German — Chinese


 Geography
Geography

 Geography
***IMF Developed countries
Geography
***IMF Developed countries

 History
History
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
TOP4
IMF Developed countries
TOP4
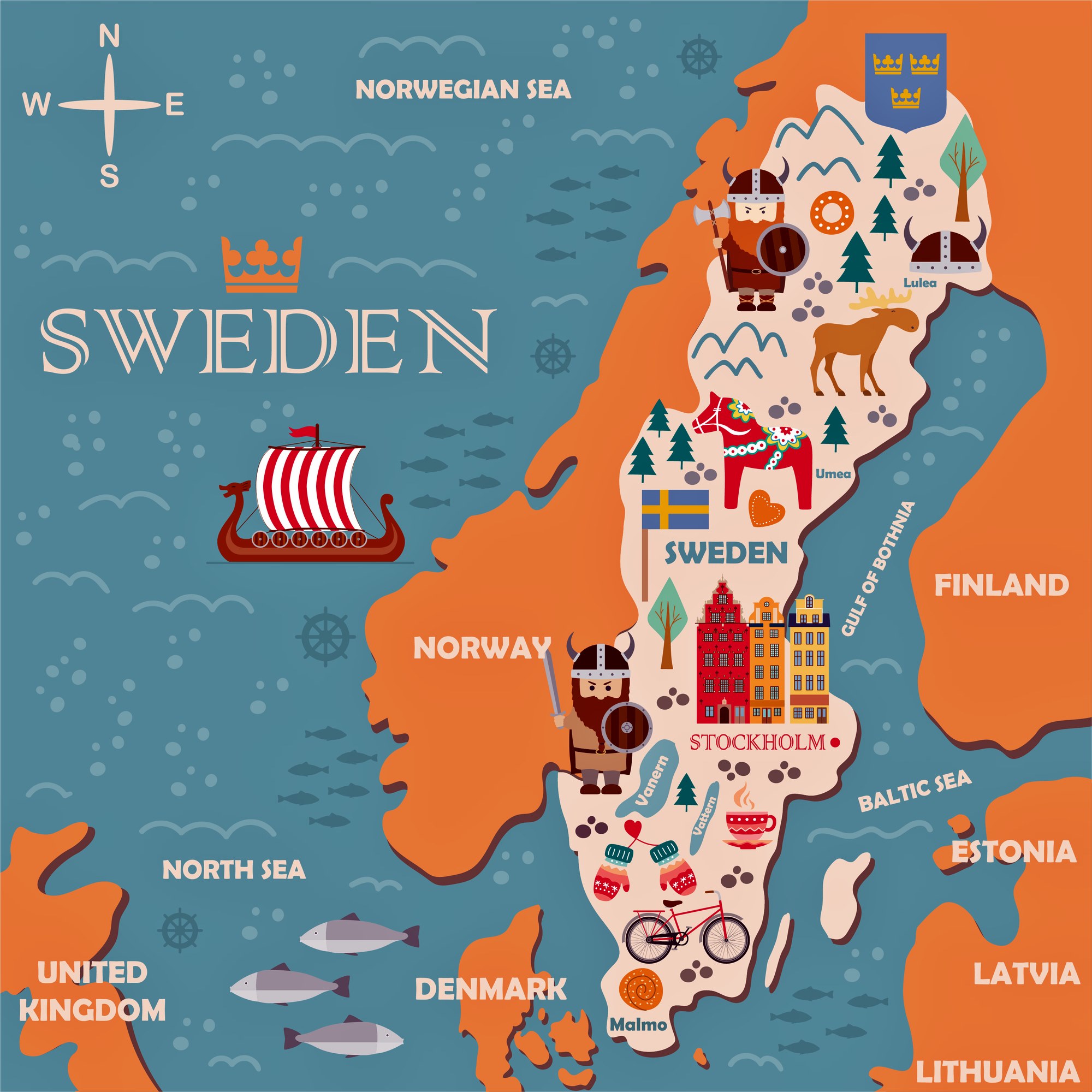
 Sweden
Sweden

 States of Europe
States of Europe
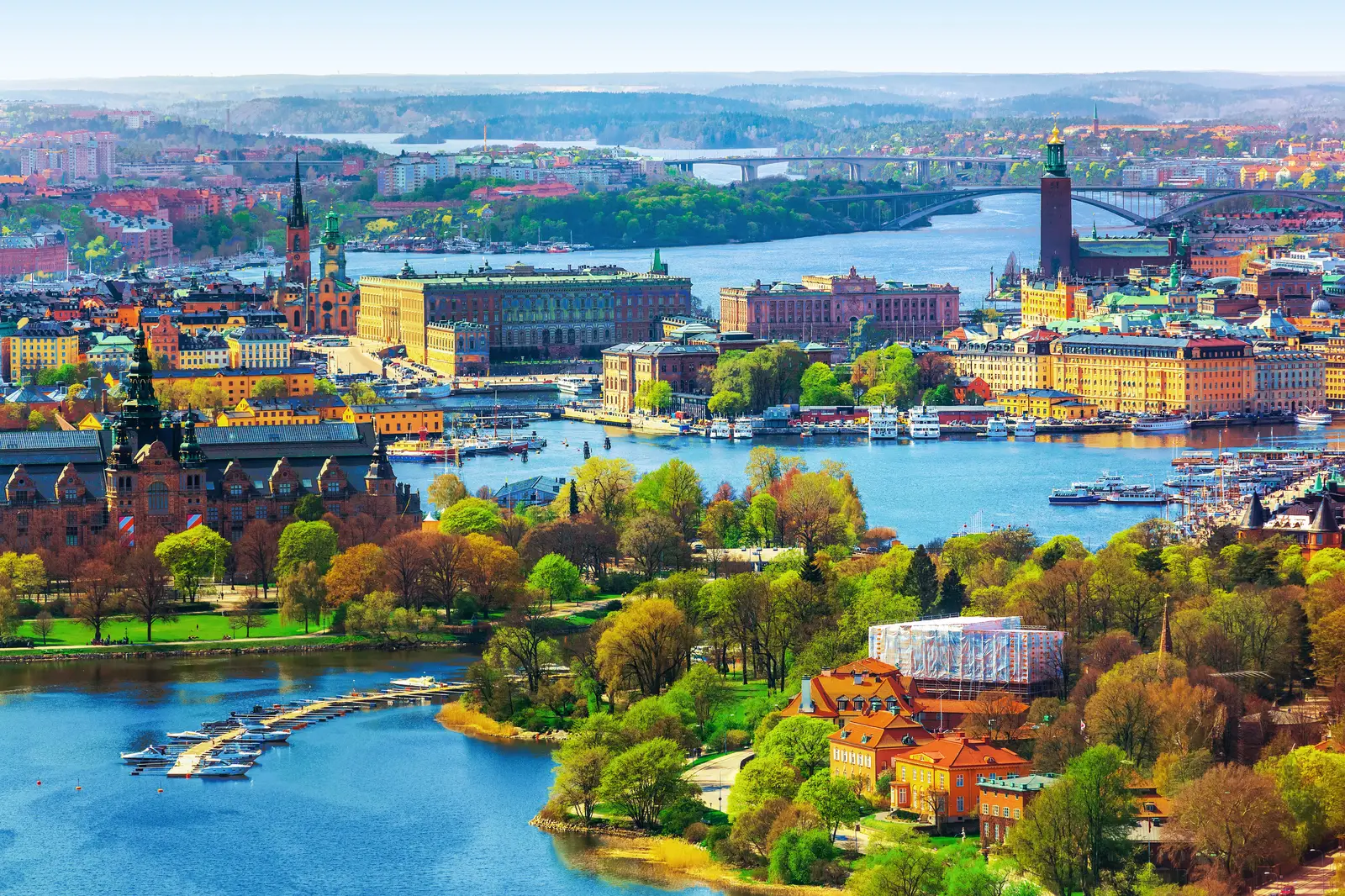

瑞典王国(瑞典语:Konungariket Sverige![]() 发音 帮助·信息),通称瑞典,是一个位于斯堪地纳维亚半岛的北欧国家,首都为斯德哥尔摩。西邻挪威,东北与芬兰接壤,西南濒临斯卡格拉克海峡和卡特加特海峡,东边为波罗的海与波的尼亚湾。即瑞典和与丹麦、德国、波兰、俄罗斯、立陶宛、拉脱维亚和爱沙尼亚隔海相望,于西南通过厄勒海峡大桥与丹麦相连。瑞典于1995年加入欧洲联盟。
发音 帮助·信息),通称瑞典,是一个位于斯堪地纳维亚半岛的北欧国家,首都为斯德哥尔摩。西邻挪威,东北与芬兰接壤,西南濒临斯卡格拉克海峡和卡特加特海峡,东边为波罗的海与波的尼亚湾。即瑞典和与丹麦、德国、波兰、俄罗斯、立陶宛、拉脱维亚和爱沙尼亚隔海相望,于西南通过厄勒海峡大桥与丹麦相连。瑞典于1995年加入欧洲联盟。
瑞典面积为449,964平方公里,为北欧第一大国家,人口约1000万[9][10]。64%的国土由森林覆盖,人口密度低,只有都会地区人口密度较高,84%的人口居住在只占国土面积1.3%的城市里[11]。瑞典是一个现代、自由与民主的高度发达国家,其公民享有高质的生活[12],政府亦非常注重环保[13][14]。
