
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科

南方共同市场(简称:Mercosur或Mercosul,西班牙语:Mercado Común del Sur、葡萄牙语:Mercado Comum do Sul、瓜拉尼语:Ñemby Ñemuha;简称共同市场或南共市[2]),又译南锥共同体,是巴西、阿根廷、乌拉圭、委内瑞拉(2017年被终止成员国资格[3])和巴拉圭五个南美洲国家的区域性贸易协定(Regional Trade Agreement, RTA),1991年巴西、阿根廷、乌拉圭及巴拉圭四国签订《亚松森协定》,并于1994年增修《黑金市议定书》,确立共同市场组织架构。成立宗旨为促进自由贸易及资本、劳动、商品的自由流通。
同时,南共市将智利、哥伦比亚、厄瓜多尔、圭亚那和苏里南列为联系国(西班牙语:Estados asociados)。[4][5]目前共同市场并没有设立观察国,而成员国被称为缔约国(西班牙语:Estados parte)。[6]
Mercosur (spanisch IPA [ˌmeɾ.ko.ˈsuɾ]) ist eine internationale Wirtschaftsorganisation in Lateinamerika. Der Name ist die abgekürzte Bezeichnung für den Mercado Común del Sur (Gemeinsamer Markt des Südens). Die ebenfalls offizielle portugiesische Bezeichnung lautet Mercosul für Mercado Comum do Sul, auf in Paraguay gesprochenem Guaraní ist Ñemby Ñemuha die geläufige Bezeichnung.
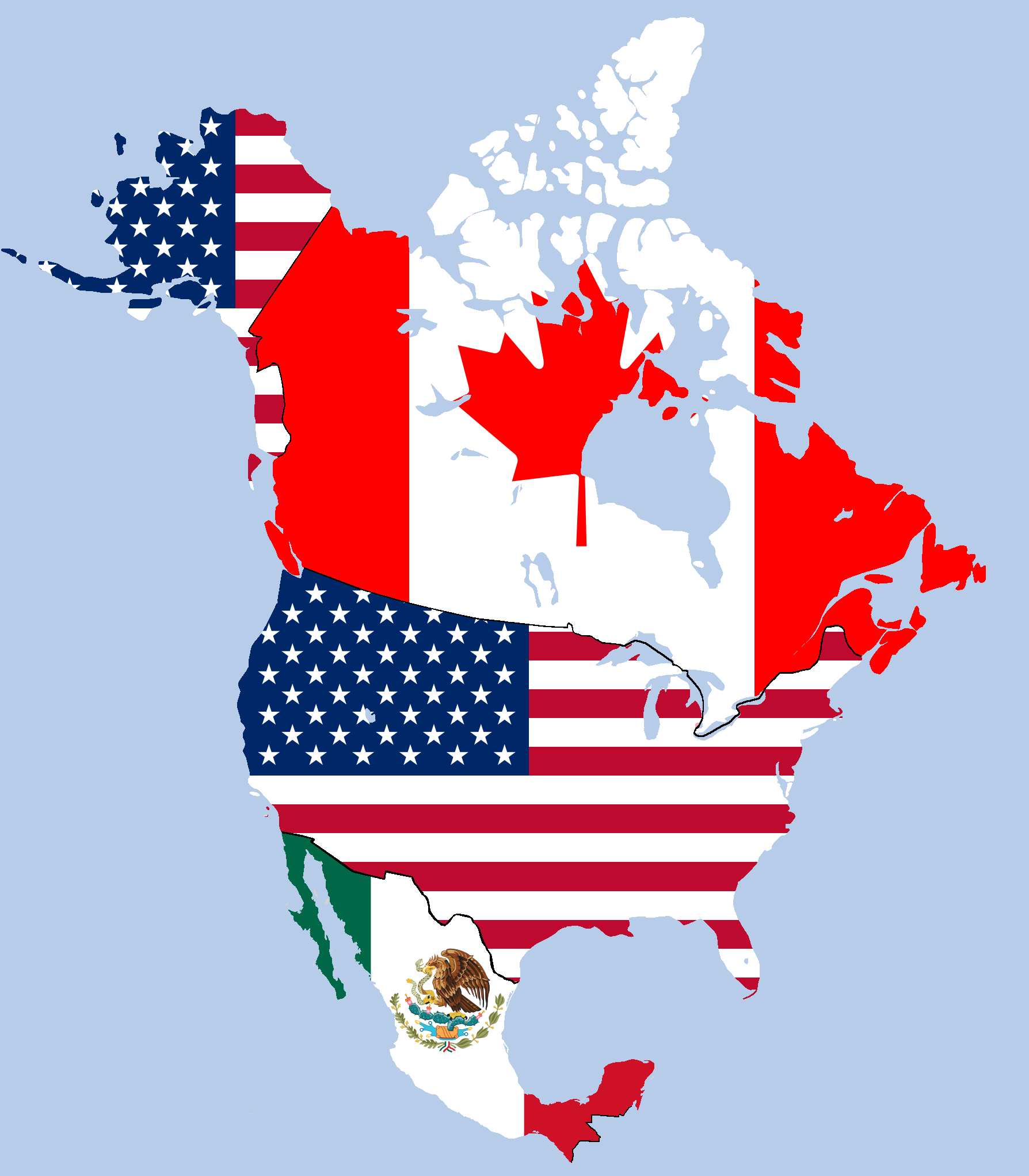
北美自由贸易协议(英语:North American Free Trade Agreement,NAFTA) 是美国、加拿大及墨西哥在1992年8月12日签署了关于三国间全面贸易的协议。与欧盟性质不一样,北美自由贸易协议不是凌驾于国家政府和国家法律上的一项协议。北美自由贸易协议于1994年1月1日正式生效。并同时宣告北美自由贸易区(North America Free Trade Area ,NAFTA)正式成立。北美自由贸易区拥有4.5亿人口,国民生产总值约17.3万亿美元,年贸易总额1.37万亿美元,其经济实力和市场规模都超过欧洲联盟,成为当时世界上最大的区域经济一体化组织。
 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam
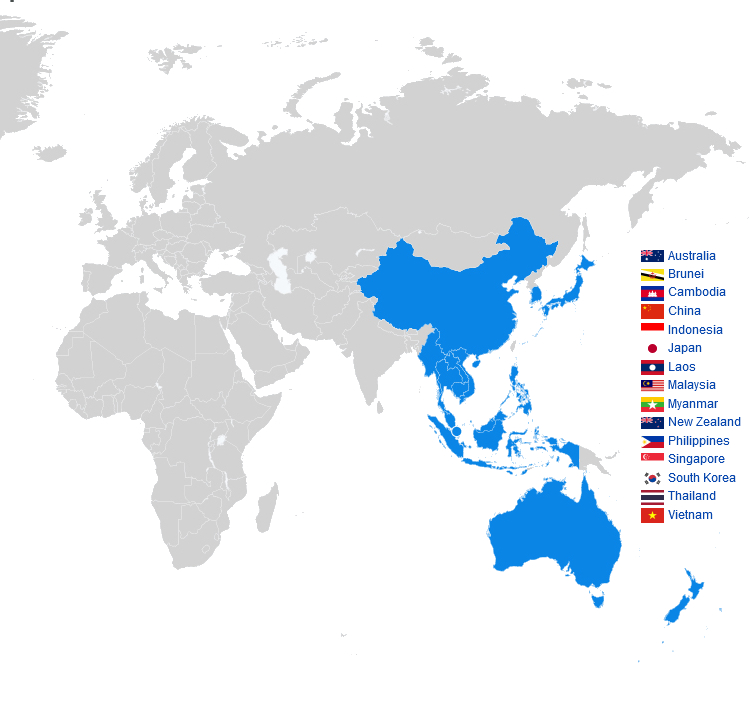
Die Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (kurz RCEP, deutsch Regionale, umfassende Wirtschaftspartnerschaft) ist ein seit 2020 bestehendes Freihandelsabkommen zwischen den zehn ASEAN-Mitgliedsstaaten und fünf weiteren Staaten in der Region Asien-Pazifik. Es ist die größte Freihandelszone der Welt.[1]
Das Projekt zur Gründung der RCEP entstand 2012, als die ASEAN-Staaten Verhandlungen mit der Volksrepublik China, Japan und Südkorea (ASEAN+3) sowie mit Indien, Australien und Neuseeland (ASEAN+6) aufgenommen hatten. Ursprünglich war die Einführung der Freihandelszone für 2017 geplant gewesen. Aufgrund von Bedenken verließ Indien 2019 die Verhandlungen. Am 15. November 2020, zum Abschluss des 37. ASEAN-Gipfeltreffens in der vietnamesischen Hauptstadt Hanoi, fand schließlich die Vertragsunterzeichnung statt.[2][3]
