
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Suriname
Suriname
 Amazonas
Amazonas
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Columbia
Columbia
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Ecuador
Ecuador

 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Peru
Peru
 Suriname
Suriname
 Animal world
Animal world
 Venezuela
Venezuela
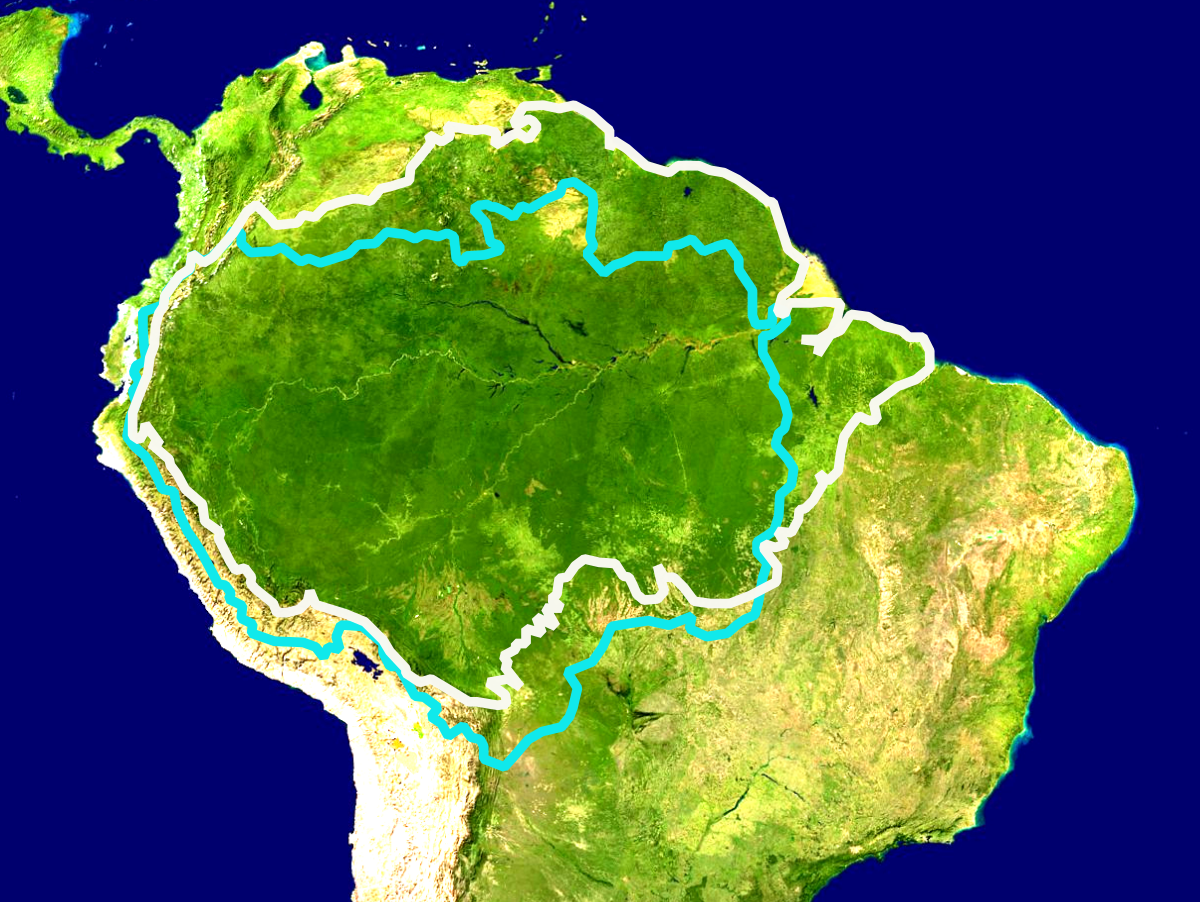
Der Amazonas-Regenwald bedeckt große Teile des Amazonasbeckens in Südamerika, welches sechs Millionen Quadratkilometer in neun Ländern umfasst. Der weitaus größte Teil des Waldes (etwa 60 Prozent) befindet sich in Brasilien. Weitere 13 Prozent befinden sich in Peru, 10 Prozent in Kolumbien sowie kleinere Teile in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivien, Guyana, Suriname sowie Französisch-Guyana. Bundesstaaten und Verwaltungseinheiten von vier Ländern tragen den Namen Amazonas.
Der Amazonas-Regenwald umfasst mehr als die Hälfte des weltweit verbliebenen Tropenwaldes und weist die größte Biodiversität aller tropischen Wälder auf. Amazonien ist eines der sechs großen Biome Brasiliens und nimmt rund 49 Prozent des brasilianischen Territoriums ein.[1] Es erstreckt sich über drei der fünf statistischen Regionen des Landes (Norte, Nordeste und Centro-Oeste). Ein 52.000 km² großes Gebiet im zentralen Amazonas-Regenwald, das den Nationalpark Jaú umfasst, wurde von der UNESCO 2000 (mit Erweiterung 2003) zum Welterbe erklärt.[2] Sozialgeographisch ist das Amazonasbecken in Brasilien der Region Amazônia Legal zugeordnet. Zum Zweck der wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung der Region wurde 1966 die Superintendência do Desenvolvimento da Amazônia (SUDAM) geschaffen.
Die langfristige Fortexistenz des Amazonas-Regenwald im Anthropozän steht im Konflikt mit den Interessen einer mächtigen Agrarindustrie:[3] Alleine der brasilianische Regenwald schrumpfte nach Regierungsangaben durch Raubbau zwischen August 2017 und Juli 2018 um insgesamt 7900 km² Wald, was der Fläche von mehr als einer Million Fußballfeldern entspricht.
アマゾン熱帯雨林(アマゾンねったいうりん、英: Amazon Rainforest、西: Selva Amazónica、葡: Floresta Amazônica)とは、南アメリカ大陸アマゾン川流域に大きく広がる、世界最大面積を誇る熱帯雨林である。2019年の大火事で10%の面積を焼失したとされる。[要出典]森林破壊が原因と見られる、木が大量に枯死する等の現象が多発しており、焼き畑と合わせて二酸化炭素大量放出の原因になっており問題になっている。
The Amazon rainforest,[a] alternatively, the Amazon Jungle, also known in English as Amazonia, is a moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), of which 5,500,000 km2 (2,100,000 sq mi) are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations.
The majority of the forest is contained within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peru with 13%, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Bolivia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela. Four nations have "Amazonas" as the name of one of their first-level administrative regions and France uses the name "Guiana Amazonian Park" for its rainforest protected area. The Amazon represents over half of the planet's remaining rainforests,[2] and comprises the largest and most biodiverse tract of tropical rainforest in the world, with an estimated 390 billion individual trees divided into 16,000 species.
La forêt amazonienne (en portugais floresta amazônica ; en espagnol selva amazónica ; en anglais Amazon rainforest), également connue sous le nom d'« Amazonie » ou « jungle amazonienne », est une forêt équatoriale d'Amérique du Sud couvrant la totalité du bassin versant du fleuve Amazone ainsi que des zones périphériques comme le plateau des Guyanes. Elle s'étend sur 9 Pays, principalement au Brésil (63%).
Avec près de 390 milliards d'arbres (16 000 espèces ; 13% des arbres de la planète ; près de 60 fois plus d'arbres « adultes » dans la forêt amazonienne que d'êtres humains sur l'ensemble de la planète)2, c'est l'une des trois plus importantes forêts primaires du monde3. Elle est souvent qualifiée de « poumon de la terre » bien qu'en réalité les océans produisent bien plus d'oxygène4 ; elle produirait entre 20% 5 et plus probablement 6% de l'oxygène6.
