
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科



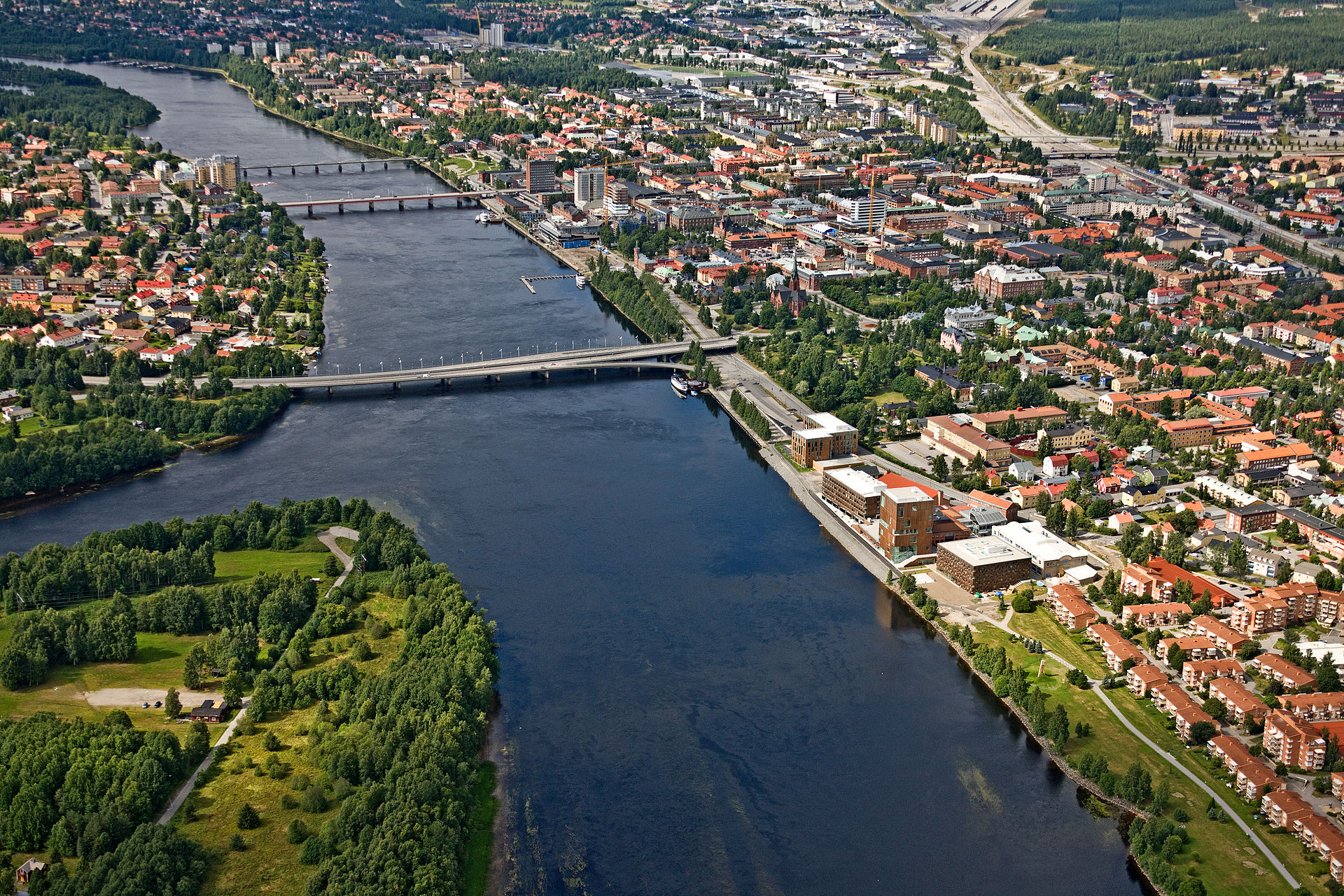
的里雅斯特(意大利语:Trieste;斯洛文尼亚语:Trst;德语:Triest)是意大利东北部靠近斯洛文尼亚边境的一个港口城市,位于亚得里亚海的里雅斯特湾的最深处,也是弗留利-威尼斯朱利亚大区和的里雅斯特省的首府。2001年人口为207,069人。
在1372年到1918年间,的里雅斯特曾是神圣罗马帝国及奥匈帝国的一部分,因而这座城市虽然在地理上显然属于南欧,但在语言、文化方面却具有明显的中欧特色,与其他意大利城市有着明显的区别。尤其是在1867年到1918年期间,的里雅斯特作为奥匈帝国的主要出海口,曾是地中海沿岸一个繁荣的港口城市和音乐与文学的中心。第一次世界大战结束后,奥匈帝国崩溃,的里雅斯特并入意大利,随之经济文化衰落下去。
现今的里雅斯特是边界城市的代表。的里雅斯特的人口混合了邻区的人种。的里雅斯特市区占优势的方言称为的里雅斯特语(的里雅斯特语:Triestin,意大利语:Triestino),是威尼斯方言在当地的变种;而在紧邻市区的部分近郊,已经开始使用斯洛文尼亚语。意大利语以及斯洛文尼亚语都被认为是本地语言,而弗留利语以及克罗地亚语也有少数人使用,由于地理位置以及历史缘故,在该城也有很多人使用德语。
的里雅斯特的经济主要依赖港口贸易以及与邻近地区的商业交易,是意大利邮船公司(Lloyd Triestino)的发祥地。在冷战时期,的里雅斯特因为地处东西方对抗前沿成为次要港口,但目前正在重振它昔日的商业影响力。在2006年的里雅斯特被选为意大利最适合居住的城市。
的里雅斯特的景点主要是众多奥匈帝国时代存留的新艺术以及新古典主义风格建筑,以其明显的中欧特色在意大利众多城市中独树一帜。该市还拥有国际理论物理中心和的里雅斯特大学。
Trieste (ascolta[?·info], AFI: /triˈɛste/[5]; Trieste in dialetto triestino; Triest in tedesco; Trst in sloveno[6]) è un comune italiano di 200 109 abitanti[2], capoluogo della regione italiana a statuto speciale Friuli-Venezia Giulia, affacciato sull'omonimo golfo nella parte più settentrionale dell'Alto Adriatico, fra la penisola italiana e l'Istria, a qualche chilometro dal confine con la Slovenia nella regione irredenta della Venezia Giulia[2].
Già capoluogo dell'omonima provincia, è sede dell'omonimo ente di decentramento regionale (EDR), istituito con Legge regionale 29 novembre 2019, n. 21 ("Esercizio coordinato di funzioni e servizi tra gli enti locali del Friuli Venezia Giulia e istituzione degli Enti di decentramento regionale"), ed operativo dal 1º luglio 2020.
