
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Woman
4x400 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Men
4x400 m Men
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Men
4x100 m Men
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *United States presidential election
*United States presidential election
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries

 Geography
Geography

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP1
TOP1
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2017 London
2017 London
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2015 Beijing
2015 Beijing
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2013 Moskau
2013 Moskau
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2009 Berlin
2009 Berlin
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2007 Osaka
2007 Osaka
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2011 Daegu
2011 Daegu
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2003 Saint-Denis
2003 Saint-Denis
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1997 Athens
1997 Athens
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1995 Gothenburg
1995 Gothenburg
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1993 Stuttgart
1993 Stuttgart
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1991 Tokyo
1991 Tokyo
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1987 Rome
1987 Rome
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1983 Helsinki
1983 Helsinki




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of Seven,G7
Group of Seven,G7
 United States
United States

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

美国是一个高度发达的资本主义国家,其政治、教育、经济、军事、文化、创新等实力领衔全球。作为世界第一军事大国,其高等教育水平和科研技术水平以及航空航天技术方面,也是当之无愧的世界第一,其科研经费投入之大、研究型高校企业之多、科研成果之丰富堪称世界典范。同时,美国还拥有苹果、微软、戴尔、惠普、波音等一系列世界著名企业。
美利坚合众国(英语:United States of America,缩写为 U.S.A.、通称为 United States、缩写为U.S.、或America、The States),中文通称美国,是由其下辖50个州、华盛顿哥伦比亚特区、五个自治领土及外岛共同组成的联邦共和国[注 1]。美国本土48州和联邦特区位于北美洲中部,东临大西洋,西临太平洋,北面是加拿大,南部和墨西哥及墨西哥湾接壤,本土位于温带、副热带地区。阿拉斯加州位于北美大陆西北方,东部为加拿大,西隔白令海峡和俄罗斯相望;夏威夷州则是太平洋中部的群岛。美国在加勒比海和太平洋还拥有多处境外领土和岛屿地区。此外,美国还在全球140多个国家和地区拥有着374个海外军事基地。
美国拥有982万平方公里国土面积,位居世界第三(依陆地面积定义为第四大国);同时拥有接近超过3.3亿人口,为世界第三人口大国。因为有着来自世界各地的大量移民,它是世界上民族和文化最多元的国家之一[14]。美国地形与气候复杂多样,是多种野生动物的家园[15]。
一万五千多年前,古印第安人自亚洲迁徙至北美大陆[16]。16世纪欧洲开始殖民北美。现今的合众国起始于东海岸的13个英属美洲殖民地。欧洲七年战争后,大不列颠王国与其殖民地之间的争议愈发剧烈,最终导致在1775年爆发美国革命。1776年7月4日,正与大不列颠进行独立战争的各殖民地派出代表,协同一致发表《独立宣言》。战争终止于1783年,大不列颠王国承认这13个北美殖民地脱离管辖而独立,与其签订《巴黎条约》。这场战争也是第一场成功脱离欧洲殖民帝国的独立战争[17]。1781年,《邦联条例》在邦联13个构成州获得通过,共同组成了邦联议会。1787年《美利坚合众国宪法》完稿,将“美利坚合众国”改制为联邦体制,联邦政府随之成立。1791年,合称为权利法案的十条宪法修正案获得批准,担保了基本民权。
美国自19世纪开始在北美通过强行移置原住民,征服及购买等方法大力扩张领土,随着逐渐不断地承认扩张领地为新州份,至1848年美国疆域已横跨整个北美大陆[18]。19世纪下半叶爆发的内战,使曾经合法的奴隶制度得以终结[19][20]。在19世纪末,美国已将其领土延伸到太平洋的夏威夷。美国经济在工业革命的推动下,自那时起也开始蓬勃发展[21]。随后美西战争的胜利,使美国势力进入加勒比海地区及太平洋西部;而参与第一次世界大战则奠定其作为一个全球性军事力量的地位。尽管在1930年代经历经济大萧条,美国在第二次世界大战获得胜利之后崛起成为超级大国。作为联合国安全理事会常任理事国,美国是世界上第一个研发出核武器,也是唯一一个曾将其投入实战的国家。战后美国与苏联进行了数十年冷战,顶峰时期的太空竞赛促使了人类第一次登月计划的成功。在1991年苏联解体后,美国成为世上唯一超级强国[22]。
美国作为一个高度发达国家,是世界上最大的进口国及第二大的商品出口国,国内生产总值按国际汇率排名世界第一、而依购买力平均则位列第二。在国民平均薪资[23]、人类发展指数、人均国内生产总值以及人均生产力[24]等社会经济学表现指标上,美国均处于世界领先地位。美国经济已步入后工业时代,服务行业占据经济主导地位,位列世界第一。同时,其生产制造业规模也极为庞大,位居于世界第二[25]。仅占据全世界4.4%人口的美国[26],贡献了世界四分之一的国内生产总值和三分之一的全球军事开支[27],这使其在经济和军事上均处于全世界最重要的地位。美国在政治和文化上是一支世界显著并影响深远的力量,也在科学研究和技术创新上占据世界领导地位[28]。美国是联合国、世界银行、国际货币基金组织、美洲国家组织等的创始成员国。
Die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika (englisch United States of America; abgekürzt USA), kurz auch Vereinigte Staaten (englisch United States, abgekürzt U.S., US) genannt und häufig auch umgangssprachlich verkürzt zu Amerika (englisch America), sind eine föderale Republik. Diese besteht aus 50 Bundesstaaten, einem Bundesdistrikt (der Hauptstadt Washington, D.C.), fünf größeren Territorien und etlichen Inselterritorien. Die 48 zusammenhängenden Continental United States (häufig Lower 48 genannt) sowie Alaska liegen in Nordamerika, während Hawaii und kleinere Außengebiete im Pazifik beziehungsweise in der Karibik liegen. Das Land weist eine sehr hohe geographische und klimatische Diversität mit einer großen Vielfalt an Tier- und Pflanzenarten auf.
Die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika sind der drittgrößte Staat der Erde, gemessen an der Fläche von 9,83 Millionen Quadratkilometern[3] (nach Russland und Kanada) und gemessen an der Bevölkerung von etwa 328 Millionen Einwohnern (nach China und Indien). Die nach Einwohnerzahl größte Stadt ist New York City, bedeutende Metropolregionen sind Los Angeles, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Philadelphia, Washington, Miami, Atlanta, Boston und San Francisco, mit jeweils über 5 Millionen Einwohnern. Der Grad der Urbanisierung liegt bei 81,96 Prozent (Stand: 2015).[9]
Bedingt durch die Einwanderung aus einer Vielzahl von Ländern sind die Vereinigten Staaten eines der ethnisch multikulturellsten Länder. Anders als in 32 Bundesstaaten gibt es auf Bundesebene keine gesetzliche Amtssprache, jedoch herrscht Englisch als De-Facto-Amtssprache vor. Im Südwesten sowie in Miami ist zusätzlich die spanische Sprache weit verbreitet. Insgesamt waren 2015 mehr als 350 Sprachen in heimischem Gebrauch, davon allein 150 indigene. Darunter waren als größte die der Yupik in Alaska, der Dakota aus der Sioux-Sprachfamilie sowie die Sprache der Apachen in Gebrauch, dann Keres, die Sprache der Pueblo-Indianer, und Cherokee.[10]
Paläoindianer wanderten vor mehr als 13.000 Jahren aus Asien in das nordamerikanische Festland der heutigen Vereinigten Staaten ein (Buttermilk Creek Complex), nachdem sie mehrere Jahrtausende zuvor das heute zu den USA gehörende Alaska besiedelt hatten. Die europäische Kolonisierung begann etwa um 1600 vorwiegend aus England, allerdings in langwieriger Auseinandersetzung mit Frankreich. Die Vereinigten Staaten gingen aus den 13 Kolonien an der Atlantikküste hervor. Streit zwischen Großbritannien und den amerikanischen Kolonien führte zur Amerikanischen Revolution. Am 4. Juli 1776 verabschiedeten Delegierte der 13 Kolonien die Unabhängigkeitserklärung der Vereinigten Staaten und somit die Gründung der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Der Amerikanische Unabhängigkeitskrieg, der mit der Anerkennung der Unabhängigkeit endete, war der erste erfolgreiche Unabhängigkeitskrieg gegen eine europäische Kolonialmacht. Die heutige Verfassung wurde am 17. September 1787 verabschiedet. Bisher wurden 27 Zusatzartikel ergänzt. Die ersten zehn Zusatzartikel, die gemeinsam als Bill of Rights bezeichnet werden, wurden 1791 ratifiziert und garantieren eine Vielzahl von unveräußerlichen Rechten.
Angetrieben von der Doktrin Manifest Destiny begannen die Vereinigten Staaten eine Expansion über Nordamerika, die sich über das 19. Jahrhundert erstreckte. Dies schloss die gewaltsame Vertreibung indigener indianischer Stämme, den Erwerb neuer Territorien u. a. im Mexikanisch-Amerikanischen Krieg und die Gründung neuer Bundesstaaten ein. Der Amerikanische Bürgerkrieg führte 1865 zum Ende der legalen Sklaverei in den Vereinigten Staaten. Zum Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts erreichten der Staat eine Ausdehnung bis zum Pazifik, ihre Wirtschaft wurde zur größten weltweit. Der Spanisch-Amerikanische Krieg und der Erste Weltkrieg bestätigten die Rolle der Vereinigten Staaten als globale Militärmacht. Aus dem Zweiten Weltkrieg gingen die USA als Supermacht und als erstes Land mit Atomwaffen hervor und wurden eines von fünf ständigen Mitgliedern im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen. Nach Ende des Kalten Krieges und dem Zerfall der Sowjetunion sind die USA die einzige verbliebene Supermacht. Sie sind Gründungsmitglied der Vereinten Nationen, der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten (OAS) und vieler weiterer internationaler Organisationen. Ihr politischer und kultureller Einfluss ist weltweit groß.
Die Vereinigten Staaten sind ein industrialisierter Staat und die größte Volkswirtschaft mit einem Bruttoinlandsprodukt in Höhe von 18,5 Billionen US-Dollar im Jahr 2016, was 25 % der nominellen oder 17 % der kaufkraftbereinigten globalen Wirtschaftsleistung entsprach.[7] Das Land hatte 2016 das achthöchste Pro-Kopf-Einkommen. Laut der Weltbank ist die Einkommensungleichverteilung in den Vereinigten Staaten eine der höchsten unter den OECD-Staaten.[11] Die Wirtschaftsleistung des Landes wird durch den Reichtum an natürlichen Ressourcen, eine gut entwickelte Infrastruktur und eine hohe durchschnittliche Produktivität begünstigt.[12][13] Obwohl die Wirtschaftsstruktur gemeinhin als postindustriell angesehen wird, ist das Land nach wie vor einer der weltgrößten Güterproduzenten.[14] Das Land war 2016 für 36 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit auf Platz 1, gefolgt von China mit 13 % und Russland mit 4,1 %.[15] Der in Folge der Terroranschläge am 11. September 2001 ausgerufene Ausnahmezustand ist seit 2001 in Kraft.[16]
アメリカ合衆国(アメリカがっしゅうこく、英語: United States of America)、通称アメリカ、米国(べいこく)は、50の州および連邦区から成る連邦共和国である[6][7]。
アメリカ本土の48州および同国首都ワシントンD.C.(コロンビア特別区)は、カナダとメキシコの間の北アメリカ中央に位置する。
アラスカ州は北アメリカ北西部の角に位置し、東ではカナダと、西ではベーリング海峡をはさんでロシアと国境を接している。ハワイ州は中部太平洋における島嶼群である。
同国は、太平洋およびカリブに5つの有人の海外領土および9つの無人の海外領土を有する。985万平方キロメートル (km2) の総面積は世界第3位または第4位、3億1千7百万人の人口は世界第3位である。
同国は世界で最も民族的に多様かつ多文化な国の1つであり、これは多数の国からの大規模な移住の産物とされている[8]。
また同国の広大な国土における地理および気候も極めて多様であり、多種多様な野生生物が存在する。
米国は先進国かつ世界最大級の国民経済を有する[9]。同国経済は、豊富な天然資源と高度な労働者の生産性により支えられている[10]。同国経済は脱工業化社会だとされている一方、世界最大の製造国のうちの1つであり続けている[11]。同国は世界の軍事支出の37%を占め[12]、世界最高位の経済・軍事大国であり、多大な影響を及ぼす政治・文化的勢力であり、科学研究・技術革新におけるリーダー的存在とされている[13]。
The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions.[f] At 3.8 million square miles (9.8 million km2), the United States is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area[g] and is slightly smaller than the entire continent of Europe's 3.9 million square miles (10.1 million km2). With a population of over 327 million people, the U.S. is the third most populous country. The capital is Washington, D.C., and the largest city by population is New York. Forty-eight states and the capital's federal district are contiguous in North America between Canada and Mexico. The State of Alaska is in the northwest corner of North America, bordered by Canada to the east and across the Bering Strait from Russia to the west. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The U.S. territories are scattered about the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, stretching across nine official time zones. The extremely diverse geography, climate, and wildlife of the United States make it one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.[19]
