
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
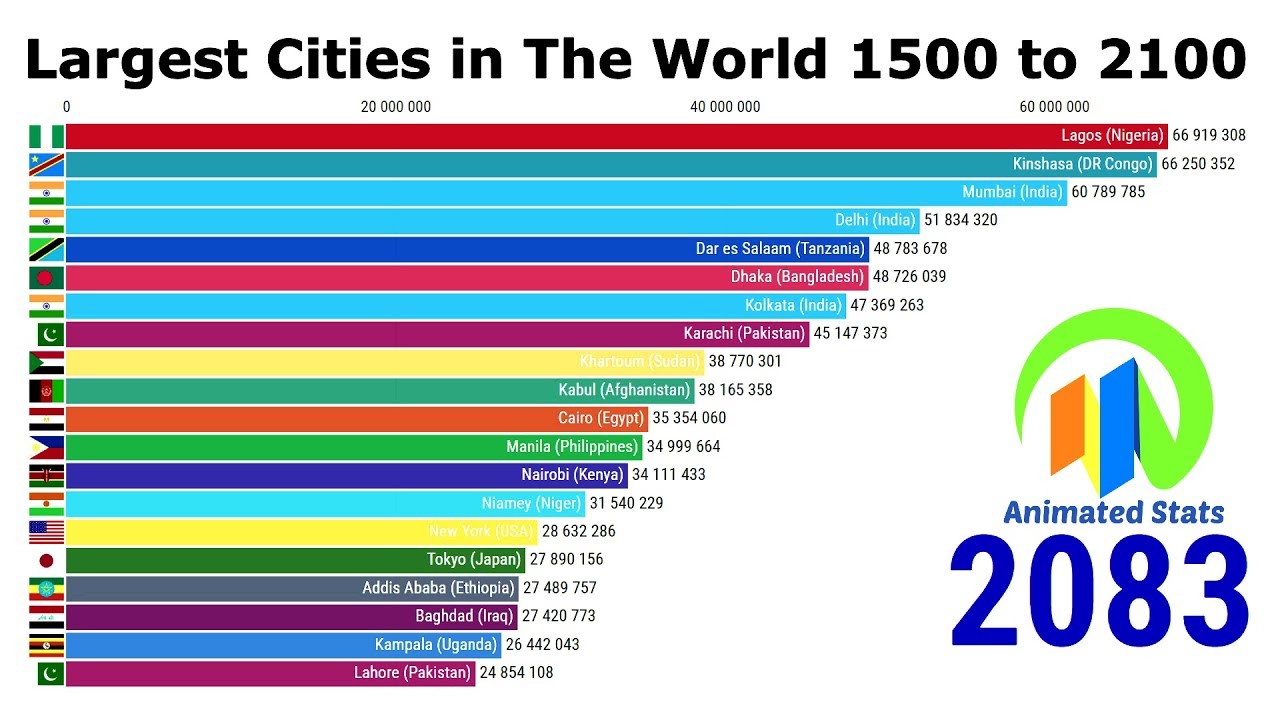
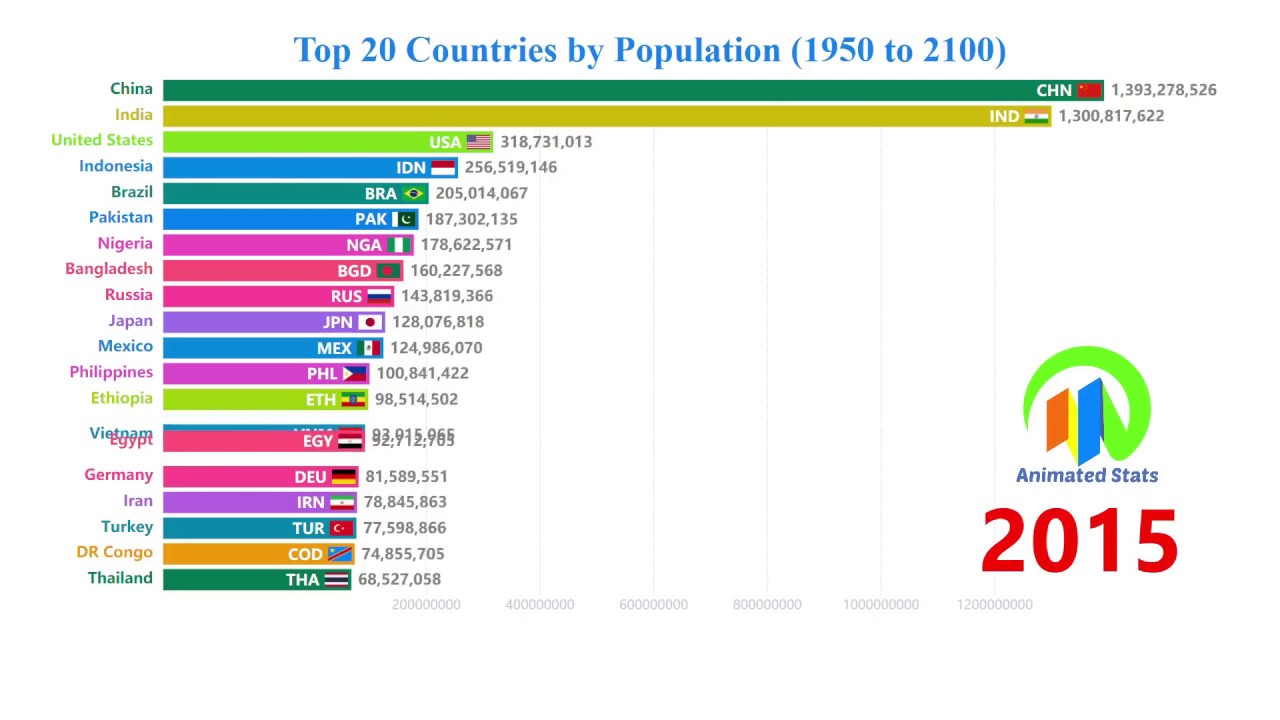
%20History%201800-2040.jpg)

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade







土耳其语(Türkçe;[ˈtyɾctʃe] (![]() 聆听) ),是一种现有7300万到8700万人使用的语言,属突厥语族,主要在土耳其本土使用,并通行于阿塞拜疆、塞浦路斯、希腊、北马其顿、罗马尼亚、乌孜别克和土库曼斯坦,以及在西欧居住的数百万土耳其裔移民(主要集中在德国)。土耳其语是突厥语族诸语中使用人数最多的语言。
聆听) ),是一种现有7300万到8700万人使用的语言,属突厥语族,主要在土耳其本土使用,并通行于阿塞拜疆、塞浦路斯、希腊、北马其顿、罗马尼亚、乌孜别克和土库曼斯坦,以及在西欧居住的数百万土耳其裔移民(主要集中在德国)。土耳其语是突厥语族诸语中使用人数最多的语言。
土耳其语起源于中亚,其最早期的文字纪录可上溯至1200年前。随着奥斯曼帝国扩张,今日土耳其语的先驱奥斯曼土耳其语的影响力亦一同往西扩张。早期的土耳其语文字采用阿拉伯字母纪录,但在1928年,土耳其国父穆斯塔法·凯末尔·阿塔土克建立共和国后着手改革国家的语言,用以标志新国家与旧有奥斯曼帝国的分别,于是改用拉丁字母,直至现今。伴随这个改革的,还包括在新国语中去除旧有从波斯语及阿拉伯语借用的词汇,改为从土耳其语原有的字根去重新组合出有关借词所代表的意思。
土耳其语一个显著的特色,其元音和谐及大量胶着语的词缀变化,句法采用主宾动词序。土耳其语有着极严谨的尊称和敬语体系,但是词汇中没有名词类别和语法性别。
Die türkische Sprache – auch Türkeitürkisch oder Osmanisch-Türkisch[1] – ist eine agglutinierende Sprache und gehört zum oghusischen Zweig der Turksprachen. Als meistgesprochene Turksprache ist sie die Amtssprache in der Türkei und neben dem Griechischen auch auf Zypern (sowie in der international nicht anerkannten Türkischen Republik Nordzypern). Außerdem wird das Türkische als lokale Amtssprache in Nordmazedonien, Rumänien und im Kosovo verwendet. Eigenbezeichnungen sind Türk dili, Türkçe [tyɾkt͡ʃe] und Türkiye Türkçesi.