Rappresenta da secoli un ponte tra l'Europa centrale e quella meridionale, mescolando caratteri mediterranei, mitteleuropei e slavi ed è il comune più popoloso[7] e densamente popolato della regione[8]. Il porto di Trieste dal 2016 è il porto italiano col maggior traffico merci ed è uno dei più importanti nel sud Europa[9][10].
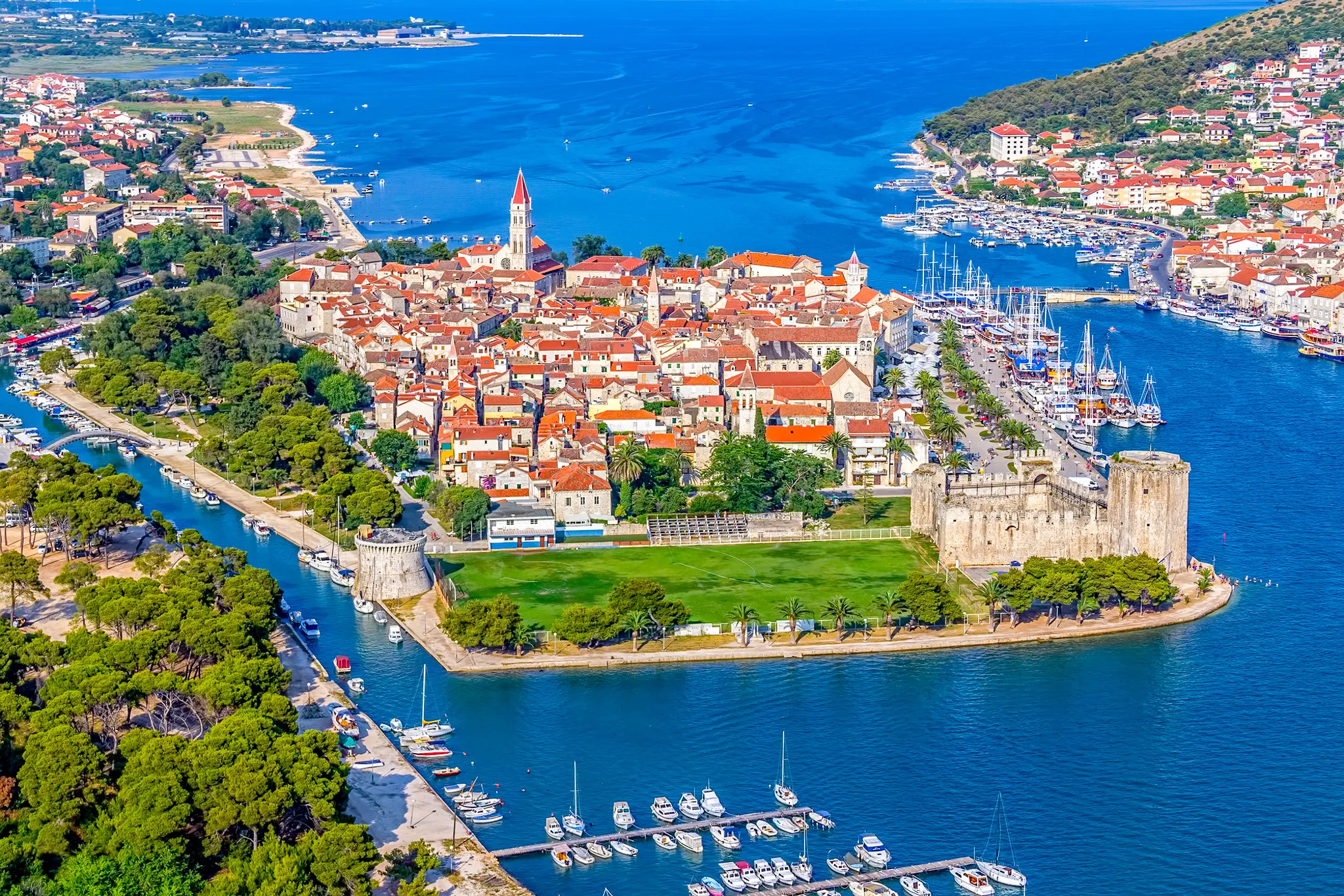

Trogir [ˈtrɔ.ɡiːr] (deutsch und ungarisch Trau, altgriechisch Τραγούριον Tragoúrion, lateinisch Tragurium, italienisch Traù) ist eine Hafenstadt in Kroatien. Sie liegt in Mitteldalmatien, etwa 15 Kilometer westlich von Split. Die gesamte Altstadt zählt seit 1997 zum Weltkulturerbe der UNESCO.
特罗吉尔(克罗地亚语:Trogir,意大利语、达尔马提亚语:Traù,拉丁语:Tragurium,希腊语:Tragurion,匈牙利语:Trau)是克罗地亚的一座古城,亚德里亚海港口,2001年人口 13,322人。特罗吉尔古城座落在克罗地亚大陆和契奥沃岛之间的一个小岛上。位在斯普利特以西27公里。





 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 Turin
Turin

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Italy
Italy
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics
 2006 Winter Olympics
2006 Winter Olympics

 Piemonte
Piemonte
 Turin
Turin
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

都灵(意大利语:Torino [toˈriːno] ![]() 聆听;皮埃蒙特语:Turin [tyˈɾiŋ];拉丁语:Augusta Taurinorum),中国大陆和港澳地区称为都灵,台湾称为杜林,是位于意大利北部的重要城市,皮埃蒙特大区和都灵广域市的首府。它坐落在波河的左岸,距离米兰大约140千米(87英里),阿尔卑斯山环绕在城市的西北。都灵中心区有面积130.17km²,人口911,534[2],是意大利人口第四多的城市;都灵城市区有面积1,126.6 km²,人口1,745,221[3];都灵都市圈有面积1,977 km²,人口2,200,000[4](占意大利总人口的3.4%[5])。
