
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Berlin
Berlin

 Belarus
Belarus

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland

 Review
Review
 Russia
Russia

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland

 Traditions
Traditions

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 World Heritage
World Heritage

一种特别在德国北海和波罗的海海岸常见的哥特式建筑是用烤砖建造起来的建筑结构.这个十二世纪开始使用那红色的烤砖作为建筑材料的独特建筑风格之所以在北部德国低地如此普及是因为这块地区缺少天然石而且运输也非常困难,由于那片地区和汉萨盟的一 致性,因此它就成为了汉萨同盟的象征.有些历史悠久的建筑也就成了联合国教科文组织世界文化遗产项目之一。
Die Backsteingotik (englisch Brick Gothic, polnisch Gotyk ceglany) umfasst gotische Bauwerke, die aus oder mit sichtbarem Backstein errichtet wurden. Sie ist vor allem in Norddeutschland, dem Ostseeraum und den Niederlanden[1] verbreitet. Ihr Verbreitungsgebiet erstreckt sich im Westen bis an die Straße von Dover und im Südosten bis nach Galizien. Der auch oft verwendete Begriff Norddeutsche Backsteingotik erfasst daher nur einen Teil der gesamten Backsteingotik. Gotische Backsteinarchitektur in Italien und Südfrankreich wird in der Regel allein den dortigen Regionalstilen zugerechnet.
Die mittelalterliche Verwendung von Backstein als Baustoff setzte nördlich der Alpen im 12. Jahrhundert ein. Die ältesten Bauten gehören deshalb noch der so genannten Backsteinromanik an. Im 16. Jahrhundert ging die Backsteingotik in die Backsteinrenaissance über. Die geografische Verbreitung des Bauens aus Backstein und mit sichtbarem Backstein unterlag vom Beginn des Hochmittelalters bis in die frühe Neuzeit aber durchaus Veränderungen. So gab es in Teilen des Münsterlandes zwischen Pionierbauten der Romanik und dem starken Backsteineinsatz in Renaissance und Barock eine zeitliche Lücke.
Viele von der Backsteingotik geprägte Altstädte und Einzelbauten wurden in die Liste des UNESCO-Welterbes aufgenommen.
Brick Gothic (German: Backsteingotik, Polish: Gotyk ceglany, Dutch: Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northwest and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places a lot of glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Sweden and Finland.
As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture.
Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figural architectural sculpture, widespread in other styles of Gothic architecture. Typical for the Baltic Sea region is the creative subdivision and structuring of walls, using built ornaments and the colour contrast between red bricks, glazed bricks and white lime plaster. Nevertheless, these characteristics are neither omnipresent nor exclusive. Many of the old town centres dominated by Brick Gothic, as well as some individual structures, have been listed as UNESCO World Heritage sites.
The real extent and the real variety of this brick architecture has to be distinguished from the view of late 19th and early 20th century, especially the years around the end of World War I, when it was instrumentalized, politically.
Indeed, about a quarter of medieval Gothic brick architecture is standing in the Netherlands, in Flanders and in French Flanders. Some dominant buildings combinations of brick and stone. But the criterion "no stone at all" looks like a trick to exclude them.[according to whom?] The towers of St Mary church in Lübeck, the very top Brick Gothic church of the Baltic Sea region, have corners of granite ashley. And many village churches in northern Germany and Poland have Brick Gothic design, but most of their walls are formed by boulders.