Paleo-Indians migrated from Siberia to the North American mainland at least 12,000 years ago.[20] European colonization began in the 16th century. The United States emerged from the thirteen British colonies established along the East Coast. Numerous disputes between Great Britain and the colonies following the French and Indian War led to the American Revolution, which began in 1775, and the subsequent Declaration of Independence in 1776. The war ended in 1783 with the United States becoming the first country to gain independence from a European power.[21] The current constitution was adopted in 1788, with the first ten amendments, collectively named the Bill of Rights, being ratified in 1791 to guarantee many fundamental civil liberties. The United States embarked on a vigorous expansion across North America throughout the 19th century, acquiring new territories,[22] displacing Native American tribes, and gradually admitting new states until it spanned the continent by 1848.[22]
During the second half of the 19th century, the Civil War led to the abolition of slavery.[23][24] By the end of the century, the United States had extended into the Pacific Ocean,[25] and its economy, driven in large part by the Industrial Revolution, began to soar.[26] The Spanish–American War and World War I confirmed the country's status as a global military power. The United States emerged from World War II as a global superpower, the first country to develop nuclear weapons, the only country to use them in warfare, and a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. During the Cold War, the United States and the Soviet Union competed in the Space Race, culminating with the 1969 Moon landing. The end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 left the United States as the world's sole superpower.[27]
The United States is the world's oldest surviving federation. It is a federal republic and a representative democracy. The United States is a founding member of the United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, Organization of American States (OAS), and other international organizations. The United States is a highly developed country, with the world's largest economy by nominal GDP and second-largest economy by PPP, accounting for approximately a quarter of global GDP.[28] The U.S. economy is largely post-industrial, characterized by the dominance of services and knowledge-based activities, although the manufacturing sector remains the second-largest in the world.[29] The United States is the world's largest importer and the second largest exporter of goods, by value.[30][31] Although its population is only 4.3% of the world total,[32] the U.S. holds 31% of the total wealth in the world, the largest share of global wealth concentrated in a single country.[33]
Despite wide income and wealth disparities, the United States continues to rank very high in measures of socioeconomic performance, including average wage, human development, per capita GDP, and worker productivity.[34][35] The United States is the foremost military power in the world, making up a third of global military spending,[36] and is a leading political, cultural, and scientific force internationally.[37]
Les États-Unis, en forme longue les États-Unis d'Amérique4 (en anglais : United States et United States of America, également connus sous les abréviations US et USA), sont un pays transcontinental dont l'essentiel du territoire se situe en Amérique du Nord. Les États-Unis ont la structure politique d'une république constitutionnelle fédérale à régime présidentiel composée de cinquante États, dont quarante-huit sont adjacents et forment le Mainland. Celui-ci est encadré par l'océan Atlantique à l'est et l'océan Pacifique à l'ouest, et se trouve bordé au nord par le Canada et au sud par le Mexique. Les deux États non limitrophes sont l'Alaska, situé à l'ouest du Canada, et Hawaï, un archipel situé au milieu de l'océan Pacifique-nord. De plus, le pays comprend quatorze territoires insulaires disséminés dans la mer des Caraïbes et le Pacifique. La géographie et le climat du pays sont extrêmement diversifiés, abritant une grande variété de faune et de flore, faisant des États-Unis l'un des 17 pays mégadivers de la planète5.
La capitale fédérale, Washington, est située dans le district de Columbia, une zone située hors des cinquante États. La monnaie est le dollar américain. Le drapeau se compose de treize bandes rouges et blanches ainsi que cinquante étoiles représentant les cinquante États fédérés de l'union. L'hymne national s'intitule The Star-Spangled Banner (La Bannière étoilée). Il n'y a pas de langue officielle aux États-Unis, bien que la langue nationale de facto soit l'anglais américain.
Avant d'être exploré et conquis par les Européens, le territoire américain est d'abord occupé par les Amérindiens qui migrent depuis l'Eurasie il y a environ 15 000 ans6. La colonisation européenne débute au XVIe siècle. Le 14 mai 1607, la colonie anglaise de Virginie est fondée ; par la suite, douze autres colonies britanniques sont fondées le long de la côte Atlantique, tandis que d'autres puissances européennes explorent le reste du territoire américain. Une série de conflits entre les Treize colonies et la Grande-Bretagne mènent à la guerre d'indépendance en 1775. La déclaration d'indépendance est proclamée le 4 juillet 1776, dans laquelle les treize colonies se fédérent pour former les États-Unis d'Amérique, la première nation décolonisée du monde7,8, reconnue par la Grande-Bretagne à la fin de la guerre en 1783. L'histoire contemporaine des États-Unis est marquée par la rivalité entre New York et Philadelphie, puis par la conquête de l'Ouest et la guerre de Sécession. Au début du XXe siècle, le pays devient une puissance industrielle qui a les moyens d'intervenir à l'extérieur de ses frontières. Il participe à la Première Guerre mondiale et subit la Grande Dépression dans les années 1930. Vainqueurs de la Seconde Guerre mondiale aux côtés des Alliés, les États-Unis deviennent une superpuissance mondiale et sont confrontés à l'URSS pendant la guerre froide.
En 2018, les États-Unis comptent environ 327 millions d'habitants2 et constituent le troisième pays le plus peuplé du monde après la Chine et l'Inde9. La superficie du pays est de 9,6 millions de km2, ce qui en fait le troisième ou quatrième pays le plus vaste du monde après la Russie, le Canada et la Chine10. La population américaine augmente grâce à un solde naturel et un solde migratoire positifs. Elle est marquée par une grande diversité ethnique en raison d'une immigration ancienne et diversifiée. L'économie nationale de type capitaliste est la plus importante au monde avec le PIB le plus élevé en 201511,12, et est alimentée par une productivité du travail élevée13. Les secteurs qui reflètent la puissance américaine sont l'agriculture, les industries de pointe et les services. L'économie américaine est aussi l'une des plus grandes manufacturières du monde14. Le pays compte 37 % de la dépense militaire mondiale15, et est une proéminente force politique et culturelle et un leader mondial dans la recherche scientifique et l'innovation technologique16,17,18,19,20. Les États-Unis sont membres de l'Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord (OTAN), de la Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (APEC), de l'Accord de libre-échange nord-américain (ALENA), de l'Organisation des États américains (OEA), de l'ANZUS, de l'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE), du G8, du G20, et membres permanents du Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies. Ils sont une puissance nucléaire depuis 1945.
Gli Stati Uniti d'America (comunemente indicati come Stati Uniti, in inglese: United States of America o anche solo United States; in sigla USA[10] o anche U.S. e impropriamente con la sineddoche "America")[11] sono una repubblica federale composta da cinquanta Stati e un distretto federale.
I quarantotto Stati contigui e il distretto di Washington D.C. (la capitale federale) occupano la fascia centrale dell'America settentrionale tra il Canada e il Messico e sono bagnati dall'oceano Atlantico a est e dall'oceano Pacifico a ovest. Lo Stato dell'Alaska occupa i territori nord-occidentali dell'America settentrionale e confina con il Canada a est e separata dallo stretto di Bering con la Russia (Asia) a ovest. Lo Stato delle Hawaii è un arcipelago a metà strada tra America e Asia nel nord del Pacifico. Il Paese ha anche cinque territori disabitati e nove territori popolati nel Pacifico e nei Caraibi.
Con 9 372 641 km² in totale e circa 325 milioni di abitanti gli Stati Uniti sono il quarto Paese al mondo per superficie e il terzo per popolazione davanti all'Indonesia e dietro alla Cina e all'India. La geografia e il clima degli Stati Uniti sono estremamente vari, con deserti, pianure, foreste e montagne che sono anche sede di una grande varietà di fauna selvatica. È una delle nazioni più multietniche e multiculturali al mondo, prodotto di larga scala dell'immigrazione da molti Paesi.
Storicamente i paleoamericani migrarono dall'Asia verso quelli che sono gli Stati Uniti circa 12 000 anni fa. La colonizzazione europea cominciò intorno al 1600 e venne per lo più dall'Inghilterra. Gli Stati Uniti ebbero origine dalle tredici colonie britanniche situate lungo la costa atlantica. Le controversie tra la Gran Bretagna e le colonie portarono alla rivoluzione americana: il 4 luglio 1776 i delegati delle tredici colonie redassero all'unanimità la dichiarazione di indipendenza, che diede ufficialmente vita agli Stati Uniti d'America. La guerra di indipendenza americana, conclusasi con il riconoscimento dell'indipendenza degli Stati Uniti dal Regno di Gran Bretagna, è stata la prima guerra per l'indipendenza da una potenza coloniale europee. La Costituzione fu adottata il 17 settembre 1787 e da allora è stata emendata ventisette volte. I primi dieci emendamenti, collettivamente denominati «Dichiarazione dei diritti» (Bill of Rights), furono ratificati nel 1791 e garantiscono molti diritti civili e libertà fondamentali.
