
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


一些早期(约公元2世纪)的日耳曼语言发展出自己的卢恩字母(runic alphabet,北欧文字),但这些文字相对来说运用并不广泛。东日耳曼语支使用哥特字母,由乌斐拉主教将圣经译为哥特语时发展创立。其后,因为基督教神甫与僧侣既讲日耳曼语,也能够读说拉丁语,所以开始用稍加修饰的拉丁字母来书写日耳曼语言。
除去标准拉丁字母,各种日耳曼语言也使用一些标音符号和其他字母。其中包括元音变音(umlaut)、ß (Eszett)、 Ø、Æ、Å、Ð、Ȝ和从如尼文中继承下来的Þ及Ƿ。传统的印刷体德语经常用黑体字。
Die germanischen Sprachen sind ein Zweig der indogermanischen Sprachfamilie. Sie umfassen etwa 15 Sprachen mit rund 500 Millionen Muttersprachlern, fast 800 Millionen einschließlich der Zweitsprecher. Ein charakteristisches Phänomen aller germanischen Sprachen gegenüber den anderen indogermanischen Sprachen sind die Veränderungen im Konsonantismus durch die Germanische Lautverschiebung.
Dieser Artikel dient der Gesamtdarstellung der germanischen Sprachen. Auf Untergruppen und einzelne Sprachen und ihre Dialekte wird verwiesen. Die urgermanische Sprache wird in einem separaten Artikel behandelt.
- Englisch ist die sprecherreichste germanische Sprache mit rund 330 Millionen Muttersprachlern und mindestens 500 Millionen Zweitsprechern.
- Deutsch wird von etwa 100 Millionen Muttersprachlern und mindestens 80 Millionen Zweitsprechern gesprochen.
- Niederländisch (25 Millionen)
- Schwedisch (10 Millionen)
- Afrikaans (6,7 Millionen, mit Zweitsprechern 16 Millionen)
- Dänisch (5,5 Millionen)
- Norwegisch (5 Millionen; Bokmål und Nynorsk)
- Niederdeutsch (ca. 5 Millionen Erst- und Zweitsprecher; Stellung als eigenständige Sprache umstritten)
- Jiddisch (1,5 Millionen)
- Scots (1,5 Millionen; Stellung als eigene Sprache umstritten)
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people[nb 1] mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa.
The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360-400 million native speakers;[3][nb 2] German, with over 100 million native speakers;[4] and Dutch, with 23 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers;[5] Low German, considered a separate collection of unstandardized dialects, with roughly 0.3 million native speakers and probably 6.7-10 million people who can understand it[6][7][8] (at least 5 million in Germany[6] and 1.7 million in the Netherlands);[9] Yiddish, once used by approximately 13 million Jews in pre-World War II Europe[10] and Scots, both with 1.5 million native speakers; Limburgish varieties with roughly 1.3 million speakers along the Dutch–Belgian–German border; and the Frisian languages with over 0.5 million native speakers in the Netherlands and Germany.
The main North Germanic languages are Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian and Swedish, which have a combined total of about 20 million speakers.
The East Germanic branch included Gothic, Burgundian, and Vandalic, all of which are now extinct. The last to die off was Crimean Gothic, spoken until the late 18th century in some isolated areas of Crimea.[11]
The SIL Ethnologue lists 48 different living Germanic languages, 41 of which belong to the Western branch and six to the Northern branch; it places Riograndenser Hunsrückisch German in neither of the categories, but it is often considered a German dialect by linguists.[12] The total number of Germanic languages throughout history is unknown as some of them, especially the East Germanic languages, disappeared during or after the Migration Period. Some of the West Germanic languages also did not survive past the Migration Period, including Lombardic. As a result of World War II, the German language suffered a significant loss of Sprachraum, as well as moribundness and extinction of several of its dialects. In the 21st century, its dialects are dying out anyway[nb 3] due to Standard German gaining primacy.[13]
The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic, also known as Common Germanic, which was spoken in about the middle of the 1st millennium BC in Iron Age Scandinavia. Proto-Germanic, along with all of its descendants, is characterised by a number of unique linguistic features, most famously the consonant change known as Grimm's law. Early varieties of Germanic entered history with the Germanic tribes moving south from Scandinavia in the 2nd century BC, to settle in the area of today's northern Germany and southern Denmark.