C'est le plus grand réservoir de biodiversité au monde, menacé par le réchauffement7, l'orpaillage et la déforestation (depuis 1970, environ 18 % de la forêt originelle a disparu). Elle abrite trois grandes aires protégées : le complexe de conservation de l'Amazonie centrale8 au Brésil, le parc national de Manú9 au Pérou et le parc national Noel Kempff Mercado10 en Bolivie ; inscrites sur la liste du patrimoine mondial par l'organisation des Nations unies pour l'éducation, la science et la culture (UNESCO). Le Parc Amazonien de Guyane, en Guyane française, est le plus grand parc national français mais aussi le plus grand parc de l'Union Européenne11. Couvrant près de 34 000 km², il constitue, avec le Parc National des montagnes du Tumucumaque qui lui est adjacent, l'un des plus grands espaces naturels protégés au monde.
L'Amazzonia è una vasta regione geografica del sud-America caratterizzata da una foresta pluviale, detta foresta amazzonica, che copre gran parte dell'omonimo bacino amazzonico, estendendosi su una superficie di sei milioni di chilometri quadrati suddivisi in nove paesi; la stragrande maggioranza della foresta (circa il 60%) si trova in Brasile; un altro 13% si trova in Perù, il 10% in Colombia e parti più piccole in Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname e Guyana francese: stati e unità amministrative di quattro di questi paesi sono appunto denominati Amazonas.
La Amazonia, también denominada Amazonía1 (en portugués: Amazônia, en francés: Amazonie, en inglés: Amazonia, en neerlandés: Amazone), es una vasta región de la parte horizontal y septentrional de América del Sur que comprende la selva tropical de la cuenca del río Amazonas. Las adyacentes regiones de las Guayanas y el Gran Chaco también poseen selvas tropicales, por lo que muchas veces se las considera parte de la Amazonia.
Esta selva amazónica es el bosque tropical más extenso del mundo.2 Se considera que su extensión llega a los 7 000 000 km² (siete millones de kilómetros cuadrados) repartidos entre nueve países, de los cuales Brasil y Perú poseen la mayor extensión, seguidos por Bolivia, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Guayana Francesa y Surinam. La Amazonia se destaca por ser una de las ecorregiones con mayor biodiversidad en el planeta.[cita requerida] Además, la Amazonia apoya a la regulación del ciclo de carbono y del cambio climático. Las anomalías que suceden en cuanto a aumento en la tasa de 

Дождевые леса Амазонии — обширный регион влажнотропических вечнозелёных широколиственных лесов — самый крупный в мире тропический лес, расположенный на обширной, почти плоской, равнине, охватывающей почти весь бассейн реки Амазонки. Собственно лес занимает 5,5 миллиона квадратных километров — половину общей площади оставшихся на планете тропических лесов. Захватывает территорию девяти государств: (Бразилия, Перу, Колумбия, Венесуэла, Эквадор, Боливия, Гайана, Суринам, Французская Гвиана).
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Caribbean Community and Common Market,CARICOM
Caribbean Community and Common Market,CARICOM
 Andrew Holness
Andrew Holness
 Dominica
Dominica
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Montserrat
Montserrat
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 Suriname
Suriname
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations


南美洲进步论坛[1][2](西班牙語:Foro para el Progreso de América del Sur、葡萄牙語:Fórum para o Progresso da América do Sul,简称Prosur)是于2019年3月22日由阿根廷、巴西、智利、哥伦比亚、厄瓜多尔、巴拉圭、秘鲁等七国总统和圭亚那驻智利大使通过联合签署《圣地亚哥宣言》而成立的南美洲地区一体化机制[3]。南美洲进步论坛将用于取代南美洲国家联盟[4][5]。南美洲进步论坛将是“南美公共政策协调机制,捍卫民主、权力独立、市场经济、议程社会,具有可持续性和适当应用”[7]。
Das Forum für den Fortschritt und die Integration von Südamerika (span: Foro para el Progreso e Integración de América del Sur, PROSUR; Portugiesisch: Fórum para o Progresso e Desenvolvimento da América do Sul, PROSUL, niederländisch: Forum voor de Vooruitgang en Integratie van Zuid-Amerika, FVIZA) ist eine Initiative von Sebastián Piñera und Iván Duque zur Schaffung eines Integrationsgremiums, das die Union Südamerikanischer Nationen ersetzen soll.
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Panama
Panama
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 Suriname
Suriname
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Venezuela
Venezuela




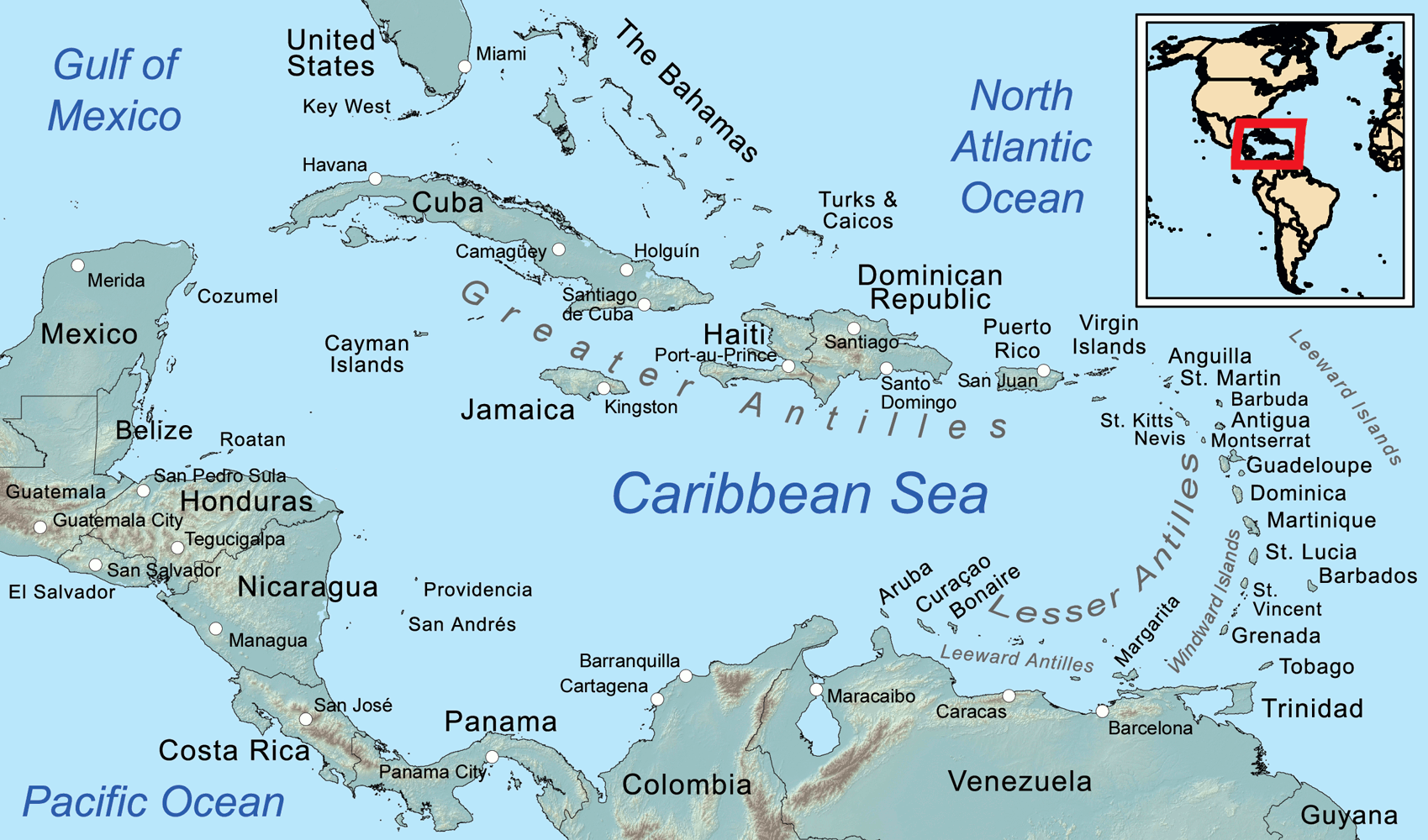
Die Karibik ist eine Region im westlichen, tropischen Teil des Atlantischen Ozeans nördlich des Äquators. Als Teil des mittelamerikanischen Subkontinents besteht sie aus den am und im Karibischen Meer gelegenen Inseln und Inselgruppen und dem Meeresgebiet zwischen ihnen. Am Westende reicht die Karibik in den Golf von Mexiko.