Gli Stati Uniti intrapresero una vigorosa espansione per tutto il XIX secolo, spinti dalla controversa dottrina del destino manifesto. L'acquisizione di nuovi territori e l'ammissione di nuovi Stati membri causarono anche numerose guerre con i popoli nativi. La guerra civile americana si concluse con l'abolizione della schiavitù negli Stati Uniti. Alla fine del XIX secolo gli Stati Uniti si estesero fino all'oceano Pacifico. La guerra ispano-americana e la prima guerra mondiale hanno confermato lo stato del Paese come potenza militare globale. Gli Stati Uniti sono usciti dalla seconda guerra mondiale come una superpotenza globale, il primo Paese dotato di armi nucleari e quale uno dei cinque membri permanenti del Consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni Unite. Dopo una grave crisi politica e sociale negli anni sessanta e settanta come conseguenza anche della sconfitta nella guerra del Vietnam, che sembrava minare il predominio mondiale statunitense, l'inattesa fine della guerra fredda e la dissoluzione dell'Unione Sovietica negli anni novanta hanno invece riconfermato il ruolo dominante degli Stati Uniti che sono rimasti l'unica superpotenza militare e politica mondiale.
Gli Stati Uniti sono un Paese sviluppato, con una stima nel 2012 del prodotto interno lordo (PIL) di 15 600 miliardi di dollari (il 19% del PIL mondiale a parità di potere di acquisto, a partire dal 2011). Il PIL pro capite degli Stati Uniti è stato il sesto più alto del mondo dal 2010, anche se la disparità di reddito del continente americano è stata anche classificata la più alta all'interno dell'OCSE e i Paesi dalla Banca Mondiale. L'economia è alimentata da un'abbondanza di risorse naturali, numerose infrastrutture ed elevata produttività. Il Paese rappresenta il 39% della spesa militare mondiale, essendo la prima potenza economica e militare, una forza politica guida nel mondo e al primo posto nel settore della ricerca scientifica e dell'innovazione tecnologica, ma anche uno stato sociale ridotto rispetto a molti altri Paesi del mondo occidentale.
Estados Unidosnota 2 (en inglés, United States, cuya abreviatura es EE. UU.),nota 3 oficialmente Estados Unidos de América (United States of America, cuya sigla oficial en inglés es USA y su contraparte en español es EUA),10 es un país soberano constituido en república federal constitucional compuesta por cincuenta estados y un distrito federal. La mayor parte del país se ubica en el medio de América del Norte —donde se encuentran sus cuarenta y ocho estados contiguos y Washington D. C., el distrito federal—, entre los océanos Pacífico y Atlántico, limita con Canadá al norte y con México al sur. El estado de Alaska está en el noroeste del continente, limita con Canadá al este, separado de Rusia al oeste por el estrecho de Bering. El estado de Hawái es un archipiélago polinesio en medio del océano Pacífico, y es el único de sus estados que no se encuentra en América. El país posee en el mar Caribe y en el Pacífico varios territorios no incorporados.
Con 9,83 millones de km²,4 y con más de 325 millones de habitantes, el país es el cuarto mayor en área total, el quinto mayor en área contigua y el tercero en población. Es una de las naciones con más diversidad de etnias y multicultura, producto de la inmigración a gran escala.11 Es la economía nacional más grande del mundo en términos nominales, con un PIB estimado en 15,7 billones de dólares (una cuarta parte del PIB global nominal) y una quinta parte del PIB global en paridad de poder adquisitivo.8
El país es la principal fuerza capitalista del planeta, además de ser líder en la investigación científica y la innovación tecnológica desde el siglo XIX y, desde comienzos del siglo XX, el principal país industrial; con altos niveles del que goza de muchas instituciones públicas y privadas de educación superior competitiva bajo políticas de admisión abiertas. En PIB PPA, EE. UU. es la segunda economía más grande, por detrás de la República Popular China.12
Los pueblos amerindios llevan miles de años habitando lo que es el territorio continental de los Estados Unidos. Esta población amerindia fue reducida por las enfermedades y la guerra después del primer contacto con los europeos. Estados Unidos fue fundado por trece colonias británicas, a lo largo de la costa atlántica. El 4 de julio de 1776, emitieron la Declaración de Independencia, que proclamó su derecho a la libre autodeterminación y el establecimiento de una unión cooperativa. Los estados rebeldes derrotaron al Imperio británico en la guerra de independencia, la primera guerra colonial de independencia exitosa.13 La Constitución de los Estados Unidos fue adoptada el 17 de septiembre de 1787; su ratificación al año siguiente hizo a los estados parte de una sola república con un gobierno central fuerte. La Carta de Derechos, que comprende diez enmiendas constitucionales que garantizan muchos derechos civiles fundamentales y las libertades, fue ratificada en 1791.
En el siglo XIX, los Estados Unidos adquirieron territorios de Francia, España, Reino Unido, México, Rusia y Japón, además de anexionarse las repúblicas de Florida, Texas, California y Hawái. En la década de 1860, las disputas entre el sur agrario y conservadurista y el norte industrial y progresista sobre los derechos de los estados y la abolición de la esclavitud provocaron la Guerra de Secesión. La victoria del norte evitó una división permanente del país y condujo al final de la esclavitud legal. Para la década de 1890, la economía nacional era la más grande del mundo14 y la guerra hispano-estadounidense y la Primera Guerra Mundial confirmaron su estatus como una potencia militar. Después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, surgió como el primer país con armas nucleares y miembro permanente del Consejo de Seguridad de las Naciones Unidas. El final de la Guerra Fría y la disolución de la Unión Soviética la dejaron como la única superpotencia internacional. El país representa dos quintas partes del gasto militar mundial y es una fuerza económica, política y cultural, líder en el mundo.1516
Соединённые Шта́ты Аме́рики (англ. United States of America), часто кратко именуемые США (англ. USA) или Соединёнными Штатами (англ. United States, U.S., в просторечии — Америкой) — государство в Северной Америке. Площадь — 9,5 млн км²[* 3][6] (4-е место в мире). Население — 327 млн человек (2018, оценка; 3-е место в мире). США имеют федеративную форму устройства, административно делятся на 50 штатов и федеральный округ Колумбия; в их подчинении также находится ряд островных территорий (Пуэрто-Рико, Виргинские Острова, Гуам и другие).
Столица — город Вашингтон, округ Колумбия, а самым крупным по численности населения является город Нью-Йорк. Соединённые Штаты граничат на севере с Канадой, на юге — с Мексикой, также имеют морскую границу с Россией. Омываются Тихим океаном с запада, Атлантическим океаном — с востока и Северным Ледовитым океаном — с севера.
Соединённые Штаты Америки были образованы в 1776 году при объединении тринадцати британских колоний, объявивших о своей независимости. Война за независимость продолжалась до 1783 года и окончилась победой колонистов. В 1787 году была принята Конституция США, а в 1791 — Билль о правах, который существенно ограничил полномочия правительства в отношении граждан. В 1860-х годах противоречия между рабовладельческими южными и промышленными северными штатами привели к началу четырёхлетней Гражданской войны. Следствием победы северных штатов стал повсеместный запрет рабства, а также восстановление страны после раскола, возникшего при объединении южных штатов в Конфедерацию и объявлении ими независимости.
Вплоть до Первой мировой войны внешнеполитическая активность США ограничивалась интересами на территориях Северной, Центральной и Южной Америки — согласно сформулированной ещё в 1823 году доктрине Монро. После Первой мировой войны Конгресс Соединённых Штатов не давал согласия на вступление страны в международные организации (например, в Лигу Наций и Палату международного правосудия при ней), что ограничивало роль США в мировой политике. Однако участие страны в антигитлеровской коалиции значительно усилило влияние США на мировой арене, и со второй половины XX века страна стала ядром капиталистического лагеря. В 1945 году США стали первой ядерной державой и первой и единственной страной, использовавшей ядерное оружие в военных действиях (атомные бомбардировки Хиросимы и Нагасаки), а с 1946 года они находились в состоянии глобального противостояния с СССР, длившегося до начала 1990-х годов, когда Советский Союз прекратил своё существование.
США располагают мощными вооружёнными силами, в том числе самыми крупными в мире военно-морскими силами; имеют постоянное место в Совете Безопасности ООН с правом вето; являются государством-учредителем Североатлантического Альянса (НАТО), одними из основателей Организации Объединенных Наций, Всемирного банка, Международного валютного фонда, Организации американских государств (ОАГ) и других международных организаций. Страна также обладает вторым (после России) ядерным потенциалом на планете по совокупной численности развёрнутых боезарядов[7][8].
Соединённые Штаты — высокоразвитая страна, обладающая первой экономикой мира по номинальному ВВП и второй по ВВП (ППС). Хотя население страны составляет лишь 4,3 % от общемирового[9], американцам принадлежит около 40 % совокупного мирового богатства[10]. Соединённые Штаты занимают лидирующие позиции в мире по ряду социально-экономических показателей, включая среднюю зарплату[11], ИЧР, ВВП на душу населения и производительность труда[12]. В то время как экономика США является постиндустриальной, характеризуется преобладанием сферы услуг и экономики знаний, производственный сектор страны остаётся вторым по величине в мире[13].
Экономика страны составляет около четверти мирового ВВП[14] и производит треть глобальных военных расходов[15], что делает США главной экономической и военной державой планеты. Кроме того, США имеют наибольшее политическое влияние в мире, а также являются лидером в сфере научных исследований и технологических инноваций и в настоящее время считаются единственной сверхдержавой планеты[16][17][18].