L'architettura gotica dei paesi baltici è una varietà regionale dell'architettura gotica, in particolare del gotico tedesco. Le aree coinvolte in questa forma di architettura medievale si affacciano sul mar Baltico e sul Mare del Nord e, da un punto di vista politico, comprendevano gli stati settentrionali del Sacro Romano Impero, le città della Lega Anseatica, i possedimenti dell'Ordine Teutonico. Il periodo interessato va dal XIII secolo al XV secolo.
Le caratteristiche distintive sono che si tratta di un'architettura prevalentemente in laterizio e di una rielaborazione originale e per certi aspetti molto distante dall'iniziale gotico francese. I paesi europei attuali che hanno testimonianze di questa architettura sono Germania, Polonia, Lituania, Lettonia, Estonia, e nell'area della storica Prussia Orientale, (Oblast di Kaliningrad Russia); alcune testimonianze sono anche presenti in Scandinavia.
Le gothique de brique (allemand : Backsteingotik) est un style d´architecture gothique du Nord de l´Europe, et plus particulièrement du Nord de l'Allemagne et des régions autour de la mer Baltique. Il s'est surtout répandu dans les villes culturellement allemandes de l'ancienne Ligue Hanséatique à partir du XIIIe siècle, puis bien au-delà par influence (Scandinavie, Flandres, toute la Pologne, Allemagne du Sud). Les bâtiments sont essentiellement constitués de briques et le style de la décoration s'est adapté aux possibilités et aux limites de ce matériaux, conférant à cette architecture une identité bien particulière.
Il existe d'autres styles d'architecture gothique en brique en Europe, plus ou moins indépendants, comme en Italie et dans la région Toulousaine en France. Le style gothique baltique ne comprend pas tout le gothique en brique d'Europe.
El gótico báltico (en alemán, Norddeutsche Backsteingotik), forma la parte mayor del gótico de ladrillos (en alemán: Backsteingotik). Es una variante de la arquitectura gótica y neogótica que apareció en la Europa septentrional. Sin la especificación "Baltico" es estendido del estrecho de Calais a la Galicia de los Cárpatos. Con la especificación "Baltico" esta concentrada en el norte de Alemania y las zonas aledañas al mar Báltico. En todas estas regiones mancan recursos naturales para construir edificios de piedra. Se extendió principalmente en las ciudades culturalmente alemanas de la antigua Liga Hanseática desde el siglo XIII, y luego por influencia (Escandinavia, toda Polonia, el sur de Alemania). Los edificios son esencialmente de ladrillo y el estilo de decoración se ha adaptado a las posibilidades y límites de este material, dando a esta arquitectura una identidad muy particular.
Кирпичная, ганзейская или северогерманская готика — разновидность готического стиля архитектуры, распространённая в Северной Германии, Польше, Белоруссии и Прибалтике в XIII—XVI веках. Красный керамический кирпич как строительный материал стал использоваться в Северной Европе в XII веке, поэтому самые древние кирпичные образцы относятся ещё к так называемой «кирпичной романике». В XVI в. кирпичную готику сменил «кирпичный ренессанс».
Для кирпичной готики характерны, с одной стороны, отсутствие скульптурных украшений, которые невозможно выполнить из кирпича, и, с другой стороны, богатство орнаментальных деталей кладки и структуризация плоскостей за счёт чередования красного либо глазурованного кирпича и известковой побелки стен.
Многие города, внешний облик которых украшают готические сооружения из красного кирпича, являются объектами Всемирного культурного наследия ЮНЕСКО.



