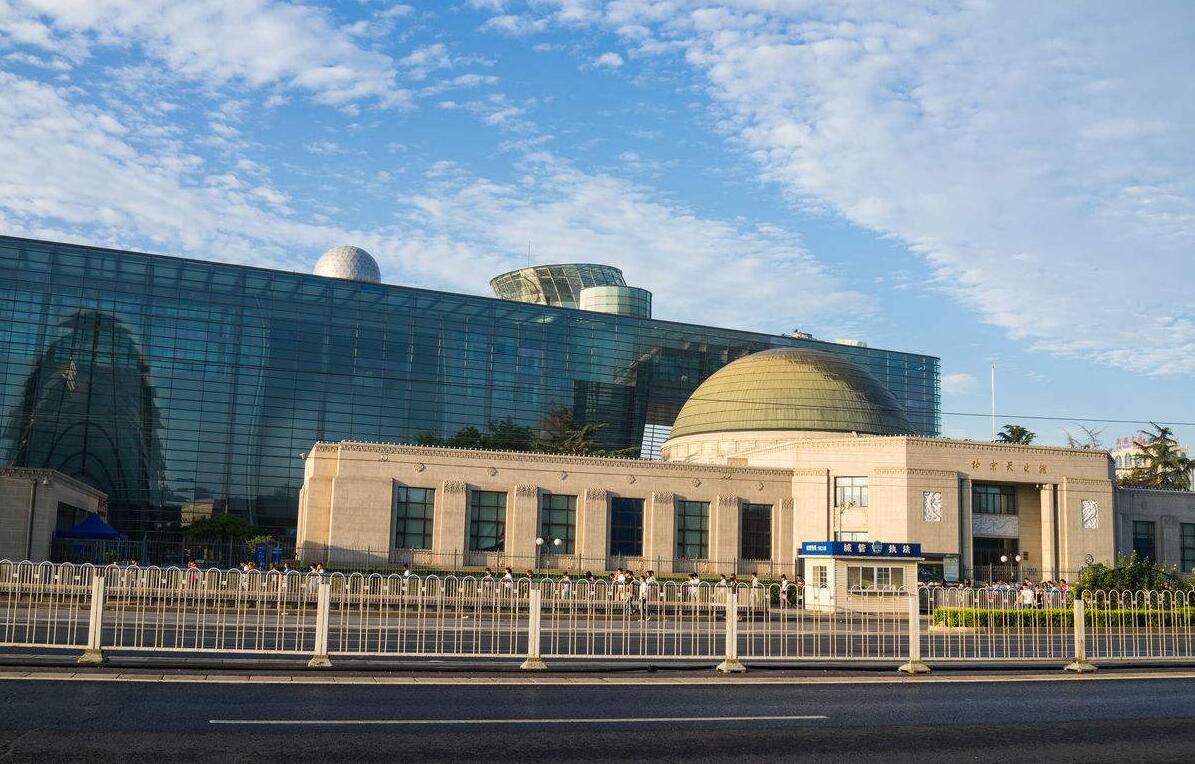

Das Beijing Planetarium besteht aus dem old planetarium, dem new planetarium, dem Digital space theater, dem 3D popular science theater, dem 4D popular science theater, dem Solar observatory, dem Optical observatory sowie der Exhibition hall.