Die türkische Sprache selbst weist eine Reihe von Dialekten auf, von denen der Istanbuler Dialekt von besonderer Bedeutung ist. Seine Phonetik ist die Basis der heutigen türkischen Hochsprache.[2] Bei der Einführung des lateinischen Alphabets für die türkische Sprache im Jahr 1928 wurde nicht auf die historische Orthographie des Osmanisch-Türkischen zurückgegriffen, sondern die Aussprache von Istanbul als Grundlage der Verschriftung herangezogen[3]. Die Dialekte innerhalb der Türkei werden in Gruppen der Schwarzmeerregion (Karadeniz Şivesi), Ostanatolien (Doğu Anadolu Şivesi), Südostanatolien (Güneydoğu Anadolu Şivesi), Zentralanatolien (İç Anadolu Şivesi), Ägäis (Ege Şivesi) und Mittelmeerregion (Akdeniz Şivesi) eingeteilt.
Die Alternativbenennung „Türkeitürkisch“ umfasst aber nicht nur die Türkei, sondern auch alle Gebiete des ehemaligen Osmanischen Reichs. Das bedeutet, dass auch die Balkan- oder Zyperntürken ein „Türkeitürkisch“ sprechen.[4]
トルコ語(トルコご、Türkçe)は、アゼルバイジャン語やトルクメン語と同じテュルク諸語の南西語群(オグズ語群)に属する言語。
テュルク諸語のうち最大の話者数をもつ。トルコ語の話者が最も多いのはトルコ共和国であり、人口の約3分の2を占めるトルコ人の母語であるほか、公用語ともなっているため約7500万人のトルコ国民のほとんどはトルコ語を話すことができる[4]。キプロス共和国もギリシャ語と並んでトルコ語を公用語としている[5]が、実際にはキプロス紛争の結果1974年に国が南北に分断され、南部のみを領するようになったキプロス共和国内にはほぼトルコ人が存在しなくなったため、名目のみの公用語となっている。逆に島の北部を領有している北キプロス・トルコ共和国は約33万人の国民のほとんどをトルコ人が占めるようになったため、トルコ語が唯一の公用語となっている。
このほか、ブルガリアに約100万人[4]、ギリシャに約15万人、そのほかマケドニア共和国やコソボにも母語話者がいる。ドイツ・オーストリア・スイス・リヒテンシュタインなど西ヨーロッパ東部〜中央ヨーロッパのトルコ系移民社会(250万人以上)でも話されているが、現地で生まれてトルコ語が満足に話せない若者も増えている[4]。
アラビア語・ペルシア語からの借用語が極めて多い他、日常語にはブルガリア語・ギリシャ語など周辺の言語からの借用語も多く、近代に入った外来語にはフランス語からのものが多い。
主に中央アジア・トルキスタンを中心に広がるトルクメン語・カザフ語・キルギス語・ウイグル語などのテュルク諸語とは近縁関係にあり、中でも同じオグズ語群に属するアゼルバイジャン語とはかなりの部分相互理解が可能である[6]。
Turkish (Türkçe (![]() listen), Türk dili), also referred to as Istanbul Turkish[8][9][10] (İstanbul Türkçesi) or Turkey Turkish (Türkiye Türkçesi), is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 70 to 80 million speakers, the national language of Turkey. Outside its native country, significant smaller groups of speakers exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia,[11] Northern Cyprus,[12] Greece,[13] the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested that the European Union add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state.[14]
listen), Türk dili), also referred to as Istanbul Turkish[8][9][10] (İstanbul Türkçesi) or Turkey Turkish (Türkiye Türkçesi), is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 70 to 80 million speakers, the national language of Turkey. Outside its native country, significant smaller groups of speakers exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia,[11] Northern Cyprus,[12] Greece,[13] the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested that the European Union add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state.[14]
To the west, the influence of Ottoman Turkish—the variety of the Turkish language that was used as the administrative and literary language of the Ottoman Empire—spread as the Ottoman Empire expanded. In 1928, as one of Atatürk's Reforms in the early years of the Republic of Turkey, the Ottoman Turkish alphabet was replaced with a Latin alphabet.