Die Karibik ist nach dem Volk der Kariben benannt, das die spanischen Eroberer auf den Kleinen Antillen (lat. ante ilium, „vorgelagerte Inseln“) vorgefunden haben. Sie wurde bzw. wird auch Westindien genannt, da man sich bei ihrer Entdeckung auf direktem Seeweg nach Indien glaubte.
カリブ海地域(カリブかいちいき、英語: The Caribbean、スペイン語: Caribe、オランダ語: ![]() Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
この地方の大部分はカリブプレート上にあり、域内には700以上の島嶼、岩礁、キー(サンゴ礁上の低い島)などがある(カリブ海地域の島の一覧)。島々の多くは島弧を形成して、カリブ海のと東渕と北縁となっている[3]。カリブ海地域の島々は、北側の大アンティル諸島と、南および東側の小アンティル諸島(リーワード・アンティル諸島を含む) から成り、大アンティル諸島やカリブ海より北に位置するバハマ諸島(バハマからタークス・カイコス諸島に至る範囲)をも含んだ、より広い範囲を指す表現としての西インド諸島の一部となっている。広い意味では、大陸の一部であるベリーズ、ベネズエラ、ガイアナ、スリナム、フランス領ギアナもカリブ海地域に含める場合がある。
地政学的には、カリブ海地域の島々は北アメリカの下位区分 (subregion) と見なされることが多く[4][5][6][7][8]、合わせて30の主権国家、海外県、属領から成っている。1954年12月15日から2010年10月10日まで、5つの統治体から成るオランダ領アンティルと称されたオランダ属領があった[9]。また、1958年1月3日から1962年5月31日まで、イギリス属領であった英語圏の領域が構成した、西インド連邦と称された短命な自治国が存在していた。クリケット西インド諸島代表は、その後も、これら諸国の多くを代表して編成され続けている。
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/;[4] Spanish: El Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Haitian Creole: Karayib; Dutch: De Caraïben; Papiamento: Karibe) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea[5] and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean)[6] and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea:[7] the Greater Antilles on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), which are sometimes considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. On the mainland, Belize, Nicaragua, the Caribbean region of Colombia, Cozumel, the Yucatán Peninsula, Margarita Island, and The Guianas (Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Guayana Region in Venezuela, and Amapá in Brazil) are often included due to their political and cultural ties with the region.[8]
A mostly tropical geography, the climates are greatly shaped by sea temperatures and precipitation, with the hurricane season regularly leading to natural disasters. Because of its tropical climate and low-lying island geography, the Caribbean is vulnerable to a number of climate change effects, including increased storm intensity, saltwater intrusion, sea-level rise and coastal erosion, and precipitation variability.[9] These weather changes will greatly change the economies of the islands, and especially the major industries of agricultural and tourism.[9]
The Caribbean was occupied by indigenous people since at least 3600 BC. When European colonization followed the arrival of Columbus, the population was quickly decimated by brutal labor practices, enslavement and disease and on many islands, Europeans supplanted the native populations with enslaved Africans. Following the independence of Haiti from France in the early 19th century and the decline of slavery in the 19th century, island nations in the Caribbean gradually gained independence, with a wave of new states during the 1950s and 60s. Because of the proximity to the United States, there is also a long history of United States intervention in the region.
The islands of the Caribbean (the West Indies) are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or then left as a subregion of their own[10][11] and are organized into 30 territories including sovereign states, overseas departments, and dependencies. From December 15, 1954, to October 10, 2010, there was a country known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five states, all of which were Dutch dependencies.[12] From January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies.
Les Caraïbes, (également nommées la Caraïbe, l'espace caraïbe, ou encore l'espace des Caraïbes) sont une région des Amériques qui comprend la mer des Caraïbes, ses îles (certaines entourées par la mer des Caraïbes et d'autres bordant à la fois la mer des Caraïbes et l'océan Atlantique Nord) et les côtes environnantes. La région est située au sud-est du golfe du Mexique et du continent nord-américain, à l'est de l'Amérique centrale et au nord de l'Amérique du Sud.
Située en grande partie sur la plaque des Caraïbes, la région compte plus de 700 îles, îlots, récifs et cayes. Les arcs insulaires délimitent les bords est et nord de la mer des Caraïbes : les Grandes Antilles au nord et les Petites Antilles au sud et à l'est (qui comprennent les îles sous le vent). Elles forment les Antilles avec l'archipel voisin de Lucayan (les Bahamas et les Îles Turques-et-Caïques), qui sont parfois considérées comme faisant partie des Caraïbes bien qu'elles ne bordent pas la mer des Caraïbes. Sur le continent, le Belize, le Nicaragua, la région caribéenne de Colombie, Cozumel, la péninsule du Yucatán, l'île de Margarita et les Guyanes (Guyane, Suriname, Guyane française, région de Guayana au Venezuela et Amapá au Brésil) sont souvent inclus en raison de leurs liens politiques et culturels avec la région.
La géographie est essentiellement tropicale et le climat est fortement influencé par la température de la mer et les précipitations, la saison des ouragans entraînant régulièrement des catastrophes naturelles. En raison de leur climat tropical et de leur géographie insulaire de basse altitude, les Caraïbes sont vulnérables à un certain nombre d'effets du changement climatique, notamment l'augmentation de l'intensité des tempêtes, l'intrusion d'eau salée, l'élévation du niveau de la mer et l'érosion côtière, ainsi que la variabilité des précipitations.
Les Caraïbes ont été occupées par des peuples indigènes depuis au moins 3600 avant J.-C. Lorsque la colonisation européenne a suivi l'arrivée de Christophe Colomb, la population a été rapidement décimée par des pratiques de travail brutales, l'esclavage et la maladie et sur de nombreuses îles, les Européens ont supplanté les populations indigènes par des Africains réduits en esclavage. Après l'indépendance d'Haïti par rapport à la France au début du XIXe siècle et le déclin de l'esclavage, les nations insulaires ont progressivement acquis leur indépendance, avec une vague de nouveaux États au cours des années 1950 et 1960. En raison de la proximité des États-Unis, il existe également une longue histoire d'intervention américaine dans la région.
Les Antilles sont souvent considérées comme une sous-région de l'Amérique du Nord, bien qu'elles soient parfois incluses dans l'Amérique centrale ou alors laissées comme une sous-région à part entière et sont organisées en 30 territoires comprenant des États souverains, des Département et région d'outre-mer et des dépendances. Du 15 décembre 1954 au 10 octobre 2010, il y avait un pays appelé Antilles néerlandaises composé de cinq États, tous dépendants des Pays-Bas. Du 3 janvier 1958 au 31 mai 1962, il y a également eu une union politique de courte durée, la Fédération des Indes occidentales, composée de dix territoires caribéens anglophones, tous dépendants des Britanniques à l'époque.
I Caraibi sono una vasta regione geografica delle Americhe che comprende tutti i paesi bagnati dal Mare Caraibico, cioè tutte le isole delle Antille e i litorali di alcuni paesi continentali del centro e sud America che si affacciano su di questo mare. L'area caraibica è costituita dalle numerose isole che separano il Golfo del Messico dal mar dei Caraibi e quest'ultimo dall'Oceano Atlantico.