 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Games industry
Games industry


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 ***Metaverse
***Metaverse

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts

 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit
 China
China

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb

中华人民共和国,通称中国[13],是位于东亚的社会主义国家,首都位于北京[14]。中国领土陆地面积约960万平方千米,是世界上纯陆地[注 13]面积第二大、陆地[注 14]面积第三大、总面积第三大或第四大的国家[注 15][15],其分为23个省份[注 16]、5个自治区、4个直辖市和2个特别行政区。被视为亚洲地区重要地域大国,也被视为潜在超级大国[16][17][18]。是世界上人口最多的国家,约有13.9亿人[8],同时也是一个多民族国家,共有已确认的民族56个,其中汉族人口占91.51%[19]。以普通话和规范汉字为国家通用语言文字,少数民族地区可使用自己民族的语言文字。
中国地势西高东低而呈现三级阶梯分布,大部分地区属于温带、副热带季风气候,地理景致与气候型态丰富多样,有冰川、丹霞、黄土、沙漠、喀斯特等多种地貌[20],北方有干草原和荒漠,南方有热带雨林,西部和西南边境则有天山山脉、帕米尔高原、喀喇昆仑山脉和喜马拉雅山脉。东临太平洋,领海由渤海(内海)以及黄海、东海、南海三大边海组成[21],水域面积约470万平方千米,分布有大小岛屿7600个[22]。
科技方面,中国在航天航空、高速铁路、新能源、核技术、超级计算机、量子网络等领域有较强实力,研发经费则位居世界第二[23]。国防预算为世界第二高,拥有世界规模最大的常备部队及三位一体的核打击能力[24][25]。自1986年实行九年义务教育制度,就读公立学校的学生由政府提供其间学费。1978年改革开放后,中国成为经济增长最快的经济体之一[26][27]。当前,中国对外贸易额世界第一,是世界上最大的商品出口国及第二大的进口国,依国内生产总值按购买力平价位列世界第一、而国际汇率则排名世界第二[28]。2017年,中国人均国内生产总值依购买力平价为18,119美元,列全球第76位;依国际汇率则为8,643美元,列全球第72位,均尚低于世界水平[10]。改革开放以来,尽管贫困问题得到极大改善,但收入差距较大,且区域间发展不均——东部沿海地区的经济较中西部及东北地区发达——的问题仍极需解决[29][30]。
1949年中国共产党在内战中取得优势,终结了中国国民党在中国大陆的统治,于同年10月1日建立了中华人民共和国中央人民政府,并与退守台湾地区的中华民国政府形成两岸分治的政治格局。遵循和平共处五项原则的外交政策,在1971年取得在联合国的中国代表权后,成为联合国安全理事会常任理事国并加入了许多国际组织。
Die Volksrepublik China (chinesisch 中华人民共和国, Pinyin Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó ![]() [tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ʐɛn˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥]), allgemein als China bezeichnet, ist ein am 1. Oktober 1949 gegründeter sozialistischer Staat in Ostasien. Mit rund 1,4 Milliarden Einwohnern stellt China das bevölkerungsreichste und gemessen an seiner Gesamtfläche das viertgrößte Land der Erde dar.[7]
[tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ʐɛn˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥]), allgemein als China bezeichnet, ist ein am 1. Oktober 1949 gegründeter sozialistischer Staat in Ostasien. Mit rund 1,4 Milliarden Einwohnern stellt China das bevölkerungsreichste und gemessen an seiner Gesamtfläche das viertgrößte Land der Erde dar.[7]
Gemäß ihrer Verfassung steht die Volksrepublik China „unter der demokratischen Diktatur des Volkes“, wird jedoch seit 1949 autoritär von der Kommunistischen Partei Chinas (KPCh) regiert. Wirtschaftlich weist China seit vielen Jahren eine hohe Dynamik auf. Auf Grundlage ihrer Reform- und Öffnungspolitik entwickelte sich China beginnend ab 1978 zu einer wirtschaftlichen und technologischen Großmacht.[8] Von der Weltbank wird das Land seit 2016 zu den Staaten mit einem Einkommensniveau im oberen Mittelfeld gerechnet. Seit 2010 ist China der Staat mit der umfangreichsten Warenausfuhr und gemessen an der Kaufkraftparität seit 2016 die größte Volkswirtschaft der Welt. Das jährliche Wirtschaftswachstum lag zwischen 2010 und 2017 im Durchschnitt bei 6,7 Prozent.[9]
Die Volksrepublik China zählt zu den offiziellen Atommächten, ist ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates sowie unter anderem Mitglied der Welthandelsorganisation, Weltbank, APEC, ASEAN, BRICS, UNESCO, Interpol, G20.
中華人民共和国(ちゅうかじんみんきょうわこく、簡体字: 中华人民共和国、繁体字: 中華人民共和國、拼音: 、英語: People's Republic of China, PRC)、通称中国(ちゅうごく、拼音: 、英語: China)は、東アジアに位置する主権国家。首都・北京市を政庁所在地とし、13億8千万人以上の人口で世界一人口が多い国でもある。
中華人民共和国憲法第一条で社会主義国家であることを明言しており、政治は中国共産党が指導的地位を有するヘゲモニー政党制を採用している[4]。
中華人民共和国は、中華民国統治下の中国で1921年に結党された中国共産党が、ソビエト連邦の支援を受けながら国共合作・抗日戦争(八路軍・新四軍)・国共内戦を経て国民政府を台湾島へ放逐[5]し、1949年10月1日に北京市で建国式典(中華人民共和国開国大典)を開催したことで成立した。
同国は国共内戦の延長で1954年に「台湾解放宣言」[6]を出し、第一次台湾海峡危機(1954年~1955年)と金門砲戦(1958年~1979年)を起こしたが武力による台湾占領には至らなかった。同国は2010年代に入ると一つの中国による台湾問題の解決を「(自国の)核心的利益の一つ」と規定するようになり、基本的には九二共識の合意に基づいた平和的な中国統一を目指しているが、一方で人民解放軍の武力による台湾制圧の可能性も指摘されている[7]。
計測方法によるが、同国は陸地面積では世界第2位[8]、総面積では世界第3位又は第4位である。同国の地形は、乾燥した北の森林ステップ、ゴビ砂漠、タクラマカン砂漠から、多湿な南の亜熱帯の森林まで広大かつ多様である。ヒマラヤ山脈、カラコルム山脈、パミール高原、天山山脈により、同国は南及び中央アジアから切り離されている。長さ世界第3位の長江及び同世界第6位の黄河は、チベット高原から人口密度の高い東の沿岸地域に流れ、古代には黄河文明や長江文明を興してきた。同国の太平洋に沿った海岸線は14,500kmの長さで、渤海、黄海、東シナ海、南シナ海に囲まれている。同国の国土は、22省級行政区、5自治区、北京市・天津市・上海市・重慶市の4直轄市、大部分が自治的な香港・マカオの2特別行政区によって構成されている。
中国は、繁栄と衰退の繰り返しだと考えられる過去2000年間の大部分で世界最大かつ最も複雑な経済を有した[9][10]。1978年における改革開放の導入以来、外資流入の勢いが増してゆき、産業構造が政策から転換して、中国は世界で最も成長率が高い主要経済大国の1つになった(#経済)。ソ連の純粋な社会主義体制と距離をとり、「経済面は有限な資本主義、政治面は一党独裁を守る」のような国家形態に変更したのである(中国特色社会主義)。
2016年時点で、同国は名目GDP及び貿易輸入額のいずれにおいても世界第2位であり(2014年には国際通貨基金・世界銀行・CIAワールドファクトブックによると購買力平価は世界最大のGDPとなった[11][12][13])、購買力平価GDPと貿易輸出額は世界一位である[14]。同国は核保有国に認められ、世界第2位の防衛予算で世界最大の常備軍を有する。中華人民共和国は1971年以来国際連合加盟国であり、中華民国の後任として安全保障理事会常任理事国である。中国は多数の公式及び非公式の多国間機構加盟国であり、WTO、APEC、BRICs、上海協力機構、BCIM、G20がこれに該当する。中国はアジアの地域大国であり、多数の解説者により潜在的な超大国として特徴付けられてきた[15][16]。なお2017年7月現在、中華人民共和国の世界遺産はイタリアについで52件ある。国内には文化遺産が22件、自然遺産が4件、複合遺産が4件存在する。
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia and the world's most populous country, with a population of around 1.404 billion.[13] Covering approximately 9,600,000 square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third- or fourth-largest country by total area.[k][19] Governed by the Communist Party of China, the state exercises jurisdiction over 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four direct-controlled municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing), and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
China emerged as one of the world's earliest civilizations, in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. For millennia, China's political system was based on hereditary monarchies, or dynasties, beginning with the semi-legendary Xia dynasty in 21st century BCE.[20] Since then, China has expanded, fractured, and re-unified numerous times. In the 3rd century BCE, the Qin reunited core China and established the first Chinese empire. The succeeding Han dynasty, which ruled from 206 BC until 220 AD, saw some of the most advanced technology at that time, including papermaking and the compass,[21] along with agricultural and medical improvements. The invention of gunpowder and movable type in the Tang dynasty (618–907) and Northern Song (960–1127) completed the Four Great Inventions. Tang culture spread widely in Asia, as the new Silk Route brought traders to as far as Mesopotamia and Horn of Africa.[22] Dynastic rule ended in 1912 with the Xinhai Revolution, when a republic replaced the Qing dynasty. The Chinese Civil War resulted in a division of territory in 1949, when the Communist Party of China established the People's Republic of China, a unitary one-party sovereign state on Mainland China, while the Kuomintang-led government retreated to the island of Taiwan. The political status of Taiwan remains disputed.
Since the introduction of economic reforms in 1978, China's economy has been one of the world's fastest-growing with annual growth rates consistently above 6 percent.[23] As of 2016, it is the world's second-largest economy by nominal GDP and largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).[24] China is also the world's largest exporter and second-largest importer of goods.[25] China is a recognized nuclear weapons state and has the world's largest standing army and second-largest defense budget.[26][27] The PRC is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council as it replaced the ROC in 1971, as well as an active global partner of ASEAN Plus mechanism. China is also a leading member of numerous formal and informal multilateral organizations, including the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), WTO, APEC, BRICS, the BCIM, and the G20. In recent times, China has been widely characterized as a global superpower.[28][29][30]
La Chined, en forme longue la république populaire de Chine (ou République populaire de Chinee, RPC, chinois simplifié : 中华人民共和国 ; chinois traditionnel : 中華人民共和國 ; pinyin : , prononcé [tʂʊŋ˥xua˧˥ɻən˧˥mɪn˧˥kʊŋ˥˩xə˧˥kuɔ˧˥] Écouter), parfois appelée Chine populaire, est un pays d'Asie de l'Est. Avec près d'1,4 milliard d'habitants, soit environ un sixième de la population mondiale, elle est le pays le plus peuplé du monde6. Elle compte huit agglomérations de plus de dix millions d'habitants, dont la capitale Pékin, Shanghai, Canton, Shenzhen et Chongqing, ainsi que plus de trente villes d'au moins deux millions d'habitants. Avec 9 596 961 km2 selon les chiffres de l'ONU7, la Chine est également le plus grand pays d'Asie orientale et le troisième ou quatrième plus grand pays du monde par superficie8. La Chine s'étend des côtes de l'océan Pacifique au Pamir et aux Tian Shan, et du désert de Gobi à l'Himalaya et aux confins de la péninsule indochinoise.
En 2014, la république populaire de Chine est la première puissance économique mondiale (en termes de PIB mesuré en parité de pouvoir d'achat)9. La Chine est également l'un des cinq membres permanents du Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies. Elle est également le premier exportateur mondial et dispose de l'arme nucléaire, de la plus grande armée du monde et du deuxième plus grand budget militaire. Gouvernée par le Parti communiste chinois, la Chine a adopté une « économie socialiste de marché » où capitalisme et contrôle politique autoritaire se côtoient en une formule spécifique. La Constitution de la république populaire de Chine la définit comme « un État socialiste de dictature démocratique populaire, dirigé par la classe ouvrière et basé sur l'alliance des ouvriers et des paysans ». Le préambule de la Constitution spécifie le rôle dirigeant du Parti communiste chinois et continue de citer officiellement le marxisme-léninisme comme idéologie de référence de l'État10.
La Chine est l'une des plus anciennes civilisations au monde, et est parfois citée comme la plus ancienne civilisation continue11. Elle trouve son origine dans la vallée du fleuve Jaune puis s'est étendue vers le sud (conquête des territoires au sud du Yangzi Jiang dès la dynastie Han), vers l'ouest (premières incursions en Asie centrale sous les Han, extension temporaire jusqu'à la mer Caspienne sous les Tang, conquête du Xinjiang et du Tibet sous les Qing12) et vers le nord (la dynastie Qing, d'origine mandchoue apporta à la Chine la Mandchourie et la Mongolie). Au cours de son histoire la Chine a été à plusieurs reprises divisée puis réunifiée ; elle a été par deux fois entièrement conquise par des étrangersf (par les Mongols au XIIIe siècle et par les Mandchous au XVIIe siècle), bien que ceux-ci aient fini par adopter les coutumes et le système administratif chinois pour gouverner l'empire. La dernière dynastie impériale, les Qing (la dynastie d'origine mandchoue qui régnait sur le pays depuis 1644), a connu une période de déclin durant la phase d'expansion coloniale des pays occidentaux, menant le pays de défaite en défaite à partir des guerres de l'opium. C'est seulement après la victoire contre l'armée japonaise en 1945 que la Chine a pu se libérer des interventions étrangères. La république populaire de Chine est proclamée le 1er octobre 1949, à la suite de la victoire militaire du Parti communiste chinois sur le Kuomintang. Elle se présente aujourd'hui comme une « république socialiste » et exerce un contrôle sur vingt-deux provincesg, cinq régions autonomes, quatre municipalités (dont Pékin) et deux régions administratives spéciales (Hong Kong et Macao).