Les langues germaniques sont une branche de la famille des langues indo-européennes qui descendent toutes du proto-germanique. L'étude de ces langues se nomme la germanistique. Elles furent d'abord parlées par les peuples germaniques, qui vivaient initialement aux frontières nord-est de l'Empire romain. Ces langues partagent plusieurs traits uniques, parmi lesquels d'importantes mutations consonantiques décrites par les lois de Grimm et de Verner (auxquelles on peut ajouter la seconde mutation consonantique pour le vieux haut-allemand), ainsi qu'un important lexique composé de radicaux non indo-européens.
Les langues germaniques les plus parlées actuellement sont celles de la branche occidentale, à savoir l'anglais, l'allemand, et le néerlandais, ainsi que les langues scandinaves, principalement le suédois, le danois et le norvégien.
Le lingue germaniche sono un gruppo linguistico appartenente alla famiglia delle lingue indoeuropee. Sono parlate dai popoli di origine germanica che si erano stabiliti nel nord Europa lungo i confini dell'Impero Romano.
Le lingue germaniche più diffuse sono l'inglese e il tedesco. Altre lingue di rilevante importanza sono l'olandese, il suo derivato afrikaans e le lingue scandinave (soprattutto danese, norvegese e svedese). Ci sono circa 53 lingue germaniche stimate dal SIL International. L'antenato di tutte è il proto-germanico.
Las lenguas germánicas son un subgrupo de la familia de lenguas indoeuropeas habladas principalmente por los pueblos germánicos. Todas las lenguas germánicas derivan de un antecesor común, el cual es tradicionalmente denominado idioma protogermánico. La primera lengua germánica documentada es el gótico (siglo IV, "Biblia de Wulfilas"), hablada por los godos y que prevaleció en la península de Crimea hasta la Edad Moderna. También muy antiguas son las inscripciones en alfabeto rúnico, grabadas en armas o joyas, que dan información sobre otros dialectos germánicos.
Las lenguas germánicas se dividen comúnmente en tres ramas: la Germánica Oriental, la Germánica Nórdica y la Germánica Occidental. Las lenguas germánicas orientales están extintas en la actualidad, y a ellas pertenecían idiomas como el gótico, el vándalo y el burgundio. En la actualidad existen el inglés, el escocés, el alemán, el bajo alemán, el sueco, el islandés, el danés, el neerlandés, el afrikáans, el noruego, el luxemburgués, el frisón, el feroés y el yidish.
El nombre de Alamannia es la latinización de una frase en alto alemán antiguo: Alle Mannen (“todos los hombres”), que engloba a todos los pueblos que habitaban esa zona en tiempos de Julio César (teutones, bucinobantes, cuados, hermiones, etc.) y fue transmitido a varias lenguas modernas, como el árabe (ألمانيا), catalán (Alemanya), galés (Yr Almaen), córnico (Almayn), francés (Allemagne), gallego (Alemaña), portugués (Alemanha), español (Alemania), y turco (Almanya), frente a los derivados del latino Germania, como el inglés (Germany). El nombre Germani es la latinización de una palabra en lenguas renanas: Germanen (“de este lado del Rin”), que fue usada por Julio César para referirse específicamente a los eburones de la Galia Bélgica (al oeste del Rin).
Герма́нские языки — ветвь индоевропейской семьи. Распространены на территории ряда стран Западной Европы (Великобритания, Германия, Австрия, Нидерланды, Бельгия, Швейцария, Люксембург, Швеция, Дания, Норвегия, Исландия, Лихтенштейн), Сев. Америки (США, Канада), юга Африки (ЮАР, Намибия), Азии (Индия), Австралии, Новой Зеландии. Общее число говорящих как на родных языках — около 550 млн чел.