聆听;皮埃蒙特语:Turin [tyˈɾiŋ];拉丁语:Augusta Taurinorum),中国大陆和港澳地区称为都灵,台湾称为杜林,是位于意大利北部的重要城市,皮埃蒙特大区和都灵广域市的首府。它坐落在波河的左岸,距离米兰大约140千米(87英里),阿尔卑斯山环绕在城市的西北。都灵中心区有面积130.17km²,人口911,534[2],是意大利人口第四多的城市;都灵城市区有面积1,126.6 km²,人口1,745,221[3];都灵都市圈有面积1,977 km²,人口2,200,000[4](占意大利总人口的3.4%[5])。
都灵是一国际化的欧洲城市,[6][7] 都灵有时被称为“意大利自由的摇篮”、[8]、“阿尔卑斯之都”、“萨沃亚之都”。它拥有众多的文化设施和其他名胜。都灵因为它的巴洛克、洛可可和新古典主义法式建筑而举世闻名。它的很多广场、城堡、庭园和宫殿(如贵妇宫),都是由西西里建筑师菲利波·尤瓦拉建造的,他在设计时借鉴了法国经典建筑凡尔赛宫。[9] 这些法式建筑的典范包括:王宫、斯杜皮尼吉行宫和苏佩尔加大教堂。许多意大利高等教育机构位于此地,如都灵大学、都灵理工大学、都灵美术学院等。还有许多重要和著名的博物馆,如埃及博物馆[10] 和安托内利尖塔。
都灵曾经是欧洲重要的政治中心。1563年,它成为了萨伏依公国的首都,随后是萨伏依王室统治下的萨丁尼亚王国的首都,最后是意大利统一之后的第一个首都(1861年—1865年)。[11] 同时,它也是萨沃亚王室(意大利王室)的故乡。[12] 虽然因为第二次世界大战,它的大部分政治意义和重要性都丢失了,它还是在战后成为了欧洲重要的工业、商业和贸易的集散地。它现在是意大利的工业中心之一,和米兰、热那亚组成了“工业铁三角”。从经济上来说,都灵紧随罗马和米兰之后,是意大利第三大城市。[13] 它的GDP高达580亿美元,排名世界第78位。[14] 虽然不像罗马、米兰那样是“世界级城市”,GaWC评其为“适合发展”级别。[15]
都灵是意大利汽车制造业的摇篮,被称为“意大利汽车之都”或者“意大利的底特律”。是汽车品牌菲亚特、蓝旗亚和阿尔法·罗密欧的总部所在地。[16][17] 都灵还拥有足球俱乐部尤文图斯和都灵,举办过2006年冬季奥林匹克运动会。一些国际空间站设备,如和谐号节点舱和哥伦布实验舱,也是在都灵制造的。
トリノ(伊: Torino (![]() 音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国ピエモンテ州にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約87万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ピエモンテ州の州都であり、トリノ県の県都。イタリア第4の人口規模を持つ。都市圏の人口は約170万人。一時は100万都市だったが昨今は人口減少が著しい。
音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国ピエモンテ州にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約87万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ピエモンテ州の州都であり、トリノ県の県都。イタリア第4の人口規模を持つ。都市圏の人口は約170万人。一時は100万都市だったが昨今は人口減少が著しい。
ミラノに次ぐイタリア第2の工業都市であり、自動車工業の拠点である。近代にはサルデーニャ王国の首都が置かれた。サヴォイア王家の王宮群は世界遺産に登録されている。
Turin (/tjʊəˈrɪn, ˈtʊərɪn/;[2] Italian: Torino [toˈriːno] (![]() listen); Piemontese: Turin [tyˈriŋ])[3] is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Turin (an administrative division of Italy) and of the Piedmont region, and was the first capital city of Italy from 1861 to 1865. The city is located mainly on the western bank of the Po River, in front of Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 883,281 (30 November 2017)[4] while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.[5]
listen); Piemontese: Turin [tyˈriŋ])[3] is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Turin (an administrative division of Italy) and of the Piedmont region, and was the first capital city of Italy from 1861 to 1865. The city is located mainly on the western bank of the Po River, in front of Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 883,281 (30 November 2017)[4] while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.[5]
The city has a rich culture and history, being known for its numerous art galleries, restaurants, churches, palaces, opera houses, piazzas, parks, gardens, theatres, libraries, museums and other venues. Turin is well known for its Renaissance, Baroque, Rococo, Neo-classical, and Art Nouveau architecture. Many of Turin's public squares, castles, gardens and elegant palazzi such as the Palazzo Madama, were built between the 16th and 18th centuries. A part of the historical center of Turin was inscribed in the World Heritage List under the name Residences of the Royal House of Savoy.