La Chine a connu une période néolithique et des âges des métaux plutôt tardive par rapport à l'Anatolie et à la Mésopotamie, mais elle a été et reste le foyer de nombreuses innovations dans les domaines des sciences et des arts6. Elle est à l'origine de nombreuses inventions majeures telles la boussole13, le papier14, le billet de banque15 ou la poudre noire16. La civilisation chinoise a fortement imprégné toute l'Asie de l'Est, notamment aux niveaux religieux (confucianisme, taoïsme et développement du bouddhisme chan), linguistique (les caractères chinois ont été utilisés dans toute la région et de nombreux mots chinois sont présents dans les langues qui y sont parlées), ainsi qu'artistique (calligraphie, peinture, imprimerie, instruments de musique).
La Cina (中國T, 中国S, ZhōngguóP), ufficialmente la Repubblica Popolare Cinese (中華人民共和國T, 中华人民共和国S, Zhōnghuá Rénmín GònghéguóP ), è uno Stato sovrano situato nell'Asia orientale ed è il paese più popoloso del mondo, con una popolazione di oltre 1,385 miliardi di persone.
La Cina è una Repubblica popolare in cui il potere è esercitato dal solo Partito Comunista Cinese (中国共产党 oppure 中共). Il governo ha sede nella capitale Pechino (北京首都) ed esercita la propria giurisdizione su ventidue province (省), cinque regioni autonome (自治区), quattro municipalità direttamente controllate 直辖市 (Pechino 北京, Tientsin 天津, Shanghai 上海 e Chongqing 重庆) e due regioni amministrative speciali 特别行政区 (Hong Kong 香港 e Macao 澳门) parzialmente autonome. La Cina rivendica la propria sovranità anche sull'isola di Formosa, che considera ufficialmente una sua provincia, sulla quale non esercita tuttavia alcun controllo diretto. L'isola è dal 1949 sotto il controllo del governo della Repubblica di Cina (Taiwan 中華民國). La complessa condizione politica di Taiwan è una delle conseguenze della guerra civile cinese che ha preceduto la fondazione della Repubblica Popolare Cinese.
Con la sua superficie di circa 9 572 900 chilometri quadrati la Cina è il terzo stato più grande del mondo per superficie. Il paesaggio della Cina è vasto e diversificato: va dalle steppe della foresta e i deserti dei Gobi e del Taklamakan nell'arido nord alle foreste subtropicali e umide del sud. L'Himalaya, il Karakoram, il Pamir e il Tian Shan sono le catene montuose che separano la Cina meridionale dall'Asia centrale. Il Fiume Azzurro (长江) e il Fiume Giallo (黄河), rispettivamente il terzo e il sesto più lunghi del mondo, scorrono dall'altopiano del Tibet verso la costa orientale densamente popolata. La costa della Cina lungo l'oceano Pacifico è lunga circa 14.500 chilometri ed è delimitata dal mare di Bohai, dal mar Giallo, dal mar Cinese Orientale e dal mar Cinese Meridionale.
L'antica civiltà cinese – una delle prime al mondo – si sviluppò inizialmente nelle pianure comprese tra il Fiume Giallo e il Fiume Azzurro. A partire dall'età del bronzo (verso la fine del II millennio a.C.) si ha evidenza di strutture feudali, in cui i nobili si raccoglievano intorno a monarchie ereditarie. Vi sono testimonianze di una casata regnante nella prima metà del I millennio a.C., nota come dinastia Zhou (周朝), il cui declino condusse alla nascita di un discreto numero di regni indipendenti in competizione per il predominio sulla regione (periodo delle Primavere e Autunni, 春秋), con stagioni di conflitto che si fecero particolarmente accese nel periodo che va dall'VIII al III secolo a.C. Nel 221 a.C. lo Stato di Qin sconfisse e conquistò i territori di tutti gli altri Stati combattenti dando vita al primo impero della storia cinese sotto la dinastia Qin (秦朝).
Da quel momento il titolo di imperatore della Cina divenne il sinonimo della raggiunta supremazia. La dinastia Qin non durò a lungo, ma i popoli precedentemente conquistati vennero poco dopo riuniti sotto l'egida della dinastia Han (汉朝, III secolo a.C.-III secolo d.C.). I quattro secoli in cui regnarono i sovrani della dinastia Han sono considerati cruciali per la definizione e affermazione della identità culturale cinese, tanto da divenire il termine con cui i cinesi definirono se stessi (con il termine appunto di etnia o popolo han, 汉族). Da allora la storia cinese ha visto l'alternarsi di periodi di divisione e fasi di unificazione, con conseguenti periodi di frammentazione, contrazione o espansione territoriale, sotto l'egida di diverse dinastie, talora di etnia straniera (come nel caso dei mongoli o dei mancesi).
L'ultima dinastia fu quella dei Qing, il cui regno si concluse nel 1911 con la fondazione della Repubblica di Cina (中华民国). Dopo la sconfitta dell'Impero giapponese (大日本皇国) durante la seconda guerra mondiale il Paese fu scosso dalla guerra civile che vedeva contrapposte le forze nazionaliste del Kuomintang (国民党), il partito che allora deteneva il governo del paese, e le forze facenti capo al Partito Comunista Cinese. Nel 1949 la guerra si concluse con la sconfitta del Kuomintang e la fuga del governo nazionalista sull'isola di Formosa, nella cui capitale Taipei (台北) ha tuttora sede l'attuale Repubblica di Cina, altresì nota come Taiwan. In seguito alla vittoria conseguita sul continente il 1º ottobre del 1949 a Pechino le forze comuniste guidate da Mao Zedong proclamarono ufficialmente la nascita della Repubblica Popolare Cinese.
Dopo l'introduzione di riforme economiche nel 1978 la Cina è diventata l'economia dalla crescita più rapida al mondo. A partire dal 2013 è la seconda economia più grande al mondo sia come PIL totale nominale, sia per parità di potere d'acquisto; è anche il più grande esportatore e importatore di merci al mondo. La Cina è ufficialmente uno Stato munito di armi nucleari e ha il più grande esercito permanente del mondo, con il secondo più grande bilancio della difesa. La Cina è membro delle Nazioni Unite dal 1971, quando ha preso il posto della Repubblica di Cina tra i seggi dei membri permanenti del Consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni Unite. La Cina è anche membro di numerose organizzazioni multilaterali,[6] tra cui l'OMC, l'APEC, il BRICS, l'Organizzazione di Shanghai per la cooperazione, il BCIM[7] e il G-20. La Cina, unanimemente riconosciuta come grande potenza dal consesso internazionale, è una potenziale superpotenza secondo un certo numero di accademici e analisti che si occupano di questioni militari, politiche ed economiche.
La República Popular China (en chino simplificado: 中华人民共和国 y en pinyin: Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó), o simplemente China (en chino simplificado: 中国 y en pinyin: Zhōngguó), es un Estado soberano situado en Asia Oriental. Es el país más poblado del mundo, con 1395 millones de habitantes, y la primera potencia económica mundial por PIB, en términos de paridad de poder adquisitivo.81617 La República Popular China es un Estado unipartidista gobernado por el Partido Comunista y tiene la sede de su gobierno en la capital, Pekín.18 Está dividida en veintidós provincias, cinco regiones autónomas, cuatro municipios bajo jurisdicción central —Pekín, Tianjin, Shanghái y Chongqing— y dos regiones administrativas especiales —Hong Kong y Macao—.19 Asimismo, China reclama la que considera provincia de Taiwán, que es controlada por la República de China con un estatus político de la isla controvertido.20
Con una superficie de 9 596 960 km²,5 China ―que tiene fronteras con catorce Estados soberanos―nota 1 es el tercer país más extenso del planeta por superficie terrestre detrás de Rusia y Canadá y el cuarto si se cuentan las masas de agua, detrás de Rusia, Canadá y Estados Unidos. El paisaje chino es vasto y diverso, desde las estepas y los desiertos del Gobi y Taklamakán en el árido norte hasta los bosques subtropicales en el húmedo sur. Las cordilleras montañosas del Himalaya, el Karakórum, Pamir y Tian Shan la separan del sur y el centro de Asia. Los ríos Yangtsé y Amarillo, tercero y sexto más largos del mundo, discurren desde la meseta tibetana hasta desembocar en las densamente pobladas costas orientales. China tiene 14 500 km de costa a lo largo del océano Pacífico,5 en donde está bañada por los mares Amarillo, de Bohai, de China Oriental y de la China Meridional.
La civilización china, una de las más antiguas del mundo, floreció en la fértil cuenca del río Amarillo. Durante milenios su sistema político se basó en monarquías hereditarias, conocidas como dinastías. La primera de las cuales fue la semimitológica dinastía Xia en torno al 2000 a. C. Desde el 221 a. C., cuando la dinastía Qin conquistó diversos Estados y formó el primer Imperio chino, el país se ha expandido, fracturado y ha sido reformado en numerosas ocasiones. La República de China derrocó a la última dinastía en 1911 y gobernó la China continental hasta 1949. Después de la derrota del Imperio del Japón en la Segunda Guerra Mundial y la retirada de sus tropas de China, el partido comunista se impuso en la Guerra Civil y proclamó la República Popular China en Pekín el 1 de octubre de 1949. El derrotado régimen de la República de China, dominado por el partido Kuomintang trasladó su gobierno a Taipéi y desde entonces, la jurisdicción de la República de China se limita a Taiwán y algunas islas periféricas.
Desde la introducción de las reformas económicas de 1978, China ha sido la economía de más rápido crecimiento del mundo, alcanzando en 2014 la primacía mundial en términos de PIB medido en paridad de poder adquisitivo y manteniéndose como la segunda potencia por PIB nominal. China es, además, el mayor exportador e importador de bienes y la primera potencia industrial.21 China dispone del segundo ejército más numeroso del mundo, posee armas nucleares y cuenta con el segundo presupuesto militar después de Estados Unidos.22 La República Popular China es miembro de la ONU desde 1971, año en que reemplazó a la República de China como miembro permanente del Consejo de Seguridad de las Naciones Unidas, y es reconocida diplomáticamente por casi todos los países del mundo. También es miembro formal o informal de numerosas organizaciones multilaterales, como la OMC, la APEC, los BRICS, la Organización de Cooperación de Shanghái y el G20. China es considerada por numerosos analistas como una superpotencia emergente.23242526
Кита́й (Кита́йская Наро́дная Респу́блика, КНР; кит. трад. 中華人民共和國, упр. 中华人民共和国, пиньинь: Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó, палл.: Чжунхуа Жэньминь Гунхэго) — государство в Восточной Азии.
Крупнейшее по численности населения государство мира (свыше 1,38 млрд[15], большинство населения — этнические китайцы, самоназвание — хань); занимает третье место в мире по территории, уступая России и Канаде.
Китайская Народная Республика, согласно конституции, — социалистическое государство[16]. Является великой державой — потенциальной сверхдержавой, экономической сверхдержавой, постоянным членом Совета безопасности ООН.
Одна из ведущих космических держав мира, обладает ядерным оружием и крупнейшей в мире армией по численности военнослужащих.
В 2010 году китайская экономика обогнала японскую и стала второй экономикой мира по номинальному ВВП[17]. С декабря 2014 года является первой экономикой мира по ВВП (ППС)[18]. КНР является мировым лидером по производству большинства видов промышленной продукции, в том числе по производству автомобилей и потребительскому спросу на них. Крупнейший мировой экспортёр («фабрика мира»). Располагает наибольшими в мире золотовалютными резервами.
Китай состоит в таких международных организациях, как ООН, АТЭС, G20, Всемирная торговая организация (ВТО; с декабря 2001 года[19]), а также ШОС и БРИКС.
Со времени провозглашения Китайской Народной Республики в 1949 году правящей партией является Коммунистическая партия Китая (КПК). Председателем КНР является Си Цзиньпин (с 2013 года).
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
Women's Soccer World Cup 2003