El Caribe es una región conformada por el mar Caribe, sus islas y las costas que rodean a este mar. La región se localiza al sureste de América del Norte, al este de América Central, al oeste de América Insular y al norte de América del Sur.
Анти́льские острова́ (также Карибы или Карибские острова) — острова в Карибском море и Мексиканском заливе, расположенные между Северной Америкой и Южной Америкой. Вместе взятые, образуют площадь в 228 662 км² с населением примерно 42 млн чел. (на начало XXI века).
Впервые название «Антильские» встречается в 1493 году у Петра Мартира д’Ангиера, современника Христофора Колумба, придворного Фердинанда Арагонского и Изабеллы Кастильской. Предположительно, были названы по полумифическому острову или архипелагу Антилия, изображавшемуся на средневековых картах.
Подразделяются на две главные группы: Большие Антильские и Малые Антильские острова:
К первым относятся 4 острова: Куба, Гаити, Ямайка и Пуэрто-Рико; из них первые два и последний (самый малый) образуют почти прямую линию, направленную западным углом Кубы к полуострову Юкатан.[1]
Острова материкового и вулканического происхождения. Большая часть их поверхности гориста; равнинные участки главным образом на Кубе и на Юго-Восточном Гаити, а также на Виргинских и Подветренных островах. Горные сооружения Больших Антильских островов высотой до 3098 м (на острове Гаити) являются продолжением структур Центральной Америки. Климат тропический, пассатный, жаркий, преимущественно летне-влажный. Осадков 1200—2000 мм в год. Характерны сильные ураганы в конце лета. Естественная растительность — саванны, летне-зеленые и листопадно-вечнозелёные тропические леса и кустарники — сохранилась мало. На наветренных склонах гор уцелели вечнозелёные леса.[2]


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Benin
Benin
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Guyana
Guyana
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Comoros
Comoros
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Mali
Mali
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Oman
Oman
 Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Senegal
Senegal
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Somalia
Somalia
 Suriname
Suriname
 Syria
Syria
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Togo
Togo
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

伊斯兰合作组织(阿拉伯语:منظمة التعاون الإسلامي;英语:Organisation of Islamic Cooperation;法语:Organisation de la coopération islamique)原名伊斯兰会议组织,是一个伊斯兰世界的政府间国际组织,为联合国大会观察员;该组织由遍及西亚(中东)、中亚、西非、北非、印度次大陆和东南亚的57个国家组成,覆盖的人口约为16亿。秘书处设在沙特阿拉伯王国的吉达市;现任秘书长是原沙特社会事务大臣Yousef Al-Othaimeen(从2016年开始)。
组织的宗旨是促进各成员国之间在经济、社会、文化和科学等方面的合作;努力消除种族隔离和种族歧视,反对一切形式的殖民主义;支持巴勒斯坦人民恢复民族权利和重返家园的斗争;支持穆斯林保障其尊严、独立和民族权利的斗争。
但要注意的是并非每个成员国是伊斯兰国家,如圭亚那、苏里南、莫桑比克、喀麦隆、乌干达和加蓬等国,伊斯兰反而是极少数人的信仰,阿尔巴尼亚则是唯一加入该组织的欧洲大陆的主权国家和联合国会员国,2011年脱离苏丹独立的南苏丹也在独立后脱离该组织的势力范围。
Die Organisation für Islamische Zusammenarbeit (arabisch منظمة التعاون الإسلامي, DMG Munaẓẓamat at-Taʿāwun al-islāmī; englisch Organization of Islamic Cooperation, OIC; französisch L’Organisation de Coopération Islamique, OCI; früher Organisation der Islamischen Konferenz) ist eine zwischenstaatliche internationale Organisation von derzeit 56 Staaten,[2] in denen der Islam Staatsreligion, Religion der Bevölkerungsmehrheit oder Religion einer nennenswerten Minderheit ist. Die Organisation nimmt für sich in Anspruch, den Islam zu repräsentieren. Mehrere größere Mitgliedsstaaten (Saudi-Arabien, Ägypten, die Türkei und der Iran) erheben hinter den Kulissen Führungsansprüche; die jeweils anderen Staaten bestreiten deren Recht dazu. Infolge dieser Rivalitäten ist die OIC seit 2017 kaum handlungsfähig.[3]
イスラム協力機構(イスラムきょうりょくきこう、アラビア語: منظمة التعاون الاسلامي、略称OIC; 英語: Organisation of Islamic Cooperation、略称OCI; フランス語: Organisation de la coopération Islamique)は、イスラム諸国をメンバーとして構成され、国際連合に対する常任代表を有する国際機構。公用語はアラビア語、英語、フランス語。かつてはイスラム諸国会議機構(منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي、英語: Organisation of the Islamic Conference、フランス語: Organisation de la Conférence Islamique)という名称であったが、2011年6月にカザフスタンのアスタナでの会議で「イスラム協力機構」への変更と紋章が決定された[1]。
イスラム諸国の政治的協力、連帯を強化すること、イスラム諸国に対する抑圧に反対し、解放運動を支援することを目的とする。
加盟国はムスリム(イスラム教徒)が国民の多数を占める西アジア、北アフリカ、西アフリカ、東アフリカ、中央アジア、南アジア、東南アジアなどの57か国、オブザーバーが5ヵ国・8組織(国連など)からなり、世界13億人のムスリムの大部分を代表する。
加盟条件としては、国内でムスリムが大多数を占めることを必ずしも条件としているわけではなく、南アメリカのいくつかの国のようにマイノリティとしてある程度のムスリム人口を抱えているだけであっても、外相会議における審査で承認されればイスラム諸国のひとつとして機構に加盟することができる。イスラム教徒が多数派を占める国はほとんど参加しているが、イスラム教徒比率の高い国のうちエチオピア(30~50%)とタンザニア(約30%)が加盟していない。イスラム教徒人口の多い国で言えばインド(約1億5000万人)や中国(約2000万人)も加盟していない。逆にイスラム教徒比率の低い国ではガボン、ウガンダ、スリナム、ガイアナなどが加盟している(それぞれ10%未満)。
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC; Arabic: منظمة التعاون الإسلامي; French: Organisation de la coopération islamique), formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an international organization founded in 1969, consisting of 57 member states, with a collective population of over 1.8 billion as of 2015 with 53 countries being Muslim-majority countries. The organisation states that it is "the collective voice of the Muslim world" and works to "safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony".[1]
The OIC has permanent delegations to the United Nations and the European Union. The official languages of the OIC are Arabic, English, and French.
L’Organisation de la coopération islamique (OCI), en arabe : منظمة التعاون الإسلامي (Munaẓẓamat at-Taʿāwun al-islāmī), en anglais : Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), appelée jusqu'en 2011 Organisation de la conférence islamique (en arabe : منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي, en anglais : Organisation of the Islamic Conference), est une organisation intergouvernementale créée le 25 septembre 1969. Son siège se situe à Djeddah en Arabie saoudite et elle possède une délégation permanente aux Nations unies.
Regroupant 57 États membres, sa vocation est de promouvoir la coopération dans les domaines économiques, sociaux, culturels et scientifiques (grâce notamment à la Banque islamique de développement), mais aussi la sauvegarde des lieux saints de l'islam ou encore le soutien au peuple palestinien. À l'échelle mondiale, il n'existe pas d'autre organisation confessionnelle dont les membres signataires soient des États.
Ses trois langues officielles sont l'arabe, l'anglais et le français2.