The city used to be a major European political center. From 1563, it was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the Royal House of Savoy, and the first capital of the unified Italy (the Kingdom of Italy) from 1861 to 1865.[6][7] Turin is sometimes called "the cradle of Italian liberty" for having been the birthplace and home of notable individuals who contributed to the Risorgimento, such as Cavour.[8]
The city currently hosts some of Italy's best universities, colleges, academies, lycea and gymnasia, such as the University of Turin, founded in the 15th century, and the Turin Polytechnic. In addition, the city is home to museums such as the Museo Egizio[9] and the Mole Antonelliana. Turin's attractions make it one of the world's top 250 tourist destinations and the tenth most visited city in Italy in 2008.[10]
Even though much of its political significance and importance had been lost by World War II, Turin became a major European crossroad for industry, commerce and trade, and is part of the famous "industrial triangle" along with Milan and Genoa. Turin is ranked third in Italy, after Milan and Rome, for economic strength.[11] With a GDP of $58 billion, Turin is the world's 78th richest city by purchasing power.[12] As of 2010, the city has been ranked by GaWC as a Gamma World city.[13] Turin is also home to much of the Italian automotive industry.[14][15]
Turin is well known as the home of the Shroud of Turin, the football teams Juventus F.C. and Torino F.C., the headquarters of automobile manufacturers FIAT, Lancia and Alfa Romeo, and as host of the 2006 Winter Olympics.
Turin (Torino en italien, Turin en piémontais) est une ville italienne, chef-lieu de la ville métropolitaine de Turin et de la région du Piémont. Turin fut la capitale des États de Savoie de 1563 à 1713, du royaume de Sicile de 1713 à 1720, du royaume de Sardaigne de 1720 à 1861 et du royaume d'Italie de 1861 à 1865.
Torino (AFI: /toˈrino/[4], ; Turin in piemontese[5]) è un comune italiano di 879 808 abitanti[2], capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana e della regione Piemonte.
Cuore di un'area metropolitana che conta quasi 2 000 000 di abitanti su una superficie approssimativa di circa 2 300 km²,[6] la città di Torino è il quarto comune italiano per popolazione, il terzo complesso economico-produttivo del Paese e costituisce uno dei maggiori poli universitari, artistici, turistici, scientifici e culturali d'Italia. Nel suo territorio sono inoltre presenti aree ed edifici inclusi in due beni protetti dall'UNESCO: alcuni palazzi e zone facenti parte del circuito di residenze sabaude in Piemonte (patrimonio dell'umanità[7]) e l'area delle colline del Po (riserva della biosfera).
Città dalla storia bimillenaria, fu fondata probabilmente come Taurasia nei pressi della posizione attuale attorno al III secolo a.C. dai Taurini, popolazione ligure (o celto-ligure) dell'Italia settentrionale, e trasformata in colonia romana da Augusto col nome di Iulia Augusta Taurinorum nel I secolo a.C. Dopo il dominio ostrogoto fu capitale di un importante ducato longobardo, per poi passare, dopo essere divenuta capitale di marca carolingia, sotto la signoria nominale dei Savoia nell'XI secolo. Città dell'omonimo ducato, nel 1563 ne divenne capitale. Dal 1720 fu capitale del Regno di Sardegna (anche se solo de facto fino alla fusione perfetta del 1847, quando lo divenne anche formalmente),[8] stato che nel XIX secolo avrebbe portato all'unificazione italiana e che fece di Torino la prima capitale del Regno d'Italia (dal 1861 al 1865).
È stata la patria, natia o adottiva, di alcuni fra i più grandi scrittori e letterati italiani del XIX e XX secolo, tra i quali Edmondo De Amicis, Emilio Salgari, Italo Calvino, Natalia Ginzburg, Norberto Bobbio, Cesare Pavese e Primo Levi.
Sede nel 2006 dei XX Giochi olimpici invernali, città natale di alcuni fra i maggiori simboli del Made in Italy nel mondo, come il Martini, il cioccolato gianduja e il caffè espresso, è il fulcro dell'industria automobilistica italiana, nonché importante centro dell'editoria, del sistema bancario e assicurativo, delle tecnologie dell'informazione, del cinema, dell'enogastronomia, del settore aerospaziale, del disegno industriale e dello sport.