瑞典是传统的铁、铜和木材出口国,其水资源也很丰富,但是石油和煤矿十分匮乏。随着运输以及通讯的进步,这些自然资源也能够更大规模地从各地开采,尤其是木材与铁矿。经济自由与教育普及而让瑞典开始历经快速的工业化,并从1890年代开始发展制造业。20世纪中期,瑞典成为一个福利国家。
1397年,瑞典与丹麦和挪威一起组成了卡尔马联合(芬兰此时还是瑞典王国的一部分)。瑞典于16世纪初脱离卡尔马联合,并且与邻国进行了多年的战争,尤其是与俄罗斯以及从未完全承认瑞典已经离开了卡尔玛联合的丹麦-挪威联合。17世纪时瑞典借由战争扩张领土,成为了强权国家,其领土面积为目前的两倍之大。[15]1809年瑞典失去了芬兰,也不再具有强权地位。之后,瑞典参与了第六次反法同盟,在1814年瑞典入侵了挪威并逼迫对方签属《莫斯条约》,从此之后,瑞典没有再参与过战争。[16] 现今,瑞典被视为极力追求人权和平等的国家之一。瑞典二战后设立福利国家社会福利的制度,并在联合国开发计划署的人类发展指数中通常名列前茅。
スウェーデン王国(スウェーデンおうこく、スウェーデン語: ![]() Konungariket Sverige)、通称スウェーデンは、北ヨーロッパのスカンディナヴィア半島に位置する立憲君主制国家。首都はストックホルム。西にノルウェー、北東にフィンランドと国境を接し、南西にカテガット海峡を挟んでデンマークと近接する。東から南にはバルト海があり、対岸のロシアやドイツとの関わりが深い。法定最低賃金は存在せず[3]、経済はスウェーデン国外の大企業や機関投資家に左右される傾向にある。
Konungariket Sverige)、通称スウェーデンは、北ヨーロッパのスカンディナヴィア半島に位置する立憲君主制国家。首都はストックホルム。西にノルウェー、北東にフィンランドと国境を接し、南西にカテガット海峡を挟んでデンマークと近接する。東から南にはバルト海があり、対岸のロシアやドイツとの関わりが深い。法定最低賃金は存在せず[3]、経済はスウェーデン国外の大企業や機関投資家に左右される傾向にある。
Sweden (/swiːdən/; Swedish: Sverige [ˈsværjɛ] (![]() listen)), officially the Kingdom of Sweden (Swedish:
listen)), officially the Kingdom of Sweden (Swedish: ![]() Konungariket Sverige (help·info)), is a Scandinavian Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north and Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund, a strait at the Swedish-Danish border. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the third-largest country in the European Union and the fifth largest country in Europe by area. Sweden has a total population of 10.2 million[3] of which 2.4 million has a foreign background.[12] It has a low population density of 22 inhabitants per square kilometre (57/sq mi). The highest concentration is in the southern half of the country.