L'Organizzazione della cooperazione islamica (in arabo: منظمة التعاون الإسلامي, Munaẓẓamat al-taʿāwun al-islāmī; in inglese: Organization of the Islamic Cooperation, OIC; in francese: Organisation de la coopération islamique, OCI) è un'organizzazione internazionale con una delegazione permanente presso le Nazioni Unite. Rappresenta 56 Stati dell'Europa, Vicino Oriente, Medio Oriente, America meridionale, Africa, Asia centrale e del Subcontinente indiano.[1]
L'organizzazione, fondata a Rabat, in Marocco, il 25 settembre 1969 con il nome Organisation of the Islamic Conference, in arabo: منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي, Munaẓẓamat al-muʾtamar al-islāmī; (FR) Organisation de la conférence islamique, mutato nell'attuale nel 2011.[2]
Ha come finalità la salvaguardia degli interessi e lo sviluppo delle popolazioni musulmane nel mondo.
Il 10 ottobre 1975 le è stato riconosciuto lo status di osservatore dell'Assemblea generale delle Nazioni Unite.
La Organización para la Cooperación Islámica (Árabe:منظمة التعاون الاسلامي); (Francés: Organisation de la Coopération Islamique); (Inglés: Organisation of Islamic Cooperation) es un organismo internacional que agrupa a los estados de confesión musulmana, creado en 1969 durante la Conferencia de Rabat y formalizada dos años después.
Su sede está en Yidda, ciudad costera de Arabia Saudí a orillas del Mar Rojo. Sus miembros son países con mayoría de población musulmana o con una comunidad significativa en ellos, con Estados miembros y observadores de África, Asia, Europa y América del Sur. El 28 de junio de 2011 se oficializó el cambio de nombre,1 anteriormente se llamó: Organización de la Conferencia Islámica (Árabe:منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي); (Francés: Organisation de la Conférence Islamique); (Inglés:Organization of the Islamic Conference).
Sus acciones se circunscriben a la actividad colaborativa entre sus miembros, sobre todo en la lucha contra el imperialismo, el neocolonialismo y por la emancipación de Palestina. Históricamente se celebraron diversos congresos que contribuyeron con su desarrollo: Lahore (1974), La Meca (1981), Casablanca (1984), Kuwait (1987), Dakar (1991). Sus repercusiones son menores que las de la Liga Árabe.
Организация исламского сотрудничества (англ. Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), араб. منظمة التعاون الاسلامي) — международная организация исламских стран (до 2011 года называлась Организация Исламская конференция (ОИК).

Die OTCA (port.: Organização do Tratado de Cooperação Amazônica / span.: Organización del Tratado de Cooperación Amazónica / engl.: Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) / niederl.: De Organisatie van de Overeenkomst voor Amazonische Samenwerking (OOAS) ) – tratado heißt im Spanischen und Portugiesischen so viel wie „Staatsvertrag“ – ist die am 2. September 2003 aus dem Amazonaspakt (Tratado de Cooperación Amazonica, TCA) hervorgegangene Organisation der acht Amazonas-Anrainerstaaten.
Der Amazonaspakt wurde 1978 ins Leben gerufen um die Zusammenarbeit der Amazonasländer zu stärken, damals in erster Linie mit dem Ziel, die jeweilige nationale Souveränität über die amazonischen Territorien gegenüber internationalen Interessen durchzusetzen. Später rückte der Gedanke der nachhaltigen Entwicklung Amazoniens immer stärker in den Vordergrund der Aktivitäten des Bündnisses.
Sitz ist seit der Gründung Brasília.
亚马逊合作条约组织是一个旨在促进亚马逊盆地可持续发展的国际组织。其成员国有:玻利维亚、巴西、哥伦比亚、厄瓜多尔、圭亚那、秘鲁、苏里南和委内瑞拉。[1]
《亚马逊合作条约》(Amazon Cooperation Treaty,ACT) 于1978年7月3日签署, 1998年修订。为了监督该条约的实施,1995年,亚马孙合作条约组织成立。2002年,该组织在巴西利亚设立了秘书处。




 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Belarus
Belarus
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Fidschi
Fidschi
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Georgia
Georgia
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Guyana
Guyana
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Libanon
Libanon
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Peru
Peru
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Silk road
Silk road
 Serbia
Serbia
 Serbia
Serbia
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Syria
Syria
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
 Cyprus
Cyprus

丝绸之路(德语:Seidenstraße;英语:Silk Road),常简称为丝路,此词最早来自于德意志帝国地理学家费迪南·冯·李希霍芬男爵于1877年出版的一套五卷本的地图集。[1]
丝绸之路通常是指欧亚北部的商路,与南方的茶马古道形成对比,西汉时张骞以长安为起点,经关中平原、河西走廊、塔里木盆地,到锡尔河与乌浒河之间的中亚河中地区、大伊朗,并联结地中海各国的陆上通道。这条道路也被称为“陆路丝绸之路”,以区别日后另外两条冠以“丝绸之路”名称的交通路线。因为由这条路西运的货物中以丝绸制品的影响最大,故得此名。其基本走向定于两汉时期,包括南道、中道、北道三条路线。但实际上,丝绸之路并非是一条 “路”,而是一个穿越山川沙漠且没有标识的道路网络,并且丝绸也只是货物中的一种。[1]:5
广义的丝绸之路指从上古开始陆续形成的,遍及欧亚大陆甚至包括北非和东非在内的长途商业贸易和文化交流线路的总称。除了上述的路线之外,还包括约于前5世纪形成的草原丝绸之路、中古初年形成,在宋代发挥巨大作用的海上丝绸之路和与西北丝绸之路同时出现,在宋初取代西北丝绸之路成为路上交流通道的南方丝绸之路。
虽然丝绸之路是沿线各君主制国家共同促进经贸发展的产物,但很多人认为,西汉的张骞在前138—前126年和前119年曾两次出使西域,开辟了中外交流的新纪元,并成功将东西方之间最后的珠帘掀开。司马迁在史记中说:“于是西北国始通于汉矣。然张骞凿空,其后使往者皆称博望侯,以为质与国外,外国由此信之”,称赞其开通西域的作用。从此,这条路线被作为“国道”踩了出来,各国使者、商人、传教士等沿着张骞开通的道路,来往络绎不绝。上至王公贵族,下至乞丐狱犯,都在这条路上留下了自己的足迹。这条东西通路,将中原、西域与大伊朗、累范特、阿拉伯紧密联系在一起。经过几个世纪的不断努力,丝绸之路向西伸展到了地中海。广义上丝路的东段已经到达了朝鲜、日本,西段至法国、荷兰。通过海路还可达意大利、埃及,成为亚洲和欧洲、非洲各国经济文化交流的友谊之路。
丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路(英语:The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road[1]),简称一带一路(英语:The Belt and Road Initiative,缩写B&R)[1],是中华人民共和国政府于2013年倡议[2]并主导的跨国经济带[3]。
一带一路范围涵盖历史上丝绸之路和海上丝绸之路行经的中国、中亚、北亚和西亚、印度洋沿岸、地中海沿岸的国家和地区。中国政府指出,“一带一路”倡议坚持共商、共建、共享的原则,努力实现沿线区域基础设施更加完善,更加安全高效,以形成更高水平的陆海空交流网络。同时使投资贸易的便利化水平更有效的提升,建立高品质、高标准的自由贸易区域网。以使沿线各国经济联系更加紧密,政治互信更加的深入,人文交流更加的广泛[4]。
Als Seidenstraße (chinesisch 絲綢之路 / 丝绸之路, Pinyin Sīchóu zhī Lù ‚die Route / Straße der Seide‘; mongolisch ᠲᠣᠷᠭᠠᠨ ᠵᠠᠮ Tôrgan Jam; kurz: 絲路 / 丝路, Sīlù) bezeichnet man ein altes Netz von Karawanenstraßen, dessen Hauptroute den Mittelmeerraum auf dem Landweg über Zentralasien mit Ostasien verband. Die Bezeichnung geht auf den im 19. Jahrhundert lebenden deutschen Geografen Ferdinand von Richthofen zurück, der den Begriff 1877 erstmals verwendet hat.