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

 Energy resource
Energy resource
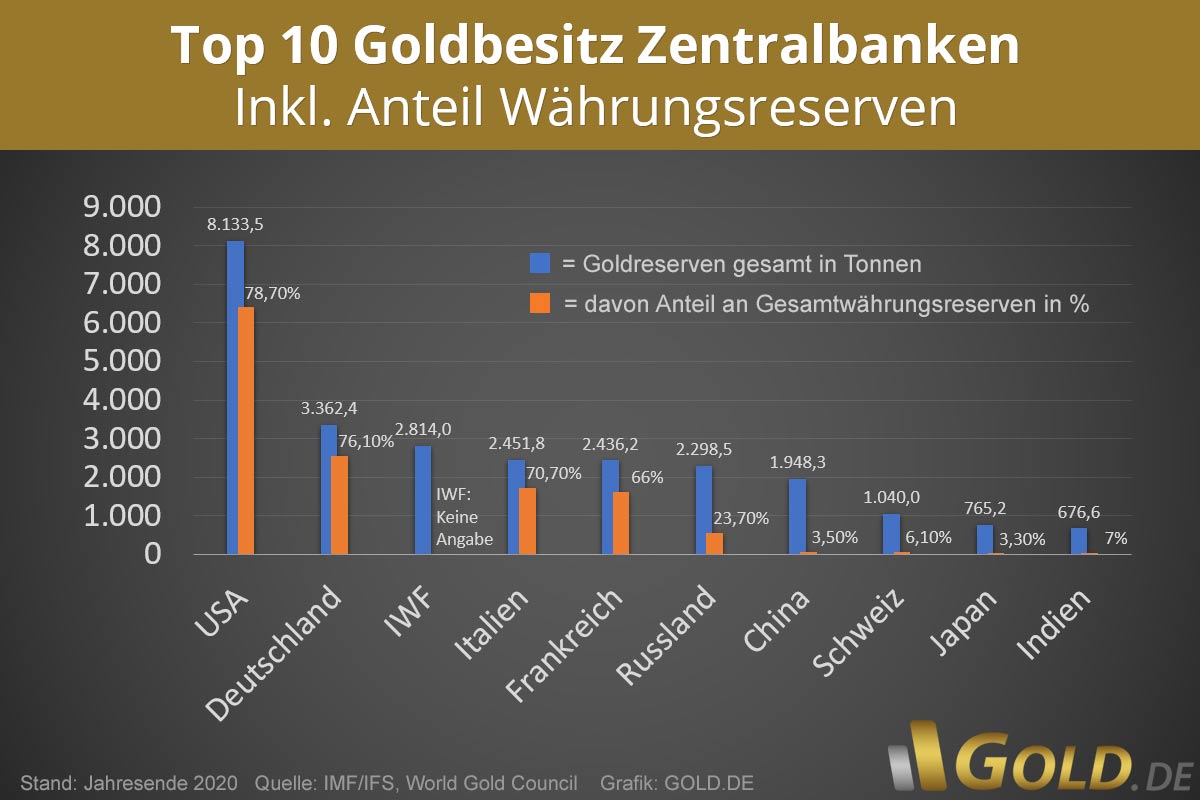
 Gold reserve
Gold reserve

 Financial
Financial

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data
 Useful info
Useful info

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade

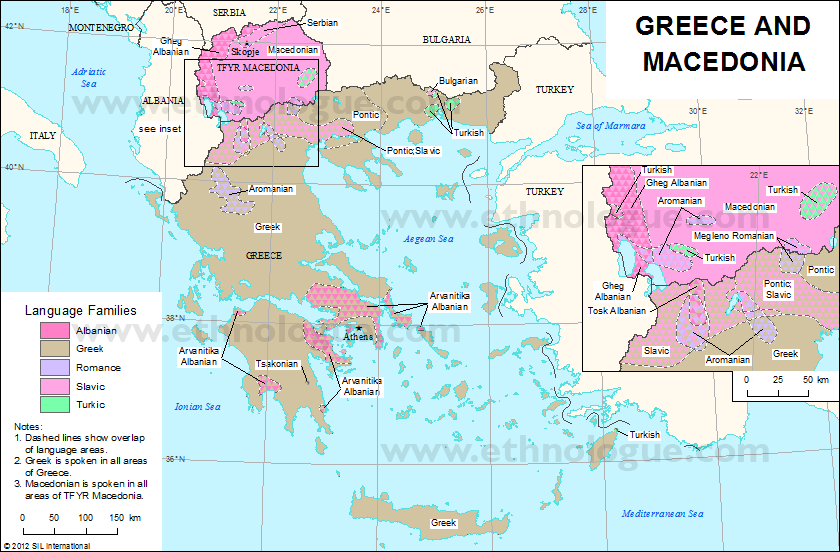
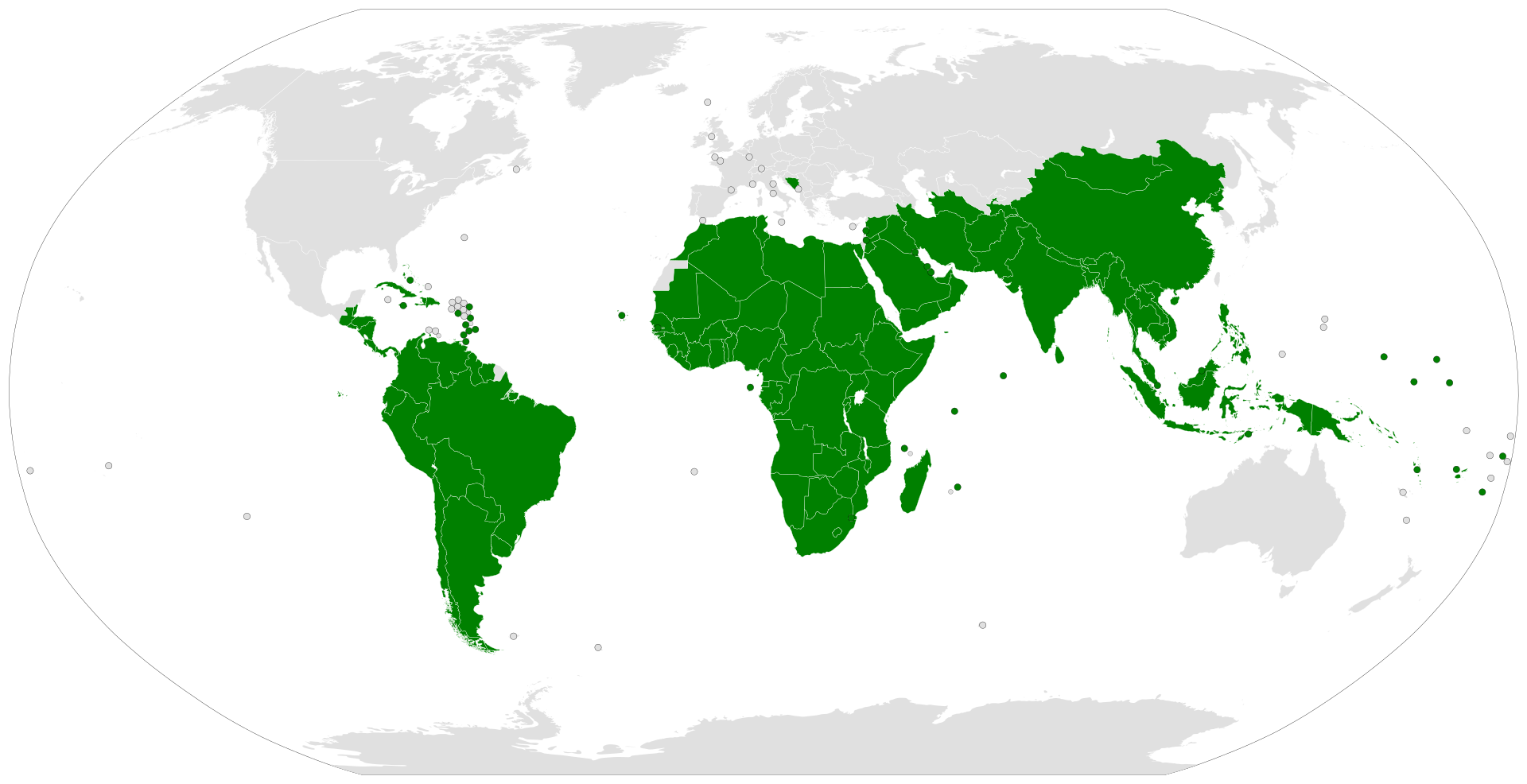




希伯来语(עִבְרִית ‘Ivrit,读音:[iv'ri:t]),属于亚非语系闪米特语族,为古代犹太民族(以色列民族或希伯来民族)一直到现代人民的民族语言、也是基督教和犹太教的宗教语言。过去2500年,希伯来语主要用于《圣经》与相关宗教方面的研究,自从20世纪特别是以色列复国以来,希伯来语作为口语在犹太人中复活,渐渐取代阿拉伯语、拉迪诺语和意第绪语,以色列复国后将希伯来语定为官方语言之一,采用希伯来字母书写;另一种官方语言是阿拉伯语(现已降级为认可的法定语言)。希伯来语亦如同其它大部分的闪语族语言般,其拼写法为横写由右到左。
Hebräisch (hebräisch עברית ‘Ivrit, ![]() moderne hebräische Aussprache?/i) gehört zur kanaanäischen Gruppe des Nordwestsemitischen und damit zur afroasiatischen Sprachfamilie, auch semitisch-hamitische Sprachfamilie genannt.