Konungariket Sverige (help·info)), is a Scandinavian Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north and Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund, a strait at the Swedish-Danish border. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the third-largest country in the European Union and the fifth largest country in Europe by area. Sweden has a total population of 10.2 million[3] of which 2.4 million has a foreign background.[12] It has a low population density of 22 inhabitants per square kilometre (57/sq mi). The highest concentration is in the southern half of the country.
Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats (Swedish Götar) and Swedes (Svear) and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia. The climate is in general very mild for its northerly latitude due to significant maritime influence, that in spite of this still retains warm continental summers. Today, the sovereign state of Sweden is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy, with a monarch as head of state, like its neighbour Norway. The capital city is Stockholm, which is also the most populous city in the country. Legislative power is vested in the 349-member unicameral Riksdag. Executive power is exercised by the government chaired by the prime minister. Sweden is a unitary state, currently divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities.
An independent Swedish state emerged during the early 12th century. After the Black Death in the middle of the 14th century killed about a third of the Scandinavian population,[13][14] the Hanseatic League threatened Scandinavia's culture, finances and languages.[dubious ] This led to the forming of the Scandinavian Kalmar Union in 1397,[15] which Sweden left in 1523. When Sweden became involved in the Thirty Years War on the Reformist side, an expansion of its territories began and eventually the Swedish Empire was formed. This became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, ending with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into personal union. Since then, Sweden has been at peace, maintaining an official policy of neutrality in foreign affairs.[16] The union with Norway was peacefully dissolved in 1905. Sweden was formally neutral through both world wars and the Cold War, albeit Sweden has since 2009 openly moved towards cooperation with NATO.
After the end of the Cold War, Sweden joined the European Union on 1 January 1995, but declined NATO membership, as well as Eurozone membership following a referendum. It is also a member of the United Nations, the Nordic Council, the Council of Europe, the World Trade Organization and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Sweden maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. It has the world's eleventh-highest per capita income and ranks highly in numerous metrics of national performance, including quality of life, health, education, protection of civil liberties, economic competitiveness, equality, prosperity and human development.[17][18][19]
La Suède (en suédois : Sverige /ˈsvæː.rjə/) – en forme longue le royaume de Suède (en suédois : Konungariket Sverige /koː.nɵŋ.a.ˈriː.kət ˈsvæː.rjə/ Écouter) – est un pays d'Europe du Nord situé en Scandinavie. Sa capitale est Stockholm et ses habitants sont appelés Suédois. Sa langue officielle et langue majoritaire est le suédois. Le finnois et le sami sont aussi parlés, principalement dans le nord du pays. Les variations régionales sont fréquentes.
La Suède a une frontière avec la Norvège à l'ouest et une autre avec la Finlande au nord-est. Au sud, la Suède est séparée du Danemark par l'Øresund, un détroit dont la section la plus étroite mesure 4 km de large. Le nord de la Suède est occupé par la Laponie, appelée Sápmi par ses habitants, les Samis, qui furent les premiers habitants du nord de la Scandinavie.