The distinctive characteristics of the Turkish language are vowel harmony and extensive agglutination. The basic word order of Turkish is subject–object–verb. Turkish has no noun classes or grammatical gender. The language makes usage of honorifics and has a strong T–V distinction which distinguishes varying levels of politeness, social distance, age, courtesy or familiarity toward the addressee. The plural second-person pronoun and verb forms are used referring to a single person out of respect.
Le turc (autonyme : Türkçe ou Türk Dili) est une langue parlée principalement en Turquie et en Chypre du Nord. Il appartient à la famille des langues turques. Bien que les langues d'autres pays turcophones, principalement des républiques de l'ancienne URSS, soient proches du turc (surtout l'azéri et le turkmène), il existe d'importantes différences phonologiques, grammaticales ou lexicales entre ces langues.
Au-delà de la Turquie elle-même, le turc est utilisé dans l'ancien territoire de l'Empire ottoman par des populations d'origine ottomane, turcique ou des populations musulmanes qui ont adopté cette langue. Ces turcophones sont nombreux en Bulgarie, en Grèce (concentrés en Thrace occidentale), dans les Balkans (Bosnie-Herzégovine et Kosovo), dans la partie nord de l'île de Chypre (République turque de Chypre du Nord), dans le nord de l'Irak (surtout à Kirkouk), en Macédoine et en Roumanie (essentiellement en Dobroudja). C'est pourquoi le turc de Turquie est aussi nommé « turc osmanlı » (Osmanlı Türkçesi).
Le turc est, typologiquement, une langue agglutinante. Elle utilise principalement des suffixes et peu de préfixes. C'est une langue SOV (sujet-objet-verbe). Elle comporte un système d'harmonie vocalique.
La lingua turca (nome nativo Türkçe o Türk dili, Türkiye Türkçesi) è una lingua appartenente al ceppo Oghuz delle lingue turche, con circa 85 milioni di madrelingua[1] in Turchia, a Cipro, in Germania e sparsi per il mondo. Il turco era parlato nell'Impero ottomano usando, per la forma scritta, una versione modificata dell'alfabeto arabo. Nel 1928 Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, nei suoi sforzi per modernizzare la Turchia, rimpiazzò l'alfabeto arabo con una versione modificata dell'alfabeto latino. Ora il turco è regolato dall'Organizzazione linguistica turca. Il turco è parlato in Turchia e da minoranze di 35 altri paesi. È usato in stati come l'Azerbaijan, la Bulgaria, la Grecia, la parte settentrionale di Cipro, occupata dalla Turchia fin dal 1974, la Macedonia del Nord, il Kosovo e l'Uzbekistan.
El idioma turco (![]() Türkçe (?·i) o Türk dili) pertenece a la familia lingüística de las lenguas túrquicas, cuya área geográfica se extiende desde el occidente de China hasta los Balcanes. Las lenguas más próximas al turco son el azerí, el gagauzo y el turcomano.
Türkçe (?·i) o Türk dili) pertenece a la familia lingüística de las lenguas túrquicas, cuya área geográfica se extiende desde el occidente de China hasta los Balcanes. Las lenguas más próximas al turco son el azerí, el gagauzo y el turcomano.
Es oficial en Turquía, donde se habla desde la época medieval, cuando los turcos procedentes de Asia Central se instalaron en Anatolia, que entonces era parte del Imperio bizantino. Es oficial también en Chipre, donde comparte cooficialidad con el griego, así como en la autoproclamada República Turca del Norte de Chipre. En algunas zonas balcánicas se habla una variedad conocida como turco otomano (Osmanlı Türkçesi), que tiene diferencias con el turco de Turquía. En varios países de la Europa occidental existen importantes comunidades de hablantes de turco, emigradas de Turquía en fechas recientes.