Turín (en italiano: Torino, en piamontés: Turin) es una ciudad, importante centro cultural y de negocios del norte de Italia, capital de la región de Piamonte, localizada principalmente en el margen izquierdo del río Po y rodeada por los Alpes. El área metropolitana de Turín, según la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, tiene una población de alrededor de 2.200.000 habitantes.2
La ciudad es rica en cultura e historia. Es conocida por sus numerosos museos de arte, sus restaurantes, sus iglesias, sus palacios, sus teatros de ópera, sus plazas, sus parques, sus jardines y sus bibliotecas, entre otros atractivos. Turín es ampliamente reconocida por su arquitectura barroca, rococo, neoclásica y Art Nouveau. Muchas de las plazas públicas de la ciudad, de los castillos, jardines y elegantes palacios (como el Palazzo Madama), fueron construidos por el arquitecto siciliano Filippo Juvarra, quien diseñó estos edificios en el estilo barroco y clásico del Palacio de Versalles, en Francia.3 Ejemplos de estos edificios de inspiración francesa incluyen el Palacio Real de Turín, el Pabellón de caza de Stupinigi y la Basílica de Superga.
Turín es frecuentemente llamada la «cuna de Italia» por ser el lugar de nacimiento de importantes políticos que contribuyeron con la unificación de Italia, como Cavour.4 La ciudad actualmente alberga algunas de las mejores universidades de Italia, como la Universidad de Turín, de seis siglos de antigüedad, y el Politécnico de Turín. También se encuentran en la ciudad museos prestigiosos e importantes, como el Museo Egipcio de Turín5 (el más antiguo en el mundo y considerado el segundo más importante en el mundo después de El Cairo por valor de los hallazgos) y la Mole Antonelliana. Los diversos monumentos y atracciones de Turín la convierten en una de los 250 principales destinos turísticos del mundo y en la décima ciudad más visitada de Italia para el año 2008.6
La ciudad solía ser un importante centro político europeo, siendo la primera capital de Italia en 1861 y la ciudad de residencia de la Casa de Saboya, la familia real de Italia.7 A pesar de que mucho de su significado e importancia política se había perdido cuando comenzó la Segunda Guerra Mundial, se convirtió en uno de los principales centros industriales y comerciales de Europa, y actualmente es una de las ciudades más industrializadas de Italia, formando junto con Milán y Génova el famoso "triángulo industrial". A pesar de tener muchos menos habitantes que Roma y Milán, Turín es la tercera ciudad más rica de Italia, después de estas.8 Con un Producto Interno Bruto de 58.000 millones de dólares, Turín es la ciudad número 78 en la lista de las más ricas del mundo por su poder adquisitivo.91011 Turín es también la sede de gran parte de la potente industria automovilística italiana.1213
La ciudad es también conocida por resguardar la «Sábana Santa», por ser la sede de los equipos de fútbol Juventus F.C. y Torino Football Club, el lugar donde se producen los coches FIAT, Lancia, Alfa Romeo, Maserati y la sede de los juegos olímpicos de invierno de 2006. Varios módulos de la Estación Espacial Internacional, como el Harmony y el Columbus, fueron fabricados en Turín.
Fue la capital del Ducado de Saboya desde 1563, luego del Reino de Cerdeña y finalmente la primera capital de Italia.14 Piero Fassino fue el alcalde de Turín, elegido en mayo de 2011 para un mandato de 5 años, representando a una coalición de centro-izquierda y fue a su vez el sucesor de Sergio Chiamparino. Desde junio de 2016, la alcaldesa es la economista Chiara Appendino, del partido Movimento 5 Estrellas.
Тури́н (итал. Torino [toˈriːno], пьем. Turin [tyˈɾiŋ]) — город в Италии, важный деловой и культурный центр северной Италии. Административный центр региона Пьемонт и одноимённой провинции Турин.
Расположен при впадении реки Дора-Рипария в реку По, на Паданской равнине у подножия Западных Альп, на подступах к Альпийским перевалам.
Четвёртый после Рима, Милана и Неаполя город Италии по количеству жителей, насчитывает около 880 тыс. чел. (2017), вместе с пригородами 1,7 миллион человек.
Город имеет богатую историю и культуру, и известен своими арт-галереями, дворцами, театрами, музеями, парками. Турин также знаменит своей архитектурой в стилях барокко, рококо, неоклассицизма и модерна.
Большая часть замков, дворцов (в частности Палаццо Мадама), садов и площадей были построены в XVI-XVIII вв. в процессе перевода столицы Савойского герцогства (позднее Сардинское королевство) из Шамбери (ныне Франция) в Турин.