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

华盛顿哥伦比亚特区(英语:Washington, D.C.),是美国的首都,原称哥伦比亚特区[注 1](District of Columbia,缩写为 D.C.),以及简称华盛顿(Washington)、特区(the District)等。中文通常简称华府。华盛顿哥伦比亚特区是大多数美国联邦政府机关、与各国驻美大使馆的所在地,也是世界银行、国际货币基金、美洲国家组织等国际组织总部的所在地,并拥有为数众多的博物馆与文化史迹。哥伦比亚特区是美国最富裕、财富高度集中的地区;该地区2015年的人均生产总值为181,185美元,冠绝全美。
1776年美国独立时的首都是费城,之后因独立战争和国家新立而屡有变迁,到1785年开始纽约被定为美国的首都。1790年7月1日,国会通过《首都选址法》,决定将首都从纽约迁至波多马克河和安那考斯迪亚河汇合处附近;但完成正式迁都前先由费城暂代首都。1800年,美国联邦政府部门从临时首都的费城迁往建设完成的华盛顿,华盛顿开始作为美国首都正式运作至今[3]。华盛顿哥伦比亚特区实际上是由美国国会直接管辖的联邦地区,因此不属于美国的任何州份。
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区位于美国东岸的中大西洋地区,属马里兰州和弗吉尼亚州的交界处,两州界河波多马克河由西北向东南流贯特区,形成特区西面的天然界限。成立之初,哥伦比亚特区是一个边长10英里(16千米)的长方形区域,不仅包括了特区现在的全部范围,还包括波多马克河西岸弗吉尼亚州亚历山德里亚县,即今日的阿灵顿县以及亚历山德里亚市。特区成立后不久,西岸的居民就因为国会过度重视东岸以及蓄奴等问题,发起了回归弗吉尼亚的运动,经他们多次请愿,美国国会于1846年7月9日通过法案,并经弗吉尼亚人民大会批准,将波多马克河南岸的土地交还南方的弗吉尼亚州。特区设立早期,波多马克河北岸有乔治城镇、华盛顿市及华盛顿县三个分开的行政区划;其中建立于1791年的华盛顿市乃为彰显乔治·华盛顿对美国建国的贡献而命名,后来发展为特区中的核心城市。依据一项1871年的立法,前述三区于1878年合并为华盛顿市,而联邦管辖的特区及华盛顿市地方政府从此辖区重叠,因此产生今日使用的“华盛顿哥伦比亚特区”合称。
Der District of Columbia oder Washington, D.C. [ˈwɔʃɪŋtn̩] ist Bundesdistrikt, Regierungssitz und seit 1800 die Hauptstadt der Vereinigten Staaten. Der Distrikt ist kein Bundesstaat und gehört auch zu keinem, er ist vielmehr dem Kongress der Vereinigten Staaten direkt unterstellt. Trotz Namensgleichheit mit dem Bundesstaat Washington wird Washington, D.C. im deutschen Sprachraum meist nur „Washington“ genannt. D.C. steht dabei für District of Columbia.
Bei der Volkszählung 2010 hatte Washington, D.C. 601.723 Einwohner.[1] Das United States Census Bureau schätzte die Einwohnerzahl zum 1. Juli 2015 auf 672.228 Einwohner, nach einem stetigen Abfall der Bevölkerung seit 1950 der erste größere Zuwachs.[2] Der Großraum Washington[3] hatte 5.582.170 Einwohner. Zusammen mit dem benachbarten Großraum Baltimore hatte die Region laut Zensus insgesamt 8.572.971 Einwohner.[4]
Mit dem Weißen Haus als Amts- und Wohnsitz des Präsidenten und dem Kapitol, das den Kongress (bestehend aus Senat und Repräsentantenhaus) beherbergt, sowie dem Obersten Gerichtshof befinden sich die Spitzen aller drei verfassungsmäßigen Gewalten in der Stadt. Washington ist darüber hinaus Sitz des Internationalen Währungsfonds, der Weltbank und der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten.
ワシントンD.C.(ワシントン・ディーシー、英: Washington, D.C.)は
同国東海岸、メリーランド州とヴァージニア州に挟まれたポトマック川河畔に位置する。
現代の主要都市としては狭隘で人口もさほど多くないが、超大国の政府所在地として国際的に強大な政治的影響力を保持する世界都市であり、また金融センターとしても高い重要性を持つ。首都としての機能を果たすべく設計された、計画都市である[† 1]。
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington or D.C., is the capital of the United States of America.[4] Founded after the American Revolution as the seat of government of the newly independent country, Washington was named after George Washington, first President of the United States and Founding Father.[5] Washington is the principal city of the Washington metropolitan area, which has a population of 6,131,977.[6] As the seat of the United States federal government and several international organizations, the city is an important world political capital.[7] Washington is one of the most visited cities in the world, with more than 20 million annual tourists.[8][9]
The signing of the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, approved the creation of a capital district located along the Potomac River on the country's East Coast. The U.S. Constitution provided for a federal district under the exclusive jurisdiction of the Congress and the District is therefore not a part of any state. The states of Maryland and Virginia each donated land to form the federal district, which included the pre-existing settlements of Georgetown and Alexandria. Named in honor of President George Washington, the City of Washington was founded in 1791 to serve as the new national capital. In 1846, Congress returned the land originally ceded by Virginia; in 1871, it created a single municipal government for the remaining portion of the District.
Washington had an estimated population of 693,972 as of July 2017, making it the 20th largest American city by population. Commuters from the surrounding Maryland and Virginia suburbs raise the city's daytime population to more than one million during the workweek. The Washington metropolitan area, of which the District is the principal city, has a population of over 6 million, the sixth-largest metropolitan statistical area in the country.
All three branches of the U.S. federal government are centered in the District: U.S. Congress (legislative), President (executive), and the U.S. Supreme Court (judicial). Washington is home to many national monuments and museums, which are primarily situated on or around the National Mall. The city hosts 177 foreign embassies as well as the headquarters of many international organizations, trade unions, non-profit, lobbying groups, and professional associations, including the Organization of American States, AARP, the National Geographic Society, the Human Rights Campaign, the International Finance Corporation, and the American Red Cross.
A locally elected mayor and a 13‑member council have governed the District since 1973. However, Congress maintains supreme authority over the city and may overturn local laws. D.C. residents elect a non-voting, at-large congressional delegate to the House of Representatives, but the District has no representation in the Senate. The District receives three electoral votes in presidential elections as permitted by the Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1961.
Washington, dans le district de Columbia (en anglais : Washington, District of Columbia), souvent appelée Washington, D.C., The District, ou simplement D.C. (pour éviter la confusion avec l'État de Washington), est une ville indépendante américaine, capitale des États-Unis. Selon les dernières estimations (2013), elle compte 646 449 habitants intra-muros sur une superficie de 177 km2 ; son aire urbaine en compte environ 5,8 millions, la septième des États-Unis.
En tant que capitale fédérale, elle ne fait pas partie des cinquante États de l'Union et dépend directement du gouvernement fédéral. À ce titre, la ville est le siège de nombreuses institutions américaines, telles que la Maison-Blanche, résidence officielle du président ; le Capitole, siège du Congrès (constitué de ses deux chambres : celle des représentants et le Sénat), ainsi que le siège de la Banque mondiale (BM), de la Cour suprême et d'autres organismes fédéraux, comme la Réserve fédérale des États-Unis (Fed). Elle accueille en outre 176 ambassades et représentations diplomatiques.
Washington est créée à la suite de la signature du Residence Act en 1790, qui prévoit la création d'une capitale fédérale. Elle est fondée en janvier 1791, sur les rives du fleuve Potomac, à proximité des villes de Georgetown et d'Alexandria. Nommée en hommage au premier président des États-Unis, George Washington, elle est construite ex nihilo selon un plan hippodamien de l'ingénieur franco-américain Pierre Charles L'Enfant. L'urbanisme diffère de la plupart des autres villes américaines car la construction de gratte-ciel y est interdite : l'architecture de Washington est marquée par une faible hauteur et un héritage de l'architecture coloniale. Peu peuplée durant la première moitié du XIXe siècle, ce n'est qu'à la fin de la guerre de Sécession qu'elle acquiert sa légitimité en tant que capitale, devenant le symbole de l'unité retrouvée.
Située sur la côte atlantique du nord-est du pays, entre le Maryland et la Virginie, la ville se trouve à soixante kilomètres au sud de Baltimore, à deux cents kilomètres de Philadelphie et trois cents kilomètres de New York. Elle marque l'extrémité méridionale de la mégalopole américaine, appelée également BosWash. Les coordonnées géographiques de la ville correspondent au point zéro, d'où sont calculées toutes les distances routières aux États-Unis. Son climat est de type subtropical humide, avec de fortes variations de température entre l'été et l'hiver.
En tant que siège de la plupart des institutions fédérales, l'économie est fortement dépendante des activités gouvernementales, qui représentent jusqu'à 50 % de son PIB au milieu du XXe siècle. Aujourd'hui, l'économie est diversifiée, notamment dans l'industrie de l'armement et de l'informatique.
La population de la ville se stabilise de nos jours autour de 600 000 habitants, après avoir connu une baisse importante depuis la Seconde Guerre mondiale, essentiellement en raison du départ des Blancs pour les banlieues environnantes. Devenue une ville en majorité composée d'Afro-Américains (50,1 %), Washington comprend historiquement plusieurs ghettos — dont certains connaissent actuellement un processus de gentrification — et est depuis sa fondation un bastion du Parti démocrate.
La ville compte plusieurs universités, dont la prestigieuse université de Georgetown, ainsi que la Bibliothèque du Congrès, plus grande bibliothèque au monde.
Washington dispose de services de polices dépendant de la municipalité ; ainsi que la Garde nationale du district de Columbia (en) qui en tant que force fédérale dépend du président lui-même. Le district de Columbia ne dispose donc pas de forces autonomes comme les Polices d'État ou les Forces de défense d'État existant dans les États de l'Union.
Washington D.C. (AFI: /ˈwɔʃʃinton/[2]; in inglese [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən]) è la capitale degli Stati Uniti d'America, con una popolazione di 672 228 abitanti[1] (5 582 170 abitanti nell'area metropolitana)[3]. Si trova sulla costa orientale degli Stati Uniti a circa 50 km dal mare, a sud dello stato del Maryland, a nord dello stato della Virginia e a 374 km circa a sud di New York.
La città di Washington coincide territorialmente e politicamente con il Distretto di Columbia[4] (in inglese: District of Columbia, in sigla D.C., distretto federale previsto dalla Costituzione dell'Unione e formalizzato dal District of Columbia Organic Act del 1801), di cui è parte integrante. Infatti, mentre in origine il distretto comprendeva le contee di Washington (donata dallo stato del Maryland) ed Alexandria (donata dallo stato della Virginia), in seguito ad un referendum del 1846 quest'ultima è tornata allo stato della Virginia e ha cambiato nome in Contea di Arlington.
Di conseguenza con il District of Columbia Organic Act del 1871,[5] il Congresso ha ufficialmente soppresso la contea di Washington, che comprendeva l'attuale città di Washington, sottoponendo l'intero territorio dapprima ad un unico governatore di nomina presidenziale, poi, dal 1845, ad un triumvirato composto da due politici e un ingegnere. Da quel momento la Città di Washington e il Distretto di Columbia divennero la stessa entità, condidivendo la personalità giuridica.[6]
Ciononostante, l'area metropolitana di Washington deborda dai confini del distretto, estendendosi anche su 7 contee del Maryland (Anne Arundel, Calvert, Charles, Frederick, Howard, Montgomery e Prince George's), su 5 contee della Virginia (Arlington, ossia l'ex Contea di Alexandria, Fairfax, Loudon, Prince William e Stafford) e su 5 città autonome dello stesso Stato (Alexandria, Fairfax, Falls Church, Manassas e Manassas Park). Gran parte dell'area è collegata da un servizio di metropolitana.
Nel 1973 le richieste per una maggiore democrazia nel distretto portarono all'approvazione del District of Columbia Home Rule Act,[7] la legge che soppresse il triumvirato e affidò l'amministrazione cittadina a un sindaco eletto dal popolo, il Mayor, e a un Consiglio comunale, il Council of the District. Il distretto, che gode di 3 voti nel collegio dei Grandi elettori del Presidente dell'Unione, non prevede nella propria legislazione la pena di morte.
Hanno sede a Washington le principali istituzioni di governo degli Stati Uniti (Presidente, Congresso, Corte Suprema), molti ministeri ed enti federali, e alcune organizzazioni internazionali, tra cui la Banca Mondiale, il Fondo Monetario Internazionale e l'Organizzazione degli Stati Americani.
Washington D. C. (/ˈwɑʃɪŋtən diˈsi/ en inglés), oficialmente denominado Distrito de Columbia (District of Columbia), es la capital de los Estados Unidos de América. Se administra como distrito federal, una entidad diferente a los cincuenta estados que componen dicha nación, y depende directamente del gobierno federal. El Distrito de Columbia fue fundado el 16 de julio de 1790, y en 1791 se oficializó, dentro del distrito, una nueva ciudad denominada Washington, al este de la ya existente Georgetown. En 1871 se unificaron los gobiernos de estas dos ciudades y del resto de poblaciones del distrito en una sola entidad, D. C.
Se localiza a orillas del río Potomac y está rodeada por los estados de Virginia al oeste, y de Maryland al norte, este y sur.
La ciudad de Washington nació como una ciudad planificada, y fue desarrollada a finales del siglo XVIII para servir como la capital nacional permanente, después de que diversas localidades ostentaran dicha posición desde la independencia del país, en 1776; en tanto, el distrito federal fue formado para marcar la diferencia entre la capital nacional y los estados. La ciudad fue nombrada en honor a George Washington, el primer presidente de los Estados Unidos. El nombre del distrito, Columbia, es el nombre poético de Estados Unidos, en referencia a Cristóbal Colón (en inglés Christopher Columbus), primer explorador en llegar a América. La ciudad es llamada comúnmente Washington, the District (el Distrito) o simplemente D. C. En el siglo XIX también se la conoció como Ciudad Federal o Ciudad de Washington.
Los centros de las tres ramas del Gobierno de los Estados Unidos se ubican en el Distrito. También situadas en la ciudad están las sedes del Banco Mundial, el FMI, la OEA, el BID, y otras instituciones nacionales e internacionales, incluyendo asociaciones profesionales y sindicatos. Debido a su importancia a nivel político, Washington es un lugar de frecuentes manifestaciones y protestas, particularmente en el National Mall. Además es un destino popular entre los turistas, debido a los numerosos monumentos y lugares de interés nacional. La ciudad es un centro de la historia y cultura estadounidense, y en ella se encuentra el complejo de museos más grande del mundo (el Instituto Smithsoniano), además de galerías de arte, universidades, catedrales, centros e instituciones de arte dramático, y escenarios de música nativa.
El Distrito de Columbia y la ciudad de Washington son gobernados por un solo gobierno municipal. Para cuestiones prácticas son considerados como la misma entidad. Éste no siempre ha sido el caso: hasta 1871 —cuando Georgetown dejó de ser una ciudad separada— había múltiples jurisdicciones dentro del Distrito.3 A pesar de que hay un gobierno municipal y un alcalde, el Congreso tiene la autoridad suprema sobre la ciudad y el distrito, lo que resulta en que los ciudadanos tengan menos autogobierno que los residentes de los estados. El Distrito tiene un delegado en el Congreso, que participa en los debates pero no tiene derecho a voto.
La población del Distrito de Columbia es de 646 449 habitantes en 2013 según estimaciones de la Oficina del Censo de los Estados Unidos.1 El área metropolitana de Washington D. C. es la octava más grande de Estados Unidos, con más de 5 millones de residentes,2 y el área metropolitana que forma junto a la cercana Baltimore tiene una población que excede los 8 millones. Si Washington D. C. fuera un estado, estaría último en cuanto a superficie (por detrás de Rhode Island), en penúltimo lugar en cuanto a población (por delante de Wyoming), en el lugar n.º 35 en cuanto a producto interno bruto y primero en densidad de población.
Aunque el Distrito de Columbia no tiene un miembro votante del Congreso los residentes todavía están obligados a pagar impuestos al gobierno federal. Esto es diferente de los territorios de Estados Unidos, como Puerto Rico, cuyos ciudadanos en general no pagan impuestos sobre la renta individual. Los residentes protestan por la falta de derechos de voto, sobre todo porque la falta de representación en el Parlamento británico fue una de las principales razones para la independencia del país del Reino Unido. La ciudad adoptó una frase de la Guerra de la Independencia, «No hay tributación sin representación», para protestar por la falta de derechos de voto.4 El eslogan también aparece en las placas de automóvil expedidas por la ciudad.5