Es una lengua aglutinante, como lo son el quechua, el finés, el japonés o el vasco, y por tanto se basa en un sistema de afijos añadidos a la raíz de las palabras que permiten expresar gran cantidad de significados con pocas palabras. El turco usa casi exclusivamente sufijos. Su morfología no suele tener excepciones y es altamente regular. Otras importantes características son la ausencia del género gramatical, el orden sintáctico es SOV, que es una lengua de núcleo final y que usa postposiciones.
Ha tenido varios sistemas de escritura. Se escribió con caracteres árabes (alfabeto turco otomano) adaptados desde el siglo XIII hasta la reforma ortográfica emprendida en los años 1920 por el gobierno de Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, que emprendió varias iniciativas de occidentalización del país para contribuir a su modernización. La reforma ortográfica vino acompañada de un intento de "depuración" nacionalista, es decir, de sustituir la ingente cantidad de préstamos lingüísticos (sobre todo árabes) por vocablos de raíz turca, objetivo vigente hoy en día que no ha cosechado los éxitos esperados.[cita requerida]
Está regulada por la Türk Dil Kurumu (TDK), la Sociedad de la Lengua Turca.
Туре́цкий язы́к (самоназвание: Türk dili (кратко: Türkçe [ˈt̪yɾktʃe] ![]() слушать), рус. историч. турской языкъ) — официальный язык Турции, входящий в тюркскую языковую семью. В качестве альтернативного названия в тюркологии используется также Türkiye Türkçesi («турецкий тюркский»).
слушать), рус. историч. турской языкъ) — официальный язык Турции, входящий в тюркскую языковую семью. В качестве альтернативного названия в тюркологии используется также Türkiye Türkçesi («турецкий тюркский»).
Современный турецкий язык относится к юго-западной (или западно-огузской) подгруппе тюркских языков. Языками, наиболее близкими к турецкому в лексическом, фонетическом и синтаксическом отношении, являются прежде всего балкано-тюркский язык гагаузов, распространённый на территории современных Молдавии, Румынии и Болгарии (собственно гагаузский и балкано-гагаузский), и южный диалект крымскотатарского языка. Чуть далее отстоит от литературного турецкого азербайджанский[3][страница не указана 536 дней] (сохранивший немало архаизмов и персидских заимствований и образующий с восточно-анатолийскими диалектами турецкого языка диалектный континуум) и, ввиду ряда фонетических и некоторых грамматических отличий, туркменский язык. Турецкий язык и в особенности его северо-западные диалекты, и гагаузский — оба сближаются с печенежским языком: ср. переходы в печенежском языке g/k > y в конце слов (beg > bey), k/g > в v интервокальной позиции (между гласными, напр., kökerçi > küverçi), t > d в начале слов (tağ > dağ), с полной аналогией в турецком и гагаузском языках: bey, güvercin, dağ/daa.
俄语(俄语:ру́сский язы́к,罗马化:russkij jazyk,发音[ˈruskʲɪj jɪˈzɨk])属于斯拉夫语族的东斯拉夫语支,是斯拉夫语族中使用人数最多的语言,是俄罗斯、白俄罗斯、吉尔吉斯斯坦及哈萨克斯坦的官方语言,主要在俄罗斯等前苏联加盟共和国中使用,且在华约的成员国里曾经被学校广泛列为第一外语教学。在苏联时代,苏联加盟共和国和自治共和国非常强调俄语的重要性。虽然很多这些苏联的加盟共和国现在开始强调使用当地语言的重要性,部分国家俄语不再是官方语言,但是俄语仍然是这些地区当前最广泛使用的共通语言。俄语属于印欧语系,是东斯拉夫语支中三个目前仍在使用的语言之一。目前发现最早的老东斯拉夫语文字是在第十世纪的内容。
俄语是欧亚大陆中分布区域最广的语言,也是斯拉夫语中最多人使用的语言。俄语也是欧洲最多人使用的母语,是俄罗斯、白俄罗斯、乌克兰1.44亿人的母语。俄语是母语人口排名的第八名,是以人口排列的语言列表中的第七名[3]。俄语是联合国的六种官方语言之一。

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data
 Useful info
Useful info

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade


 Geography
Geography
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Literature
Literature
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand


 Aerospace
Aerospace