東アジア地域包括的経済連携(ひがしアジアちいきほうかつてきけいざいれんけい、英語: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership; RCEP、アールセップ、域内包括的経済連携)とは、ASEAN加盟10カ国(ブルネイ、カンボジア、インドネシア、ラオス、マレーシア、ミャンマー、フィリピン、シンガポール、タイ、ベトナム)と、そのFTAパートナー5カ国(オーストラリア、中国、日本、ニュージーランド、韓国)の間で提案されている、アジア太平洋地域の自由貿易協定であり、世界の人口の3割、世界のGDPの3割を占める15カ国が交渉に参加している。交渉国15カ国は世界の人口の30%、GDPの30%弱を占めている[1]。
FTAパートナーであるインドは、交渉が開始された2011年からRCEP交渉に参加していたが、主に中国からの製造品やオーストラリアやニュージーランドからの農産物・乳製品のダンピング懸念を理由に、交渉の最終時点の2019年11月に交渉から離脱した[2]。2020年11月15日に第4回RCEP首脳会議の席上で協定は署名された[3]。
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP; /ˈɑːrsɛp/ AR-sep) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history.[1] It was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam, and will take effect within two years, after it has been ratified by the member countries.[2][3][4]
The trade pact, which includes a mix of high-income,[note 1] middle-income,[note 2] and low-income countries,[note 3] was conceived at the 2011 ASEAN Summit in Bali, Indonesia, while its negotiations were formally launched during the 2012 ASEAN Summit in Cambodia.[5][6][7] It was expected to eliminate about 90% of the tariffs on imports between its signatories within 20 years of coming into force, and establish common rules for e-commerce, trade, and intellectual property.[8]
The RCEP is the first free trade agreement between China, Japan, and South Korea, three of the four largest economies in Asia.[8] At the time it was signed, analysts predicted that it would help stimulate the economy amid the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as "pull the economic centre of gravity back towards Asia," and amplify the decline of the United States in economic and political affairs.[6][9][10]