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Fuel cell vehicle
*Fuel cell vehicle



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Hydrogen propulsion
*Hydrogen propulsion

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 ***Hydrogen Energy
***Hydrogen Energy

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD



 Aerospace
Aerospace

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts
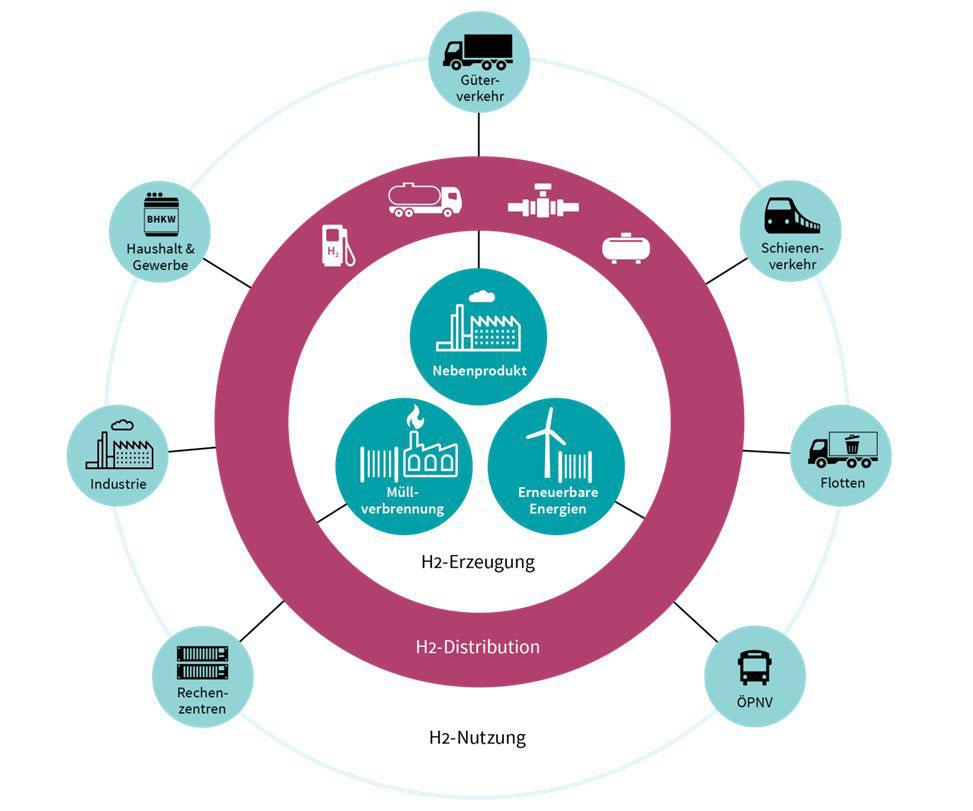


 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Zurich
Zurich
 Silk road
Silk road

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans
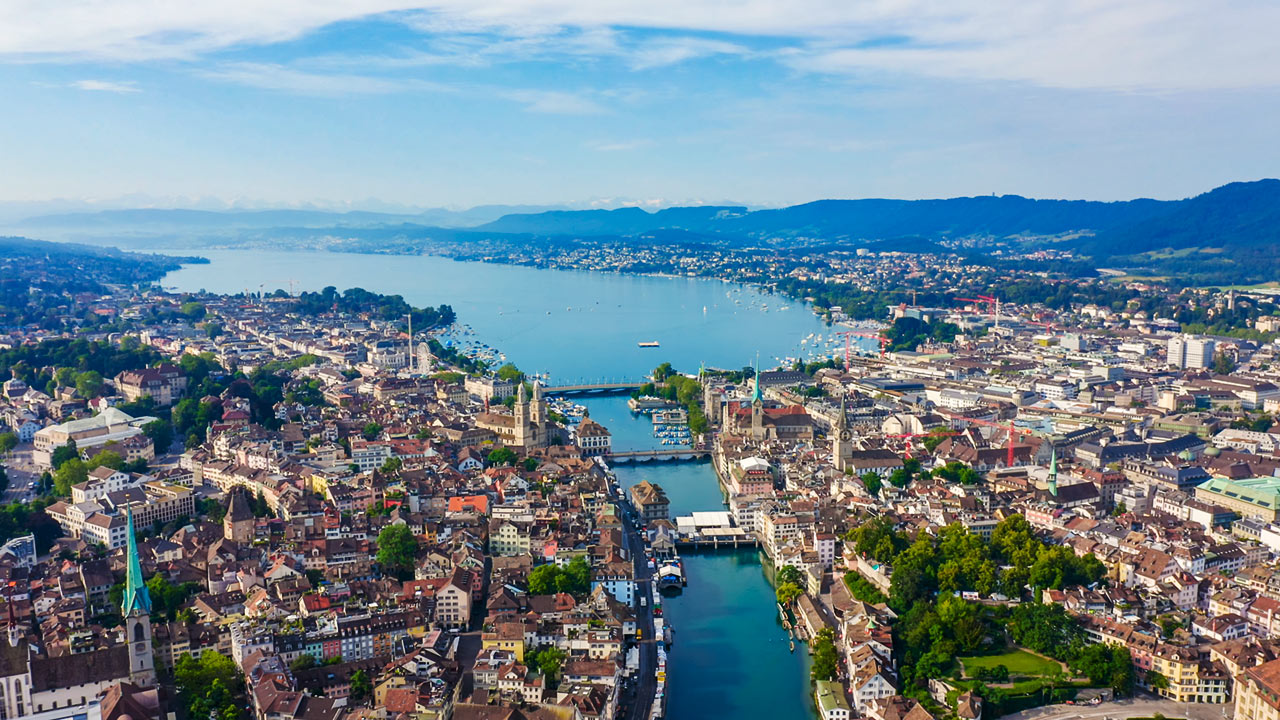