Auf der antiken Seidenstraße wurde in westliche Richtung hauptsächlich Seide, gen Osten vor allem Wolle, Gold und Silber gehandelt.[1] Nicht nur Kaufleute, Gelehrte und Armeen nutzten ihr Netz, sondern auch Ideen, Religionen und ganze Kulturkreise diffundierten und migrierten auf den Routen von Ost nach West und umgekehrt: hierüber kamen z. B. der Nestorianismus (aus dem spätantiken Römischen Reich) und der Buddhismus (von Indien) nach China.[1]
Die 6.400 Kilometer[1] lange Route begann in Xi’an und folgte dem Verlauf der Chinesischen Mauer in Richtung Nordwesten, passierte die Taklamakan-Wüste, überwand das Pamirgebirge und führte über Afghanistan in die Levante; von hier wurden die Handelsgüter dann über das Mittelmeer verschifft. Nur wenige Kaufleute reisten auf der gesamten Route, die Waren wurden eher gestaffelt über Zwischenhändler transportiert.
Ihre größte Bedeutung erreichte das Handels- und Wegenetz zwischen 115 v. Chr. und dem 13. Jahrhundert n. Chr. Mit dem allmählichen Verlust römischen Territoriums in Asien und dem Aufstieg Arabiens in der Levante wurde die Seidenstraße zunehmend unsicher und kaum noch bereist. Im 13. und 14. Jahrhundert wurde die Strecke unter den Mongolen wiederbelebt, u. a. benutzte sie zu der Zeit der Venezianer Marco Polo um nach Cathay (China) zu reisen. Nach weit verbreiteter Ansicht war die Route einer der Hauptwege, über die Mitte des 14. Jahrhunderts Pestbakterien von Asien nach Europa gelangten und dort den Schwarzen Tod verursachten.[1]
Teile der Seidenstraße sind zwischen Pakistan und dem autonomen Gebiet Xinjiang in China heute noch als asphaltierte Fernstraße vorhanden (-> Karakorum Highway). Die alte Straße inspirierte die Vereinten Nationen zu einem Plan für eine transasiatische Fernstraße. Von der UN-Wirtschafts- und Sozialkommission für Asien und den Pazifik (UNESCAP) wird die Einrichtung einer durchgehenden Eisenbahnverbindung entlang der Route vorangetrieben, der Trans-Asian Railway.[1]
Die "Neue Seidenstraße", das "One Belt, One Road"-Projekt der Volksrepublik China unter ihrem Staatspräsident Xi Jinping umfasst landgestützte (Silk Road Economic Belt) und maritime (Maritime Silk Road) Infrastruktur- und Handelsrouten, Wirtschaftskorridore und Transportlinien von China über Zentralasien und Russland bzw. über Afrika nach Europa, dazu werden verschiedenste Einrichtungen (z. B. Tiefsee- oder Containerterminals) und Verbindungen (wie Bahnlinien oder Gaspipelines) entwickelt bzw. ausgebaut. Bestehende Korridore sind einerseits Landverbindungen über die Türkei oder Russland und andererseits Anknüpfungen zum Hafen von Shanghai, über Hongkong und Singapur nach Indien und Ostafrika, Dubai, den Suez-Kanal, den griechischen Hafen Piräus nach Venedig.[2]
Das Projekt One Belt, One Road (OBOR, chinesisch 一帶一路 / 一带一路, Pinyin Yídài Yílù ‚Ein Band, Eine Straße‘, neuerdings Belt and Road, da „One“ zu negativ besetzt war) bündelt seit 2013 die Interessen und Ziele der Volksrepublik China unter Staatspräsident Xi Jinping zum Auf- und Ausbau interkontinentaler Handels- und Infrastruktur-Netze zwischen der Volksrepublik und zusammen 64 weiteren Ländern Afrikas, Asiens und Europas. Die Initiative bzw. das Gesamtprojekt betrifft u. A. rund 62 % der Weltbevölkerung und ca. 35 % der Weltwirtschaft.[1][2]
Umgangssprachlich wird das Vorhaben auch „Belt and Road Initiative“ (B&R, BRI) bzw. ebenso wie das Projekt Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA) auch „Neue Seidenstraße“ (新絲綢之路 / 新丝绸之路, Xīn Sīchóuzhīlù) genannt. Es bezieht sich auf den geografischen Raum des historischen, bereits in der Antike genutzten internationalen Handelskorridors „Seidenstraße“; zusammengefasst handelt es sich um zwei Bereiche, einen nördlich gelegenen zu Land mit sechs Bereichen unter dem Titel Silk Road Economic Belt und einen südlich gelegenen Seeweg namens Maritime Silk Road.
シルクロード(絹の道、英語: Silk Road, ドイツ語: Seidenstraße, 繁体字:絲綢之路, 簡体字:丝绸之路)は、中国と地中海世界の間の歴史的な交易路を指す呼称である。絹が中国側の最も重要な交易品であったことから名付けられた。その一部は2014年に初めて「シルクロード:長安-天山回廊の交易路網」としてユネスコの世界遺産に登録された。
「シルクロード」という名称は、19世紀にドイツの地理学者リヒトホーフェンが、その著書『China(支那)』(1巻、1877年)においてザイデンシュトラーセン(ドイツ語:Seidenstraßen;「絹の道」の複数形)として使用したのが最初であるが、リヒトホーフェンは古来中国で「西域」と呼ばれていた東トルキスタン(現在の中国新疆ウイグル自治区)を東西に横断する交易路、いわゆる「オアシスの道(オアシスロード)」を経由するルートを指してシルクロードと呼んだのである。リヒトホーフェンの弟子で、1900年に楼蘭の遺跡を発見したスウェーデンの地理学者ヘディンが、自らの中央アジア旅行記の書名の一つとして用い、これが1938年に『The Silk Road』の題名で英訳されて広く知られるようになった。
シルクロードの中国側起点は長安(陝西省西安市)、欧州側起点はシリアのアンティオキアとする説があるが、中国側は洛陽、欧州側はローマと見る説などもある。日本がシルクロードの東端だったとするような考え方もあり、特定の国家や組織が経営していたわけではないのであるから、そもそもどこが起点などと明確に定められる性質のものではない。
現在の日本でこの言葉が使われるときは、特にローマ帝国と秦・漢帝国、あるいは大唐帝国の時代の東西交易が念頭に置かれることが多いが、広くは近代(大航海時代)以前のユーラシア世界の全域にわたって行われた国際交易を指し、南北の交易路や海上の交易路をも含める。つまり、北方の「草原の道(ステップロード)」から南方の「海の道(シーロード)」までを含めて「シルクロード」と呼ばれるようになっているわけである。
シルクロード経済ベルトと21世紀海洋シルクロード(シルクロードけいざいベルトと21せいきかいようシルクロード、拼音: Sīchóu zhī lù jīngjìdài hé èrshíyī shìjì hǎishàng sīchóu zhī lù、英語: The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road)とは、2014年11月10日に中華人民共和国北京市で開催されたアジア太平洋経済協力首脳会議で、習近平総書記が提唱した経済圏構想である。
略称は一帯一路(いったいいちろ、拼音: Yídài yílù、英語: The Belt and Road Initiative, BRI; One Belt, One Road Initiative, OBOR)。
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West. It was central to cultural interaction between the regions for many centuries.[1][2][3] The Silk Road refers to both the terrestrial and the maritime routes connecting East Asia and Southeast Asia with East Africa, West Asia and Southern Europe.