Le partenariat régional économique global1, ou en anglais : Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), est un projet d'accord de libre-échange entre quinze pays autour de l'océan Pacifique. C'est l'accord commercial le plus important du monde2.
Il inclut les dix pays membres de l'ASEAN, à savoir : la Birmanie, Brunei, le Cambodge, l'Indonésie, le Laos, la Malaisie, les Philippines, Singapour, la Thaïlande et le Vietnam ; ainsi que cinq autres pays qui possèdent déjà un accord de libre-échange bilatéral avec l'ASEAN, à savoir : l'Australie, la Chine, le Japon, la Corée du Sud et la Nouvelle-Zélande.
Il Partenariato Economico Globale Regionale (in lingua inglese Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) è un accordo di libero scambio nella regione dell'Asia Pacifica tra i dieci stati dell'ASEAN (cioè Brunei, Cambogia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Filippine, Singapore, Thailandia e Vietnam) e cinque dei loro partner di libero scambio: Australia, Cina, Giappone, Nuova Zelanda e Corea del Sud. I 15 paesi membri rappresentano circa il 30% della popolazione mondiale e del PIL, rendendolo il più grande blocco commerciale.[1] È stato firmato al vertice dell'ASEAN virtuale ospitato in Vietnam il 15 novembre 2020,[2][3] e dovrebbe entrare in vigore entro due anni, dopo che sarà stato ratificato dai paesi membri.[4]
Il patto commerciale, che comprende un mix di alto reddito, reddito medio, e paesi a basso reddito, è stato concepito al vertice dell'ASEAN del 2011 a Bali,[5] mentre i negoziati sono stati avviati ufficialmente nel corso del vertice dell'ASEAN del 2012 in Cambogia.[6]
L'RCEP è il primo accordo di libero scambio tra Cina, Giappone e Corea del Sud (tre delle quattro maggiori economie asiatiche) ed è il primo accordo multilaterale di libero scambio a includere la Cina.[7] Al momento della firma, gli analisti prevedevano che avrebbe aiutato a stimolare l'economia durante la pandemia di COVID-19, e "avrebbe attirato il centro di gravità economico verso l'Asia".