*苏黎世州拥有120万人口,几乎是瑞 士全国人口的六分之一。苏黎世市居民人口则为36万左右。当地人口的大多数除德语外,都至少会讲另一种外语。瑞士约有370万人(占瑞士总人口的一半)在 距离苏黎世中心一小时车程的范围内生活和工作。100家瑞士最大的企业中,有85家总部设在苏黎世地区。全球最大的美世人力资源咨询公司的“最适宜居住城 市”调查显示,苏黎世被认为是世界上生活质量整体指标最高的城市。
苏黎世(德语:Zürich [ˈt͡syːrɪç];瑞士德语:Züri [ˈt͡syɾi]),又译苏黎士,是瑞士联邦的最大城市(2012年城市人口约38万,市区人口近110万,包括郊区在内的苏黎世都会区人口达190万。),苏黎世州的首府。苏黎世是瑞士主要的商业和文化中心(瑞士的政治中心和首都在伯尔尼)。苏黎世是瑞士银行业的代表城市,世界金融中心之一,瑞士联合银行、瑞士信贷银行和许多私人银行都将总部设在苏黎世。苏黎世国际机场是瑞士全国最大的机场。国际足球联合会总部也设在苏黎世。根据2006年[3]和2007年[4]的部分调查显示,苏黎世在这两年的世界最佳居住城市评选中高居全球首位。
“苏黎世”的名称可能来源于凯尔特语中的“Turus”,一项有力的证据就是在出土的公元2世纪罗马帝国占领时期的墓志铭上发现了古代该城名称的罗马化形式——“Turicum”。
Zürich (zürichdeutsch Züri [ˈt͡sʏrɪ],[4] französisch Zurich [zyʁik], italienisch Zurigo [dzuˈriːɡo], rätoromanisch [tuˈritɕ]) ist eine Stadt, politische Gemeinde sowie Hauptort des gleichnamigen Kantons Zürich.
Die Stadt Zürich ist mit 402'762 Einwohnern (Stand 31. Dezember 2016)[5] die grösste Stadt der Schweiz und weist eine Bevölkerungsdichte von 4384 Einwohnern pro Quadratkilometer auf. Die Stadt Zürich gibt die Wohnbevölkerung nach dem wirtschaftlichen Wohnsitzbegriff (umfasst unter anderem auch Wochenaufenthalter, Asylsuchende, Flüchtlinge mit vorläufiger Aufnahme) mit 425'795 Personen per Mai 2018 an.[6] Mit 32,1 Prozent (31. Dezember 2016)[7] weist Zürich einen überdurchschnittlich hohen Ausländeranteil (registrierte Bevölkerung ohne Schweizer Bürgerrecht) auf. Das Umland ist dicht besiedelt, so dass in der Agglomeration Zürich etwa 1,3 Millionen[8] und in der Metropolitanregion Zürich etwa 1,83 Millionen Menschen leben.[9] Der Bezirk Zürich ist mit dem Stadtgebiet identisch.
Die Stadt liegt im östlichen Schweizer Mittelland, an der Limmat am Ausfluss des Zürichsees. Ihre Einwohner werden Zürcher genannt (bzw. Stadtzürcher zur Differenzierung von den übrigen Einwohnern des Kantons).
Das aus dem römischen Stützpunkt Turicum entstandene Zürich wurde 1262 freie Reichsstadt und 1351 Mitglied der Eidgenossenschaft. Die Stadt des Reformators Huldrych Zwingli erlebte im Industriezeitalter ihren Aufstieg zur heutigen Wirtschaftsmetropole der Schweiz. 2014 wurde Zürich der Ehrentitel „Reformationsstadt Europas“ durch die Gemeinschaft Evangelischer Kirchen in Europa verliehen.[10]
Mit ihrem Hauptbahnhof, dem grössten Bahnhof der Schweiz, und dem Flughafen ist die Stadt Zürich ein kontinentaler Verkehrsknotenpunkt. Dank der ansässigen Grossbanken (u. a. UBS und Credit Suisse) und Versicherungen (Zurich Insurance Group und Swiss Re) ist sie ein internationaler Finanzplatz und der grösste Finanzplatz der Schweiz, gefolgt von Genf und Lugano. Daneben beherbergt die Stadt mit der Eidgenössischen Technischen Hochschule Zürich und der Universität Zürich die zwei grössten universitären Hochschulen der Schweiz. Trotz der vergleichsweise geringen Einwohnerzahl wird Zürich zu den Weltstädten gezählt. Zürich ist das wichtigste Zentrum der Schweizer Medien- und Kreativbranche.[11] Mit seiner Lage am Zürichsee, seiner gut erhaltenen mittelalterlichen Altstadt und einem vielseitigen Kulturangebot und Nachtleben ist es zudem ein Zentrum des Tourismus.
Seit Jahren wird Zürich neben Genf als eine der Städte mit der weltweit höchsten Lebensqualität[12][13] und zugleich mit den höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten[14][15][16] weltweit gelistet.
チューリッヒ(ドイツ語: Zürich, ドイツ語発音: [ˈtsyːrɪç]; スイスドイツ語: Züri )は、スイス最大の都市でチューリッヒ州の州都である。スイス中央部にあり[1] 、チューリッヒ湖の北西端に位置している。チューリッヒ市の人口は約390,000人で[2]、チューリッヒ都市圏地域には200万人近くが居住している[3]。チューリッヒは鉄道、道路、航空など交通の要衝で、チューリッヒ国際空港やチューリッヒ中央駅共にスイスでは最大規模で交通量が多い。7,000年間継続的に人が居住しているが、チューリッヒはローマ人により創建された紀元前15年のトゥリクムTuricumと呼ばれていた時代に遡る。中世、チューリッヒは独立性と帝国直接身分を得ており、1519年にはフルドリッヒ・ツヴィングリが導くスイスのドイツ語圏でのプロテスタント宗教改革の発祥とその中心であった[4]。
チューリッヒは欧州有数の世界都市であり、2016年に発表された「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界16位と評価された[5]。また、世界の巨大な金融センターの一つに含まれる[6]。2017年の調査によると、世界11位の金融センターであり、ヨーロッパの都市ではロンドンに次ぐ2位である[7]。街には多くの金融機関や大手銀行、研究開発センターが立地している。これは、法人税率の低さが海外の企業が本社を設置する際に魅力的であるためである。ライフスタイルマガジン (Monocle) の2012年の生活の質の調査 "Quality of Life Survey" でチューリッヒはリストされた25都市中1位であった[8]。いくつかの調査によれば、2006年から2008年にチューリッヒは世界で最も居住に適した都市 との評価があり、同様にヨーロッパでは最も裕福な都市とされた[9][10][11]。2014年、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス・人材・文化・政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第31位の都市と評価されており、同国では第1位である[12]。治安・教育水準・各種インフラ等バランスよく整っている。なかでも金融においてはひときわ有名であり、数多くの金融機関・投資ファンド・投資家が存在している。特にチューリッヒに拠点を置く投機筋は「チューリッヒの小鬼」[13]と呼ばれ国際市場に大きな影響力を持っている。国際サッカー連盟(FIFA)をはじめとして、多くの国際機関・国際団体の本部も存在する。多くの博物館や美術館がチューリッヒ市内には立地しており、その中にはスイス国立博物館やチューリッヒ美術館が含まれる[14]。チューリッヒはまたドイツ語圏では最も重要な劇場の一つがある[15]。
Zürich or Zurich (/ˈzjʊərɪk/ ZEWR-ik; see below for other names) is the largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland[3] at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. The municipality has approximately 400,028[4] inhabitants, the urban agglomeration 1.315 million[5] and the Zürich metropolitan area 1.83 million.[6] Zürich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zürich Airport and railway station are the largest and busiest in the country.
Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zürich was founded by the Romans, who, in 15 BC, called it Turicum. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years ago.[7] During the Middle Ages, Zürich gained the independent and privileged status of imperial immediacy and, in 1519, became a primary centre of the Protestant Reformation in Europe under the leadership of Huldrych Zwingli.[8]
The official language of Zürich is German,[a] but the main spoken language is the local variant of the Alemannic Swiss German dialect, Zürich German.
Many museums and art galleries can be found in the city, including the Swiss National Museum and the Kunsthaus.[9] Schauspielhaus Zürich is one of the most important theatres in the German-speaking world.[10]
Zürich is a leading global city and among the world's largest financial centres despite having a relatively small population.[11] The city is home to a large number of financial institutions and banking companies. Most of Switzerland's research and development centres are concentrated in Zürich and the low tax rates attract overseas companies to set up their headquarters there.
Monocle's 2012 "Quality of Life Survey" ranked Zürich first on a list of the top 25 cities in the world "to make a base within".[12] According to several surveys from 2006 to 2008, Zürich was named the city with the best quality of life in the world as well as the wealthiest city in Europe in terms of GDP per capita.[13][14][15] The Economist Intelligence Unit's Global Liveability Ranking[16] sees Zürich rank among the top ten most liveable cities in the world.
Zurich (/zy.ʁik/) (allemand : Zürich /ˈtsyːʁɪç/, en Suisse /ˈtsyːrɪx/ Zürich, suisse allemand : Züri /ˈtsyɾi/, italien : Zurigo /dzuˈriːɡo/, romanche : Turitg /tuˈritɕ/) est une cité alémanique de Suisse, capitale du canton de Zurich. Même si l'allemand est la langue officielle, les Zurichois parlent le Züritüütsch, un dialecte de l'alémanique qui emprunte d'ailleurs certains termes à d'autres langues en plus de l'allemand dont le français, l'italien, ou encore l'anglais3. C'est une cité très cosmopolite, comptant 30 % d'étrangers. Dans son article intitulé « World's most expensive place to live is... » du 15 février 2012, The Economist classe Zurich comme étant la ville la plus chère au monde. Depuis, la ville occupe régulièrement la deuxième place dans le classement du journal britannique, juste derrière Hong Kong. Le cabinet Mercer la classe en deuxième position de 221 villes dans le monde en 2012 pour sa qualité de vie, juste derrière Amsterdam et devant Vienne 4.
Alors que Berne est la capitale de la Confédération suisse et un centre politique, Zurich est le centre économique, financier, scientifique et artistique international majeur du pays. Elle est la ville concentrant le plus d'établissements bancaires et financiers du pays, et fait d'ailleurs partie des « villes mondiales » de catégorie Alpha- selon la GaWC. Zurich est ainsi le sixième centre bancaire et financier mondial, derrière Londres, New York, Hong Kong, Singapour et Tokyo.
Zurich est la ville la plus peuplée de Suisse avec une population de près de 402 800 habitants en décembre 2016. L'agglomération, quant à elle, compte environ 1,3 million d'habitants, ce qui fait de Zurich une « petite » métropole en comparaison d'autres cités ayant une importance similaire5.
Située au bord du lac de Zurich (Zurichsee), le quatrième plus grand lac de Suisse en termes de superficie, Zurich est un lieu de villégiature apprécié par la bourgeoisie suisse, allemande et autrichienne, notamment en raison de la beauté de sa vue et de son centre historique, ainsi que de la douceur exceptionnelle de son climat. La rivière la traversant, la Limmat, a été classée rivière urbaine la plus propre d'Europe selon le Département de l'Agriculture des États-Unis en 2015. Les Zurichois ont l'habitude de s'y baigner, en plein cœur de la ville, en été.
Zurigo (/ʣuˈrigo/; in tedesco Zürich, pronunciato [ˈʦyːʀɪç]; in alemanno Züri; in francese Zurich, [zyˈʁik]; in romancio Turitg; in latino Turicum) è, con 402.762 abitanti, la maggiore città della Svizzera, nonché il capoluogo del cantone omonimo. È divisa in 12 quartieri. L'agglomerato urbano raggiunge 1,3 milioni di abitanti[1] e la sua regione metropolitana 1,83 milioni.
Zúrich4 (en alemán Zürich [ˈtsyːʁɪç] o [ˈtsʏrɪç], en francés Zurich [zyʁik], en italiano Zurigo [dzuˈriːɡo],5 en romanche Turitg [tuˈritɕ]) es la principal ciudad de la Confederación Suiza, con una población de 404 783 habitantes en 2014 y un área metropolitana de 1 392 396 de habitantes. Es la capital del cantón de Zúrich y se encuentra ubicada en el distrito de Zúrich, en la llanura central de Suiza y próxima a los Alpes. Es el motor financiero (en Zúrich se encuentra la banca internacional) y centro cultural del país, siendo además una ciudad galardonada con el título de ciudad con mayor calidad de vida en el mundo por dos ocasiones consecutivas (2006-2008).67
Los primeros asentamientos en la ciudad se remontan hasta el año 15 a. C., con la fundación de la aduana romana Turicum, y en el siglo X adquirió el estatus de ciudad. Rodeando al pequeño casco antiguo se disponen los Kreise (distritos) de Zúrich, ordenados según el sentido de las agujas del reloj. La ciudad moderna sirve de contraste con la histórica, gracias a los numerosos y vanguardistas bancos, tiendas de lujo y modernos bares y cafés. Uno de los símbolos de la ciudad es el lago de Zúrich.
Цю́рих (нем. Zürich [ˈtsyːrɪç]; швейц. Züri [tsy:ri], фр. Zurich, итал. Zurigo) — город на северо-востоке Швейцарии. Столица немецкоязычного кантона Цюрих и административный центр одноимённого округа.
С населением в 397 тыс. человек (2015 год), Цюрих является крупнейшим городом страны. В пределах агломерации проживает более 1 млн человек.
Расположен на берегу Цюрихского озера при выходе из него реки Лиммат, в долине между горными вершинами Утлиберг и Цюрихберг.
Относится к глобальным городам. Крупнейший финансовый центр Швейцарии: местонахождение штаб-квартир страховых компаний и банков, в том числе международных UBS и Credit Suisse, швейцарской фондовой биржи и одной из штаб-квартир центрального банка Швейцарии. Крупный научный центр: университет и высшая техническая школа. В 2011 году Цюрих занял второе место в мире по качеству жизни[3], в 2012 году признан самым дорогим городом мира[4].
Над историческим центром возвышаются романо-готические соборы Гросмюнстер, Фраумюнстер и церковь святого Петра. На острове расположена ратуша в стиле ренессанса.
В древности на месте Цюриха существовало кельтско-германское поселение, в I веке до н. э. получившее римское название Турикум. Как город впервые упоминается в 929 году. В XIII—XVII веках был имперским городом. В XIV веке вошёл в Швейцарский союз. В XVI веке один из центров Реформации во главе с Цвингли. Во 2-й половине XIX века превратился в финансовый центр страны.
 European Union
European Union
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 International cities
International cities
 Astronomy
Astronomy