The Silk Road derives its name from the lucrative trade in silk carried out along its length, beginning in the Han dynasty (207 BCE–220 CE). The Han dynasty expanded the Central Asian section of the trade routes around 114 BCE through the missions and explorations of the Chinese imperial envoy Zhang Qian.[4] The Chinese took great interest in the safety of their trade products and extended the Great Wall of China to ensure the protection of the trade route.[5]
Trade on the Road played a significant role in the development of the civilizations of China, Korea,[6] Japan,[2] India, Iran, Afghanistan, Europe, the Horn of Africa and Arabia, opening long-distance political and economic relations between the civilizations.[7] Though silk was the major trade item exported from China, many other goods were traded, as well as religions, syncretic philosophies, sciences, and technologies. Diseases, most notably plague, also spread along the Silk Road.[8] In addition to economic trade, the Silk Road was a route for cultural trade among the civilizations along its network.[9]
Traders in ancient history included the Bactrians, Sogdians, Syrians, Jews, Arabs, Iranians, Turkmens, Chinese, Malays, Indians, Somalis, Greeks, Romans, Georgians, Armenians, and Azerbaijanis.[10]
In June 2014, UNESCO designated the Chang'an-Tianshan corridor of the Silk Road as a World Heritage Site. The Indian portion is on the tentative site list.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) or the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road is a development strategy adopted by the Chinese government. The 'belt' refers to the overland interconnecting infrastructure corridors; the Silk Road Economic Belt (SREB) component. The 'road' refers to the sea route corridors; the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (MSR) component.[2] The initiative focuses on connectivity and cooperation between Eurasian countries, primarily the People's Republic of China (PRC).
Until 2016 the initiative was known in English as the One Belt and One Road Initiative (OBOR) but the Chinese came to consider the emphasis on the word "one" as misleading.[3]
The Chinese government calls the initiative "a bid to enhance regional connectivity and embrace a brighter future".[4] Independent observers, however, see it as a push for Chinese dominance in global affairs with a China-centered trading network.[5][6]
La route de la soie est un réseau ancien de routes commerciales entre l'Asie et l'Europe, reliant la ville de Chang'an (actuelle Xi'an) en Chine à la ville d'Antioche, en Syrie médiévale (aujourd'hui en Turquie). Elle tire son nom de la plus précieuse marchandise qui y transitait : la soie.
La route de la soie était un faisceau de pistes par lesquelles transitaient de nombreuses marchandises, et qui monopolisa les échanges Est-Ouest pendant des siècles. Les plus anciennes traces connues de la route de la soie, comme voie de communication avec les populations de l'Ouest, remontent à « 2000 avant notre ère au moins ». Les Chinois en fixent l'ouverture au voyage de Zhang Qian en 138-1261. Mais la route de la soie s'est développée surtout sous la dynastie Han (221 av. J.-C. - 220 ap. J.-C.), en particulier Han Wudi.
Puis sous la dynastie Tang (618-907). À partir du XVe siècle, la route de la soie est progressivement abandonnée, l'instabilité des guerres turco-byzantines, puis la chute de Constantinople poussent en effet les Occidentaux à chercher une nouvelle route maritime vers les Indes. L'abandon de la route de la soie correspond ainsi au début de la période des « Grandes découvertes » durant laquelle les techniques de transport maritime deviennent de plus en plus performantes. Du côté chinois, les empereurs Ming Yongle, puis Ming Xuanzong chargent, à la même époque, l'amiral Zheng He d'expéditions maritimes similaires.
La nouvelle route de la soie ou la Ceinture et la Route2 (stratégie aussi appelée OBOR en anglais pour One Belt, One Road3) est à la fois un ensemble de liaisons maritimes et de voies ferroviaires entre la Chine et l'Europe passant par le Kazakhstan, la Russie, la Biélorussie, la Pologne, l'Allemagne, la France et le Royaume-Uni.
Le nouveau nom est Initiative route et ceinture (Belt and Road Initiative, B&R selon l’acronyme anglais) afin de marquer le fait que ce projet ne se limite pas à une seule route4.
Outre l'amélioration de la connectivité ferroviaire, il s'agit aussi d'une stratégie de développement pour promouvoir la coopération entre les pays sur une vaste bande s'étendant à travers l'Eurasie et pour renforcer la position de la Chine sur le plan mondial, par exemple en préservant la connexion de la Chine avec le reste du monde en cas de tensions militaires sur ses zones côtières5.
La Nouvelle route de la soie a été dévoilée à l'automne 2013 par le gouvernement chinois en tant que pendant terrestre du collier de perles6 ; elle est l'une des priorités de la diplomatie chinoise, sous la présidence de Xi Jinping7.
Selon CNN, ce projet englobera 68 pays représentant 4,4 milliards d’habitants et 62 % du PIB mondial8.
Per via della seta (in cinese: 絲綢之路T, 丝绸之路S, sī chóu zhī lùP; persiano: راه ابریشم, Râh-e Abrisham) s'intende il reticolo, che si sviluppava per circa 8.000 km, costituito da itinerari terrestri, marittimi e fluviali lungo i quali nell'antichità si erano snodati i commerci tra l'impero cinese e quello romano.
Le vie carovaniere attraversavano l'Asia centrale e il Medio Oriente, collegando Chang'an (oggi Xi'an), in Cina, all'Asia Minore e al Mediterraneo attraverso il Medio Oriente e il Vicino Oriente. Le diramazioni si estendevano poi a est alla Corea e al Giappone e, a Sud, all'India. Il nome apparve per la prima volta nel 1877, quando il geografo tedesco Ferdinand von Richthofen (1833-1905) pubblicò l'opera Tagebucher aus China. Nell'Introduzione von Richthofen nomina la Seidenstraße, la «via della seta».
La destinazione finale della seta che su di essa viaggiava (non certo da sola ma insieme a tante altre merci preziose) era Roma, dove per altro non si sapeva con precisione quale ne fosse l'origine (se animale o vegetale) e da dove provenisse. Altre merci altrettanto preziose viaggiavano in senso inverso, e insieme alle merci viaggiavano grandi idee e religioni (concetti fondamentali di matematica, geometria, astronomia) in entrambi i sensi, manicheismo, e nestorianesimo verso oriente. Sulla via della seta compì un complesso giro quasi in tondo anche il buddhismo, dall'India all'Asia Centrale alla Cina e infine al Tibet (il tutto per trovare itinerari che permettessero di evitare le quasi invalicabili montagne dell'Himalaya).
Questi scambi commerciali e culturali furono determinanti per lo sviluppo e il fiorire delle antiche civiltà dell'Egitto, della Cina, dell'India e di Roma, ma furono di grande importanza anche nel gettare le basi del mondo medievale e moderno.
La Nuova via della seta è un'iniziativa strategica della Cina per il miglioramento dei collegamenti e della cooperazione tra paesi nell'Eurasia. Comprende le direttrici terrestri della "zona economica della via della seta" e la "via della seta marittima del XXI secolo" (in cinese: 丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路S, Sīchóu zhī lù jīngjìdài hé èrshíyī shìjì hǎishàng sīchóu zhī lùP), ed è conosciuta anche come "iniziativa della zona e della via" (一带一路S, tradotta comunemente in inglese con Belt and Road Initiative, BRI) o "una cintura, una via" e col corrispondente iniziale acronimo inglese OBOR (One belt, one road), poi modificato in BRI per sottolineare l'estensione del progetto non esclusivo solo della Cina[1], nonostante la prospettiva sinocentrica, com'è stato illustrato in un recente studio italiano[2].
Partendo dallo sviluppo delle infrastrutture di trasporto e logistica, la strategia mira a promuovere il ruolo della Cina nelle relazioni globali, favorendo i flussi di investimenti internazionali e gli sbocchi commerciali per le produzioni cinesi. L'iniziativa di un piano organico per i collegamenti terrestri (la cintura) è stata annunciata pubblicamente dal presidente cinese Xi Jinping a settembre del 2013, e la via marittima ad ottobre dello stesso anno, contestualmente alla proposta di costituire la Banca asiatica d'investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), dotata di un capitale di 100 miliardi di dollari USA, di cui la Cina stessa sarebbe il principale socio, con un impegno pari a 29,8 miliardi e gli altri paesi asiatici (tra cui l'India e la Russia) e dell'Oceania avrebbero altri 45 miliardi (l'Italia si è impegnata a sottoscrivere una quota di 2,5 miliardi).