Avec un territoire d'une superficie de 449 964 km2, la Suède est le cinquième plus grand pays d'Europe après la Russie, l'Ukraine, la France et l'Espagne. La Suède possède une faible densité de population, sauf dans les zones métropolitaines. Le taux d'urbanisation est de 84 % alors que les villes n'occupent qu'1,3 % du territoire. La sauvegarde de l'environnement et l'enjeu des énergies renouvelables sont généralement la priorité des hommes politiques, ainsi que d'une grande partie de la population. En 2014, le 'Global Green Economy Index' classe la Suède premier pays le plus écologique au monde2.
La Suède est depuis longtemps un grand exportateur de fer, de cuivre et de bois. L'industrialisation, qui a commencé dans les années 1890, a permis à la Suède de se développer, et d'obtenir constamment de nos jours une bonne place dans les classements européens sur l'Indice de développement humain (IDH). La Suède possède de grandes réserves d'eau potable, mais manque de ressources énergétiques fossiles comme le charbon ou le pétrole.
La Suède moderne est issue de l'Union de Kalmar, créée en 1397. Le pays fut unifié au XVIe siècle par le roi Gustav Vasa. Au XVIIe siècle, la Suède conquiert de nouveaux territoires et forme un empire colonial. Cependant, la majeure partie de ces territoires devra être abandonnée au XVIIIe siècle. Au début du XIXe siècle, la Finlande et d'autres territoires sont perdus. Après sa dernière guerre en 1814, la Suède connaît la paix, adoptant une politique de non-alignement en temps de paix et de neutralité en temps de guerre. La Suède fait partie de l'Union européenne depuis 1995, mais pas de la zone euro.
Selon l'indice de démocratie du groupe de presse britannique The Economist Group, la Suède est un des pays les plus démocratiques au monde (premier en 2008, troisième en 2017 derrière la Norvège et l'Islande). De plus, le 31 décembre 2010, elle reçoit le prix de l'Excellence 2010 (pays le mieux réputé).
La Svezia (AFI: /ˈzvɛtsːja/[6]; in svedese: Sverige, /ˈsvæːɾ(i)jə/ ), ufficialmente chiamata Regno di Svezia (in svedese: Konungariket Sverige), è uno Stato dell'Unione Europea, situato nella penisola scandinava.
Confina con la Norvegia a ovest e con la Finlandia a nord-est; è bagnata dal Mar Baltico e dal Golfo di Botnia a est, e dagli stretti dello Skagerrak e del Kattegat a sud-ovest; lo stretto dell'Øresund, che separa la Svezia dalla Danimarca, è dal 2000 attraversato dal ponte omonimo che collega i due Paesi rispettivamente tra Malmö e Copenaghen.
Con i suoi 449 964 km² di superficie la Svezia è il quinto Stato più esteso d'Europa dopo Russia, Ucraina, Francia e Spagna, nonché il terzo dell'Unione. Si estende per una lunghezza di oltre 1.500 chilometri in linea d'aria da nord a sud. La densità della popolazione è bassa e tende a concentrarsi nelle città principali. Il territorio interno è per buona parte occupato da foreste. Lo Stato è ricco di risorse naturali (legname, ferro, acqua) e l'economia svedese permette alla popolazione di godere di uno fra i più elevati tenori di vita al mondo[7][8]: la Svezia è saldamente ai primi posti[9] nelle classifiche dell'ONU sullo sviluppo umano.
La Svezia è una monarchia parlamentare il cui sovrano è, dal 1973, Carlo XVI Gustavo, il primo ministro è Stefan Löfven. Lo svedese è lingua ufficiale dal 1º luglio 2009. L'ingresso nell'Unione europea avvenne il 1º gennaio 1995.
Fino al XIX secolo la Svezia era, invece, uno degli Stati più poveri d'Europa[10][11]. In seguito, lo sviluppo dei trasporti permise un intenso sfruttamento delle sue risorse naturali (legname e ferro), fattore che portò a un vigoroso sviluppo. Un elevato livello di istruzione e le liberalizzazioni economiche contribuirono, alla fine dell'Ottocento, all'affermarsi di un'avanzata industria manifatturiera. I primi decenni del XX secolo furono caratterizzati dall'affermarsi dello stato sociale, che rimane tra i più efficienti al mondo[12][13][14].