Турин иногда называют «колыбелью итальянской свободы», за то, что он является родным городом заметных политиков и людей, внесших большой вклад в Рисорджименто, например Камилло Бенсо ди Кавур. В городе находятся множество университетов, колледжей, академий, лицеев и гимназий. Среди них основанный в XV веке Туринский университет. Самыми известными достопримечательностями Турина являются Египетский музей и символ города Моле Антонеллиана. Эти и многие другие достопримечательности делают город привлекательным для туристов со всего мира и позволяют Турину входить в десятку самых посещаемых городов Италии[3].
Город в XIX веке являлся важным политическим центром Европы. В 1861 году Турин стал первой столицей объединенной Италии и наряду с этим являлся столицей для Савойского дома, правящей династии Королевства Италии. Несмотря на то, что большая часть политической значимости Турина была растеряна после отмены монархии в Италии, город остается важным промышленным, экономическим и торговым центром Европы и Италии. Турин является третьим по экономическим показателям городом страны, после Милана и Рима. Также Турин является своего рода столицей автомобилестроения Италии. В городе располагаются штаб-квартиры компаний FIAT, Lancia, Iveco.
Город известен в мире благодаря христианской реликвии — Туринской плащанице, а также футбольным командам «Ювентус» и «Торино». Турин — столица зимних Олимпийских игр 2006 года.
Покровителем города считается Св. Иоанн Креститель (итал. San Giovanni Battista). Праздник города — 24 июня.
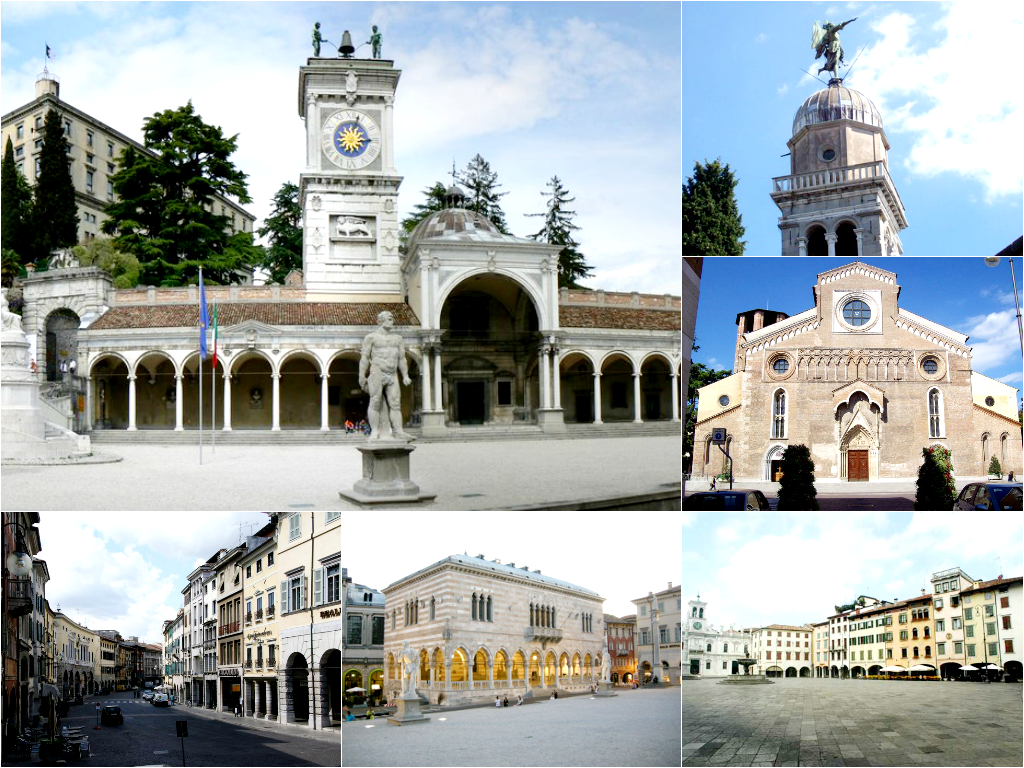




乌尔姆(Ulm)是德国巴登-符腾堡州的一座城市,位于多瑙河畔。它附近的大城市有东南部约70公里远的奥格斯堡和130公里远的慕尼黑和西北约100公里远的斯图加特。乌尔姆与与其隔岸相望的属于巴伐利亚州的新乌尔姆一起是这个地区的文化和商业中心。乌尔姆位于伊勒河和布劳河注入多瑙河的入口处,它的西部是施瓦本山,城市的北部是山地。乌尔姆的大多数城区位于多瑙河西部,只有三个城区位于多瑙河东。
乌尔姆(德語:Ulm,德语发音:[ˈʔʊlm] (![]() 聆聽))是德国巴登-符腾堡州的一座非县辖城市,位于多瑙河畔。它附近的大城市有东南部约70公里远的奥格斯堡和130公里远的慕尼黑和西北约100公里远的斯图加特。乌尔姆与与其隔岸相望的属于巴伐利亚州的新乌尔姆一起是这个地区的文化和商业中心,亦是科学家爱因斯坦的出生地。
聆聽))是德国巴登-符腾堡州的一座非县辖城市,位于多瑙河畔。它附近的大城市有东南部约70公里远的奥格斯堡和130公里远的慕尼黑和西北约100公里远的斯图加特。乌尔姆与与其隔岸相望的属于巴伐利亚州的新乌尔姆一起是这个地区的文化和商业中心,亦是科学家爱因斯坦的出生地。
Ulm [ʊlm] ![]()