La Ruta de la Seda fue una red de rutas comerciales organizadas a partir del negocio de la seda china desde el siglo I a. C., que se extendía por todo el continente asiático, conectando a China con Mongolia, el subcontinente indio, Persia, Arabia, Siria, Turquía, Europa y África. Sus diversas rutas comenzaban en la ciudad de Chang'an (actualmente Xi'an) en China, pasando entre otras por Karakórum (Mongolia), el Paso de Khunjerab (China/Pakistán), Susa (Persia), el Valle de Fergana (Tayikistán), Samarcanda (Uzbekistán), Taxila (Pakistán), Antioquía en Siria, Alejandría (Egipto), Kazán (Rusia) y Constantinopla (actualmente Estambul, Turquía) a las puertas de Europa, llegando hasta los reinos hispánicos en el siglo XV, en los confines de Europa y a Somalia y Etiopía en el África oriental.
El término "Ruta de la Seda" fue creado por el geógrafo alemán Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen, quien lo introdujo en su obra Viejas y nuevas aproximaciones a la Ruta de la Seda, en 1877. Debe su nombre a la mercancía más prestigiosa que circulaba por ella, la seda, cuya elaboración era un secreto que solo los chinos conocían. Los romanos (especialmente las mujeres de la aristocracia) se convirtieron en grandes aficionados de este tejido, tras conocerlo antes del comienzo de nuestra era a través de los partos, quienes se dedicaban a su comercio. Muchos productos transitaban estas rutas: piedras y metales preciosos (diamantes de Golconda, rubíes de Birmania, jade de China, perlas del golfo Pérsico), telas de lana o de lino, ámbar, marfil, laca, especias, porcelana, vidrio, materiales manufacturados, coral, etc.
En junio de 2014, la Unesco eligió un tramo de la Ruta de la Seda como Patrimonio de la Humanidad con la denominación Rutas de la Seda: red viaria de la ruta del corredor Chang’an-Tian-shan. Se trata de un tramo de 5000 kilómetros de la gran red viaria de las Rutas de la Seda que va desde la zona central de China hasta la región de Zhetysu, situada en el Asia Central, incluyendo 33 nuevos sitios en China, Kazajistán y Kirguistán.1
La Iniciativa del Cinturón y Ruta de la Seda o Belt and Road Initiative, abreviada BRIZNA (también One Belt, One Road, abreviado OBOR y también la Nueva Ruta de la Seda) y NRS (Nueva Ruta de la Seda) por las siglas en español, es el nombre con que se conoce el proyecto político-económico del Secretario General del Partido Comunista de China, Xi Jinping, que propuso en septiembre de 2013 en sus respectivos viajes a Rusia, Kazajistán y Bielorrusia. Bajo el pretexto de que "hace más de dos milenios, las personas diligentes y valientes de Eurasia exploraron y abrieron nuevas vías de intercambio comercial y cultural que unían las principales civilizaciones de Asia, Europa y África, colectivamente llamadas ruta de la seda por generaciones posteriores", el proyecto quiere conectar Europa, Asia del Sur-Oriental, Asia Central y el Oriente Medio, mediante el modelo económico, e implícitamente político, chino.12
El proyecto parte de la reconstrucción de la antigua ruta de la seda y la creación de una ruta marítima paralela, de aquí el nombre de "Cinturón y Ruta". El proyecto afecta a 60 países, el 75% de las reservas energéticas conocidas al mundo, el 70% de la población mundial y generaría el 55% del PIB mundial. El gobierno comunista chino tiene previsto invertir unos 1,4 billones de dólares. Se trataría de un cinturón económico, pero, que algunos comentaristas occidentales ya denominamos "Plan Marshall del siglo XXI al estilo chino". Esta afirmación se sostiene por el hecho que el propio Secretario General Xi Jinping asegura que el proyecto tiene cinco pilares: comunicación política, circulación monetaria, entente entre pueblos, conectividad vital y fluidez. Todo ello se ha visto reflejado de acá el inicio de su puesta en marcha a través de las inversiones importantes con planes de ayuda para empresas chinas interesadas en el mercado exterior. China por el contrario se defiende y argumenta que no se trata de ningún plan Marshall visto que las condiciones políticas impuestas entonces con el Plan Marshall no existen en este proyecto. Pero, artículos de prensa van más allá de las simples afirmaciones de Plan Marshall a la china y hablan directamente de "nuevo orden mundial chino", atrás quedaría la orden mundial norteamericano.3
Nicola Casarini, director de Investigación para Asia del Instituto Affari Internacionali de Roma, sostiene que se trata de una iniciativa ambiciosa que pretende dar cabida en exceso de capacidad interna y a la voluntad de reestructuración de diferentes sectores estratégicos del país, como la industria pesando. La ruta, sin embargo, ha reactivado, a pesar de pretender ser un medio de pacificación de Oriente Medio, las antiguas tensiones del siglo XIX. A la India y Japón, se añade ahora Rusia y los EE.UU. El presidente proyecta la Belt and Road Initiative por unos treinta años. Así el proyecto tendría que estar terminado para el 2049, año donde el país rememoraría los 100 años de fundación de la República Popular.
Вели́кий шёлковый путь — караванная дорога, связывавшая Восточную Азию со Средиземноморьем в древности и в Средние века. В первую очередь использовался для вывоза шёлка из Китая, с чем и связано его название. Путь был проложен во II веке до н. э., вёл из Сианя через Ланьчжоу в Дуньхуан, где раздваивался: северная дорога проходила через Турфан, далее пересекала Памир и шла в Фергану и казахские степи, южная — мимо озера Лоб-Нор по южной окраине пустыни Такла-Макан через Яркенд и Памир (в южной части) вела в Бактрию, а оттуда — в Парфию, Индию и на Ближний Восток вплоть до Средиземного моря. Термин введён немецким географом Фердинандом фон Рихтгофеном в 1877 году.
«Оди́н по́яс и один путь» (кит. 一带一路) — выдвинутое в 2010-х годах Китайской Народной Республикой (КНР) предложение объединённых проектов «Экономического пояса Шёлкового пути» и «Морского Шёлкового пути XXI века».
Предложение было впервые выдвинуто председателем КНР Си Цзиньпином во время визитов в Казахстан и в Индонезию осенью 2013 года[1]. В таких политических документах, как «План социально-экономического развития на 2015 год» и «Доклад о работе правительства», строительство «Одного пояса и одного пути» было включено в список важных задач, поставленных перед новым правительством Китая. Министр иностранных дел Китая Ван И подчеркнул, что осуществление этой инициативы станет «фокусом» внешнеполитической деятельности КНР в 2015 году. Подтверждено, что этот огромный проект будет включён и в план «13-й пятилетки», который будет принят в 2016 году[2]. Суть данной китайской инициативы заключается в поиске, формировании и продвижении новой модели международного сотрудничества и развития с помощью укрепления действующих региональных двусторонних и многосторонних механизмов и структур взаимодействий с участием Китая. На основе продолжения и развития духа древнего Шёлкового пути «Один пояс и один путь» призывает к выработке новых механизмов регионального экономического партнерства, стимулированию экономического процветания вовлечённых стран, укреплению культурных обменов и связей во всех областях между разными цивилизациями, а также содействию мира и устойчивого развития[3]. По официальным данным Китая, «Один пояс и один путь» охватывает большую часть Евразии, соединяя развивающиеся страны, в том числе «новые экономики», и развитые страны. На территории мегапроекта сосредоточены богатые запасы ресурсов, проживает 63 % населения планеты, а предположительный экономический масштаб — 21 трлн долларов США[4].




 Geography
Geography
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Climate
Climate
 International cities
International cities
 History
History
 Sport
Sport