La Asociación Económica Integral Regional (abreviado RCEP por sus siglas en inglés) es un acuerdo de libre comercio (TLC) entre los diez estados miembros de la Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN) (Brunéi, Camboya, Indonesia, Laos, Malasia, Myanmar, Filipinas, Singapur, Tailandia , Vietnam) y cinco estados de Asia-Pacífico con los que la ASEAN tiene acuerdos de libre comercio existentes (Australia, China, Japón, Corea del Sur y Nueva Zelanda). El tratado fue firmado en la Cumbre de la ASEAN del 15 de noviembre de 202012 y se espera que entre en vigor en un plazo inferior a dos años, después de que sea ratificado por todos los estados miembros.
Incluye estados con PIBs muy diversos,3 conformando entre los 15 países en torno al 30% de la población mundial y el 30% del Producto Mundial Bruto.
Las negociaciones se iniciaron formalmente en noviembre de 2012 en la Cumbre de la ASEAN en Camboya.4 El RCEP se considera una alternativa al Acuerdo de Asociación Transpacífico (TPP, por sus siglas en inglés), un acuerdo comercial propuesto que incluye varias naciones de Asia y América, pero excluye a China y la India.5 Tras la salida de Estados Unidos durante la presidencia de Donald Trump del TPP se retomaron con más fuerza las negociaciones en el RCEP y se firmó el acuerdo en noviembre de 2020 por las naciones de la ASEAN, incluida China.6 El pacto entrará en vigor cuando los países que lo han firmado procedan a tramitar su ratificación a nivel nacional.7
El tratado RCEP es el primer tratado de libre comercio entre China, Japón y Corea del sur (tres de las cuatro grandes economías asiáticas), y es el primer tratado multilateral que incluye a China.8 En el momento de la firma, los analistas predijeron que ayudaría en la recuperación de la economía tras la pandemia de COVID-19, así como a empujar el centro de gravedad de la economía mundial hacia Asia.9
Всесторо́ннее региона́льное экономи́ческое партне́рство, сокращенно ВРЭП (англ. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) — это соглашение о «зоне свободной торговли плюс» («ЗСТ +»), охватывающее 10 государств-членов Ассоциации государств Юго-Восточной Азии (АСЕАН) (Бруней, Вьетнам, Индонезия, Камбоджа, Лаос, Малайзия, Мьянма, Сингапур, Таиланд, Филиппины) и 6 государств, с которыми у АСЕАН уже подписаны соглашения о свободной торговле (Австралия, Индия, КНР, Новая Зеландия, Республика Корея и Япония). ВРЭП охватывает 4 развитые и 12 развивающихся государств. Начало переговоров было положено 20 ноября 2012 г. на саммите АСЕАН в Камбодже[1].
Соглашение о создании ВРЭП было подписано в Ханое 15 ноября 2020 года. Его вступление в силу создаст крупнейшую в мире зону свободной торговли с примерно 2,2 млрд потребителями и объемом ВВП в $28 трлн, что составляет более 32% от общего мирового объема ВВП.[2].
 Angola
Angola
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Comoros
Comoros
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Sambia
Sambia
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania

南亚区域合作联盟(英语:South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)是1985年12月8日成立的旨在推动南亚人民间友谊、信任与理解的平台,由孟加拉国、不丹、印度、马尔代夫、尼泊尔、巴基斯坦和斯里兰卡七国政府发起成立。2005年11月13日,接受阿富汗为成员。缅甸、模里西斯、澳大利亚、中华人民共和国、日本、大韩民国、欧盟、美国和伊朗成为观察员。
Die Südasiatische Vereinigung für regionale Kooperation (auch Südasiatische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft) (von englisch South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) (SAARC) wurde am 8. Dezember 1985 in Dhaka (Bangladesch) gegründet und hat ihren Sitz in der nepalesischen Hauptstadt Kathmandu. Gründungsmitglieder sind Indien, Pakistan, Bangladesch, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan und die Malediven. Im April 2007 trat Afghanistan auf dem Gipfeltreffen in Neu-Delhi der Organisation bei. Die Volksrepublik China, Japan, die Europäische Union, Südkorea, die Vereinigten Staaten und der Iran besitzen Beobachterstatus.