Suecia (en sueco: ![]() Sverige (?·i) [ˈsværjɛ]), oficialmente Reino de Suecia (en sueco:
Sverige (?·i) [ˈsværjɛ]), oficialmente Reino de Suecia (en sueco: ![]() Konungariket Sverige (?·i)), es un país escandinavo de Europa del Norte que forma parte de la Unión Europea (UE). Limita al norte con Noruega y Finlandia, al este con Finlandia y el golfo de Botnia, al sur con el mar Báltico y al oeste con el mar del Norte y Noruega. Tiene fronteras terrestres con Noruega y Finlandia, y está conectado a Dinamarca por el puente de Öresund. Su ciudad más poblada es Estocolmo,5 que es también su capital.
Konungariket Sverige (?·i)), es un país escandinavo de Europa del Norte que forma parte de la Unión Europea (UE). Limita al norte con Noruega y Finlandia, al este con Finlandia y el golfo de Botnia, al sur con el mar Báltico y al oeste con el mar del Norte y Noruega. Tiene fronteras terrestres con Noruega y Finlandia, y está conectado a Dinamarca por el puente de Öresund. Su ciudad más poblada es Estocolmo,5 que es también su capital.
Con una extensión de 450 295 km²,1 es el quinto país más extenso de Europa. En 2016, contaba con una población total de poco más de 10 millones de personas, de las cuales el 98 % cuenta con acceso a Internet, lo que lo convierte en el país con la mayor penetración del servicio en el mundo. Tiene una densidad de población de solo 22 h/km², similar a otros países de su entorno. Cerca del 84 % de la población vive en zonas urbanas.6 Los suecos disfrutan de un alto nivel de vida, con una organización y cultura corporativa no jerárquica, y colectivista en comparación con sus homólogos anglosajones.7 La conservación de la naturaleza, la protección del medio ambiente y la eficacia energética son, por lo general, una prioridad en la formulación de políticas y cuentan con acogida por gran parte del pueblo.89. Mantiene el modelo nórdico de bienestar que brinda asistencia sanitaria universal y educación terciaria gratuita a sus ciudadanos, tiene el undécimo ingreso per cápita más alto del mundo y ocupa un lugar destacado en numerosas mediciones de desarrollo humano, incluida la calidad de vida, salud, educación, igualdad, y prosperidad.10
Durante mucho tiempo fue un importante exportador de hierro, cobre y madera. La mejora de los transportes y las comunicaciones ha permitido la explotación a gran escala de bienes naturales, sobre todo la madera y el mineral de hierro. En la década de 1980, la escolarización universal y la industrialización permitieron al país desarrollar una exitosa industria manufacturera. Tiene una rica oferta de energía hidráulica, pero carece de petróleo y de yacimientos de carbón importantes. En el siglo XX se ubicó constantemente entre los países con mejor Índice de Desarrollo Humano (IDH), actualmente ocupando la séptima posición.
La Suecia moderna surgió de la Unión de Kalmar en 1397, y de la unificación del país por el rey Gustavo Vasa en el siglo XVI. En el siglo XVII, amplió sus territorios para formar el Imperio sueco. La mayor parte de los territorios conquistados fuera de la península escandinava se perdieron durante los siguientes siglos. La mitad oriental de Suecia constituida por la mitad oriental de Norrland y Österland se perdió frente a Rusia en 1809. Desde 1814, no ha participado en ningún conflicto, manteniendo una política exterior de paz y neutralidad en tiempo de guerra.11
Шве́ция (швед. Sverige ), официальное название — Короле́вство Шве́ция (швед. Konungariket Sverige ) — государство в Северной Европе на Скандинавском полуострове.
Территория составляет 447 435 км², а население — более 10 миллионов человек — по этим показателям является крупнейшим скандинавским государством. Среди государств Европы занимает 5-е место по территории.