moderne hebräische Aussprache?/i) gehört zur kanaanäischen Gruppe des Nordwestsemitischen und damit zur afroasiatischen Sprachfamilie, auch semitisch-hamitische Sprachfamilie genannt.
Die Basis aller späteren Entwicklungsformen des Hebräischen ist die Sprache der heiligen Schrift der Juden, der hebräischen Bibel, deren Quellschriften im Laufe des 1. Jahrtausends v. Chr. entstanden und kontinuierlich redigiert und erweitert und schließlich um die Zeitenwende kodifiziert wurden. (Alt-)Hebräisch wird daher oft mit dem Begriff „Biblisch-Hebräisch“ gleichgesetzt, selbst wenn dies weniger sprachhistorisch als literaturhistorisch begründet ist: Althebräisch als die Sprache des größten Teiles des Alten Testamentes. In der Bibel wird die Sprache שְׂפַת כְּנַעַן sefat kena‘an („Sprache Kanaans“, Jes 19,18) oder יהודית jehudit („jüdisch“, „judäisch“; Jes 36,11 2Kö 18,26+28 2Chr 32,18 Neh 13,24) genannt. Nach der Zerstörung des Jerusalemer Tempels durch Nebukadnezar II. im Jahre 586 v. Chr. und dem darauf folgenden Babylonischen Exil kam die dortige Amtssprache Aramäisch unter den Juden in Umlauf, sodass das Hebräische fortan in Konkurrenz zum Aramäischen stand und viele Einflüsse von ihm aufnahm.
Nach der Zerstörung des Zweiten Tempels zu Jerusalem im Jahre 70 n. Chr. verlagerte sich das Zentrum jüdischen Lebens von Judäa nach Galiläa und ins Exil. Etwa ab dem Jahre 200 hörte Hebräisch auf, Alltagssprache zu sein. Es blieb indessen eine Sakralsprache, wurde jedoch nie ausschließlich zu liturgischen Zwecken benutzt, sondern auch zur Abfassung von philosophischen, medizinischen, juristischen und poetischen Texten, sodass sich das Vokabular des Mittelhebräischen im Laufe der Jahrhunderte erweitern konnte. Es ist ebenfalls bezeugt, dass sich die verstreuten jüdischen Gemeinden zur Verständigung untereinander des Hebräischen bedienten.