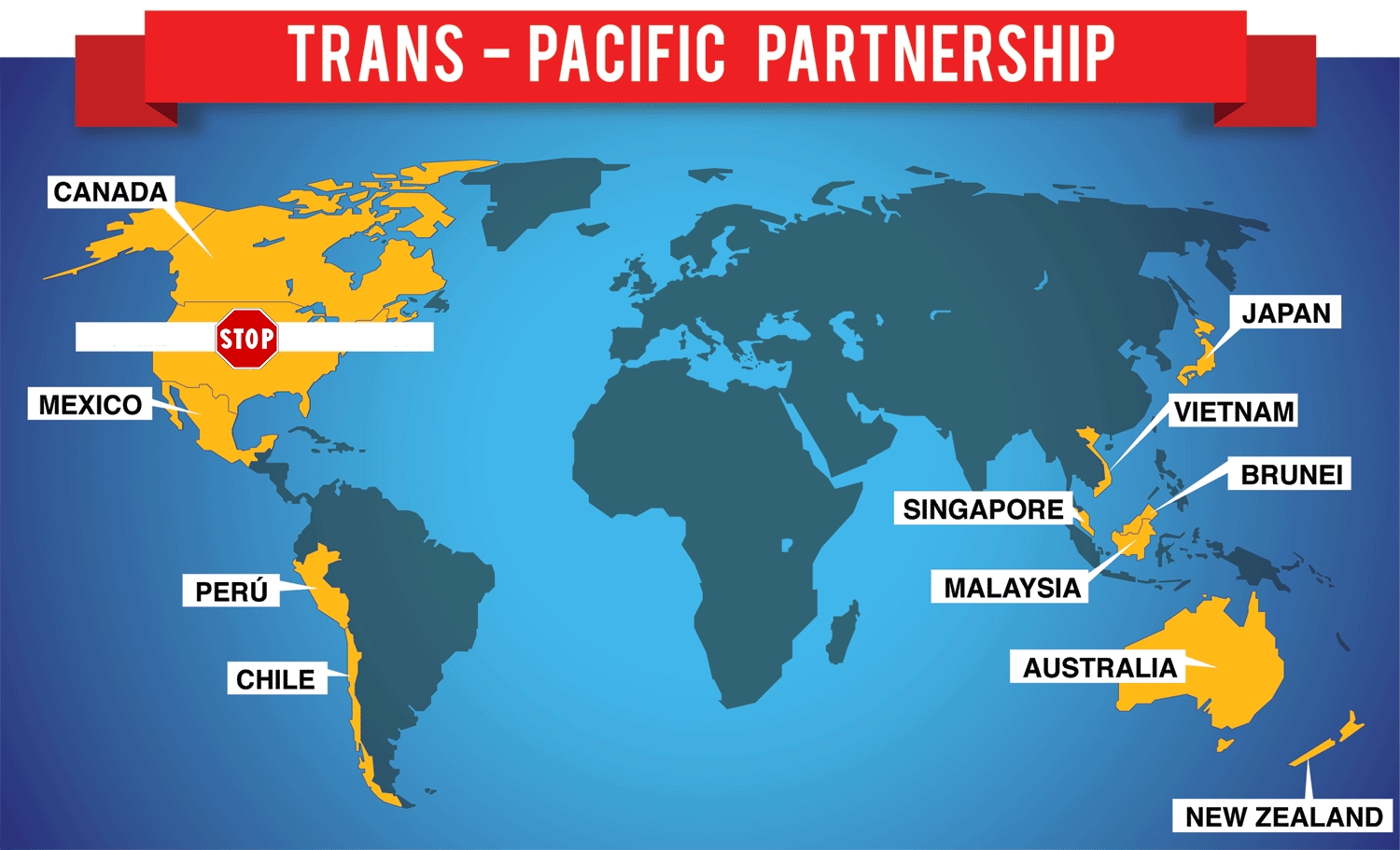
 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Peru
Peru
 Singapore
Singapore
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan

 European Union
European Union