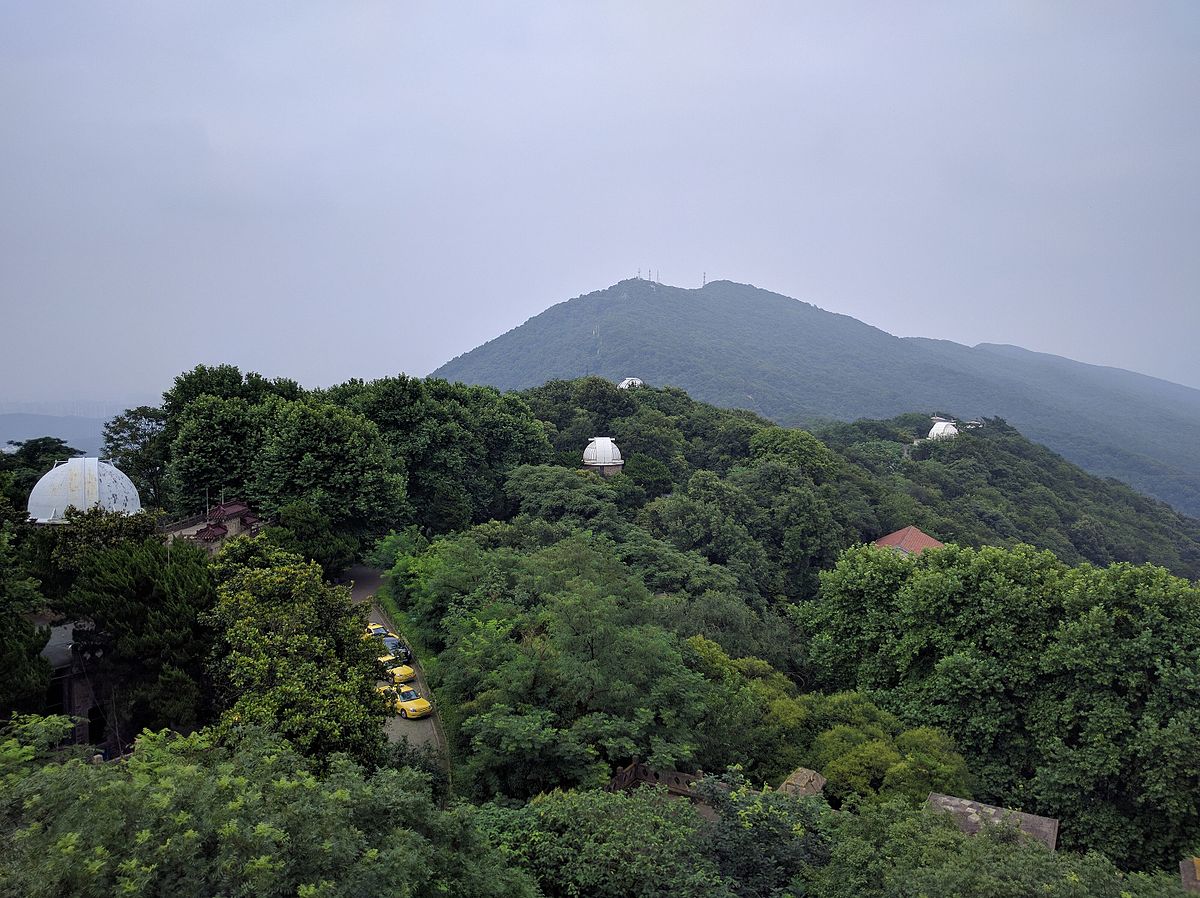

Das Purple-Mountain-Observatorium (chin. 紫金山天文台, Zĭjīnshān Tiānwéntái) ist eine Sternwarte nahe der Stadt Nanjing in der Volksrepublik China. Das Observatorium liegt im östlichen Randgebiet der Stadt auf einer Hügelkuppe im Westen der Purpurberge in einer Höhe von 267 m über dem Meeresspiegel.
Der Bau der Sternwarte begann 1929. Fünf Jahre später, 1934, wurde der Beobachtungsbetrieb aufgenommen. Heute ist sie ein modernes astronomisches Observatorium, das der Chinesischen Akademie der Wissenschaften unterstellt ist.
Am Purple-Mountain-Observatorium wurden drei Kometen entdeckt, darunter der periodische 60P/Tsuchinshan. Zu den Entdeckungen zählen darüber hinaus 147 Asteroiden, unter anderem die Trojaner (2223) Sarpedon, (2363) Cebriones und (2456) Palamedes, sowie ferner auch der nach der Warte benannte (3494) Purple Mountain.
(Quelle:Wikipedia)
 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM
 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA
 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 California-CA
California-CA
 Architecture
Architecture
 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France