 Berlin
Berlin
 Germany
Germany
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
Women's Soccer World Cup 2011

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 League of Legends
League of Legends
 League of Legends World Championship
League of Legends World Championship
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 Silk road
Silk road

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 World Heritage
World Heritage
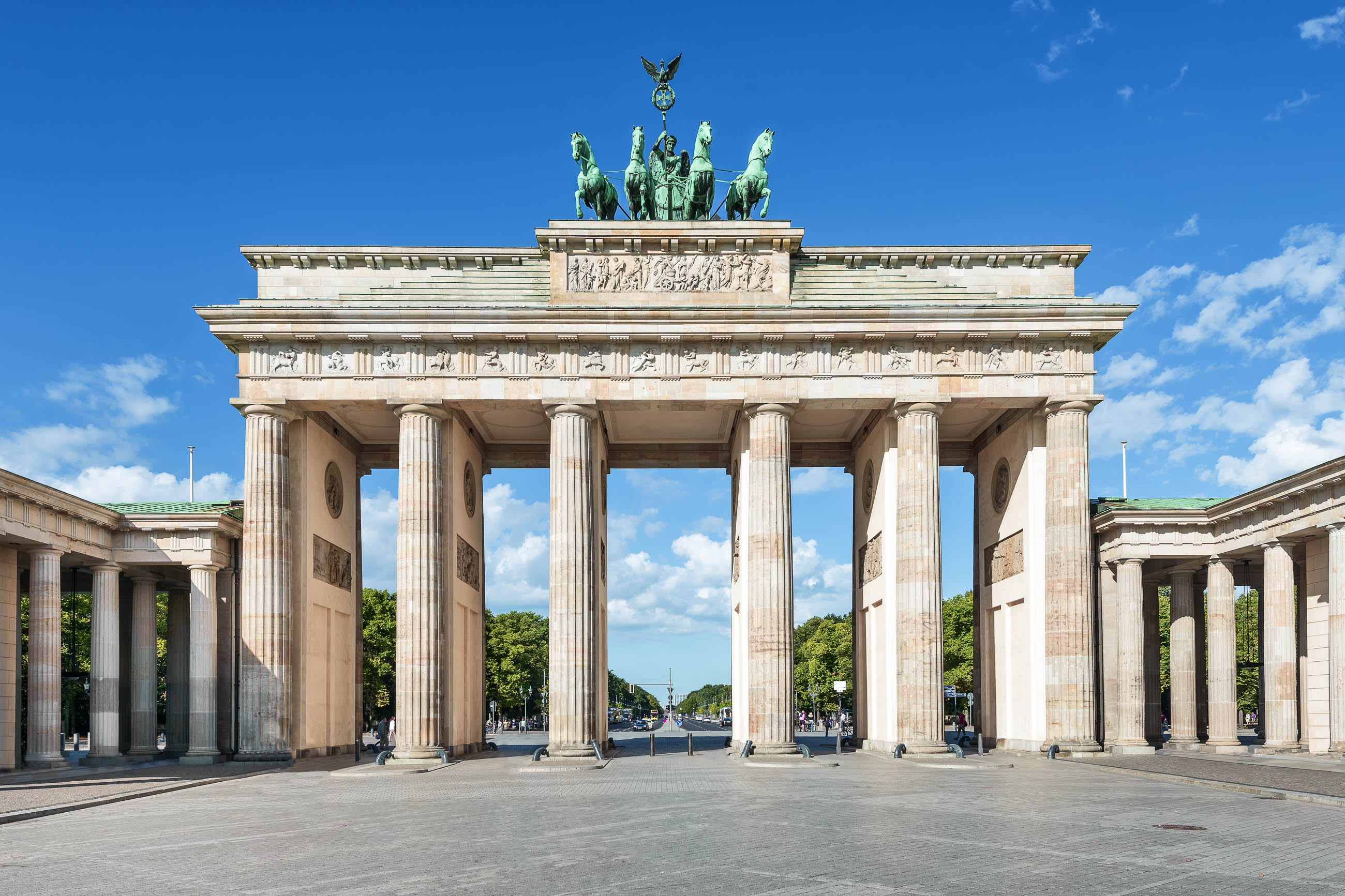

柏林(德语:Berlin,德语发音: [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] (![]() listen))是德国首都,也是德国最大的城市,现有居民约340万人。柏林位于德国东北部,四面被勃兰登堡州环绕,施普雷河和哈维尔河流经该市。柏林也是德国十六个联邦州之一,和汉堡、不来梅同为德国僅有的三個的城市州。
listen))是德国首都,也是德国最大的城市,现有居民约340万人。柏林位于德国东北部,四面被勃兰登堡州环绕,施普雷河和哈维尔河流经该市。柏林也是德国十六个联邦州之一,和汉堡、不来梅同为德国僅有的三個的城市州。
柏林是欧盟區內人口第2多的城市以及城市面积第8大的城市。它是柏林-勃兰登堡都会区的中心,有来自超过190个国家的5百万人口。地理上位于欧洲平原,受温带季节性气候影响。城市周围三分之一的土地由森林、公园、花园、河流和湖泊组成。
该市第一次有文字记载是在13世纪,柏林连续的成为以下这些国家的首都:普鲁士王国(1701年-1870年)、德意志帝国(1871年-1918年)、魏玛共和国(1919年-1933年)、納粹德國(1933年-1945年)。在1920年代,柏林是世界第3大自治市。第二次世界大战后,城市被分割;东柏林成为了东德的首都,而西柏林事实上成为了西德在东德的一块飛地,被柏林墙围住。直到1990年两德统一,该市重新获得了全德国首都的地位,驻有147个外国大使馆。
柏林无论是从文化、政治、传媒还是科学上讲都称的上是世界级城市。该市经济主要基于服务业,包括多种多样的创造性产业、传媒集团、议会举办地点。柏林扮演了一个欧洲大陆上航空与铁路运输交通枢纽的角色,同时它也是欧盟内游客数量最多的城市之一。主要的产业包括信息技术、制药、生物工程、生物科技、光学电子、交通工程和可再生能源。
柏林都会区有知名大学、研究院、体育赛事、管弦乐队、博物馆和知名人士。城市的历史遗存使该市成为国际电影产品的交流中心。该市在节日活动、建筑的 多样化、夜生活、当代艺术、公共交通网络以及高质量生活方面得到了广泛认可。柏林已经发展成一个全球焦点城市,以崇尚自由生活方式和现代精神的年轻人和艺 术家而闻名。
Berlin ![]() [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] ist die Bundeshauptstadt der Bundesrepublik Deutschland und zugleich eines ihrer Länder.[12] Die Stadt Berlin ist mit rund 3,6 Millionen Einwohnern die bevölkerungsreichste und mit 892 Quadratkilometern die flächengrößte Gemeinde Deutschlands.[5] Sie bildet das Zentrum der Metropolregion Berlin/Brandenburg (rund 6 Millionen Einwohner) und der Agglomeration Berlin (rund 4,5 Millionen Einwohner). Der Stadtstaat besteht aus zwölf Bezirken. Neben den Flüssen Spree und Havel befinden sich im Stadtgebiet kleinere Fließgewässer sowie zahlreiche Seen und Wälder.
[bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] ist die Bundeshauptstadt der Bundesrepublik Deutschland und zugleich eines ihrer Länder.[12] Die Stadt Berlin ist mit rund 3,6 Millionen Einwohnern die bevölkerungsreichste und mit 892 Quadratkilometern die flächengrößte Gemeinde Deutschlands.[5] Sie bildet das Zentrum der Metropolregion Berlin/Brandenburg (rund 6 Millionen Einwohner) und der Agglomeration Berlin (rund 4,5 Millionen Einwohner). Der Stadtstaat besteht aus zwölf Bezirken. Neben den Flüssen Spree und Havel befinden sich im Stadtgebiet kleinere Fließgewässer sowie zahlreiche Seen und Wälder.
Urkundlich erstmals im 13. Jahrhundert erwähnt, war Berlin im Verlauf der Geschichte und in verschiedenen Staatsformen Residenz- und Hauptstadt Brandenburgs, Preußens und des Deutschen Reichs. Ab 1949 war der Ostteil der Stadt Hauptstadt der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik. Mit der deutschen Wiedervereinigung im Jahr 1990 wurde Berlin wieder gesamtdeutsche Hauptstadt und in der Folge Sitz der Bundesregierung, des Bundespräsidenten, des Bundestages, des Bundesrates sowie zahlreicher Bundesministerien und Botschaften.
Zu den bedeutenden Wirtschaftszweigen in Berlin gehören unter anderem der Tourismus, die Kreativ- und Kulturwirtschaft, die Biotechnologie und Gesundheitswirtschaft mit Medizintechnik und pharmazeutischer Industrie, die Informations- und Kommunikationstechnologien, die Bau- und Immobilienwirtschaft, der Handel, die Optoelektronik, die Energietechnik sowie die Messe- und Kongresswirtschaft. Die Stadt ist ein europäischer Knotenpunkt des Schienen- und Luftverkehrs. Berlin zählt zu den aufstrebenden, internationalen Zentren für innovative Unternehmensgründer und verzeichnet jährlich hohe Zuwachsraten bei der Zahl der Erwerbstätigen.[13]
Berlin gilt als Weltstadt der Kultur, Politik, Medien und Wissenschaften.[14][15][16][17] Die Universitäten, Forschungseinrichtungen, Sportereignisse und Museen Berlins genießen internationalen Ruf.[18] Die Metropole trägt den UNESCO-Titel Stadt des Designs und ist eines der meistbesuchten Zentren des Kontinents.[19] Berlins Architektur, Festivals, Nachtleben und vielfältige Lebensbedingungen sind weltweit bekannt.[20]
ベルリン(独: Berlin ドイツ語発音: [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] (![]() 音声ファイル)、伯林)は、ドイツ北東部、ベルリン・ブランデンブルク大都市圏地域の中心に位置する都市である。16ある連邦州のうちの一つで、市域人口は350万人[1]とドイツでは最大の都市で欧州連合の市域人口ではロンドンに次いで2番目に多く、都市的地域の人口は7番目に多い。[3]同国の首都と定められている[4]。
音声ファイル)、伯林)は、ドイツ北東部、ベルリン・ブランデンブルク大都市圏地域の中心に位置する都市である。16ある連邦州のうちの一つで、市域人口は350万人[1]とドイツでは最大の都市で欧州連合の市域人口ではロンドンに次いで2番目に多く、都市的地域の人口は7番目に多い。[3]同国の首都と定められている[4]。
ベルリンが属するベルリン・ブランデンブルク大都市圏地域の人口は590万人に達し[6]、190カ国を超える海外出身者も暮らす[7]。ベルリンはヨーロッパ平原に位置し温帯の季節的な気候の影響を受ける。市域の3分の1は森林、公園、庭園、河川や湖で構成されている[8]。ベルリンが最初に文書に言及されたのは13世紀のことで、それ以後プロイセン王国(1701-1918)やドイツ帝国(1871-1918)、ヴァイマル共和政(1919-1933)、ナチス・ドイツ(1933-1945)の首都であった[9]。1920年には「大ベルリン」の成立により市域が大幅に拡大し、現在とほぼ同じ領域となった。1920年代には世界で3番目に大きな都市であった[10]。第二次世界大戦後、ベルリンは東ドイツの首都である東ベルリンと、西ドイツの事実上の飛び地で周辺をベルリンの壁(1961-1989)で囲まれた西ベルリンに分断された[11]。1990年のドイツ再統一によりベルリンは再び首都としての地位を得て[12]、147の大使館が置かれる[13][14]。ベルリンは文化や政治、メディア、科学の世界都市である[15][16][17]。アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界14位の都市と評価された[18]。
経済的にはサービス産業を基盤とし創造産業やメディア産業、コンベンション会場などが包括されている。ベルリンはまた、欧州大陸の航空や鉄道交通の中枢でもあり[19][20] 、代表的な観光地である。重要な産業にはIT、製薬、生物医学技術、生物工学、電子工学、交通工学、再生可能エネルギーが含まれる。 ベルリンは有名な大学や調査機関、管弦楽団、博物館、著名人が本拠としており多くのスポーツイベントも催されている他[21]、都市の光景や歴史的な遺産は国際的な映画製作には人気な場所となっている[22]。ベルリンでは多く祭典や多様な建築、ナイトライフ、現代芸術、公共交通機関の路線網、世界で最も居住に適した都市など様々な分野でも良く知られた都市である[23]。
ドイツ最大の都市であり立法・行政の中心地ではあるが、地方分権の歴史が長いドイツでは、司法の中心地はカールスルーエ、金融と交通の中心地はフランクフルト、産業の中心地はルール地方、ミュンヘン、シュトゥットガルト、ケルンとされ、東京(日本)やソウル(韓国)、パリ(フランス)のような一極集中という状態はない[24]。戦間期には科学技術や文学、哲学、芸術などが発展しヴァイマル文化によりドイツはもっとも進んだ国となった[25][26]。1988年の欧州文化首都に選ばれている[27]。現代の都市ベルリンは発展の一方で、特に東側の人口停滞などから都市構造の変革が進められている[28]。
Berlin (/bɜːrˈlɪn/; German pronunciation: [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn]) is the capital and the largest city of Germany, as well as one of its 16 constituent states. With a steadily growing population of approximately 3.7 million,[4] Berlin is the second most populous city proper in the European Union behind London and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union.[5] Located in northeastern Germany on the banks of the rivers Spree and Havel, it is the centre of the Berlin-Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, which has roughly 6 million residents.[6][7][8][9] Due to its location in the European Plain, Berlin is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate. Around one-third of the city's area is composed of forests, parks, gardens, rivers, canals and lakes.[10]
First documented in the 13th century and situated at the crossing of two important historic trade routes,[11] Berlin became the capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1417–1701), the Kingdom of Prussia (1701–1918), the German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), and the Third Reich (1933–1945).[12] Berlin in the 1920s was the third largest municipality in the world.[13] After World War II and its subsequent occupation by the victorious countries, the city was divided; West Berlin became a de facto West German exclave, surrounded by the Berlin Wall (1961–1989) and East German territory.[14] East Berlin was declared capital of East Germany, while Bonn became the West German capital. Following German reunification in 1990, Berlin once again became the capital of all of Germany.
Berlin is a world city of culture, politics, media and science.[15][16][17][18] Its economy is based on high-tech firms and the service sector, encompassing a diverse range of creative industries, research facilities, media corporations and convention venues.[19][20] Berlin serves as a continental hub for air and rail traffic and has a highly complex public transportation network. The metropolis is a popular tourist destination.[21] Significant industries also include IT, pharmaceuticals, biomedical engineering, clean tech, biotechnology, construction and electronics.
Berlin is home to world-renowned universities, orchestras, museums, and entertainment venues, and is host to many sporting events.[22] Its Zoological Garden is the most visited zoo in Europe and one of the most popular worldwide. With the world's oldest large-scale movie studio complex, Berlin is an increasingly popular location for international film productions.[23] The city is well known for its festivals, diverse architecture, nightlife, contemporary arts and a very high quality of living.[24] Since the 2000s Berlin has seen the emergence of a cosmopolitan entrepreneurial scene.[25]
Berlin (prononcé [bɛʁ.lɛ̃] ; en allemand Berlin [bɛɐ̯.ˈliːn] Écouter) est la capitale1 et la plus grande ville d'Allemagne. Institutionnellement, c’est une ville-État nommée Land de Berlin.
Située dans le nord-est du pays, Berlin compte environ 3,7 millions d'habitants2. Ses habitants s'appellent les Berlinois. Elle est la deuxième ville et la septième agglomération la plus peuplée de l'Union européenne. L'agglomération de Berlin s'étend sur 892 km2 et compte 4,4 millions d'habitants. La région métropolitaine de Berlin-Brandebourg qui cumule les Länder de Berlin et de Brandebourg regroupe au total près de 6 millions d'habitants.
Fondée au XIIIe siècle, Berlin a été successivement capitale de l'électorat du Brandebourg (1247-1701), du royaume de Prusse (1701-1871), de l'Empire allemand (1871-1918), de la République de Weimar (1919-1933) et du Troisième Reich (1933-1945). Après 1945 et jusqu'à la chute du mur de Berlin en 1989, la ville est partagée en quatre secteurs d'occupation. Pendant la Guerre froide, le secteur soviétique de la ville, nommé Berlin-Est, est devenu la capitale de la République démocratique allemande, tandis que Berlin-Ouest était politiquement rattachée à la République fédérale d'Allemagne, devenant ainsi un bastion avancé du « Monde libre » à l'intérieur du Bloc communiste. Après la chute du mur, Berlin redevint, en 1990, la capitale de l'Allemagne alors réunifiée, et les principales institutions fédérales y emménagèrent en 1999.
Berlin est une ville mondiale culturelle et artistique de premier plan. La ville abrite 166 musées, 142 bibliothèques et 60 théâtres. En 2014, Berlin a accueilli 11,87 millions de visiteurs (+4,8 % plus qu'en 2013)3, dont 4,52 millions de visiteurs étrangers (+5,2 %).
Berlino (AFI: /berˈlino/[2]; in tedesco: Berlin, /bɛɐ̪ ˈliːn/, ) è la maggiore città e anche un Bundesland della Germania, quindi una "città-stato". Capitale federale della Repubblica Federale di Germania e sede del suo governo, è uno dei più importanti centri politici, culturali, scientifici, fieristici e mediatici d'Europa e, dopo Londra, il secondo comune più popoloso dell'Unione europea, con 3.531.201 abitanti.
In passato è stata la capitale della Marca di Brandeburgo (1417-1801), del Regno di Prussia (1701-1918), dell'Impero tedesco (1871-1918), della Repubblica di Weimar (1919-1933) e del Terzo Reich (1933-1945).
L'area metropolitana ha una superficie complessiva di 2.851 km² ed una popolazione di 5.103.778 abitanti, mentre la regione metropolitana di Berlino e Brandeburgo ha una superficie di 30.370 km² ed una popolazione[3] di 7.220.12 abitanti.
Berlín (Berlin en alemán (![]() [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] (?·i))) es la capital de Alemania y uno de los dieciséis estados federados alemanes. Se localiza al noreste de Alemania. Por la ciudad fluyen los ríos Esprea, Havel, Panke, Dahme y Wuhle. Con una población de 3,5 millones de habitantes, Berlín es la ciudad más poblada del país y de Europa Central, así como la primera ciudad en población y la séptima aglomeración urbana entre los países de la Unión Europea (si bien se convertirá en la sexta una vez la salida del Reino Unido de la Unión Europea se haga efectiva).2
[bɛɐ̯ˈliːn] (?·i))) es la capital de Alemania y uno de los dieciséis estados federados alemanes. Se localiza al noreste de Alemania. Por la ciudad fluyen los ríos Esprea, Havel, Panke, Dahme y Wuhle. Con una población de 3,5 millones de habitantes, Berlín es la ciudad más poblada del país y de Europa Central, así como la primera ciudad en población y la séptima aglomeración urbana entre los países de la Unión Europea (si bien se convertirá en la sexta una vez la salida del Reino Unido de la Unión Europea se haga efectiva).2
Fundada en 1237 como Cölln, Berlín fue sucesivamente capital del Reino de Prusia (1701-1918), de la República de Weimar (1919-1933) y del Tercer Reich (1933-1945). Después de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, la ciudad fue dividida; la parte este de la ciudad se convirtió en la capital de la República Democrática Alemana, mientras que la región oeste de la ciudad se convirtió en un enclave de la República Federal de Alemania en el interior de la Alemania Oriental.
Berlín es una ciudad mundial y un centro cultural y artístico de primer nivel. Es una de las ciudades más influyentes en el ámbito político de la Unión Europea y en 2006 fue elegida Ciudad Creativa por la Unesco.3 En 2009 la ciudad recibió el Premio Príncipe de Asturias de la Concordia.
Берли́н (нем. Berlin [bɛɐ̯ˈliːn], произношение ) — столица и крупнейший город Германии, второй по населению (после Лондона) и пятый по площади город Евросоюза.
Является одной из 16 земель в составе ФРГ. Город расположен на берегах рек:
- Шпрее (в связи с чем его называют «Афинами на Шпрее»),
- Хафель в центре федеральной земли Бранденбург (частью последней Берлин не является с 1920 года).
Около 1200 года на месте современного Берлина располагались два торговых поселения — Кёлльн и Берлин. Точная дата получения ими городских прав неизвестна. Городские права Кёльна впервые упоминаются в 1237 году, городские права Берлина — в 1244 году. В 1307 году города объединились и образовали общую городскую управу. В 1400 году население объединённого Берлина составляло 8000 человек. Историческое название «Кёльн» нашло своё отражение в названии берлинского района Нойкёльн.
Берлин был столицей маркграфства/курфюршества Бранденбургского (с 1417 года), Пруссии (после объединения курфюршества Бранденбург с герцогством Пруссия) и после создания Германской империи стал её столицей.
После Второй мировой войны в соответствии с решениями Ялтинской конференции Берлин, хоть и находился на территории советской зоны оккупации Германии, был разделён четырьмя державами-победительницами на оккупационные секторы. Позднее три сектора оккупации союзников были преобразованы в Западный Берлин, получивший статус особого государственного образования, но безусловно тесно связанного с ФРГ. Передвижение между секторами Берлина длительное время оставалось относительно свободным, и в целях предотвращения утечки населения в западные секторы правительством ГДР было принято решение о возведении Берлинской стены, окружившей с 13 августа 1961 года Западный Берлин. Берлинская стена, ставшая одним из главных символов холодной войны, просуществовала до 1989 года. После объединения Германии в 1990 году её столицей стал воссоединённый Берлин. В 1994 году туда переехала из Бонна администрация президента и в 1999 году — бундестаг и ведомство федерального канцлера вместе с федеральными министерствами.
Сегодня Берлин является мировым культурным центром. Это крупный европейский транспортный узел и один из самых посещаемых городов на континенте. Университеты, исследовательские институты и музеи Берлина известны во всём мире. В городе живут и работают художники, дипломаты и иммигранты со всех уголков планеты.




 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 Marathon
Marathon

 Berlin
Berlin
 Germany
Germany

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Athletics International
Athletics International
 World Marathon Majors
World Marathon Majors
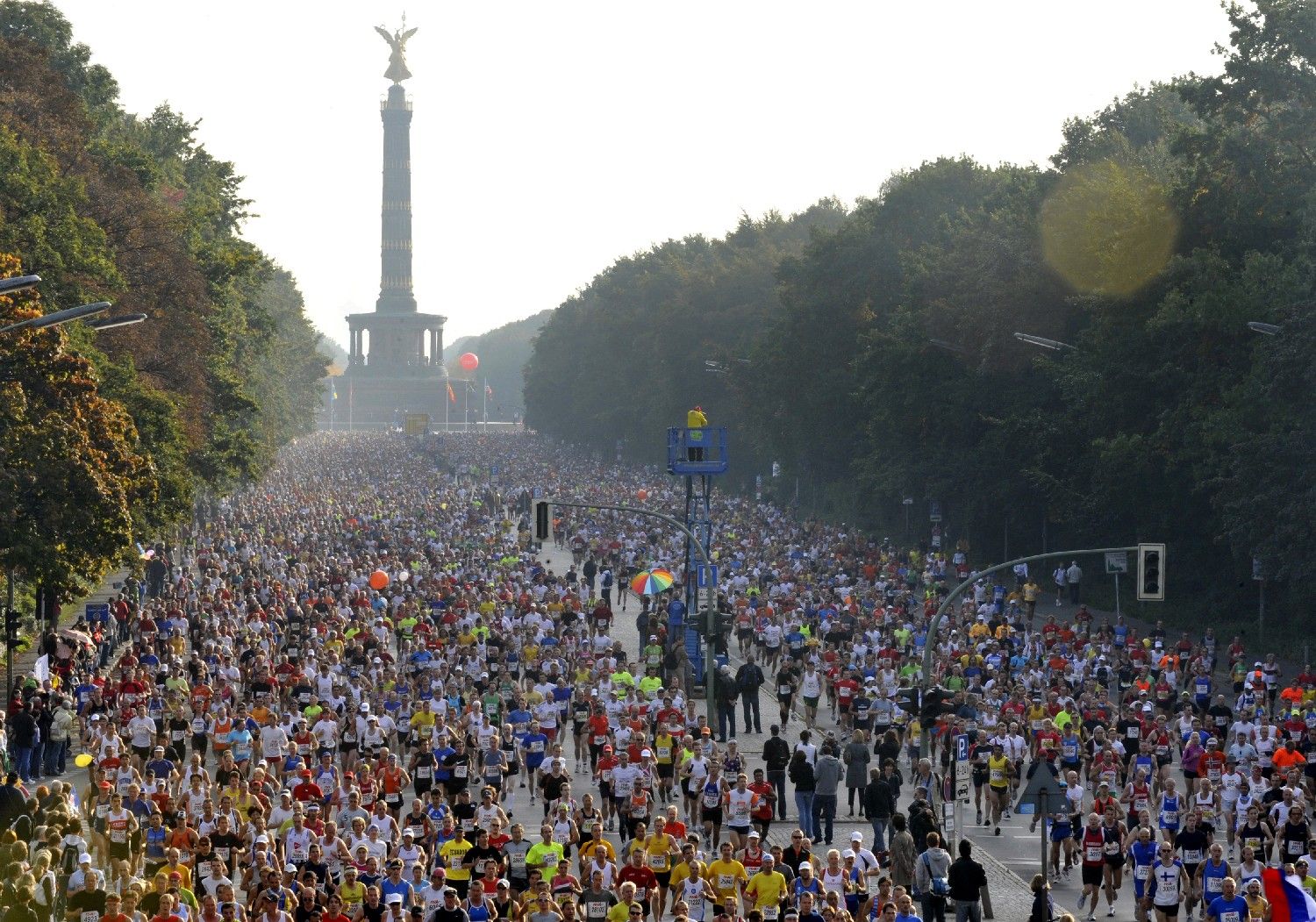

Der Berlin-Marathon (derzeit offizieller Name BMW BERLIN-MARATHON) ist ein jährlich in Berlin stattfindender Straßen- und Volkslauf. Der vom SC Charlottenburg veranstaltete Lauf fand erstmals im Oktober 1974 als Berliner Volksmarathon statt und ist heute Deutschlands teilnehmerstärkste Marathon-Laufveranstaltung.
Der aktuelle Modus des Berlin-Marathons ist eine Zweitages-Veranstaltung (Samstag/Sonntag). Neben dem Hauptlauf am Sonntag über 42,195 km (inkl. Rollstuhlfahrer und Handbiker) gibt es am Samstag einen Mini-Marathon für Schüler über die letzten 4,2195 km der Originalstrecke sowie einen Marathon für Inlineskater.
Der Lauf ist einer der World Marathon Majors und gehört neben den Veranstaltungen in New York, Boston und London zu den größten und renommiertesten Marathonläufen der Welt. Nach den durchschnittlichen Zeiten der jeweils besten zehn Ergebnisse der Männer und der Frauen ist die Berliner Strecke die schnellste der Welt[1]. Im Berlin Marathon wurden dreizehn offizielle IAAF-Weltrekorde aufgestellt, zuletzt die von Eliud Kipchoge (2022, 2:01:09 h) und Tigist Assefa (2023, 2:11:53 h).


PIPES & DRUMS, MILITARY- UND BLASMUSIK – DAS GRÖSSTE TATTOO DEUTSCHLANDS IN BERLIN. Der Begriff „Tattoo“ stammt vom niederländischen „tap toe“ ab (zu Deutsch: „Zapfhahn zu“ bzw. „Zapfenstreich“). Mit Aussprache dieses traditionell militärischen Befehls des Kommandanten wurde einst der Zapfhahn geschlossen und damit die Nachtruhe im Quartier eingeleitet. Dieses Signal wurde mit einem Musikinstrument gegeben. Die englische Sprache bildete dann daraus das Wort „Tattoo“. Durch den traditionellen Brauch der damaligen musikalischen Untermalung bekam das Wort „Tattoo“ die weltweit bekannte Bedeutung eines Militärmusikfestivals zugeteilt.
 Architecture
Architecture
 Museum
Museum
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Art
Art
 Fashion world
Fashion world
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Music
Music
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment