
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC



Pelpung Thubten Chökhor Ling (tib.: dpal spungs thub bstan chos 'khor gling; kurz: Pelpung Chökhor Ling, tib.: dpal spungs chos 'khor gling; དཔལ་སྤུངས་ཆོས་འཁོར་གླིང་། auch: Palpung) ist der Name eines 1727 vom 8. Tai Situpa Chökyi Chungne[1] (1699/1700–1774) in Dêgê, Kham, gegründeten Klosters.[2] Es ist das Mutterkloster der Karma-Kagyü-Schule des tibetischen Buddhismus in Osttibet und Hauptsitz der Chamgon Kenting Tai Situpas. Im Laufe der Zeit entwickelte sich Pelpung Thubten Chökhor Ling zu einem Zentrum der „Buddhistischen Ökumene“ (Rime). Alle Zweigklöster und Zentren Pelpung Thubten Chökhor Lings tragen ebenfalls den Namen Pelpung und sind weltweit in der „Pelpung-Kongregation“ zusammengefasst. Pelpung bedeutet „glorreiche Vereinigung von Studium und Praxis“, oder "Festung der Vortrefflichkeit"[3].
 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
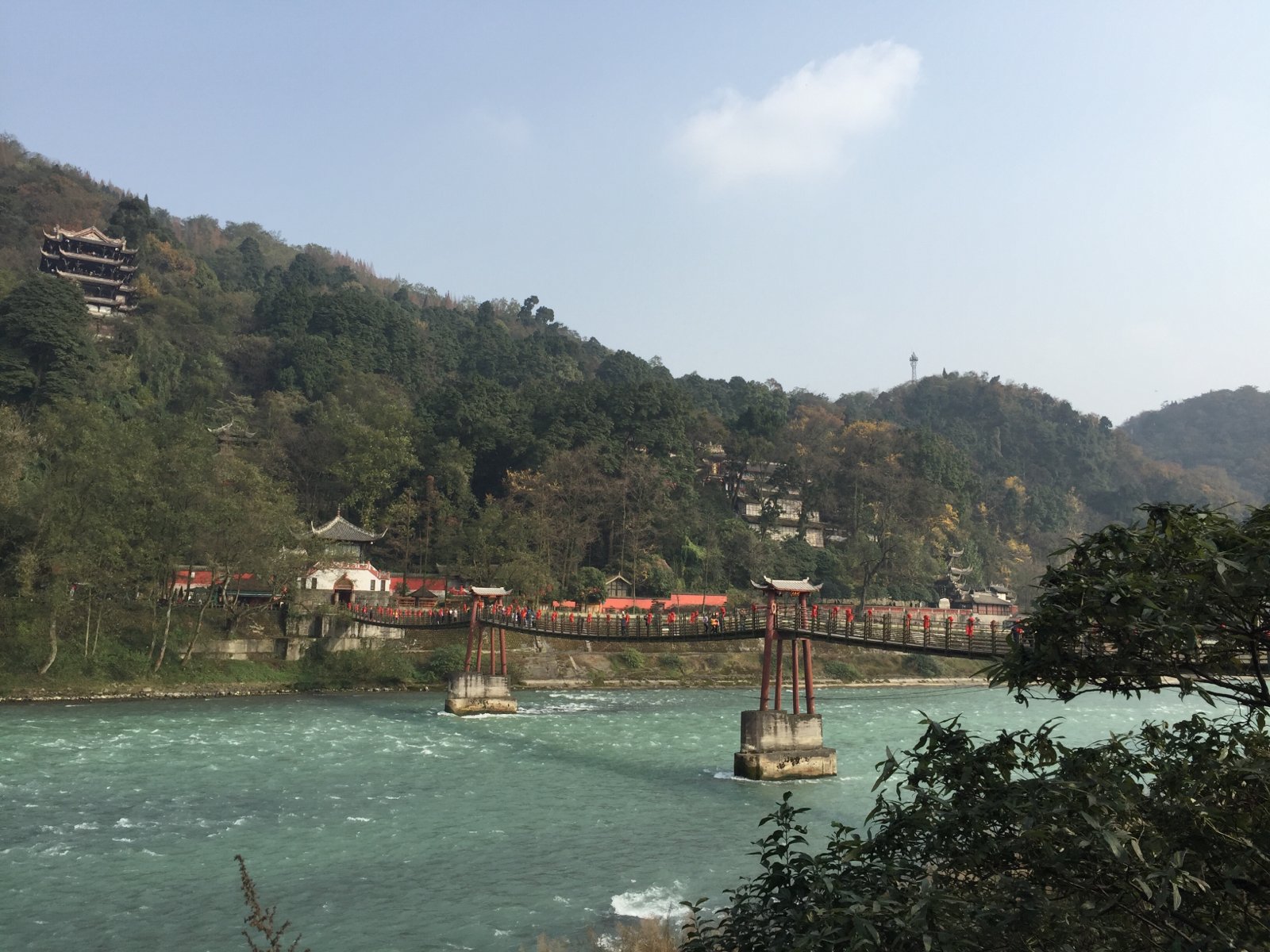
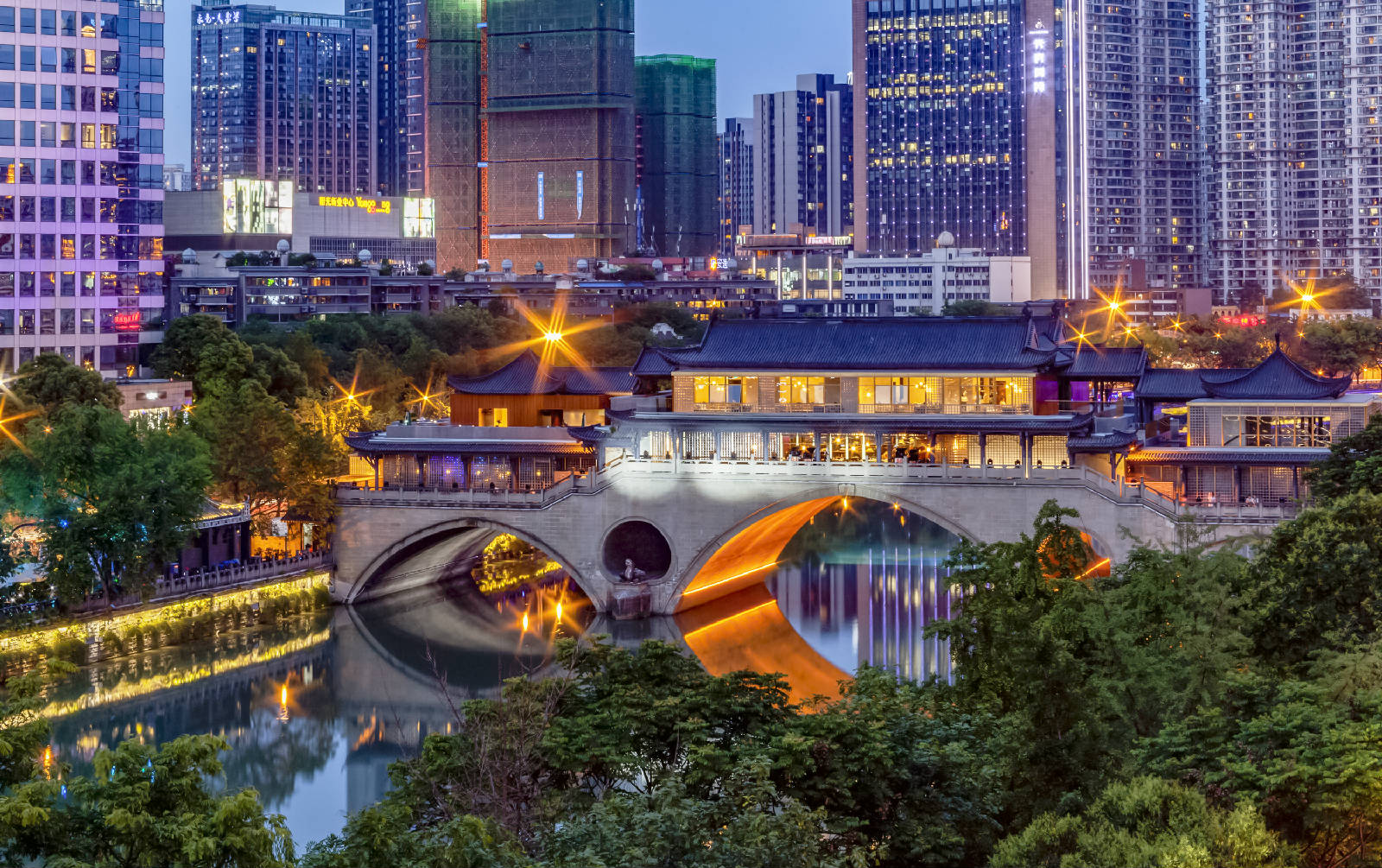
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Railway
Railway
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ




 *Changjiang|Yangtze River
*Changjiang|Yangtze River

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Hydroelectric power plants
Hydroelectric power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Hydropower
Hydropower
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
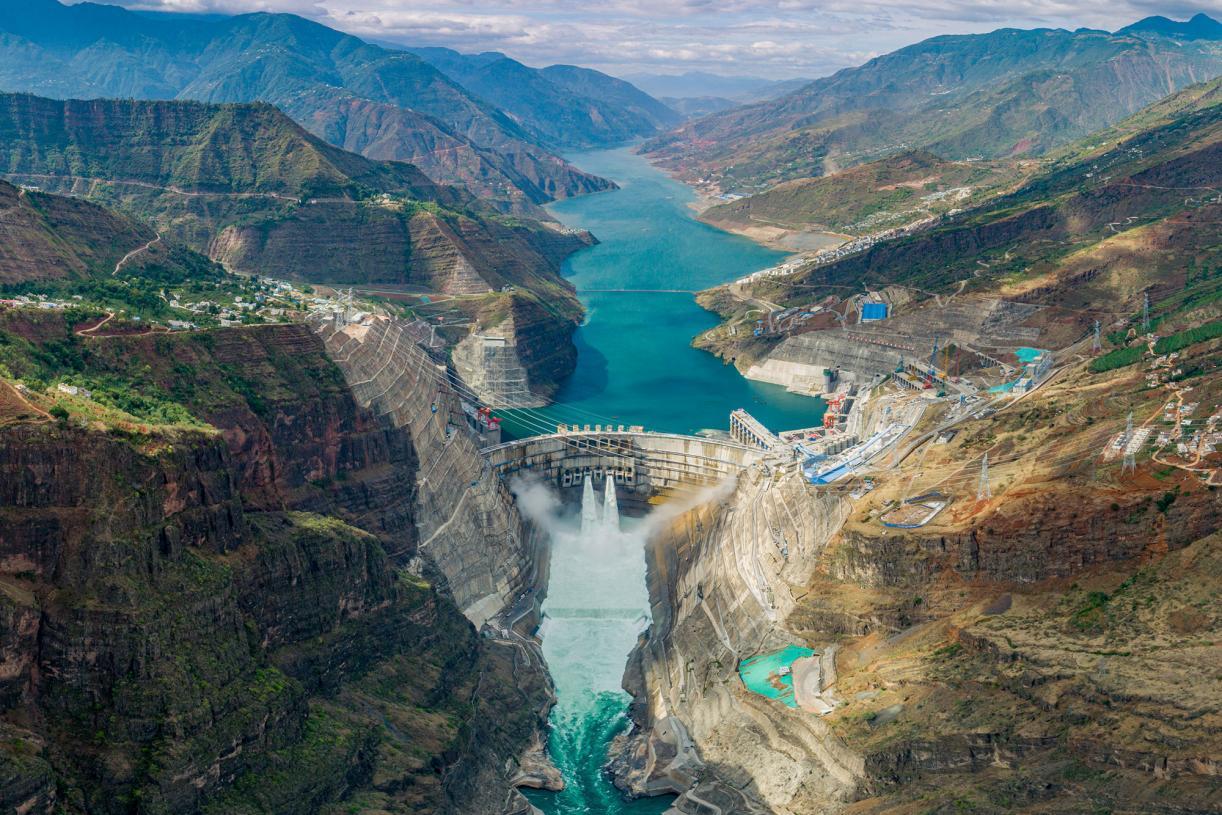

白鹤滩水电站 是一座位于中国云南省巧家县与四川省凉山彝族自治州宁南县交界的金沙江峡谷的水电站,坝址左岸距四川省宁南县城约66 km,距西昌市195 km;右岸距巧家县城约45 km,距昆明292 km。是金沙江下游四个水电梯级电站中的第二个梯级[1],是中国继三峡水电站和溪洛渡水电站之后的第三座 10 GW 级巨型水电站,建成后将成为世界装机容量仅次于三峡水电站的第二大水电站,发电量第三大水电站,和世界单机容量最大的水电站。[2]
白鹤滩水电站枢纽由拦河坝、泄洪消能设施、引水发电系统等主要建筑物组成。拦河坝为混凝土双曲拱坝,坝顶高程834 m,最大坝高289 m。泄洪建筑物由坝身6个表孔和7个深孔、坝后水垫塘、左岸3条无压泄洪直洞组成。引水隧洞采用单机单洞竖井式布置,尾水系统采用2机共用1条尾水隧洞的布置形式,左右岸各布置4条尾水隧洞,其中左岸结合3条、右岸结合2条导流洞布置。左右岸地下厂房内各布置8台 1.000 GW 水轮发电机,是世界首座单机容量达到 1 GW 等级的水轮发电机组[3]。电站总装机容量16.00 GW,保证出力5.50 GW,多年平均发电量64.1 TWh,正常蓄水位825 m,死水位765 m,水库总库容20.6 km3,调节库容10.4 km3,防洪库容7.5 km3,施工总工期144个月[4]。
白鹤滩工程以发电为主,兼顾防洪。工程建成后还有拦沙、发展库区航运和改善下游通航条件等综合利用效益,工程投资将超过1,700亿元[5],是中国“西电东送”的核心电源点之一[6]。
Die Baihetan-Talsperre (chinesisch 白鶴灘大壩 / 白鹤滩大坝, Pinyin Báihètan Dàbà) ist eine große im Bau befindliche Talsperre mit einem Wasserkraftwerk am Jinsha Jiang (chin. Bezeichnung für den Oberlauf des Jangtsekiang), in den Provinzen Sichuan und Yunnan im Südwesten von China. Das Bauwerk wird eine der höchsten Talsperren der Erde sein; und es könnte möglicherweise bei seiner Fertigstellung, am Volumen des Bauwerks gemessen, das drittgrößte in China und das viertgrößte der Erde werden. Die Vorbereitungen für die Bauarbeiten sind seit 2010 in Gang; das Bauwerk soll planmäßig 2021–2022 fertig sein.[1]
Die installierte Gesamtleistung des Wasserkraftwerks soll ca. 16.000 MW betragen.[2][3][4] Damit wird es das zweitgrößte Wasserkraftwerk der Erde nach dem Drei-Schluchten-Damm und vor Itaipú werden (vgl. Liste der größten Wasserkraftwerke der Erde).
Etwa 67.000 Menschen müssen für das Projekt umgesiedelt werden.[5]
The Baihetan Dam (simplified Chinese: 白鹤滩大坝; traditional Chinese: 白鶴灘大壩; pinyin: Báihètān Dàbà) is a large hydroelectric dam under construction on the Jinsha River, an upper stretches of the Yangtze River in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, in the southwest of China. The dam is a 277 m tall double-curvature arch dam with a crest elevation of 827 m. Its width will be 72 m at the base and 13 m at the crest.[3]
The facility will generate power by utilizing 16 turbines, each with a generating capacity of 1,000 MW, taking the generating capacity to 16,000 MW.[4] In terms of generating capacity, it will be the second largest hydroelectric power plant in the world, after the Three Gorges Dam.[5] When finished, it will be the third largest dam in China and the fourth in the world, in terms of dam volume. The dam was originally scheduled to be constructed between 2009 and 2018.[6] Actual construction started in 2017, with the dam to be start partial operational by 2021.[7]
Le barrage de Baihetan (chinois simplifié : 白鹤滩水电站 ; pinyin : Báihètān shuǐdiànzhàn) est un barrage hydroélectrique en construction sur la rivière Jinsha (nom donné au cours supérieur du fleuve Yangzi Jiang), dans le sud-ouest de la Chine.
Avec une puissance installée de 16 GW, le Barrage de Baihetan sera à sa livraison en 2022 le deuxième le plus puissant du monde, seulement surpassé par le barrage des Trois-Gorges et ses 22,5 GW, également sur le Yangzi Jiang en Chine. Il sera par la même occasion la deuxième centrale électrique la plus puissante au monde, tous types confondus1.
Le barrage de Baihetan comportera les turbines hydrauliques les plus puissantes jamais conçues, les premières à atteindre le seuil symbolique de 1 GW.
Haut de 289 mètres et large de 709 m, il sera en outre le quatrième barrage le plus haut du monde et l'un des plus grands barrages-voûtes.
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel


 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Traditions
Traditions