Die Erneuerung des Hebräischen mit dem Ziel seiner Etablierung als jüdische Nationalsprache in Palästina begann im späten 19. Jahrhundert auf Initiative von Elieser Ben-Jehuda. 1889 gründete er in Jerusalem den „Rat der hebräischen Sprache“, den Vorläufer der Akademie für die hebräische Sprache, mit dem Ziel, die seit etwa 1700 Jahren kaum noch gesprochene Sprache der Bibel wiederzubeleben. In der Folgezeit entstand das moderne Hebräisch (auf Deutsch oft als Ivrit bezeichnet), dessen Unterschiede zum biblischen Hebräisch im Schriftbild und der Morphologie äußerst gering, in der Syntax und dem Vokabular zum Teil gravierend sind.

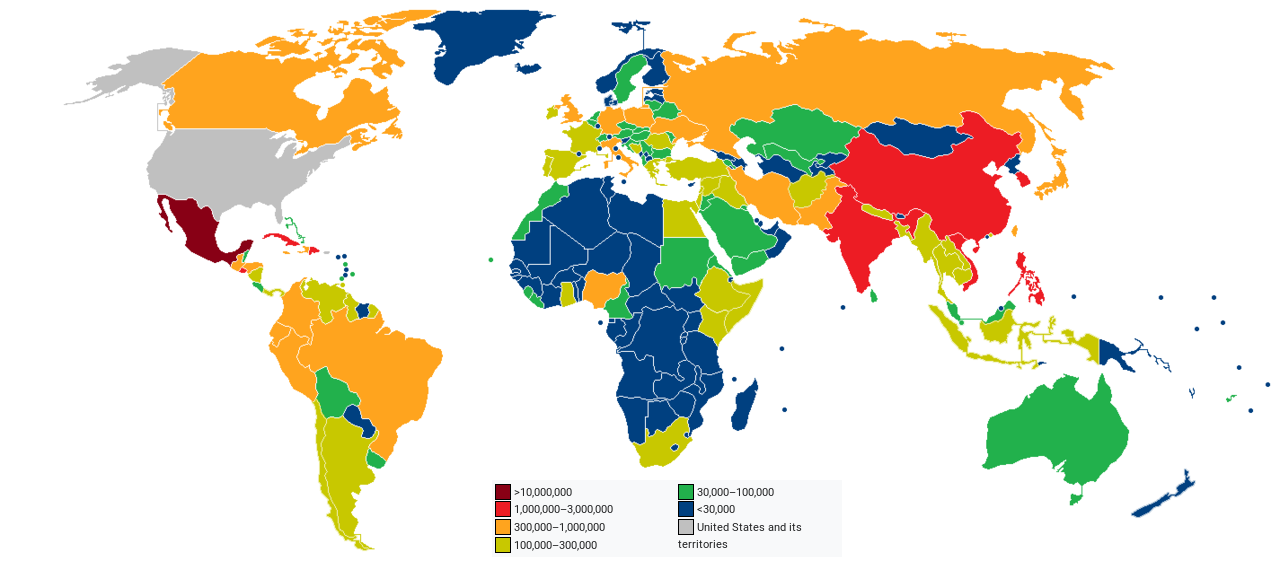
| Country of birth | Population (2019) | 2018–2019 change |
|---|---|---|
| Total foreign-born | +204,297 | |
| -239,954 | ||
| +35,222 | ||
| +28,287 | ||
| +31,492 | ||
| -7,229 | ||
| +38,026 | ||
| +16,030 | ||
| -8,444 | ||
| -214 | ||
| +104,508 | ||
| +18,587 | ||
| -16,506 |
 Geography
Geography
 Literature
Literature
 United Nations
United Nations
 History
History
 Art
Art
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Party and government
Party and government
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Religion
Religion