![]() ist eine Universitätsstadt in Baden-Württemberg. Sie liegt an der Donau am südöstlichen Rand der Schwäbischen Alb an der Grenze zu Bayern. Die Stadt hat über 126.000 Einwohner (Stand Ende 2020), bildet einen eigenen Stadtkreis und ist Sitz des Landratsamts des angrenzenden Alb-Donau-Kreises. Ulm ist nach dem Landesentwicklungsplan Baden-Württemberg eines von insgesamt 14 Oberzentren des Landes und bildet mit Neu-Ulm eines der länderübergreifenden Doppelzentren Deutschlands mit ca. 190.000 Einwohnern. Ulm ist die größte Stadt im Regierungsbezirk Tübingen und in der Region Donau-Iller, zu der auch Gebiete des bayerischen Regierungsbezirks Schwaben gehören.
ist eine Universitätsstadt in Baden-Württemberg. Sie liegt an der Donau am südöstlichen Rand der Schwäbischen Alb an der Grenze zu Bayern. Die Stadt hat über 126.000 Einwohner (Stand Ende 2020), bildet einen eigenen Stadtkreis und ist Sitz des Landratsamts des angrenzenden Alb-Donau-Kreises. Ulm ist nach dem Landesentwicklungsplan Baden-Württemberg eines von insgesamt 14 Oberzentren des Landes und bildet mit Neu-Ulm eines der länderübergreifenden Doppelzentren Deutschlands mit ca. 190.000 Einwohnern. Ulm ist die größte Stadt im Regierungsbezirk Tübingen und in der Region Donau-Iller, zu der auch Gebiete des bayerischen Regierungsbezirks Schwaben gehören.
Die Stadt ist bekannt für ihr gotisches Münster, dessen Kirchturm mit 161,53 Metern der höchste der Welt ist. Weiterhin bemerkenswert ist die lange bürgerliche Tradition Ulms mit der ältesten Verfassung einer deutschen Stadt und einem Stadttheater, dessen Anfänge bis ins Jahr 1641 zurückreichen. In der Vergangenheit war Ulm Ausgangspunkt der Auswanderung der Donauschwaben, die mit sogenannten Ulmer Schachteln in ihre neuen Heimatländer im Südosten Europas fuhren.
Ulm, erstmals am 22. Juli 854 urkundlich genannt, war Königspfalz und Freie Reichsstadt, ab 1802 bayerisch, seit 1810 württembergisch, nach 1945 württemberg-badenisch und seit 1952 baden-württembergisch. Seit 1810 ist Ulm getrennt von seinem ehemaligen Gebiet rechts der Donau, das bei Bayern blieb und auf dem sich die Stadt Neu-Ulm entwickelte.
Berühmte Persönlichkeiten sind beispielsweise der in Ulm geborene Albert Einstein (1879–1955), die Widerstandskämpfer Hans (1918–1943) und Sophie Scholl (1921–1943), die ab 1932 in Ulm aufwuchsen, sowie die Schauspielerin Hildegard Knef (1925–2002), die in Ulm geboren wurde, und der deutsche Gestalter und Grafikdesigner Otl Aicher (1922–1991), der in Ulm geboren wurde und aufwuchs.

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Important port
Important port
 Architecture
Architecture
 Grand Est
Grand Est
 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel